
Aromatic ring current
Encyclopedia
An aromatic ring current is an effect observed in aromatic
molecules such as benzene
and naphthalene
. If a magnetic field
is directed perpendicular
to the plane of the aromatic system, a ring current is induced in the delocalized π electrons of the aromatic ring. This is a direct consequence of Ampère's law
; since the electrons involved are free to circulate, rather than being localized in bonds as they would be in most non-aromatic molecules, they respond much more strongly to the magnetic field.
Aromatic ring currents are relevant to NMR spectroscopy
, as they dramatically influence the chemical shift
s of 13C
and 1H
nuclei
in aromatic molecules, as well as in any organic or inorganic aromatic molecule. The effect helps distinguish these nuclear environments and is therefore of great use in molecular structure determination. In benzene, the ring protons experience deshielding because the induced magnetic field has the same direction as the external field and their chemical shift
is 7.3 ppm compared to 5.6 to the vinylic proton in cyclohexene
. In contrast any proton inside the aromatic ring experiences shielding because both fields are in opposite direction. This effect can be observed in cyclooctadecanonaene
([18]annulene) with 6 inner protons at −3 ppm.
The situation is reversed in antiaromatic compounds. In the dianion of [18]annulene the inner protons are strongly deshielded at 20.8 ppm and 29.5 ppm with the outer electrons significantly shielded (with respect to the reference) at −1.1 ppm. Hence a diamagnetic ring current or diatropic ring current is associated with aromaticity whereas a paratropic ring current signals antiaromaticity.
A similar effect is observed in three-dimensional fullerene
s; in this case it is called a sphere current .
Numerous attempts have been made to quantify aromaticity
with respect to the observed ring current. One method is called diamagnetic susceptibility exaltation Λ
defined as the difference between the measured magnetic susceptibility
of a compound and a calculated value based on group additivity tables. Benzene
is clearly aromatic (Λ = −13.4), borazine
(Λ = −1.7) and cyclohexane
(Λ = 1.1) are not aromatic and cyclobutadiene
(Λ = +18) is antiaromatic.
Another measurable quantity is the chemical shift
of lithium
ions Li+ in complexes of lithium with aromats because lithium tends to coordinate to the face
of the aromatic rings. Thus the lithium atom in cyclopentadienyl
lithium (CpLi) has a chemical shift of −8.6 ppm (aromatic) and its Cp2Li− complex a shift of −13.1.
Both methods suffer from the disadvantage that values depend on ring size. The nucleus-independent chemical shift (NICS) is a computational method
that calculates the absolute magnetic shieldings at the center of the ring taken with reversed sign. In this method negative NICS values indicate aromaticity and positive values antiaromaticity.
Yet another method called the harmonic oscillator model of aromaticity (HOMA) is defined as a normalized sum
of squared deviations
of bond length
s from the optimal value, which is assumed to be realized for a fully aromatic system . An aromat has HOMA value 1 whereas a non-aromatic compound has value 0. For all-carbon systems, a HOMA value is obtained making use of this equation:
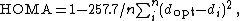
with the value of 257.7 the normalization value, n-number of CC bonds, dopt the optimized bond length (1.388 angstrom
) and di the experimental or computed bond length.
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, Aromaticity is a chemical property in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibit a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August...
molecules such as benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
and naphthalene
Naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings...
. If a magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
is directed perpendicular
Perpendicular
In geometry, two lines or planes are considered perpendicular to each other if they form congruent adjacent angles . The term may be used as a noun or adjective...
to the plane of the aromatic system, a ring current is induced in the delocalized π electrons of the aromatic ring. This is a direct consequence of Ampère's law
Ampère's law
In classical electromagnetism, Ampère's circuital law, discovered by André-Marie Ampère in 1826, relates the integrated magnetic field around a closed loop to the electric current passing through the loop...
; since the electrons involved are free to circulate, rather than being localized in bonds as they would be in most non-aromatic molecules, they respond much more strongly to the magnetic field.
Aromatic ring currents are relevant to NMR spectroscopy
NMR spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy, is a research technique that exploits the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei to determine physical and chemical properties of atoms or the molecules in which they are contained...
, as they dramatically influence the chemical shift
Chemical shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule...
s of 13C
Carbon-13
Carbon-13 is a natural, stable isotope of carbon and one of the environmental isotopes. It makes up about 1.1% of all natural carbon on Earth.- Detection by mass spectrometry :...
and 1H
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively-charged proton and a single negatively-charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force...
nuclei
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
in aromatic molecules, as well as in any organic or inorganic aromatic molecule. The effect helps distinguish these nuclear environments and is therefore of great use in molecular structure determination. In benzene, the ring protons experience deshielding because the induced magnetic field has the same direction as the external field and their chemical shift
Chemical shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule...
is 7.3 ppm compared to 5.6 to the vinylic proton in cyclohexene
Cyclohexene
Cyclohexene is a hydrocarbon with the formula C6H10. This cycloalkene is a colorless liquid with a sharp smell. It is an intermediate in various industrial processes...
. In contrast any proton inside the aromatic ring experiences shielding because both fields are in opposite direction. This effect can be observed in cyclooctadecanonaene
Cyclooctadecanonaene
Cyclooctadecanonaene or [18]annulene is an annulene with chemical formula . This hydrocarbon obeys Hückel's rule and is, therefore, an aromatic compound...
([18]annulene) with 6 inner protons at −3 ppm.
The situation is reversed in antiaromatic compounds. In the dianion of [18]annulene the inner protons are strongly deshielded at 20.8 ppm and 29.5 ppm with the outer electrons significantly shielded (with respect to the reference) at −1.1 ppm. Hence a diamagnetic ring current or diatropic ring current is associated with aromaticity whereas a paratropic ring current signals antiaromaticity.
A similar effect is observed in three-dimensional fullerene
Fullerene
A fullerene is any molecule composed entirely of carbon, in the form of a hollow sphere, ellipsoid, or tube. Spherical fullerenes are also called buckyballs, and they resemble the balls used in association football. Cylindrical ones are called carbon nanotubes or buckytubes...
s; in this case it is called a sphere current .
Relative aromaticity
| Selected NICS values / ppm | |
| Pyrrole Pyrrole Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colourless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3... |
−15.1 |
| Thiophene Thiophene Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a flat five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. Related to thiophene are benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene, containing the thiophene ring fused with one and two benzene... |
−13.6 |
| Furan Furan Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen. The class of compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.... |
−12.3 |
| naphthalene Naphthalene Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings... |
−9.9 |
| Benzene Benzene Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6.... |
−9.7 |
| Tropylium | −7.6 |
| Cyclopentadiene Cyclopentadiene Cyclopentadiene is an organic compound with the formula C5H6. This colorless liquid has a strong and unpleasant odor. At room temperature, this cyclic diene dimerizes over the course of hours to give dicyclopentadiene via a Diels–Alder reaction... |
−3.2 |
| Cyclohexane Cyclohexane Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is used as a nonpolar solvent for the chemical industry, and also as a raw material for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, both of which being intermediates used in the production of nylon... |
−2.2 |
| Pentalene Pentalene Pentalene is a polycyclic hydrocarbon composed of two fused cyclopentadiene rings. It has chemical formula C8H6. It is antiaromatic, because it has 4n pi electrons. For this reason it dimerizes even at temperatures as low as -100°C.... |
18.1 |
| Heptalene Heptalene Heptalene is a polycyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C12H10, composed of two fused cycloheptatriene rings.... |
22.7 |
| Cyclobutadiene Cyclobutadiene Cyclobutadiene is the smallest [n]-annulene , an extremely unstable hydrocarbon having a lifetime shorter than five seconds in the free state. It has chemical formula 44 and a rectangular structure verified by infrared studies. This is in contrast to the square geometry predicted by simple Hückel... |
27.6 |
Numerous attempts have been made to quantify aromaticity
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, Aromaticity is a chemical property in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibit a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August...
with respect to the observed ring current. One method is called diamagnetic susceptibility exaltation Λ
Lambda
Lambda is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is related to the Phoenician letter Lamed . Letters in other alphabets that stemmed from lambda include the Roman L and the Cyrillic letter El...
defined as the difference between the measured magnetic susceptibility
Magnetic susceptibility
In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility \chi_m is a dimensionless proportionality constant that indicates the degree of magnetization of a material in response to an applied magnetic field...
of a compound and a calculated value based on group additivity tables. Benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
is clearly aromatic (Λ = −13.4), borazine
Borazine
Borazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula 33. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene...
(Λ = −1.7) and cyclohexane
Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is used as a nonpolar solvent for the chemical industry, and also as a raw material for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, both of which being intermediates used in the production of nylon...
(Λ = 1.1) are not aromatic and cyclobutadiene
Cyclobutadiene
Cyclobutadiene is the smallest [n]-annulene , an extremely unstable hydrocarbon having a lifetime shorter than five seconds in the free state. It has chemical formula 44 and a rectangular structure verified by infrared studies. This is in contrast to the square geometry predicted by simple Hückel...
(Λ = +18) is antiaromatic.
Another measurable quantity is the chemical shift
Chemical shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule...
of lithium
Lithium
Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly...
ions Li+ in complexes of lithium with aromats because lithium tends to coordinate to the face
Hapticity
The term hapticity is used to describe how a group of contiguous atoms of a ligand are coordinated to a central atom. Hapticity of a ligand is indicated by the Greek character 'eta', η. A superscripted number following the η denotes the number of contiguous atoms of the ligand that are bound to...
of the aromatic rings. Thus the lithium atom in cyclopentadienyl
Cyclopentadienyl
In organic chemistry, cyclopentadienyl is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C5H5. Cyclopentadienyl are closely related to cyclopentadiene. Cyclopentadienyl have five carbon atoms bonded together in a pentagonal planar ring, all five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms...
lithium (CpLi) has a chemical shift of −8.6 ppm (aromatic) and its Cp2Li− complex a shift of −13.1.
Both methods suffer from the disadvantage that values depend on ring size. The nucleus-independent chemical shift (NICS) is a computational method
Computational chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses principles of computer science to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses the results of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into efficient computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules and solids...
that calculates the absolute magnetic shieldings at the center of the ring taken with reversed sign. In this method negative NICS values indicate aromaticity and positive values antiaromaticity.
Yet another method called the harmonic oscillator model of aromaticity (HOMA) is defined as a normalized sum
Normalization (statistics)
In one usage in statistics, normalization is the process of isolating statistical error in repeated measured data. A normalization is sometimes based on a property...
of squared deviations
Squared deviations
In probability theory and statistics, the definition of variance is either the expected value , or average value , of squared deviations from the mean. Computations for analysis of variance involve the partitioning of a sum of squared deviations...
of bond length
Bond length
- Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter...
s from the optimal value, which is assumed to be realized for a fully aromatic system . An aromat has HOMA value 1 whereas a non-aromatic compound has value 0. For all-carbon systems, a HOMA value is obtained making use of this equation:
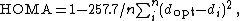
with the value of 257.7 the normalization value, n-number of CC bonds, dopt the optimized bond length (1.388 angstrom
Ångström
The angstrom or ångström, is a unit of length equal to 1/10,000,000,000 of a meter . Its symbol is the Swedish letter Å....
) and di the experimental or computed bond length.

