
Boston campaign
Encyclopedia
The Boston campaign was the opening campaign
of the American Revolutionary War
. The campaign was primarily concerned with the formation of American colonial irregular militia units, and their transformation into a unified Continental Army
. The campaign's military conflicts started with the Battles of Lexington and Concord
on April 19, 1775, in which colonial militia
s muster
ed to defend against the seizure of military stores in Concord, Massachusetts
by British Army
regulars. Some British units were defeated in a confrontation at Concord's North Bridge
, and the entire British expedition suffered significant casualties during a running battle back to Charlestown
against an ever-growing number of colonial militia.
The accumulated militia surrounded the city of Boston, beginning the Siege of Boston
. The main action during the siege, the Battle of Bunker Hill
on June 17, 1775, was one of the bloodiest encounters of the entire war. There were also numerous skirmishes near Boston and the coastal areas of Boston, resulting in either loss of life, military supplies, or both.
In July 1775, George Washington
took command of the assembled militia and transformed them into a more coherent army. On March 4, 1776, the colonial army fortified Dorchester Heights
with cannon capable of reaching Boston and British ships in the harbor. The siege (and the campaign) ended on March 17, 1776, with the withdrawal of British forces from Boston.
passed the Townshend Acts
, which imposed import duties on paper, glass, paint, and other common items imported into the American colonies
. The Sons of Liberty
and other Patriot
organizations responded with a variety of protest actions. They organized boycotts of the goods subject to the duty, and they harassed and threatened the customs personnel who collected the duties, many of whom were either corrupt or related to Provincial leaders. Francis Bernard, then Governor
of the Province of Massachusetts Bay
, requested military forces to protect the King's personnel. In October 1768, British troops arrived in the city of Boston and occupied
the city. Tensions led to the Boston Massacre
on March 5, 1770, and the Boston Tea Party
on December 16, 1773.
In response to the Tea Party and other protests, Parliament enacted the Intolerable Acts
to punish the colonies. With the Massachusetts Government Act
of 1774 it effectively abolished the provincial government of Massachusetts. General
Thomas Gage
, already the commander-in-chief
of British troops in North America, was also appointed governor of Massachusetts and was instructed by King George's
government to enforce royal authority in the troublesome colony. However, popular resistance compelled the newly appointed royal officials in Massachusetts to resign or to seek refuge in Boston. Gage commanded four regiment
s of British regulars (about 4,000 men) from his headquarters in Boston, but the countryside was largely controlled by Patriot sympathizers.
 On September 1, 1774, British soldiers removed gunpowder
On September 1, 1774, British soldiers removed gunpowder
and other military supplies in a surprise raid on a powder magazine near Boston. This expedition alarmed the countryside, and thousands of American Patriots sprang into action, amid rumors that war was at hand. Although it proved to be a false alarm, this event—known as the Powder Alarm
—caused all concerned to proceed more carefully in the days ahead, and essentially provided a "dress rehearsal" for events seven months later. Partly in response to this action, the colonists carried off military supplies from several forts in New England and distributed them among the local militias.
On the night of April 18, 1775, General Gage sent 700 men to seize munitions stored by the colonial militia at Concord
. Several riders — including Paul Revere
— alerted the countryside, and when the British troops entered Lexington
on the morning of April 19, they found about 80 minutemen formed up on the village common. Shots were exchanged, eight Minutemen were killed, the outnumbered colonial militia dispersed, and the British moved on to Concord. At Concord, the troops searched for military supplies, but found relatively little, as the colonists, having received warnings that such an expedition might happen, had taken steps to hide many of the supplies. During the search, there was a confrontation at the North Bridge
. A small company of British troops fired on a much larger column of colonial militia, which returned fire, and eventually rout
ed those troops, which returned to the village center and rejoined the other troops there. By the time the "redcoats
" or "lobster backs" (as the British soldiers were called) began the return march to Boston, several thousand militiamen had gathered along the road. A running fight ensued, and the British detachment suffered heavily before reaching Charlestown
. With the Battle of Lexington and Concord — the "shot heard 'round the world" — the war had begun.
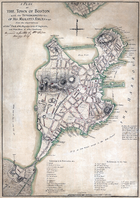 In the aftermath of the failed Concord expedition, the thousands of militiamen that had converged on Boston remained. Over the next few days, more arrived from further afield, including companies from New Hampshire, Connecticut, and Rhode Island. Under the command of Artemas Ward
In the aftermath of the failed Concord expedition, the thousands of militiamen that had converged on Boston remained. Over the next few days, more arrived from further afield, including companies from New Hampshire, Connecticut, and Rhode Island. Under the command of Artemas Ward
, they surrounded the city, blocking its land approaches and putting the occupied city under siege
. The British regulars fortified the high points in the city.
to raid farmers for supplies. In response, the colonials began clearing those islands of supplies useful to the British. One of these actions was contested by the British in the Battle of Chelsea Creek
, but it resulted in the loss of two British soldiers and the British ship Diana. The need for building materials and other supplies led Admiral Samuel Graves
to authorize a Loyalist (American Revolution)
merchant to send his ships from Boston to Machias in the District of Maine
, accompanied by a Royal Navy schooner. The Machias townspeople rose up, seizing the merchant vessels and then the schooner after a short battle
in which its commander was killed. Their resistance and that of other coastal communities led Graves to authorize an expedition of reprisal in October whose sole significant act was the Burning of Falmouth
. The outrage in the colonies over this action contributed to the passing of legislation by the Second Continental Congress
that established the Continental Navy
.
The colonial army also had issues with supply, and with command. Its diverse militias needed to be organized, fed, clothed, and armed, and command needed to be coordinated, as each militia leader was responsible to his province's congress.
, John Burgoyne
, and Henry Clinton
. They formulated a plan to break out of the city, which was finalized on June 12. Reports of these plans made their way to the commanders of the besieging forces, who decided that additional defensive steps were necessary.
On the night of June 16–17, 1775, a detachment of the colonial army stealthily marched onto the Charlestown peninsula, which the British had abandoned in April, and fortified Bunker Hill and Breed's Hill
. On June 17, British forces under General Howe attacked and seized the Charlestown peninsula in the Battle of Bunker Hill
. This battle was technically a British victory, but losses (about 1/2 the attacking forces killed or wounded, including a significant fraction of the entire British officer corps in all of North America) were so heavy that the attack was not followed up. The siege was not broken, and General Gage was recalled to England in September and replaced by General Howe as the British commander-in-chief.
, meeting in Philadelphia, had received reports of the situation outside Boston when it began to meet in May 1775. In response to the confusion over command in the camps there, and in response to the May 10 capture of Fort Ticonderoga
, the need for unified military organization became clear. Congress officially adopted the forces outside Boston as the Continental Army
on May 26, and named George Washington
its commander-in-chief on June 15. Washington left Philadelphia for Boston on June 21, but did not learn of the action at Bunker Hill until he reached New York City
.

stock, which was eventually alleviated by powder shipments from Philadelphia. The British were also busy bringing in reinforcements; by the time of Washington's arrival the British had more than 10,000 men in the city.
Throughout the summer and fall of 1775, both sides dug in, with occasional skirmishes, but neither side chose to take any significant action. Congress, seeking to take some initiative and to capitalize on the capture of Ticonderoga, authorized an invasion of Canada
, after several letters to the inhabitants of Canada were rejected by the French-speaking and British colonists there. In September, Benedict Arnold
led 1,100 troops on an expedition through the wilderness of Maine, which was drawn from the army assembled outside Boston.
Washington faced a personnel crisis toward the end of 1775, as most of the troops in the army had enlistments that expired at the end of 1775. He introduced a number of recruitment incentives and was able to keep the army sufficiently large to maintain the siege, although it was by then smaller than the besieged forces.
, a difficult feat engineered by Henry Knox
. When the guns were placed on Dorchester Heights
in the course of one day, overlooking the British positions, the British situation became untenable. While General Howe planned an attack to reclaim the high ground, a snowstorm prevented its execution. The British, after threatening to burn the city if their departure was hindered, evacuated
the city on March 17, 1776 and sailed for temporary refuge in Halifax
, Nova Scotia
. The local militias dispersed and, in April, General Washington took most of the Continental Army
to fortify New York City
and the start of the New York and New Jersey campaign
.
 The British were essentially driven from New England as a result of this campaign, although there (as elsewhere in the colonies) they continued to receive support from local Loyalist
The British were essentially driven from New England as a result of this campaign, although there (as elsewhere in the colonies) they continued to receive support from local Loyalist
s, especially in Newport, Rhode Island
, from which they drove most of the local Patriot
s. The campaign, as well as the final result of the war as a whole, were a significant blow to British prestige and confidence in its military. The senior military leaders of the campaign were criticized for their actions (Clinton, for example, while he went on to command the British forces in North America, would take much of the blame for the British loss of the war), and others either saw no more action in the war (Gage), or were ultimately disgraced (Burgoyne, who surrendered his army at Saratoga). While the British continued to control the seas, and had military successes on the ground (notably in New York, New Jersey
, and Pennsylvania
), their actions that led to these conflicts had the effect of uniting the Thirteen Colonies in opposition to the crown. As a result, they were never able to marshal enough support from Loyalists to regain meaningful political control of the colonies.
The colonies, in spite of their differences, united themselves as a consequence of these events, granting the Second Continental Congress
(predecessor to the modern U.S. Congress
) sufficient authority and funding to conduct the revolution as a unified whole, including funding and outfitting the military forces that formed as a result of this campaign.
Military campaign
In the military sciences, the term military campaign applies to large scale, long duration, significant military strategy plan incorporating a series of inter-related military operations or battles forming a distinct part of a larger conflict often called a war...
of the American Revolutionary War
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
. The campaign was primarily concerned with the formation of American colonial irregular militia units, and their transformation into a unified Continental Army
Continental Army
The Continental Army was formed after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War by the colonies that became the United States of America. Established by a resolution of the Continental Congress on June 14, 1775, it was created to coordinate the military efforts of the Thirteen Colonies in...
. The campaign's military conflicts started with the Battles of Lexington and Concord
Battles of Lexington and Concord
The Battles of Lexington and Concord were the first military engagements of the American Revolutionary War. They were fought on April 19, 1775, in Middlesex County, Province of Massachusetts Bay, within the towns of Lexington, Concord, Lincoln, Menotomy , and Cambridge, near Boston...
on April 19, 1775, in which colonial militia
Militia
The term militia is commonly used today to refer to a military force composed of ordinary citizens to provide defense, emergency law enforcement, or paramilitary service, in times of emergency without being paid a regular salary or committed to a fixed term of service. It is a polyseme with...
s muster
Muster (military)
The term muster designates the process or event for the of accounting for members in a military unit. Within the United States Army Reserve, it is an annual event used for screening purposes.-Historical:...
ed to defend against the seizure of military stores in Concord, Massachusetts
Concord, Massachusetts
Concord is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, in the United States. As of the 2010 census, the town population was 17,668. Although a small town, Concord is noted for its leading roles in American history and literature.-History:...
by British Army
British Army
The British Army is the land warfare branch of Her Majesty's Armed Forces in the United Kingdom. It came into being with the unification of the Kingdom of England and Scotland into the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707. The new British Army incorporated Regiments that had already existed in England...
regulars. Some British units were defeated in a confrontation at Concord's North Bridge
Old North Bridge, Concord, Massachusetts
The North Bridge, often colloquially called the Old North Bridge, across the Concord River in Concord, Massachusetts, is a historical site in the Battle of Concord, the first day of battle in the Revolutionary War....
, and the entire British expedition suffered significant casualties during a running battle back to Charlestown
Charlestown, Massachusetts
Charlestown is a neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, United States, and is located on a peninsula north of downtown Boston. Charlestown was originally a separate town and the first capital of the Massachusetts Bay Colony; it became a city in 1847 and was annexed by Boston on January 5, 1874...
against an ever-growing number of colonial militia.
The accumulated militia surrounded the city of Boston, beginning the Siege of Boston
Siege of Boston
The Siege of Boston was the opening phase of the American Revolutionary War, in which New England militiamen—who later became part of the Continental Army—surrounded the town of Boston, Massachusetts, to prevent movement by the British Army garrisoned within...
. The main action during the siege, the Battle of Bunker Hill
Battle of Bunker Hill
The Battle of Bunker Hill took place on June 17, 1775, mostly on and around Breed's Hill, during the Siege of Boston early in the American Revolutionary War...
on June 17, 1775, was one of the bloodiest encounters of the entire war. There were also numerous skirmishes near Boston and the coastal areas of Boston, resulting in either loss of life, military supplies, or both.
In July 1775, George Washington
George Washington
George Washington was the dominant military and political leader of the new United States of America from 1775 to 1799. He led the American victory over Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army from 1775 to 1783, and presided over the writing of...
took command of the assembled militia and transformed them into a more coherent army. On March 4, 1776, the colonial army fortified Dorchester Heights
Fortification of Dorchester Heights
The Fortification of Dorchester Heights was a decisive action early in the American Revolutionary War that precipitated the end of the siege of Boston and the withdrawal of British troops from that city....
with cannon capable of reaching Boston and British ships in the harbor. The siege (and the campaign) ended on March 17, 1776, with the withdrawal of British forces from Boston.
Background
In 1767, the British ParliamentParliament of Great Britain
The Parliament of Great Britain was formed in 1707 following the ratification of the Acts of Union by both the Parliament of England and Parliament of Scotland...
passed the Townshend Acts
Townshend Acts
The Townshend Acts were a series of laws passed beginning in 1767 by the Parliament of Great Britain relating to the British colonies in North America. The acts are named after Charles Townshend, the Chancellor of the Exchequer, who proposed the program...
, which imposed import duties on paper, glass, paint, and other common items imported into the American colonies
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were English and later British colonies established on the Atlantic coast of North America between 1607 and 1733. They declared their independence in the American Revolution and formed the United States of America...
. The Sons of Liberty
Sons of Liberty
The Sons of Liberty were a political group made up of American patriots that originated in the pre-independence North American British colonies. The group was formed to protect the rights of the colonists from the usurpations by the British government after 1766...
and other Patriot
Patriot (American Revolution)
Patriots is a name often used to describe the colonists of the British Thirteen United Colonies who rebelled against British control during the American Revolution. It was their leading figures who, in July 1776, declared the United States of America an independent nation...
organizations responded with a variety of protest actions. They organized boycotts of the goods subject to the duty, and they harassed and threatened the customs personnel who collected the duties, many of whom were either corrupt or related to Provincial leaders. Francis Bernard, then Governor
Governor of Massachusetts
The Governor of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts is the executive magistrate of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, United States. The current governor is Democrat Deval Patrick.-Constitutional role:...
of the Province of Massachusetts Bay
Province of Massachusetts Bay
The Province of Massachusetts Bay was a crown colony in North America. It was chartered on October 7, 1691 by William and Mary, the joint monarchs of the kingdoms of England and Scotland...
, requested military forces to protect the King's personnel. In October 1768, British troops arrived in the city of Boston and occupied
Military occupation
Military occupation occurs when the control and authority over a territory passes to a hostile army. The territory then becomes occupied territory.-Military occupation and the laws of war:...
the city. Tensions led to the Boston Massacre
Boston Massacre
The Boston Massacre, called the Boston Riot by the British, was an incident on March 5, 1770, in which British Army soldiers killed five civilian men. British troops had been stationed in Boston, capital of the Province of Massachusetts Bay, since 1768 in order to protect and support...
on March 5, 1770, and the Boston Tea Party
Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was a direct action by colonists in Boston, a town in the British colony of Massachusetts, against the British government and the monopolistic East India Company that controlled all the tea imported into the colonies...
on December 16, 1773.
In response to the Tea Party and other protests, Parliament enacted the Intolerable Acts
Intolerable Acts
The Intolerable Acts or the Coercive Acts are names used to describe a series of laws passed by the British Parliament in 1774 relating to Britain's colonies in North America...
to punish the colonies. With the Massachusetts Government Act
Massachusetts Government Act
The Massachusetts Government Act was passed by the Parliament of Great Britain and became a law on May 20, 1774. The act is one of the Intolerable Acts , designed to suppress dissent and restore order in the Province of Massachusetts Bay...
of 1774 it effectively abolished the provincial government of Massachusetts. General
General
A general officer is an officer of high military rank, usually in the army, and in some nations, the air force. The term is widely used by many nations of the world, and when a country uses a different term, there is an equivalent title given....
Thomas Gage
Thomas Gage
Thomas Gage was a British general, best known for his many years of service in North America, including his role as military commander in the early days of the American War of Independence....
, already the commander-in-chief
Commander-in-Chief
A commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
of British troops in North America, was also appointed governor of Massachusetts and was instructed by King George's
George III of the United Kingdom
George III was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of these two countries on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until his death...
government to enforce royal authority in the troublesome colony. However, popular resistance compelled the newly appointed royal officials in Massachusetts to resign or to seek refuge in Boston. Gage commanded four regiment
Regiment
A regiment is a major tactical military unit, composed of variable numbers of batteries, squadrons or battalions, commanded by a colonel or lieutenant colonel...
s of British regulars (about 4,000 men) from his headquarters in Boston, but the countryside was largely controlled by Patriot sympathizers.
War begins

Gunpowder
Gunpowder, also known since in the late 19th century as black powder, was the first chemical explosive and the only one known until the mid 1800s. It is a mixture of sulfur, charcoal, and potassium nitrate - with the sulfur and charcoal acting as fuels, while the saltpeter works as an oxidizer...
and other military supplies in a surprise raid on a powder magazine near Boston. This expedition alarmed the countryside, and thousands of American Patriots sprang into action, amid rumors that war was at hand. Although it proved to be a false alarm, this event—known as the Powder Alarm
Powder Alarm
The Powder Alarm was a massive popular reaction to the removal of gunpowder from a magazine by British soldiers under orders from General Thomas Gage, royal governor of the Province of Massachusetts Bay, on September 1, 1774...
—caused all concerned to proceed more carefully in the days ahead, and essentially provided a "dress rehearsal" for events seven months later. Partly in response to this action, the colonists carried off military supplies from several forts in New England and distributed them among the local militias.
On the night of April 18, 1775, General Gage sent 700 men to seize munitions stored by the colonial militia at Concord
Concord, Massachusetts
Concord is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, in the United States. As of the 2010 census, the town population was 17,668. Although a small town, Concord is noted for its leading roles in American history and literature.-History:...
. Several riders — including Paul Revere
Paul Revere
Paul Revere was an American silversmith and a patriot in the American Revolution. He is most famous for alerting Colonial militia of approaching British forces before the battles of Lexington and Concord, as dramatized in Henry Wadsworth Longfellow's poem, Paul Revere's Ride...
— alerted the countryside, and when the British troops entered Lexington
Lexington, Massachusetts
Lexington is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 31,399 at the 2010 census. This town is famous for being the site of the first shot of the American Revolution, in the Battle of Lexington on April 19, 1775.- History :...
on the morning of April 19, they found about 80 minutemen formed up on the village common. Shots were exchanged, eight Minutemen were killed, the outnumbered colonial militia dispersed, and the British moved on to Concord. At Concord, the troops searched for military supplies, but found relatively little, as the colonists, having received warnings that such an expedition might happen, had taken steps to hide many of the supplies. During the search, there was a confrontation at the North Bridge
Old North Bridge, Concord, Massachusetts
The North Bridge, often colloquially called the Old North Bridge, across the Concord River in Concord, Massachusetts, is a historical site in the Battle of Concord, the first day of battle in the Revolutionary War....
. A small company of British troops fired on a much larger column of colonial militia, which returned fire, and eventually rout
Rout
A rout is commonly defined as a chaotic and disorderly retreat or withdrawal of troops from a battlefield, resulting in the victory of the opposing party, or following defeat, a collapse of discipline, or poor morale. A routed army often degenerates into a sense of "every man for himself" as the...
ed those troops, which returned to the village center and rejoined the other troops there. By the time the "redcoats
Red coat (British army)
Red coat or Redcoat is a historical term used to refer to soldiers of the British Army because of the red uniforms formerly worn by the majority of regiments. From the late 17th century to the early 20th century, the uniform of most British soldiers, , included a madder red coat or coatee...
" or "lobster backs" (as the British soldiers were called) began the return march to Boston, several thousand militiamen had gathered along the road. A running fight ensued, and the British detachment suffered heavily before reaching Charlestown
Charlestown, Massachusetts
Charlestown is a neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, United States, and is located on a peninsula north of downtown Boston. Charlestown was originally a separate town and the first capital of the Massachusetts Bay Colony; it became a city in 1847 and was annexed by Boston on January 5, 1874...
. With the Battle of Lexington and Concord — the "shot heard 'round the world" — the war had begun.
Siege of Boston

Artemas Ward
Artemas Ward was an American major general in the American Revolutionary War and a Congressman from Massachusetts...
, they surrounded the city, blocking its land approaches and putting the occupied city under siege
Siege of Boston
The Siege of Boston was the opening phase of the American Revolutionary War, in which New England militiamen—who later became part of the Continental Army—surrounded the town of Boston, Massachusetts, to prevent movement by the British Army garrisoned within...
. The British regulars fortified the high points in the city.
Need for supplies
While the British were able to resupply the city by sea, supplies in Boston were short. Troops were sent out to some of the islands in Boston HarborBoston Harbor
Boston Harbor is a natural harbor and estuary of Massachusetts Bay, and is located adjacent to the city of Boston, Massachusetts. It is home to the Port of Boston, a major shipping facility in the northeast.-History:...
to raid farmers for supplies. In response, the colonials began clearing those islands of supplies useful to the British. One of these actions was contested by the British in the Battle of Chelsea Creek
Battle of Chelsea Creek
The Battle of Chelsea Creek was the second military engagement of the Boston campaign of the American Revolutionary War. It is also known as the Battle of Noddle's Island, Battle of Hog Island and the Battle of the Chelsea Estuary...
, but it resulted in the loss of two British soldiers and the British ship Diana. The need for building materials and other supplies led Admiral Samuel Graves
Samuel Graves
Admiral Samuel Graves RN was a British Admiral who is probably best known for his role early in the American War of Independence.-Military career:Graves joined the Royal Navy in 1732...
to authorize a Loyalist (American Revolution)
Loyalist (American Revolution)
Loyalists were American colonists who remained loyal to the Kingdom of Great Britain during the American Revolutionary War. At the time they were often called Tories, Royalists, or King's Men. They were opposed by the Patriots, those who supported the revolution...
merchant to send his ships from Boston to Machias in the District of Maine
District of Maine
The District of Maine was a legal designation for what is now the U.S. state of Maine from American independence until the Missouri Compromise on March 4, 1820, after which it gained its independence from Massachusetts and became the 23rd state in the Union...
, accompanied by a Royal Navy schooner. The Machias townspeople rose up, seizing the merchant vessels and then the schooner after a short battle
Battle of Machias
The Battle of Machias was the first naval engagement of the American Revolutionary War...
in which its commander was killed. Their resistance and that of other coastal communities led Graves to authorize an expedition of reprisal in October whose sole significant act was the Burning of Falmouth
Burning of Falmouth
The Burning of Falmouth was an attack by a fleet of Royal Navy vessels on the town of Falmouth, Massachusetts . The fleet was commanded by Captain Henry Mowat...
. The outrage in the colonies over this action contributed to the passing of legislation by the Second Continental Congress
Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a convention of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that started meeting on May 10, 1775, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, soon after warfare in the American Revolutionary War had begun. It succeeded the First Continental Congress, which met briefly during 1774,...
that established the Continental Navy
Continental Navy
The Continental Navy was the navy of the United States during the American Revolutionary War, and was formed in 1775. Through the efforts of the Continental Navy's patron, John Adams and vigorous Congressional support in the face of stiff opposition, the fleet cumulatively became relatively...
.
The colonial army also had issues with supply, and with command. Its diverse militias needed to be organized, fed, clothed, and armed, and command needed to be coordinated, as each militia leader was responsible to his province's congress.
Bunker Hill
Late in May, General Gage received by sea about 2,000 reinforcements and a trio of generals who would play a vital role in the war: William HoweWilliam Howe, 5th Viscount Howe
William Howe, 5th Viscount Howe, KB, PC was a British army officer who rose to become Commander-in-Chief of British forces during the American War of Independence...
, John Burgoyne
John Burgoyne
General John Burgoyne was a British army officer, politician and dramatist. He first saw action during the Seven Years' War when he participated in several battles, mostly notably during the Portugal Campaign of 1762....
, and Henry Clinton
Henry Clinton (American War of Independence)
General Sir Henry Clinton KB was a British army officer and politician, best known for his service as a general during the American War of Independence. First arriving in Boston in May 1775, from 1778 to 1782 he was the British Commander-in-Chief in North America...
. They formulated a plan to break out of the city, which was finalized on June 12. Reports of these plans made their way to the commanders of the besieging forces, who decided that additional defensive steps were necessary.
On the night of June 16–17, 1775, a detachment of the colonial army stealthily marched onto the Charlestown peninsula, which the British had abandoned in April, and fortified Bunker Hill and Breed's Hill
Breed's Hill
Breed's Hill is a glacial drumlin located in the Charlestown section of Boston, Massachusetts. It is best known as the location where in 1775, early in the American Revolutionary War, most of the fighting in the Battle of Bunker Hill took place...
. On June 17, British forces under General Howe attacked and seized the Charlestown peninsula in the Battle of Bunker Hill
Battle of Bunker Hill
The Battle of Bunker Hill took place on June 17, 1775, mostly on and around Breed's Hill, during the Siege of Boston early in the American Revolutionary War...
. This battle was technically a British victory, but losses (about 1/2 the attacking forces killed or wounded, including a significant fraction of the entire British officer corps in all of North America) were so heavy that the attack was not followed up. The siege was not broken, and General Gage was recalled to England in September and replaced by General Howe as the British commander-in-chief.
Formation of the Continental Army
The Second Continental CongressSecond Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a convention of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that started meeting on May 10, 1775, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, soon after warfare in the American Revolutionary War had begun. It succeeded the First Continental Congress, which met briefly during 1774,...
, meeting in Philadelphia, had received reports of the situation outside Boston when it began to meet in May 1775. In response to the confusion over command in the camps there, and in response to the May 10 capture of Fort Ticonderoga
Capture of Fort Ticonderoga
The Capture of Fort Ticonderoga occurred during the American Revolutionary War on May 10, 1775, when a small force of Green Mountain Boys led by Ethan Allen and Colonel Benedict Arnold overcame a small British garrison at the fort and looted the personal belongings of the garrison...
, the need for unified military organization became clear. Congress officially adopted the forces outside Boston as the Continental Army
Continental Army
The Continental Army was formed after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War by the colonies that became the United States of America. Established by a resolution of the Continental Congress on June 14, 1775, it was created to coordinate the military efforts of the Thirteen Colonies in...
on May 26, and named George Washington
George Washington
George Washington was the dominant military and political leader of the new United States of America from 1775 to 1799. He led the American victory over Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army from 1775 to 1783, and presided over the writing of...
its commander-in-chief on June 15. Washington left Philadelphia for Boston on June 21, but did not learn of the action at Bunker Hill until he reached New York City
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
.

Stalemate
Following the Battle of Bunker Hill, the siege was effectively stalemated, as neither side had either a clearly dominant position, or the will and materiel to significantly alter its position. When Washington took command of the army in July, he determined that its size had reduced from 20,000 to about 13,000 men fit for duty. He also established that the battle had severely depleted the army's powderGunpowder
Gunpowder, also known since in the late 19th century as black powder, was the first chemical explosive and the only one known until the mid 1800s. It is a mixture of sulfur, charcoal, and potassium nitrate - with the sulfur and charcoal acting as fuels, while the saltpeter works as an oxidizer...
stock, which was eventually alleviated by powder shipments from Philadelphia. The British were also busy bringing in reinforcements; by the time of Washington's arrival the British had more than 10,000 men in the city.
Throughout the summer and fall of 1775, both sides dug in, with occasional skirmishes, but neither side chose to take any significant action. Congress, seeking to take some initiative and to capitalize on the capture of Ticonderoga, authorized an invasion of Canada
Invasion of Canada (1775)
The Invasion of Canada in 1775 was the first major military initiative by the newly formed Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. The objective of the campaign was to gain military control of the British Province of Quebec, and convince the French-speaking Canadiens to join the...
, after several letters to the inhabitants of Canada were rejected by the French-speaking and British colonists there. In September, Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold V was a general during the American Revolutionary War. He began the war in the Continental Army but later defected to the British Army. While a general on the American side, he obtained command of the fort at West Point, New York, and plotted to surrender it to the British forces...
led 1,100 troops on an expedition through the wilderness of Maine, which was drawn from the army assembled outside Boston.
Washington faced a personnel crisis toward the end of 1775, as most of the troops in the army had enlistments that expired at the end of 1775. He introduced a number of recruitment incentives and was able to keep the army sufficiently large to maintain the siege, although it was by then smaller than the besieged forces.
Siege ends
By early March 1776, heavy cannons that had been captured at Fort Ticonderoga were moved to BostonNoble train of artillery
The noble train of artillery, also known as the Knox Expedition, was an expedition led by Continental Army Colonel Henry Knox to transport heavy weaponry that had been captured at Fort Ticonderoga to the Continental Army camps outside Boston, Massachusetts during the winter of 1775–1776.Knox went...
, a difficult feat engineered by Henry Knox
Henry Knox
Henry Knox was a military officer of the Continental Army and later the United States Army, and also served as the first United States Secretary of War....
. When the guns were placed on Dorchester Heights
Fortification of Dorchester Heights
The Fortification of Dorchester Heights was a decisive action early in the American Revolutionary War that precipitated the end of the siege of Boston and the withdrawal of British troops from that city....
in the course of one day, overlooking the British positions, the British situation became untenable. While General Howe planned an attack to reclaim the high ground, a snowstorm prevented its execution. The British, after threatening to burn the city if their departure was hindered, evacuated
Evacuation Day (Massachusetts)
March 17 is Evacuation Day, a holiday observed in Suffolk County and also by the public schools in Cambridge and Somerville, Massachusetts. The holiday commemorates the evacuation of British forces from the city of Boston following the Siege of Boston, early in the American Revolutionary War...
the city on March 17, 1776 and sailed for temporary refuge in Halifax
Halifax Regional Municipality, Nova Scotia
Halifax Regional Municipality is the capital of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada. The Regional Municipality had a 2006 census population of 372,679, while the metropolitan area had a 2010 estimated population of 403,188, and the urban area of Halifax had a population of 282,924...
, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The name of the province is Latin for "New Scotland," but "Nova Scotia" is the recognized, English-language name of the province. The provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the...
. The local militias dispersed and, in April, General Washington took most of the Continental Army
Continental Army
The Continental Army was formed after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War by the colonies that became the United States of America. Established by a resolution of the Continental Congress on June 14, 1775, it was created to coordinate the military efforts of the Thirteen Colonies in...
to fortify New York City
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
and the start of the New York and New Jersey campaign
New York and New Jersey campaign
The New York and New Jersey campaign was a series of battles for control of New York City and the state of New Jersey in the American Revolutionary War between British forces under General Sir William Howe and the Continental Army under General George Washington in 1776 and the winter months of 1777...
.
Legacy

Loyalist (American Revolution)
Loyalists were American colonists who remained loyal to the Kingdom of Great Britain during the American Revolutionary War. At the time they were often called Tories, Royalists, or King's Men. They were opposed by the Patriots, those who supported the revolution...
s, especially in Newport, Rhode Island
Newport, Rhode Island
Newport is a city on Aquidneck Island in Newport County, Rhode Island, United States, about south of Providence. Known as a New England summer resort and for the famous Newport Mansions, it is the home of Salve Regina University and Naval Station Newport which houses the United States Naval War...
, from which they drove most of the local Patriot
Patriot (American Revolution)
Patriots is a name often used to describe the colonists of the British Thirteen United Colonies who rebelled against British control during the American Revolution. It was their leading figures who, in July 1776, declared the United States of America an independent nation...
s. The campaign, as well as the final result of the war as a whole, were a significant blow to British prestige and confidence in its military. The senior military leaders of the campaign were criticized for their actions (Clinton, for example, while he went on to command the British forces in North America, would take much of the blame for the British loss of the war), and others either saw no more action in the war (Gage), or were ultimately disgraced (Burgoyne, who surrendered his army at Saratoga). While the British continued to control the seas, and had military successes on the ground (notably in New York, New Jersey
New York and New Jersey campaign
The New York and New Jersey campaign was a series of battles for control of New York City and the state of New Jersey in the American Revolutionary War between British forces under General Sir William Howe and the Continental Army under General George Washington in 1776 and the winter months of 1777...
, and Pennsylvania
Philadelphia campaign
The Philadelphia campaign was a British initiative in the American Revolutionary War to gain control of Philadelphia, which was then the seat of the Second Continental Congress...
), their actions that led to these conflicts had the effect of uniting the Thirteen Colonies in opposition to the crown. As a result, they were never able to marshal enough support from Loyalists to regain meaningful political control of the colonies.
The colonies, in spite of their differences, united themselves as a consequence of these events, granting the Second Continental Congress
Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a convention of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that started meeting on May 10, 1775, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, soon after warfare in the American Revolutionary War had begun. It succeeded the First Continental Congress, which met briefly during 1774,...
(predecessor to the modern U.S. Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
) sufficient authority and funding to conduct the revolution as a unified whole, including funding and outfitting the military forces that formed as a result of this campaign.
See also
- Saratoga CampaignSaratoga campaignThe Saratoga Campaign was an attempt by Great Britain to gain military control of the strategically important Hudson River valley in 1777 during the American Revolutionary War...
- Northern theater of the American Revolutionary War after SaratogaNorthern theater of the American Revolutionary War after SaratogaThe Northern theater of the American Revolutionary War after Saratoga consisted of a series of battles between American revolutionaries and British forces, from 1778 to 1782 during the American Revolutionary War. It is characterized by two primary areas of activity...

