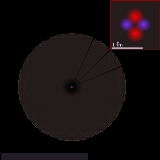
Atomic nucleus
Overview
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s and neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s at the center of an atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford
Ernest Rutherford
Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson OM, FRS was a New Zealand-born British chemist and physicist who became known as the father of nuclear physics...
's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden
Ernest Marsden
Sir Ernest Marsden was an English-New Zealand physicist. He was born in East Lancashire, living in Rishton and educated at Queen Elizabeth's Grammar School, Blackburn, where an inter-house trophy rewarding academic excellence bears his name.He met Ernest Rutherford at the University of Manchester...
, under the direction of Rutherford. The proton–neutron model of nucleus was proposed by Dmitry Ivanenko in 1932. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the orbiting electrons.
The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of (femtometre
Femtometre
The femtometre is an SI unit of length equal to 10-15 metres. This distance can also be called fermi and was so named in honour of Enrico Fermi and is often encountered in nuclear physics as a characteristic of this scale...
) for hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
(the diameter of a single proton) to about for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium.
Unanswered Questions

