Borabenzene
Encyclopedia
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
instead of the carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
of a benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
. A free borabenzene, which has no donor ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
on the boron
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
, has not yet been isolated despite its simple structure and the chemical robustness of boron
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
-carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
bonds
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
. The instability of this molecule results from the high Lewis acidity
Lewis acid
]The term Lewis acid refers to a definition of acid published by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1923, specifically: An acid substance is one which can employ a lone pair from another molecule in completing the stable group of one of its own atoms. Thus, H+ is a Lewis acid, since it can accept a lone pair,...
of the boron
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
due to its electron deficiency
Electron deficiency
Electron deficiency occurs when a compound has too few valence electrons for the connections between atoms to be described as covalent bonds. Electron deficient bonds are often better described as 3-center-2-electron bonds...
. All attempts to create a free borabenzene have resulted in formations of complexes
Complex (chemistry)
In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex, is an atom or ion , bonded to a surrounding array of molecules or anions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents...
with anionic or neutral ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
s (even a nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
can coordinate to a borabenzene). However, the complexes with anionic ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
s, called boratabenzenes, show rich chemistry including the coordination chemistry as anionic π-type ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
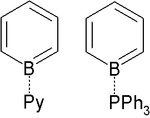
s. Borabenzene is also stable with electron donor molecules such as pyridine
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
or triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P3 - often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature...
.
Properties as ligands
Boratabenzenes have a negative chargeElectric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
on their six-membered rings and act as strong π-donating ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
s like a cyclopentadienyl
Cyclopentadienyl complex
A cyclopentadienyl complex is a metal complex with one or more cyclopentadienyl groups . Based on the type of bonding between the metals and the cyclopentadienyl]] moieties, cyclopentadienyl complexes are classified into the following three categories: a) π-complexes, b) σ-complexes, and c) ionic...
anion, which is often used in transition metal
Transition metal
The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some...
complexes
Complex (chemistry)
In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex, is an atom or ion , bonded to a surrounding array of molecules or anions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents...
. In fact, sandwich or half-sandwich type complexes
Metallocene
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions bound to a metal center in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula 2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride, vanadocene dichloride...
of many transition metal
Transition metal
The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some...
s have been reported using boratabenzenes, and the zirconium
Zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name of zirconium is taken from the mineral zircon. Its atomic mass is 91.224. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that resembles titanium...
sandwich complexes
Metallocene
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions bound to a metal center in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula 2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride, vanadocene dichloride...
exhibit catalytic activity in ethylene
Ethylene
Ethylene is a gaseous organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest alkene . Because it contains a carbon-carbon double bond, ethylene is classified as an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Ethylene is widely used in industry and is also a plant hormone...
polymerization
Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form three-dimensional networks or polymer chains...
similar to zirconocenes
Metallocene
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions bound to a metal center in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula 2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride, vanadocene dichloride...
, which are the cyclopentadienyl counterparts
Metallocene
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions bound to a metal center in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula 2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride, vanadocene dichloride...
.
Family of boratabenzenes
Several boracyclic compounds are involved in the family of boratabenzenes: 1-boratanaphthaleneNaphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings...
, 9-borathaanthracene
Anthracene
Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal-tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes...
, boracyclooctatetraene
Annulene
Annulenes are completely conjugated monocyclic hydrocarbons. They have the general formula CnHn or CnHn+1...
, and 2,2’-diboratabiphenyl
Biphenyl
Biphenyl is an organic compound that forms colorless crystals. It has a distinctively pleasant smell. Biphenyl is an aromatic hydrocarbon with a molecular formula 2...
. Among these compounds, 2,2’-diboratabiphenyl
Biphenyl
Biphenyl is an organic compound that forms colorless crystals. It has a distinctively pleasant smell. Biphenyl is an aromatic hydrocarbon with a molecular formula 2...
is the first bidentate
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
Lewis acid
Lewis acid
]The term Lewis acid refers to a definition of acid published by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1923, specifically: An acid substance is one which can employ a lone pair from another molecule in completing the stable group of one of its own atoms. Thus, H+ is a Lewis acid, since it can accept a lone pair,...
based on a borabenzene framework, so it is regarded as a Lewis acid
Lewis acid
]The term Lewis acid refers to a definition of acid published by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1923, specifically: An acid substance is one which can employ a lone pair from another molecule in completing the stable group of one of its own atoms. Thus, H+ is a Lewis acid, since it can accept a lone pair,...
analogue of 2,2’-bipyridine, a common bidentate ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
. This compound forms polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon analogues containing boron
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
and nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s, which show characteristic optical and electrochemical properties due to the charge transfer between the boron
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
and nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s.
Reactions
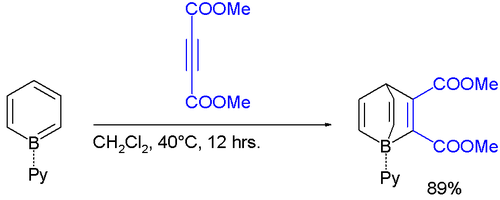
Borabenzene is known to react with electron-deficient alkyneAlkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
s in a Diels-Alder reaction
Diels-Alder reaction
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. The reaction can proceed even if some of the atoms in the newly formed ring are not carbon...
to the boron
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
pendants of barrelene
Barrelene
Barrelene is a bicyclic organic compound with chemical formula C8H8 and systematic name bicyclo[2.2.2]octa-2,5,7-triene. First synthesized and described by H. E. Zimmerman in 1960 the name derives from the obvious resemblance with a barrel, with the staves being three ethylene units attached to two...
called borabarrelenes :
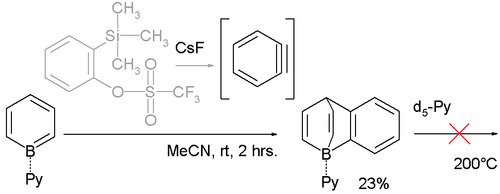
Likewise the benzoborabarrelene is accessible through reaction with benzyne through 2-(Trimethylsilyl)phenyl triflate and caesium fluoride
Caesium fluoride
Caesium fluoride , is an inorganic compound usually encountered as a hygroscopic white solid. It is more soluble and more readily dissociated than sodium fluoride or potassium fluoride. It is available in anhydrous form, and if water has been absorbed it is easy to dry by heating at 100 °C for...
:
The boron atom in these barrelene compounds is pyramidalized (the sum of the C-B-C angles is 311° not 327°) leading to even greater Lewis acid
Lewis acid
]The term Lewis acid refers to a definition of acid published by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1923, specifically: An acid substance is one which can employ a lone pair from another molecule in completing the stable group of one of its own atoms. Thus, H+ is a Lewis acid, since it can accept a lone pair,...
strength. This is evident from the unusual small B-N bond length
Bond length
- Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter...
of 158 picometer compared to 165pm for ordinary B-N bonds in borane-pyridine adducts.
Another remarkable manifestation of this property is their reluctance to surrender the pyridine ligand (for example in exchange for deuterated pyridine d5-Py) even at 200 °C.
In contrast to ordinary barrelene
Barrelene
Barrelene is a bicyclic organic compound with chemical formula C8H8 and systematic name bicyclo[2.2.2]octa-2,5,7-triene. First synthesized and described by H. E. Zimmerman in 1960 the name derives from the obvious resemblance with a barrel, with the staves being three ethylene units attached to two...
s, this benzobarrelene is also resistant to Ring opening metathesis polymerisation
Ring opening metathesis polymerisation
Ring-opening metathesis polymerization is a type of olefin metathesis chain-growth polymerization that produces industrially important products. The driving force of the reaction is relief of ring strain in cyclic olefins and a wide variety of catalysts have been discovered...
.
See also
- 6-membered aromatic rings with one carbon replaced by another group: borabenzene, benzeneBenzeneBenzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
, silabenzeneSilabenzeneA silabenzene is a heteroaromatic compound containing one or more silicon atoms instead of carbon atom in benzene. A single substitution gives silabenzene proper; additional substitutions give a disilabenzene , trisilabenzene , etc.Silabenzenes have been the targets of many theoretical and...
, germanabenzeneGermanabenzeneGermabenzene is the parent representative of a group of chemical compounds containing in their molecular structure a benzene ring with a carbon atom replaced by a germanium atom. Germabenzene itself has been studied theoretically, but has not been synthesized...
, stannabenzeneStannabenzeneStannabenzene is the parent representative of a group of organotin compounds that are related to benzene with a carbon atom replaced by a tin atom. Stannabenzene itself has been studied by computational chemistry, but has not been isolated....
, pyridinePyridinePyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
, phosphorinePhosphorinePhosphorine is a heavier element analog of pyridine, containing a phosphorus atom instead of an aza- moiety. It is also called phosphabenzene and belongs to the phosphaalkene class. Phosphorine is a planar aromatic compound with 88% of the aromaticity of that of benzene...
, pyrylium saltPyrylium saltA pyrylium salt is a salt containing a pyrylium cation or a derivative of it. The pyrylium cation is a conjugated 6-membered carbon ring system with one carbon atom replaced by a positively charged oxygen atom. It is, like benzene, an aromatic compound...