
Annulene
Encyclopedia
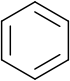
annulene.svg.png)
Conjugated system
In chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in compounds with alternating single and multiple bonds, which in general may lower the overall energy of the molecule and increase stability. Lone pairs, radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the...
monocyclic
Cyclic compound
In chemistry, a cyclic compound is a compound in which a series of atoms is connected to form a loop or ring.While the vast majority of cyclic compounds are organic, a few inorganic substances form cyclic compounds as well, including sulfur, silanes, phosphanes, phosphoric acid, and triboric acid. ...
hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
s. They have the general formula CnHn (when n is an even number) or CnHn+1 (when n is an odd number). The IUPAC naming conventions
IUPAC nomenclature
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry ....
are that annulenes with 7 or more carbon atoms are named as [n]annulene, where n is the number of carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s in their ring, though sometimes the smaller annulenes are referred to using the same notation, and benzene is sometimes referred to simply as annulene.
The first three annulenes are cyclobutadiene
Cyclobutadiene
Cyclobutadiene is the smallest [n]-annulene , an extremely unstable hydrocarbon having a lifetime shorter than five seconds in the free state. It has chemical formula 44 and a rectangular structure verified by infrared studies. This is in contrast to the square geometry predicted by simple Hückel...
, benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
, and cyclooctatetraene
Cyclooctatetraene
1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene is an unsaturated derivative of cyclooctane, with the formula C8H8. It is also known as [8]annulene. This polyunsaturated hydrocarbon is a colorless to light yellow flammable liquid at room temperature...
([8]annulene). Some annulenes, namely cyclobutadiene, cyclodecapentaene
Cyclodecapentaene
Cyclodecapentaene or [10]annulene is an annulene with molecular formula C10H10. This organic compound is a conjugated 10 pi electron cyclic system and according to Huckel's rule it should display aromaticity. It is not aromatic, however, because of a combination of steric strain and angular strain...
or [10]annulene, cyclododecahexaene
Cyclododecahexaene
Cyclododecahexaene or [12]annulene is a member of a series of annulenes with some interest in organic chemistry with regard to the study of aromaticity These compounds are in general unstable due to their antiaromaticity and built-up of steric strain...
or [12]annulene and cyclotetradecaheptaene
Cyclotetradecaheptaene
Cyclotetradecaheptaene is an aromatic annulene with molecular formula C14H14. It is somewhat unstable due to ring strain....
([14]annulene), are unstable, with cyclobutadiene extremely so.
Annulenes may be aromatic (benzene, [14]annulene, cyclooctadecanonaene
Cyclooctadecanonaene
Cyclooctadecanonaene or [18]annulene is an annulene with chemical formula . This hydrocarbon obeys Hückel's rule and is, therefore, an aromatic compound...
or [18] annulene), non-aromatic ([10]annulene), or anti-aromatic (cyclobutadiene). Only cyclobutadiene and benzene are fully planar, though [14] and [18]annulene with all trans double bonds (placing the hydrogens inside the ring) can achieve the planar conformation needed for aromaticity, with [14] and [18]annulene following Hückel's rule
Hückel's rule
In organic chemistry, Hückel's rule estimates whether a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties. The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was first worked out by physical chemist Erich Hückel in 1931...
with 4n+2 π electrons
Pi bond
In chemistry, pi bonds are covalent chemical bonds where two lobes of one involved atomic orbital overlap two lobes of the other involved atomic orbital...
. [14]annulene does exhibit some ring strain
Ring strain
In organic chemistry, ring strain is the tendency of a cyclic molecule, such as cyclopropane, to destabilize when its atoms are in non-favorable high energy spatial orientations...
due to steric hindrance.
Many of the larger annulenes, [18]annuelene for example, are large enough to minimize the van der Waals strain of internal hydrogens and thermodynamically qualify as aromatic. However, none of the larger annulenes are as stable as benzene, as their reactivity more closely resembles a conjugated polyene than an aromatic hydrocarbon.
In annulyne
Annulyne
Annulynes or 1,2-didehydroannulenes are conjugated monocyclic hydrocarbons with alternating alkene bonds in addition to at least one alkyne bond....
s, one double bond is replaced by an alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
bond.
External links
- NIST Chemistry WebBook - [18]annulene
- Structure of [14] and [18]annulene

