Business process management
Encyclopedia
Business process management (BPM) is a holistic management
approach focused on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. It promotes business effectiveness
and efficiency
while striving for innovation
, flexibility, and integration with technology. BPM attempts to improve processes continuously. It can therefore be described as a "process optimization
process." It is argued that BPM enables organizations to be more efficient, more effective and more capable of change than a functionally focused, traditional hierarchical management approach.
An empirical study by Kohlbacher (2009) indicates that BPM helps organizations to gain higher customer satisfaction
, product quality, delivery speed and time-to-market speed. An empirical study by Vera & Kuntz (2007) conducted in the German hospital sector indicates that BPM has a positive impact on organizational efficiency.
comprises a "series or network of value-added activities, performed by their relevant roles or collaborators, to purposefully achieve the common business goal." These processes are critical to any organization, as they can generate revenue and often represent a significant proportion of costs. As a managerial approach, BPM considers processes to be strategic assets of an organization that must be understood, managed, and improved to deliver value added products and services to clients. This foundation is very similar to other Total Quality Management
or Continuous Improvement Process
methodologies or approaches. BPM goes a step further by stating that this approach can be supported, or enabled, through technology to ensure the viability of the managerial approach in times of stress
and change. In fact, BPM is an approach to integrate an organizational "change capability" that is both human and technological. As such, many BPM articles and pundits often discuss BPM from one of two viewpoints: people and/or technology.
Roughly speaking, the idea of business process is as traditional as concepts of tasks
, department
, production
, output
s. The management and improvement approach, with formal definitions and technical modeling, has been around since the early 1990s (see business process modeling
). Note that in the IT
community, the term 'business process' is often used as synonymous of management of middleware
processes; or integrating application software
tasks. This viewpoint may be overly restrictive - a limitation to keep in mind when reading software engineering
paper
s that refer to "business processes" or to "business process modeling".
Although the initial focus of BPM was on the automation of business processes with the use of information technology, it has since been extended to integrate human-driven processes in which human interaction takes place in series or parallel with the use of technology. For example (in workflow
systems), when individual steps in the business process require human intuition or judgment to be performed, these steps are assigned to appropriate members within the organization.
More advanced forms such as human interaction management
are in the complex interaction between human workers in performing a workgroup task. In this case, many people and systems interact in structured, ad-hoc, and sometimes completely dynamic ways to complete one to many transactions.
BPM can be used to understand organizations through expanded views that would not otherwise be available to organize and present, such as relationships between processes. When included in a process model, these relationships provide for advanced reporting and analysis. BPM is regarded by some as the backbone of enterprise content management
.
Because BPM allows organizations to abstract business process from technology infrastructure, it goes far beyond automating business processes (software) or solving business problems (suite). BPM enables business to respond to changing consumer, market, and regulatory demands faster than competitors - creating competitive advantage.
technology has allowed the coupling of BPM to other methodologies, such as Six Sigma
. BPM tools allow users to:
This brings with it the benefit of being able to simulate changes to business processes based on real-life data (not assumed knowledge). Also, the coupling of BPM to industry methodologies allows users to continually streamline and optimize the process to ensure that it is tuned to its market need.
Good design reduces the number of problems over the lifetime of the process. Whether or not existing processes are considered, the aim of this step is to ensure that a correct and efficient theoretical design is prepared.
The proposed improvement could be in human-to-human, human-to-system, and system-to-system workflows, and might target regulatory, market, or competitive challenges faced by the businesses.
It also involves running "what-if analysis" on the processes: "What if I have 75% of resources to do the same task?" "What if I want to do the same job for 80% of the current cost?".
that executes the required steps of the process; however, in practice, these applications rarely execute all the steps of the process accurately or completely. Another approach is to use a combination of software and human intervention; however this approach is more complex, making the documentation process difficult.
As a response to these problems, software has been developed that enables the full business process (as developed in the process design activity) to be defined in a computer language which can be directly executed by the computer. The system will either use services in connected applications to perform business operations (e.g. calculating a repayment plan for a loan) or, when a step is too complex to automate, will ask for human input. Compared to either of the previous approaches, directly executing a process definition can be more straightforward and therefore easier to improve. However, automating a process definition requires flexible and comprehensive infrastructure, which typically rules out implementing these systems in a legacy IT environment.
Business rules have been used by systems to provide definitions for governing behaviour, and a business rule engine can be used to drive process execution and resolution.
In addition, this information can be used to work with customers and suppliers to improve their connected processes. Examples of the statistics are the generation of measures on how quickly a customer order is processed or how many orders were processed in the last month. These measures tend to fit into three categories: cycle time, defect rate and productivity.
The degree of monitoring depends on what information the business wants to evaluate and analyze and how business wants it to be monitored, in real-time, near real-time or ad-hoc. Here, business activity monitoring
(BAM) extends and expands the monitoring tools generally provided by BPMS.
Process mining
is a collection of methods and tools related to process monitoring. The aim of process mining is to analyze event logs extracted through process monitoring and to compare them with an process model. Process mining allows process analysts to detect discrepancies between the actual process execution and the a priori model as well as to analyze bottlenecks.
includes retrieving process performance information from modeling or monitoring phase; identifying the potential or actual bottleneck
s and the potential opportunities for cost savings or other improvements; and then, applying those enhancements in the design of the process. Overall, this creates greater business value.
, Inc recognize the BPM suite space through three different lenses:
However, over the past few years, standalone integration-centric and document-centric offerings have matured into separate, standalone markets that include BPM plus much more.
 While the steps can be viewed as a cycle, economic or time constraints are likely to limit the process to only a few iterations. This is often the case when an organization uses the approach for short to medium term objectives rather than trying to transform the organizational culture. True iterations are only possible through the collaborative efforts of process participants. In a majority of organizations, complexity will require enabling technology (see below) to support the process participants in these daily process management challenges.
While the steps can be viewed as a cycle, economic or time constraints are likely to limit the process to only a few iterations. This is often the case when an organization uses the approach for short to medium term objectives rather than trying to transform the organizational culture. True iterations are only possible through the collaborative efforts of process participants. In a majority of organizations, complexity will require enabling technology (see below) to support the process participants in these daily process management challenges.
To date, many organizations often start a BPM project or program with the objective to optimize an area that has been identified as an area for improvement.
In the financial sector, BPM is critical to make sure the system delivers a quality service while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Currently, the international standards for the task have limited BPM to the application in the IT sector, and ISO/IEC 15944 covers the operational aspects of the business. However, some corporations with the culture of best practices do use standard operating procedures to regulate their operational process. Other standards are currently being worked upon to assist in BPM implementation (BPMN, Enterprise Architecture
, Business Motivation Model
).
. Still others limit the definition to "modeling" (see Business model
ing).
BPM is now considered a critical component of Operational Intelligence
(OI) solutions to deliver real-time, actionable information. This real-time information can be acted upon in a variety of ways - alerts can be sent or executive decisions can be made using real-time dashboards. OI solutions use real-time information to take automated action based on pre-defined rules so that security measures and or exception management processes can be initiated.
These are partial answers and the technological offerings continue to evolve. The BPMS term may not survive. Today it encompasses the concept of supporting the managerial approach through enabling technology. The BPMS should enable all stakeholders to have a firm understanding of an organization and its performance. The BPMS should facilitate business process change throughout the life cycle stated above. This assists in the automation of activities, collaboration, integration with other systems, integrating partners through the value chain, etc. For instance, the size and complexity of daily tasks often requires the use of technology to model efficiently. These models facilitate automation and solutions to business problems. These models can also become executable to assist in monitoring and controlling business processes. As such, some people view BPM as "the bridge between Information Technology (IT) and Business.". In fact, an argument can be made that this "holistic approach" bridges organizational and technological silos.
There are four critical components of a BPM Suite:
BPM also addresses many of the critical IT issues underpinning these business drivers, including:
Validation of BPMS is another technical issue that vendors and users need to be aware of, if regulatory compliance is mandatory. The validation task could be performed either by an authenticated third party or by the users themselves. Either way, validation documentation will need to be generated. The validation document usually can either be published officially or retained by users.
Holism
Holism is the idea that all the properties of a given system cannot be determined or explained by its component parts alone...
approach focused on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. It promotes business effectiveness
Effectiveness
Effectiveness is the capability of producing a desired result. When something is deemed effective, it means it has an intended or expected outcome, or produces a deep, vivid impression.-Etymology:...
and efficiency
Efficiency
Efficiency in general describes the extent to which time or effort is well used for the intended task or purpose. It is often used with the specific purpose of relaying the capability of a specific application of effort to produce a specific outcome effectively with a minimum amount or quantity of...
while striving for innovation
Innovation
Innovation is the creation of better or more effective products, processes, technologies, or ideas that are accepted by markets, governments, and society...
, flexibility, and integration with technology. BPM attempts to improve processes continuously. It can therefore be described as a "process optimization
Process optimization
Process optimization is the discipline of adjusting a process so as to optimize some specified set of parameters without violating some constraint. The most common goals are minimizing cost, maximizing throughput, and/or efficiency...
process." It is argued that BPM enables organizations to be more efficient, more effective and more capable of change than a functionally focused, traditional hierarchical management approach.
An empirical study by Kohlbacher (2009) indicates that BPM helps organizations to gain higher customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction, a term frequently used in marketing, is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation...
, product quality, delivery speed and time-to-market speed. An empirical study by Vera & Kuntz (2007) conducted in the German hospital sector indicates that BPM has a positive impact on organizational efficiency.
Overview
A business processBusiness process
A business process or business method is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product for a particular customer or customers...
comprises a "series or network of value-added activities, performed by their relevant roles or collaborators, to purposefully achieve the common business goal." These processes are critical to any organization, as they can generate revenue and often represent a significant proportion of costs. As a managerial approach, BPM considers processes to be strategic assets of an organization that must be understood, managed, and improved to deliver value added products and services to clients. This foundation is very similar to other Total Quality Management
Total Quality Management
Total quality management or TQM is an integrative philosophy of management for continuously improving the quality of products and processes....
or Continuous Improvement Process
Continuous Improvement Process
A continuous improvement process is an ongoing effort to improve products, services, or processes. These efforts can seek "incremental" improvement over time or "breakthrough" improvement all at once...
methodologies or approaches. BPM goes a step further by stating that this approach can be supported, or enabled, through technology to ensure the viability of the managerial approach in times of stress
Stress (biology)
Stress is a term in psychology and biology, borrowed from physics and engineering and first used in the biological context in the 1930s, which has in more recent decades become commonly used in popular parlance...
and change. In fact, BPM is an approach to integrate an organizational "change capability" that is both human and technological. As such, many BPM articles and pundits often discuss BPM from one of two viewpoints: people and/or technology.
Roughly speaking, the idea of business process is as traditional as concepts of tasks
Task (project management)
In project management a task is an activity that needs to be accomplished within a defined period of time. An assignment is a task under the responsibility of an assignee which should have a start and end date defined. One or more assignments on a task puts the task under execution. Completion of...
, department
Departmentalization
Departmentalization refers to the process of grouping activities into departments.Division of labour creates specialists who need coordination. This coordination is facilitated by grouping specialists together in departments....
, production
Production, costs, and pricing
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to industrial organization:Industrial organization – describes the behavior of firms in the marketplace with regard to production, pricing, employment and other decisions...
, output
Output
Output is the term denoting either an exit or changes which exit a system and which activate/modify a process. It is an abstract concept, used in the modeling, system design and system exploitation.-In control theory:...
s. The management and improvement approach, with formal definitions and technical modeling, has been around since the early 1990s (see business process modeling
Business process modeling
Business Process Modeling in systems engineering is the activity of representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current process may be analyzed and improved. BPM is typically performed by business analysts and managers who are seeking to improve process efficiency and quality...
). Note that in the IT
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
community, the term 'business process' is often used as synonymous of management of middleware
Middleware
Middleware is computer software that connects software components or people and their applications. The software consists of a set of services that allows multiple processes running on one or more machines to interact...
processes; or integrating application software
Application software
Application software, also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks. Examples include enterprise software, accounting software, office suites, graphics software and media players. Many application programs deal principally with...
tasks. This viewpoint may be overly restrictive - a limitation to keep in mind when reading software engineering
Software engineering
Software Engineering is the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software, and the study of these approaches; that is, the application of engineering to software...
paper
Paper
Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
s that refer to "business processes" or to "business process modeling".
Although the initial focus of BPM was on the automation of business processes with the use of information technology, it has since been extended to integrate human-driven processes in which human interaction takes place in series or parallel with the use of technology. For example (in workflow
Workflow
A workflow consists of a sequence of connected steps. It is a depiction of a sequence of operations, declared as work of a person, a group of persons, an organization of staff, or one or more simple or complex mechanisms. Workflow may be seen as any abstraction of real work...
systems), when individual steps in the business process require human intuition or judgment to be performed, these steps are assigned to appropriate members within the organization.
More advanced forms such as human interaction management
Human interaction management
Human Interaction Management is a set of management principles, patterns and techniques complementary to Business process management...
are in the complex interaction between human workers in performing a workgroup task. In this case, many people and systems interact in structured, ad-hoc, and sometimes completely dynamic ways to complete one to many transactions.
BPM can be used to understand organizations through expanded views that would not otherwise be available to organize and present, such as relationships between processes. When included in a process model, these relationships provide for advanced reporting and analysis. BPM is regarded by some as the backbone of enterprise content management
Enterprise content management
Enterprise Content Management is a formalized means of organizing and storing an organization's documents, and other content, that relate to the organization's processes...
.
Because BPM allows organizations to abstract business process from technology infrastructure, it goes far beyond automating business processes (software) or solving business problems (suite). BPM enables business to respond to changing consumer, market, and regulatory demands faster than competitors - creating competitive advantage.
technology has allowed the coupling of BPM to other methodologies, such as Six Sigma
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a business management strategy originally developed by Motorola, USA in 1986. , it is widely used in many sectors of industry.Six Sigma seeks to improve the quality of process outputs by identifying and removing the causes of defects and minimizing variability in manufacturing and...
. BPM tools allow users to:
- Vision - strategize functions and processes
- Define - baseline the process or the process improvement
- Model - simulate the change to the process.
- Analyze - compare the various simulations to determine an optimal improvement
- Improve - select and implement the improvement
- Control - deploy this implementation and by use of User defined dashboards monitor the improvement in real time and feed the performance information back into the simulation model in preparation for the next improvement iteration.
- Re-engineer - revamp the processes from scratch for better results
This brings with it the benefit of being able to simulate changes to business processes based on real-life data (not assumed knowledge). Also, the coupling of BPM to industry methodologies allows users to continually streamline and optimize the process to ensure that it is tuned to its market need.
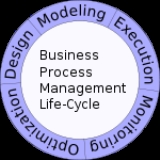
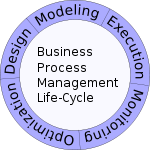
BPM life-cycle
Business process management activities can be grouped into six categories: vision, design, modeling, execution, monitoring, and optimization.
Vision
Functions are designed around the strategic vision and goals of an organization. Each function is attached with a list of processes. Each functional head in an organization is responsible for certain sets of processes made up of tasks which are to be executed and reported as planned. Multiple processes are aggregated to function accomplishments and multiple functions are aggregated to and achieve organizational goals.Design
Process Design encompasses both the identification of existing processes and the design of "to-be" processes. Areas of focus include representation of the process flow, the actors within it, alerts & notifications, escalations, Standard Operating Procedures, Service Level Agreements, and task hand-over mechanisms.Good design reduces the number of problems over the lifetime of the process. Whether or not existing processes are considered, the aim of this step is to ensure that a correct and efficient theoretical design is prepared.
The proposed improvement could be in human-to-human, human-to-system, and system-to-system workflows, and might target regulatory, market, or competitive challenges faced by the businesses.
Modeling
Modeling takes the theoretical design and introduces combinations of variables (e.g., changes in rent or materials costs, which determine how the process might operate under different circumstances).It also involves running "what-if analysis" on the processes: "What if I have 75% of resources to do the same task?" "What if I want to do the same job for 80% of the current cost?".
Execution
One of the ways to automate processes is to develop or purchase an applicationApplication software
Application software, also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks. Examples include enterprise software, accounting software, office suites, graphics software and media players. Many application programs deal principally with...
that executes the required steps of the process; however, in practice, these applications rarely execute all the steps of the process accurately or completely. Another approach is to use a combination of software and human intervention; however this approach is more complex, making the documentation process difficult.
As a response to these problems, software has been developed that enables the full business process (as developed in the process design activity) to be defined in a computer language which can be directly executed by the computer. The system will either use services in connected applications to perform business operations (e.g. calculating a repayment plan for a loan) or, when a step is too complex to automate, will ask for human input. Compared to either of the previous approaches, directly executing a process definition can be more straightforward and therefore easier to improve. However, automating a process definition requires flexible and comprehensive infrastructure, which typically rules out implementing these systems in a legacy IT environment.
Business rules have been used by systems to provide definitions for governing behaviour, and a business rule engine can be used to drive process execution and resolution.
Monitoring
Monitoring encompasses the tracking of individual processes, so that information on their state can be easily seen, and statistics on the performance of one or more processes can be provided. An example of the tracking is being able to determine the state of a customer order (e.g. ordered arrived, awaiting delivery, invoice paid) so that problems in its operation can be identified and corrected.In addition, this information can be used to work with customers and suppliers to improve their connected processes. Examples of the statistics are the generation of measures on how quickly a customer order is processed or how many orders were processed in the last month. These measures tend to fit into three categories: cycle time, defect rate and productivity.
The degree of monitoring depends on what information the business wants to evaluate and analyze and how business wants it to be monitored, in real-time, near real-time or ad-hoc. Here, business activity monitoring
Business activity monitoring
Business activity monitoring is software that aids in monitoring of business activities, as those activities are implemented in computer systems....
(BAM) extends and expands the monitoring tools generally provided by BPMS.
Process mining
Process mining
Process mining is a process management technique that allows for the analysis of business processes based on event logs. The basic idea is to extract knowledge from event logs recorded by an information system...
is a collection of methods and tools related to process monitoring. The aim of process mining is to analyze event logs extracted through process monitoring and to compare them with an process model. Process mining allows process analysts to detect discrepancies between the actual process execution and the a priori model as well as to analyze bottlenecks.
Optimization
Process optimizationProcess optimization
Process optimization is the discipline of adjusting a process so as to optimize some specified set of parameters without violating some constraint. The most common goals are minimizing cost, maximizing throughput, and/or efficiency...
includes retrieving process performance information from modeling or monitoring phase; identifying the potential or actual bottleneck
Bottleneck
A bottleneck is a phenomenon where the performance or capacity of an entire system is limited by a single or limited number of components or resources. The term bottleneck is taken from the 'assets are water' metaphor. As water is poured out of a bottle, the rate of outflow is limited by the width...
s and the potential opportunities for cost savings or other improvements; and then, applying those enhancements in the design of the process. Overall, this creates greater business value.
Re-engineering
When the process becomes too noisy and optimization is not fetching the desire output, it is recommended to re-engineer the entire process cycle. BPR has become an integral part of organizations to achieve efficiency and productivity at work.BPM Suites on market
Forrester ResearchForrester Research
Forrester Research is an independent technology and market research company that provides its clients with advice about technology's impact on business and consumers. Forrester Research has five research centers in the US: Cambridge, Massachusetts; New York, New York; San Francisco, California;...
, Inc recognize the BPM suite space through three different lenses:
- human-centric BPM, e.g. Software AG webMethodsWebMethodswebMethods is an enterprise software company, acquired by Software AG, focused on application integration, business process integration and B2B partner integration. Founded in 1996, the company pioneered the use of web services to connect software applications together within a single organization...
- integration-centric BPM (Enterprise Service Bus), e.g. Microsoft BizTalk Server
- document-centric BPM (Dynamic Case Management), e.g. Microsoft SharePointMicrosoft SharePointMicrosoft SharePoint is a web application platform developed by Microsoft. First launched in 2001, SharePoint is typically associated with web content management and document management systems, but it is actually a much broader platform of web technologies, capable of being configured into a wide...
Server
However, over the past few years, standalone integration-centric and document-centric offerings have matured into separate, standalone markets that include BPM plus much more.
Practice

To date, many organizations often start a BPM project or program with the objective to optimize an area that has been identified as an area for improvement.
In the financial sector, BPM is critical to make sure the system delivers a quality service while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Currently, the international standards for the task have limited BPM to the application in the IT sector, and ISO/IEC 15944 covers the operational aspects of the business. However, some corporations with the culture of best practices do use standard operating procedures to regulate their operational process. Other standards are currently being worked upon to assist in BPM implementation (BPMN, Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
, Business Motivation Model
Business Motivation Model
The Business Motivation Model in enterprise architecture provides a scheme and structure for developing, communicating, and managing business plans in an organized manner...
).
BPM technology
Some define the BPM System or Suite (BPMS) as "the whole of BPM." Others relate the important concept of information moving between enterprise software packages and immediately think of Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)Service-oriented architecture
In software engineering, a Service-Oriented Architecture is a set of principles and methodologies for designing and developing software in the form of interoperable services. These services are well-defined business functionalities that are built as software components that can be reused for...
. Still others limit the definition to "modeling" (see Business model
Business model
A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value...
ing).
BPM is now considered a critical component of Operational Intelligence
Operational Intelligence
Operational intelligence is a form of real-time dynamic, business analytics that delivers visibility and insight into business operations. Operational intelligence solutions run query analysis against live feeds and event data to deliver real-time, actionable information...
(OI) solutions to deliver real-time, actionable information. This real-time information can be acted upon in a variety of ways - alerts can be sent or executive decisions can be made using real-time dashboards. OI solutions use real-time information to take automated action based on pre-defined rules so that security measures and or exception management processes can be initiated.
These are partial answers and the technological offerings continue to evolve. The BPMS term may not survive. Today it encompasses the concept of supporting the managerial approach through enabling technology. The BPMS should enable all stakeholders to have a firm understanding of an organization and its performance. The BPMS should facilitate business process change throughout the life cycle stated above. This assists in the automation of activities, collaboration, integration with other systems, integrating partners through the value chain, etc. For instance, the size and complexity of daily tasks often requires the use of technology to model efficiently. These models facilitate automation and solutions to business problems. These models can also become executable to assist in monitoring and controlling business processes. As such, some people view BPM as "the bridge between Information Technology (IT) and Business.". In fact, an argument can be made that this "holistic approach" bridges organizational and technological silos.
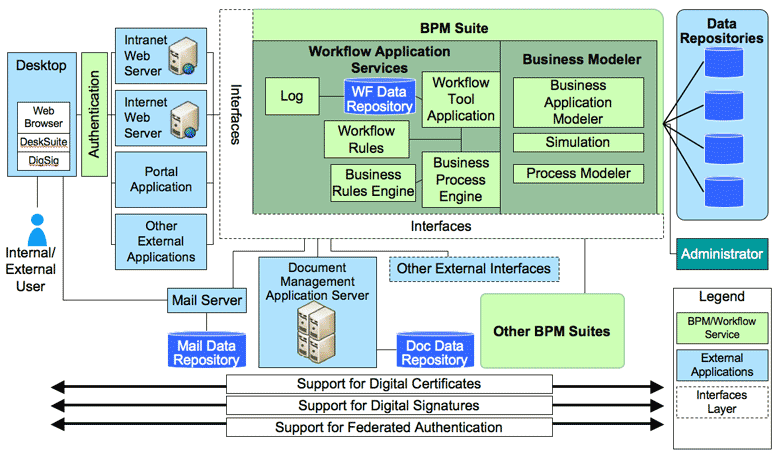
There are four critical components of a BPM Suite:
- Process Engine – a robust platform for modeling and executing process-based applications, including business rules
- Business Analytics — enable managers to identify business issues, trends, and opportunities with reports and dashboards and react accordingly
- Content Management — provides a system for storing and securing electronic documents, images, and other files
- Collaboration Tools — remove intra- and interdepartmental communication barriers through discussion forums, dynamic workspaces, and message boards
BPM also addresses many of the critical IT issues underpinning these business drivers, including:
- Managing end-to-end, customer-facing processes
- Consolidating data and increasing visibility into and access to associated data and information
- Increasing the flexibility and functionality of current infrastructure and data
- Integrating with existing systems and leveraging emerging service oriented architecture (SOAs)
- Establishing a common language for business-IT alignment
Validation of BPMS is another technical issue that vendors and users need to be aware of, if regulatory compliance is mandatory. The validation task could be performed either by an authenticated third party or by the users themselves. Either way, validation documentation will need to be generated. The validation document usually can either be published officially or retained by users.
See also
- Business activity monitoringBusiness activity monitoringBusiness activity monitoring is software that aids in monitoring of business activities, as those activities are implemented in computer systems....
- Business intelligenceBusiness intelligenceBusiness intelligence mainly refers to computer-based techniques used in identifying, extracting, and analyzing business data, such as sales revenue by products and/or departments, or by associated costs and incomes....
- Business process automationBusiness process automationBusiness process automation, or BPA, is the strategy a business uses to automate processes in order to contain costs. It consists of integrating applications, restructuring labor resources and using software applications throughout the organization....
- Business process reengineeringBusiness process reengineeringBusiness process re-engineering is the analysis and design of workflows and processes within an organization.According to Davenport a business process is a set of logically related tasks performed to achieve a defined business outcome....
- Comparison of business integration softwareComparison of business integration softwareThis article is a comparison of business integration and business process automation software.-Scope:Scope of this comparison:* Service-oriented architecture implementations;* Message-oriented middleware and message brokers;...
- Enterprise planning systems
- WorkflowWorkflowA workflow consists of a sequence of connected steps. It is a depiction of a sequence of operations, declared as work of a person, a group of persons, an organization of staff, or one or more simple or complex mechanisms. Workflow may be seen as any abstraction of real work...

