Canadian Arctic Archipelago
Encyclopedia
The Canadian Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Arctic Archipelago, is a Canadian
archipelago
north of the Canadian
mainland in the Arctic
. Situated in the north
ern extremity of North America
and covering about 1424500 km² (550,002.5 sq mi), this group of 36,563 island
s comprises much of the territory of Northern Canada
– most of Nunavut
and part of the Northwest Territories
.
The archipelago extends some 2400 km (1,491.3 mi) longitudinally and 1900 km (1,180.6 mi) from the mainland to Cape Columbia
, the northernmost point on Ellesmere Island
. It is bounded on the west by the Beaufort Sea
; on the northwest by the Arctic Ocean
; on the east by Greenland
, Baffin Bay
and Davis Strait
; and on the south by Hudson Bay
and the Canadian mainland. The various islands are separated from each other and the continental mainland by a series of waterways collectively known as the Northwestern Passages
. Two large peninsulas, Boothia
and Melville
, extend northward from the mainland.
The archipelago consists of 36,563 islands, of which 94 are classified as major islands, being larger than 130 km² (50 sq mi), and cover a total area of 1400000 km² (540,543 sq mi). The islands of the archipelago over 10000 km² (3,861 sq mi), in order of descending area, are:
* NT = Northwest Territories
, NU = Nunavut

 After Greenland, the archipelago is the world’s largest high-Arctic land area. The climate of the islands is arctic
After Greenland, the archipelago is the world’s largest high-Arctic land area. The climate of the islands is arctic
, and the terrain consists of tundra
except in mountainous areas. Most of the islands are uninhabited; human settlement is extremely thin and scattered, being mainly coastal Inuit
settlements on the southern islands.
British claims on the islands were based on the explorations in the 1570s by Martin Frobisher
. Canadian sovereignty, originally (1870–80) only over island portions that drained into Foxe Basin
, Hudson Bay and Hudson Strait
, over all of them was not established until the 1880 transfer by Britain to Canada of the remaining islands; the District of Franklin
was established in 1895, which comprised almost all of the archipelago; the district was dissolved upon the creation of Nunavut in 1999. Canada claims all the waterways of the Northwestern Passages as Canadian Internal Waters
; however the United States
and most other maritime countries view these as international waters
. Disagreement over the passages' status has raised Canadian concerns about environmental enforcement, national security, and general sovereignty. Hans Island
, in the Nares Strait
east of Ellesmere Island, is a territory currently contested between Canada and Denmark
.
----
Islands not on map
Wales Island, 68°01′N 086°40′WBelcher Islands, 56°20′N 079°30′WLong Island, 54°52′N 079°25′WAkimiski Island, 53°00′N 081°20′WCharlton Island, 52°00′N 079°26′WEllesmere Island, 79°49′N 078°00′WMeighen Island, 79°59′N 099°30′WAxel Heiberg Island, 79°26′N 090°46′WEllef Ringnes Island, 78°37′N 101°56′WAmund Ringnes Island, 78°19′N 096°25′WCornwall Island, 77°37′N 094°52′WGraham Island, 77°26′N 090°30′WNorth Kent Island, 76°40′N 090°15′WBaillie-Hamilton Island, 75°53′N 094°35′WLittle Cornwallis Island, 75°30′N 096°30′WCornwallis Island, 75°05′N 095°00′WDevon Island, 75°15′N 088°00′WBylot Island, 73°13′N 078°34′WBaffin Island, 69°00′N 072°00′WJens Munk Island, 69°40′N 079°40′WKoch Island, 69°35′N 078°20′WBray Island, 69°20′N 077°00′WRowley Island, 69°05′N 078°52′WFoley Island, 68°30′N 075°00′W
Air Force Island, 67°58′N 074°05′WPrince Charles Island, 67°45′N 076°00′WVansittart Island, 65°50′N 084°00′WWhite Island, 65°46′N 084°53′WSouthampton Island, 64°30′N 084°30′WResolution Island, 61°35′N 065°00′WLoks Land Island, 62°26′N 064°38′WAkpatok Island, 60°25′N 068°08′WBig Island, 62°43′N 070°43′WSalisbury Island, 63°35′N 077°00′WNottingham Island, 63°17′N 077°55′WMansel Island, 62°00′N 079°50′WCoats Island, 62°35′N 082°45′WBeechey Island, 74°43′N 091°51′WDuke of York Archipelago, 68°15′N 112°30′WGateshead Island, 70°35′N 100°25′WHaig-Thomas Island, 78°15′N 094°30′WHans Island, 80°49′N 066°27′WKilliniq Island, 60°22′N 064°37′WJenny Lind Island, 68°43′N 101°58′WOttawa Islands, 59°34′N 080°16′WPrince Leopold Island, 74°01′N 090°04′WSkraeling Island, 78°55′N 075°40′WTrodely Island, 52°14′N 079°26′WWeston Island, 52°32′N 079°35′W
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
archipelago
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
north of the Canadian
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
mainland in the Arctic
Arctic
The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost...
. Situated in the north
North
North is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.North is one of the four cardinal directions or compass points. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west.By convention, the top side of a map is north....
ern extremity of North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and covering about 1424500 km² (550,002.5 sq mi), this group of 36,563 island
Island
An island or isle is any piece of sub-continental land that is surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, cays or keys. An island in a river or lake may be called an eyot , or holm...
s comprises much of the territory of Northern Canada
Northern Canada
Northern Canada, colloquially the North, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut...
– most of Nunavut
Nunavut
Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993...
and part of the Northwest Territories
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
.
The archipelago extends some 2400 km (1,491.3 mi) longitudinally and 1900 km (1,180.6 mi) from the mainland to Cape Columbia
Cape Columbia
Cape Columbia is the northernmost point of land of Canada, located on Ellesmere Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut. It marks the westernmost coastal point of Lincoln Sea in the Arctic Ocean...
, the northernmost point on Ellesmere Island
Ellesmere Island
Ellesmere Island is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. Lying within the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, it is considered part of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, with Cape Columbia being the most northerly point of land in Canada...
. It is bounded on the west by the Beaufort Sea
Beaufort Sea
The Beaufort Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska, west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after hydrographer Sir Francis Beaufort...
; on the northwest by the Arctic Ocean
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions...
; on the east by Greenland
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for...
, Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay , located between Baffin Island and the southwest coast of Greenland, is a marginal sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea...
and Davis Strait
Davis Strait
Davis Strait is a northern arm of the Labrador Sea. It lies between mid-western Greenland and Nunavut, Canada's Baffin Island. The strait was named for the English explorer John Davis , who explored the area while seeking a Northwest Passage....
; and on the south by Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay , sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada. It drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, southeastern Nunavut, as well as parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota,...
and the Canadian mainland. The various islands are separated from each other and the continental mainland by a series of waterways collectively known as the Northwestern Passages
Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage is a sea route through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways amidst the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans...
. Two large peninsulas, Boothia
Boothia Peninsula
Boothia Peninsula is a large peninsula in Nunavut's northern Canadian Arctic, south of Somerset Island. The northern part, Murchison Promontory, is the northernmost point of mainland Canada, and thus North America....
and Melville
Melville Peninsula
Melville Peninsula is a large peninsula in the Canadian Arctic. Since 1999, it has been part of Nunavut. Before that, it was part of the District of Franklin. It's separated from Southampton Island by Frozen Strait. The narrow isthmus connecting the peninsula to the mainland is styled the “Rae...
, extend northward from the mainland.
The archipelago consists of 36,563 islands, of which 94 are classified as major islands, being larger than 130 km² (50 sq mi), and cover a total area of 1400000 km² (540,543 sq mi). The islands of the archipelago over 10000 km² (3,861 sq mi), in order of descending area, are:
| Name | Location* | Area rank | | Population (2001) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World | Canada | ||||
| Baffin Island Baffin Island Baffin Island in the Canadian territory of Nunavut is the largest island in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, the largest island in Canada and the fifth largest island in the world. Its area is and its population is about 11,000... |
NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
507451 km² (195,928 sq mi) | 5 | 1 | 9,563 |
| Victoria Island | NT Northwest Territories The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south... , NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
217291 km² (83,897 sq mi) | 9 | 2 | 1,707 |
| Ellesmere Island Ellesmere Island Ellesmere Island is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. Lying within the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, it is considered part of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, with Cape Columbia being the most northerly point of land in Canada... |
NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
196236 km² (75,767 sq mi) | 10 | 3 | 168 |
| Banks Island Banks Island One of the larger members of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, Banks Island is situated in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada. It is separated from Victoria Island to its east by the Prince of Wales Strait and from the mainland by Amundsen Gulf to its south. The Beaufort Sea lies... |
NT Northwest Territories The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south... |
70028 km² (27,038 sq mi) | 24 | 5 | 114 |
| Devon Island Devon Island Devon Island , claimed to be the largest uninhabited island on Earth, is located in Baffin Bay, Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is one of the larger members of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, the second-largest of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, Canada's sixth largest island, and the 27th... |
NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
55247 km² (21,331 sq mi) | 27 | 6 | 0 |
| Axel Heiberg Island Axel Heiberg Island Axel Heiberg Island is an island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located in the Arctic Ocean, it is the 31st largest island in the world and Canada's seventh largest island. According to Statistics Canada, it has an area of .... |
NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
43178 km² (16,671 sq mi) | 32 | 7 | 0 |
| Melville Island | NT Northwest Territories The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south... , NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
42149 km² (16,274 sq mi) | 33 | 8 | 0 |
| Southampton Island Southampton Island Southampton Island is a large island at the entrance to Hudson Bay at Foxe Basin. One of the larger members of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, Southampton Island is part of the Kivalliq Region in Nunavut, Canada. The area of the island is stated as by Statistics Canada . It is the 34th largest... |
NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
41214 km² (15,913 sq mi) | 34 | 9 | 721 |
| Prince of Wales Island | NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
33339 km² (12,872 sq mi) | 40 | 10 | 0 |
| Somerset Island | NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
24786 km² (9,570 sq mi) | 46 | 12 | 0 |
| Bathurst Island Bathurst Island A member of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, Bathurst Island is one of the Queen Elizabeth Islands in Nunavut Territory, Canada. The area of the island is estimated at , making it the 54th largest island in the world and Canada's 13th largest island. It is uninhabited.The island is low-lying with... |
NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
16042 km² (6,194 sq mi) | 54 | 13 | 0 |
| Prince Patrick Island Prince Patrick Island A member of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, Prince Patrick Island is the westernmost of the Queen Elizabeth Islands in the Northwest Territories of Canada. The area of the island is , making it the 55th largest island in the world and Canada's 14th largest island... |
NT Northwest Territories The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south... |
15848 km² (6,119 sq mi) | 55 | 14 | 0 |
| King William Island King William Island King William Island is an island in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut and forms part of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. In area it is between and making it the 61st largest island in the world and Canada's 15th largest island... |
NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
13111 km² (5,062 sq mi) | 61 | 15 | 960 |
| Ellef Ringnes Island Ellef Ringnes Island Ellef Ringnes Island is one of the Sverdrup Islands in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Also a member of the Queen Elizabeth Islands and Canadian Arctic Archipelago, it is located in the Arctic Ocean, east of Borden Island, and west of Amund Ringnes Island... |
NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
11295 km² (4,361 sq mi) | 69 | 16 | 0 |
| Bylot Island Bylot Island Bylot Island lies off the northern end of Baffin Island in Nunavut Territory, Canada. At it is ranked 71st largest island in the world and Canada's 17th largest island. It is also one of the largest uninhabited islands in the world. While there are no permanent settlements on this Canadian Arctic... |
NU Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
11067 km² (4,273 sq mi) | 72 | 17 | 0 |
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
, NU = Nunavut
Nunavut
Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993...


Climate of the Arctic
The climate of the Arctic is characterized by long, cold winters and short, cool summers. There is a large amount of variability in climate across the Arctic, but all regions experience extremes of solar radiation in both summer and winter...
, and the terrain consists of tundra
Tundra
In physical geography, tundra is a biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons. The term tundra comes through Russian тундра from the Kildin Sami word tūndâr "uplands," "treeless mountain tract." There are three types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine...
except in mountainous areas. Most of the islands are uninhabited; human settlement is extremely thin and scattered, being mainly coastal Inuit
Inuit
The Inuit are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic regions of Canada , Denmark , Russia and the United States . Inuit means “the people” in the Inuktitut language...
settlements on the southern islands.
British claims on the islands were based on the explorations in the 1570s by Martin Frobisher
Martin Frobisher
Sir Martin Frobisher was an English seaman who made three voyages to the New World to look for the Northwest Passage...
. Canadian sovereignty, originally (1870–80) only over island portions that drained into Foxe Basin
Foxe Basin
Not to be confused with Fox Bay, Falkland IslandsFoxe Basin is a shallow oceanic basin north of Hudson Bay, in Nunavut, Canada, located between Baffin Island and the Melville Peninsula...
, Hudson Bay and Hudson Strait
Hudson Strait
Hudson Strait links the Atlantic Ocean to Hudson Bay in Canada. It lies between Baffin Island and the northern coast of Quebec, its eastern entrance marked by Cape Chidley and Resolution Island. It is long...
, over all of them was not established until the 1880 transfer by Britain to Canada of the remaining islands; the District of Franklin
District of Franklin
The District of Franklin was a regional administrative district of Canada's Northwest Territories. The district consisted of the Canadian high Arctic Islands, notably Ellesmere Island, Baffin Island, and Victoria Island...
was established in 1895, which comprised almost all of the archipelago; the district was dissolved upon the creation of Nunavut in 1999. Canada claims all the waterways of the Northwestern Passages as Canadian Internal Waters
Canadian Internal Waters
Canadian Internal Waters is a Canadian term that refers to "...the waters on the landward side of the baselines of the territorial sea of Canada,..."....
; however the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and most other maritime countries view these as international waters
International waters
The terms international waters or trans-boundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regional seas and estuaries, rivers, lakes, groundwater systems , and wetlands.Oceans,...
. Disagreement over the passages' status has raised Canadian concerns about environmental enforcement, national security, and general sovereignty. Hans Island
Hans Island
Hans Island is a small, uninhabited barren knoll measuring , located in the centre of the Kennedy Channel of Nares Strait—the strait that separates Ellesmere Island from northern Greenland and connects Baffin Bay with the Lincoln Sea...
, in the Nares Strait
Nares Strait
Nares Strait is a waterway between Ellesmere Island and Greenland that is the northern part of Baffin Bay where it meets the Lincoln Sea. From south to north, the strait includes Smith Sound, Kane Basin, Kennedy Channel, Hall Basin and Robeson Channel...
east of Ellesmere Island, is a territory currently contested between Canada and Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
.
----
Map with links to islands
|
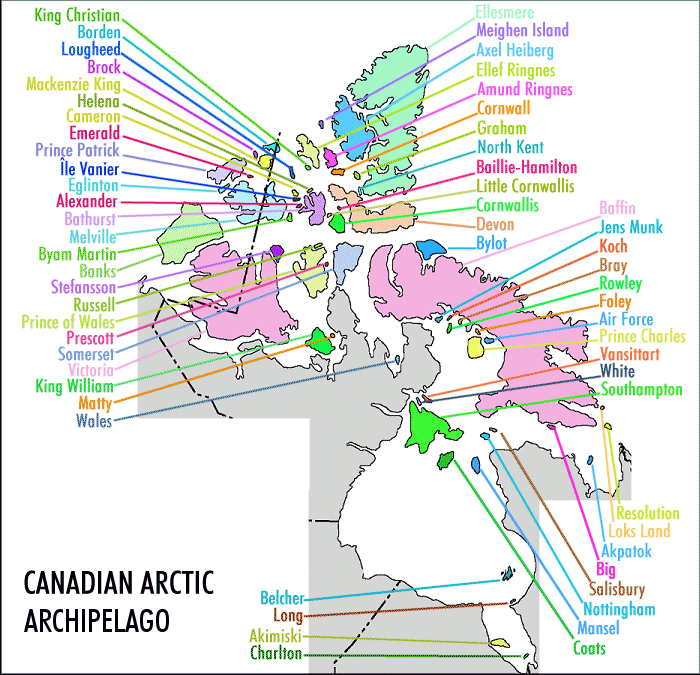 |
|
Islands not on map
- BeecheyBeechey IslandBeechey Island is an island located in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago of Nunavut, Canada, in Wellington Channel. It is separated from the southwest corner of Devon Island by Barrow Strait...
- Duke of YorkDuke of York ArchipelagoThe Duke of York Archipelago is an uninhabited island group in the Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the Coronation Gulf.The archipelago is composed of the islands of Akvitlak Islands, Anchor Island, Bate Islands, Hatoayok Island, Hokagon Island, Kabviukvik Island, Kingak Island,...
- GatesheadGateshead IslandGateshead Island is an island located in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. Located in M'Clintock Channel, the area of Gateshead Island is around . It is an important polar bear denning area....
- Haig-ThomasHaig-Thomas IslandHaig-Thomas Island is one of the Sverdrup Islands in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in Massey Sound, between Amund Ringnes Island and Axel Heiberg Island. It is also a member of the Queen Elizabeth Islands and the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. It is named for the British explorer...
- HansHans IslandHans Island is a small, uninhabited barren knoll measuring , located in the centre of the Kennedy Channel of Nares Strait—the strait that separates Ellesmere Island from northern Greenland and connects Baffin Bay with the Lincoln Sea...
- KilliniqKilliniq IslandKilliniq Island is a small, remote island in northeastern Canada. Located at the extreme northern tip of Labrador between Ungava Bay and the Labrador Sea, it is notable in that it contains the only land border between Nunavut territory and the province of Newfoundland and Labrador...
- Jenny LindJenny Lind Island-History:The island is uninhabited but still has an active North Warning System. Originally part of the Distant Early Warning Line, the site is known as CAM-1.-References:***...
- OttawaOttawa IslandsThe Ottawa Islands are a group of uninhabited islands situated in the eastern edge of Canada's Hudson Bay. The group comprises 24 small islands, located at approximately 60N 80W. The main islands include Booth Island, Bronson Island, Eddy Island, Gilmour Island, J. Gordon Island, Pattee Island,...
- Prince Leopold
- SkraelingSkraeling IslandSkraeling Island lies off the east coast of Ellesmere Island in the Canadian territory of Nunavut.-History:The Norse referred to the indigenous peoples they encountered in Greenland and the New World as skræling , and the sagas make it clear that the Norse considered the natives...
- TrodeleyTrodely islandTrodely Island is an uninhabited Canadian arctic island located in the southeastern part of James Bay in the territory of Nunavut. It is northwest of Charlton Island....
- WestonWeston IslandWeston Island is an uninhabited island in James Bay and is part of Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is lies between South Twin Island and Trodely Island....
Mapping
King Christian Island, 77°45′N 102°00′WBorden Island, 78°33′N 111°10′WLougheed Island, 77°24′N 105°15′WBrock Island, 77°51′N 114°27′WMackenzie King Island, 77°43′N 111°57′WHelena Island, 76°40′N 101°00′WCameron Island, 77°48′N 101°51′WEmerald Isle, 76°48′N 114°07′WPrince Patrick Island, 76°45′N 119°30′WÎle Vanier, 76°10′N 103°15′WEglinton Island, 75°46′N 118°27′WAlexander Island, 75°52′N 102°37′WBathurst Island, 75°46′N 099°47′WMelville Island, 75°30′N 111°30′WByam Martin Island, 75°12′N 104°17′WBanks Island, 73°00′N 121°30′WStefansson Island, 73°30′N 105°30′WRussell Island, 74°00′N 098°25′WPrince of Wales Island, 72°36′N 098°32′WPrescott Island, 73°03′N 096°49′WSomerset Island, 73°15′N 093°30′WVictoria Island, 71°00′N 110°00′WKing William Island, 68°58′N 097°14′WMatty Island, 69°28′N 095°40′WWales Island, 68°01′N 086°40′WBelcher Islands, 56°20′N 079°30′WLong Island, 54°52′N 079°25′WAkimiski Island, 53°00′N 081°20′WCharlton Island, 52°00′N 079°26′WEllesmere Island, 79°49′N 078°00′WMeighen Island, 79°59′N 099°30′WAxel Heiberg Island, 79°26′N 090°46′WEllef Ringnes Island, 78°37′N 101°56′WAmund Ringnes Island, 78°19′N 096°25′WCornwall Island, 77°37′N 094°52′WGraham Island, 77°26′N 090°30′WNorth Kent Island, 76°40′N 090°15′WBaillie-Hamilton Island, 75°53′N 094°35′WLittle Cornwallis Island, 75°30′N 096°30′WCornwallis Island, 75°05′N 095°00′WDevon Island, 75°15′N 088°00′WBylot Island, 73°13′N 078°34′WBaffin Island, 69°00′N 072°00′WJens Munk Island, 69°40′N 079°40′WKoch Island, 69°35′N 078°20′WBray Island, 69°20′N 077°00′WRowley Island, 69°05′N 078°52′WFoley Island, 68°30′N 075°00′W
Air Force Island, 67°58′N 074°05′WPrince Charles Island, 67°45′N 076°00′WVansittart Island, 65°50′N 084°00′WWhite Island, 65°46′N 084°53′WSouthampton Island, 64°30′N 084°30′WResolution Island, 61°35′N 065°00′WLoks Land Island, 62°26′N 064°38′WAkpatok Island, 60°25′N 068°08′WBig Island, 62°43′N 070°43′WSalisbury Island, 63°35′N 077°00′WNottingham Island, 63°17′N 077°55′WMansel Island, 62°00′N 079°50′WCoats Island, 62°35′N 082°45′WBeechey Island, 74°43′N 091°51′WDuke of York Archipelago, 68°15′N 112°30′WGateshead Island, 70°35′N 100°25′WHaig-Thomas Island, 78°15′N 094°30′WHans Island, 80°49′N 066°27′WKilliniq Island, 60°22′N 064°37′WJenny Lind Island, 68°43′N 101°58′WOttawa Islands, 59°34′N 080°16′WPrince Leopold Island, 74°01′N 090°04′WSkraeling Island, 78°55′N 075°40′WTrodely Island, 52°14′N 079°26′WWeston Island, 52°32′N 079°35′W
See also
- List of islands of Canada
- List of Canadian islands by area
- British Arctic TerritoriesBritish Arctic TerritoriesBritish Arctic Territories were territories claimed by Britain in North America, consisting of the islands of what is now known in Canada as the High Arctic....

