
Berenice (port)
Encyclopedia
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
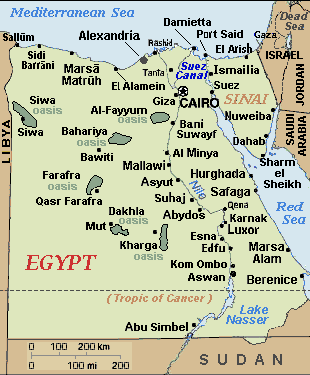
: ), also known as Baranis and now known as Medinet-el Haras, is an ancient seaport of Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
on the west coast of the Red Sea
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
. It is situated about 825 km south of Suez
Suez
Suez is a seaport city in north-eastern Egypt, located on the north coast of the Gulf of Suez , near the southern terminus of the Suez Canal, having the same boundaries as Suez governorate. It has three harbors, Adabya, Ain Sokhna and Port Tawfiq, and extensive port facilities...
and 260 km east of Aswan
Aswan
Aswan , formerly spelled Assuan, is a city in the south of Egypt, the capital of the Aswan Governorate.It stands on the east bank of the Nile at the first cataract and is a busy market and tourist centre...
.
It was founded or certainly converted from a village into a city, by Ptolemy II (285 BC—246 BC), who named it after his mother, Berenice I of Egypt
Berenice I of Egypt
Berenice I was a Greek Macedonian noblewoman and through her marriage to Ptolemy I Soter, became the first Queen of the Ptolemaic dynasty of Egypt.-Family:...
. Troglodytica refers to the aboriginal people of the region, the "Troglodytai
Troglodytae
The Troglodytae or Troglodyti , were a people mentioned in various locations by many ancient Greek and Roman geographers and historians including Agatharcides, Strabo, Diodorus Siculus, Pliny, Tacitus, Josephus, etc....
" or "cave dwellers". Although the name is attested by several ancient writers, the more ancient Ptolemaic inscriptions read Trogodytai (which G.W.B. Huntingford has speculated could be related to the same root as Tuareg). It is possible that later copyists confused this name with the more common term Troglodytai.
Built at the head of a gulf, the Sinus Immundus, or Foul Bay
Foul Bay
Foul Bay is an inlet of water on the Egyptian side of the Red Sea. It is located slightly north of the Tropic of Cancer. The town which lies at the most inland section of the bay is Berenice. The northern part of Foul Bay is a peninsula called Ras Banas....
, of Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
, it was sheltered on the north by Ras Benas (Lepte Extrema). A lofty range of mountains runs along this side of the African coast, and separates Berenice from the Nile Valley. The emerald mines of Zabara and Saket are in its neighbourhood. The harbour is indifferent, but was improved by art. Berenice stood upon a narrow rim of shore between the hills and the Red Sea. The harbor of Berenice was sheltered from the northeast wind by the island Ophiodes
Ophiodes
-Classification:Genus Ophiodes*Ophiodes intermedius*Ophiodes striatus*Ophiodes vertebralis*Ophiodes yacupoi...
' onMouseout='HidePop("63137")' href="/topics/Strabo">Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
xvi. p. 770; Diod. iii. 39), which was rich in topazes.
History
Berenice was quite famous and prosperous in antiquity. The city is noted by most ancient geographers, including Strabo, Pliny the ElderPliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
(vi. 23, 26, 29, 33), and Stephanus of Byzantium
Stephanus of Byzantium
Stephen of Byzantium, also known as Stephanus Byzantinus , was the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled Ethnica...
(s. v.). Its prosperity after the third century was owing in great measure to three causes: the favour of the Macedon
Macedon
Macedonia or Macedon was an ancient kingdom, centered in the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, the region of Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south....
ian kings, its safe anchorage, and its being a terminus of the great road from Coptos, which rendered Berenice and Myos Hormos
Myos Hormos
Myos Hormos was a Red Sea port constructed by the Ptolemies around the 3rd century BC. Following excavations carried out recently by David Peacock and Lucy Blue of the University of Southampton, it is thought to have been located on the present-day site of Quseir al-Quadim , eight kilometres north...
the two principal emporia of the trade between Aethiopia and Egypt on the one hand, and Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
and Tamilakkam on the other. The road across the desert from Coptos was 258 Roman miles long, or eleven days' journey. The road was provided with watering stations (Greek hydreumata, see Hadhramaut
Hadhramaut
Hadhramaut, Hadhramout, Hadramawt or Ḥaḍramūt is the formerly independent Qu'aiti state and sultanate encompassing a historical region of the south Arabian Peninsula along the Gulf of Aden in the Arabian Sea, extending eastwards from Yemen to the borders of the Dhofar region of Oman...
); the wells and halting places of the caravans are enumerated by Pliny (vi. 23. s. 26), and in the Itineraries (Antonin.
Antonine Itinerary
The Antonine Itinerary is a register of the stations and distances along the various roads of the Roman empire, containing directions how to get from one Roman settlement to another...
p. 172, f.). Belzoni (Travels, vol. ii. p. 35) found traces of several of these stations.
From the 1st century BC until the 2nd century AD Berenice was one of the trans-shipping points of trade between India, Arabia, and Upper Egypt. It was connected to Lower Egypt by the Via Hadriana
Via Hadriana
The Via Hadriana was an ancient Roman road established by the emperor Hadrian, running from Antinopolis to the Red Sea at Berenike. It was finished in 137 AD...
in 137. The coastal trade from Berenice along the coast of the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
is described in the anonymous 1st century AD handbook Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea or Periplus of the Red Sea is a Greco-Roman periplus, written in Greek, describing navigation and trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports like Berenice along the coast of the Red Sea, and others along Northeast Africa and India...
. In the 4th century Berenice again become an active port, but after the 6th century the port was abandoned. Under the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
, Berenice formed a district in itself, with its peculiar prefect, who was entitled Praefectus Berenicidis, or P. montis Berenicidis. (Orelli, Inscr. Lat. no. 3880, f.)
In 1818 the ruins of Berenice were identified by Giovanni Battista Belzoni
Giovanni Battista Belzoni
Giovanni Battista Belzoni , sometimes known as The Great Belzoni, was a prolific Venetian explorer of Egyptian antiquities.-Early life:...
, confirming an earlier opinion of D'Anville. Since then, several excavations have been undertaken. The port is now nearly filled up, has a sand-bar at its entrance and can be reached only by small craft. Most important of the ruins is a temple; the remnants of its sculptures and inscriptions preserve the name of Tiberius
Tiberius
Tiberius , was Roman Emperor from 14 AD to 37 AD. Tiberius was by birth a Claudian, son of Tiberius Claudius Nero and Livia Drusilla. His mother divorced Nero and married Augustus in 39 BC, making him a step-son of Octavian...
and the figures of many deities, including a (goddess?) Alabarch or Arabarch, also the name of the head magistrate of the Jews in Alexandria
Alexandria
Alexandria is the second-largest city of Egypt, with a population of 4.1 million, extending about along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the north central part of the country; it is also the largest city lying directly on the Mediterranean coast. It is Egypt's largest seaport, serving...
under Ptolemaic
Ptolemaic Egypt
Ptolemaic Egypt began when Ptolemy I Soter invaded Egypt and declared himself Pharaoh of Egypt in 305 BC and ended with the death of queen Cleopatra VII of Egypt and the Roman conquest in 30 BC. The Ptolemaic Kingdom was a powerful Hellenistic state, extending from southern Syria in the east, to...
and Roman rule
Aegyptus (Roman province)
The Roman province of Egypt was established in 30 BC after Octavian defeated his rival Mark Antony, deposed his lover Queen Cleopatra VII and annexed the Ptolemaic kingdom of Egypt to the Roman Empire. The province encompassed most of modern-day Egypt except for the Sinai Peninsula...
. The temple is of sandstone and soft calcareous stone, in the Egyptian style. It is 102 feet (31.1 m) long, and 43 wide. A portion of its walls is sculptured with well-executed basso relieves, of Greek workmanship, and hieroglyphics
Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs were a formal writing system used by the ancient Egyptians that combined logographic and alphabetic elements. Egyptians used cursive hieroglyphs for religious literature on papyrus and wood...
also occasionally occur on the walls. Belzoni said that the city measured 1600 feet (487.7 m) from north to south, and 2,000 from east to west. He estimated the ancient population at 10,000. (Researches, vol. ii. p. 73.)
Recent archaeological finds
Excavations were launched at Berenike in 1994 by a team of archaeologists from the University of DelawareUniversity of Delaware
The university is organized into seven colleges:* College of Agriculture and Natural Resources* College of Arts and Sciences* Alfred Lerner College of Business and Economics* College of Earth, Ocean and Environment* College of Education and Human Development...
led by Prof. Steven E. Sidebotham, with partners from several other institutions and continued until 2001. Work was resumed by teams from the University of Delaware and the Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology, University of Warsaw
University of Warsaw
The University of Warsaw is the largest university in Poland and one of the most prestigious, ranked as best Polish university in 2010 and 2011...
, Poland, in the winter of 2007/2008 and is still continuing.
A large number of significant finds have been made providing evidence of the cargo from the Malabar Coast
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is a long and narrow coastline on the south-western shore line of the mainland Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing mountain...
and the presence of Tamil people
Tamil people
Tamil people , also called Tamils or Tamilians, are an ethnic group native to Tamil Nadu, India and the north-eastern region of Sri Lanka. Historic and post 15th century emigrant communities are also found across the world, notably Malaysia, Singapore, Mauritius, South Africa, Australia, Canada,...
from South India and Jaffna
Jaffna
Jaffna is the capital city of the Northern Province, Sri Lanka. It is the administrative headquarters of the Jaffna district located on a peninsula of the same name. Jaffna is approximately six miles away from Kandarodai which served as a famous emporium in the Jaffna peninsula from classical...
being at this last outpost of the Roman Empire.
- "Among the unexpected discoveries at Berenike were a range of ancient Indian goods, including the largest single concentration (7.55 kg) of black peppercorns ever recovered in the classical Mediterranean world (“imported from southern India” and found inside a large vessel made of Nile silt in a temple courtyard); substantial quantities of Indian-made fine ware and kitchen cooking ware and Indian style pottery; Indian-made sail cloth, basketry, matting, etc. from trash dumps; a large quantity of teak wood, black pepper, coconuts, beads made of precious and semi-precious stones, cameo blanks; “a Tamil Brahmi graffito mentioning Korra, a South Indian chieftain”; evidence that “inhabitants from Tamil South India (which then included most of Kerala) were living in Berenike, at least in the early Roman period”; evidence that the Tamil population implied the probable presence of Buddhist worshippers; evidence of Indians at another Roman port 300 km north of Berenike; Indian-made ceramics on the Nile road; a rock inscription mentioning an Indian passing through en route; “abundant evidence for the use of ships built and rigged in India”; and proof “that teak wood (endemic to South India), found in buildings in Berenike, had clearly been reused”(from dismantled ships)."
In 2009 the first find of frankincense
Frankincense
Frankincense, also called olibanum , is an aromatic resin obtained from trees of the genus Boswellia, particularly Boswellia sacra, B. carteri, B. thurifera, B. frereana, and B. bhaw-dajiana...
was reported and "two blocks of resin from the Syrian fir tree (Abies cilicica
Abies cilicica
Abies cilicica, or Cilicia Fir, is a species of conifer in the Pinaceae family.It is found in Lebanon, Syria, and Turkey.In 2009 at Berenice Troglodytica, the Egypto-Roman port on the Red Sea, archaeologists found: "two blocks of resin from the Syrian fir tree , one weighting about 190 g and the...
), one weighting about 190 g and the other about 339 g, recovered from 1st-century AD contexts in one of the harbor trenches. Produced in areas of greater Syria and Asia Minor, this resin and its oil derivative were used in mummification, as an antiseptic, a diuretic, to treat wrinkles, extract worms and promote hair growth."

