
Amban
Encyclopedia

Manchu language
Manchu is a Tungusic endangered language spoken in Northeast China; it used to be the language of the Manchu, though now most Manchus speak Mandarin Chinese and there are fewer than 70 native speakers of Manchu out of a total of nearly 10 million ethnic Manchus...
word meaning "high official," which corresponds to a number of different official titles in the Qing
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
imperial government. For instance, members of the Grand Council
Grand Council
The Grand Council or Junjichu was an important policy-making body in the Qing Empire. It was established in 1733 by the Yongzheng Emperor...
were called Coohai nashūn-i amban (
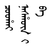 ) in Manchu and Qing governor-generals were called Uheri kadalara amban (
) in Manchu and Qing governor-generals were called Uheri kadalara amban (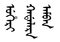 ).
).The word amban was transcribed into Chinese as 昂邦 (angbang).
By far the most known ambans were the Qing imperial residents (Manchu
Manchu language
Manchu is a Tungusic endangered language spoken in Northeast China; it used to be the language of the Manchu, though now most Manchus speak Mandarin Chinese and there are fewer than 70 native speakers of Manchu out of a total of nearly 10 million ethnic Manchus...
:
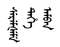 Seremšeme tehe amban; Chinese
Seremšeme tehe amban; ChineseChinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
: Zhùzhá Dàchén 駐紮大臣; and Tibetan
Tibetan language
The Tibetan languages are a cluster of mutually-unintelligible Tibeto-Burman languages spoken primarily by Tibetan peoples who live across a wide area of eastern Central Asia bordering the Indian subcontinent, including the Tibetan Plateau and the northern Indian subcontinent in Baltistan, Ladakh,...
: Ngang pai) in Tibet
Tibet
Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
, Qinghai
Qinghai
Qinghai ; Oirat Mongolian: ; ; Salar:) is a province of the People's Republic of China, named after Qinghai Lake...
, Mongolia
Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest...
and Xinjiang
Xinjiang
Xinjiang is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. It is the largest Chinese administrative division and spans over 1.6 million km2...
, which recognized Qing authority, but were not governed as regular provinces and retained many of their existing institutions.
The Qing imperial residents can be roughly compared to a European resident
Resident (title)
A Resident, or in full Resident Minister, is a government official required to take up permanent residence in another country. A representative of his government, he officially has diplomatic functions which are often seen as a form of indirect rule....
in a protectorate
Protectorate
In history, the term protectorate has two different meanings. In its earliest inception, which has been adopted by modern international law, it is an autonomous territory that is protected diplomatically or militarily against third parties by a stronger state or entity...
(e.g. a British Indian princely state
Princely state
A Princely State was a nominally sovereign entitity of British rule in India that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule such as suzerainty or paramountcy.-British relationship with the Princely States:India under the British Raj ...
), the real rapport depending on historical circumstances rather than a general job description for every amban, while his authority often was very extensive, rather like a provincial governor.
Tibet
The Qing Emperor appointed an amban in TibetTibet
Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
(Chinese: Zhùzàng Dàchén 駐藏大臣), who represented Qing authority over the Buddhist theocracy of Tibet, and commanded over 2,000 troops stationed in Lhasa
Lhasa
Lhasa is the administrative capital of the Tibet Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China and the second most populous city on the Tibetan Plateau, after Xining. At an altitude of , Lhasa is one of the highest cities in the world...
. The chief amban was aided by an assistant amban (Bāngbàn Dàchén 幫辦大臣) and both of them reported to the Qing Lifan Yuan
Lifan Yuan
The Lifan Yuan was an agency in the Qing government which supervised the Qing Empire's Mongolian dependencies and oversaw the appointments of Ambans in Tibet. It was first created in the 17th century. It has various translations in English, e.g...
. Their duties included acting as intermediary between China and the Hindu kingdom of Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
(Ghorkhas Country); a secretary (Yíqíng zhāngjīng 夷情章京) dealt with native affairs. Three Chinese commissioners (liángtái 糧台), of the class of sub-prefects, were stationed at Lhasa, Tashilumbo and Ngari.
The Qing imperial resident in Tibet was introduced in 1727 and most ambasa were appointed from the Manchu Eight Banners
Eight Banners
The Eight Banners were administrative divisions into which all Manchu families were placed. They provided the basic framework for the Manchu military organization...
, a few were Han Chinese or Mongol. The Emperors used ambasa to influence Tibetan politics, and the Qianlong
Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor was the sixth emperor of the Manchu-led Qing Dynasty, and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. The fourth son of the Yongzheng Emperor, he reigned officially from 11 October 1735 to 8 February 1796...
, Jiaqing
Jiaqing Emperor
The Jiaqing Emperor was the seventh emperor of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and the fifth Qing emperor to rule over China, from 1796 to 1820....
and Daoguang
Daoguang Emperor
The Daoguang Emperor was the eighth emperor of the Manchurian Qing dynasty and the sixth Qing emperor to rule over China, from 1820 to 1850.-Early years:...
Emperors each decreed that the Dalai Lama
Dalai Lama
The Dalai Lama is a high lama in the Gelug or "Yellow Hat" branch of Tibetan Buddhism. The name is a combination of the Mongolian word далай meaning "Ocean" and the Tibetan word bla-ma meaning "teacher"...
and Panchen Lama
Panchen Lama
The Panchen Lama , or Bainqên Erdê'ni , is the highest ranking Lama after the Dalai Lama in the Gelugpa lineage of Tibetan Buddhism...
were bound to follow the leadership or guidance of the ambasa in carrying out the administration of Tibet.
Zhao Erfeng
Zhao Erfeng
Zhao Erfeng was a Qing official and Chinese bannerman, who belonged to the Plain Blue Banner. He is known for being the last amban in Tibet, appointed in March, 1908. Lien Yu , a Manchu, was appointed as the other amban...
, a Han chinese Bannerman
Eight Banners
The Eight Banners were administrative divisions into which all Manchu families were placed. They provided the basic framework for the Manchu military organization...
, was appointed as Amban of Tibet by the Qing government. He was killed during the Xinhai Revolution
Xinhai Revolution
The Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, also known as Revolution of 1911 or the Chinese Revolution, was a revolution that overthrew China's last imperial dynasty, the Qing , and established the Republic of China...
by Chinese Republican Revolutionary forces intent on overthrowing the Qing dynasty. After the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1912, the Manchu Amban Lien Yu and his Chinese soldiers were expelled from Lhasa.
Altishahr
Altishahr, meaning six cities, consisted of UyghurUyghur people
The Uyghur are a Turkic ethnic group living in Eastern and Central Asia. Today, Uyghurs live primarily in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China...
cities of Yarkand, Kashgar, Khotan, Kuche, Aksu, and Yangi Hisar (or Ush-Turfan). The Qing dynasty's wars with the Zunghar Khanate
Zunghar Khanate
The Zunghar Khanate was a nomadic power on the Eurasian steppe. It covered the area called Dzungaria and stretched from the west end of the Great Wall of China to present-day eastern Kazakhstan, and from present-day northern Kyrgyzstan to southern Siberia .In 1678 Galdan received from the Dalai...
pushed them into the area and by 1759 they had obtained control of this region. After the rebellion of Yakub Beg
Yakub Beg
Muhammad Yaqub Bek was a [Turkic peoples] adventurer who became head of the kingdom of Kashgaria.-Spelling variants:In English-language literature, the name of Yaqub Beg has also been spelt as Yakub Beg , Yakoob Beg , or Ya`qūb Beg...
, Altishahr was incorporated into the administration of Xinjiang, which became a formal province in the Qing empire in 1884. Between 1761 and 1865, the Qing Empire appointed an imperial resident (Manchu:
 hebei amban; Chinese: zǒnglǐ huíjiāng shìwù cānzàn dàchén 總理回疆事務參贊大臣) to Altishahr, which today forms part of southern Xinjiang
hebei amban; Chinese: zǒnglǐ huíjiāng shìwù cānzàn dàchén 總理回疆事務參贊大臣) to Altishahr, which today forms part of southern XinjiangXinjiang
Xinjiang is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. It is the largest Chinese administrative division and spans over 1.6 million km2...
. The imperial resident, who resided in Kashgar
Kashgar
Kashgar or Kashi is an oasis city with approximately 350,000 residents in the western part of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Kashgar is the administrative centre of Kashgar Prefecture which has an area of 162,000 km² and a population of approximately...
, Ush Turfan
Aksu Prefecture
Aksu Prefecture is located in mid-western Xinjiang, China. It has an area of 132,500 km² and 2.19 million inhabitants .The name Aksu is Turkic for 'white water'.-Geography:...
or Yarkand and exercised Qing authority over the region. The imperial resident was controlled with local imperial agents (Manchu:
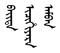 Baita icihiyara amban; Chinese: Bànshì dàchén 辦事大臣), who were sent to most important cities in the region, where they ruled in conjunction with the local officials (hakim beg, Chinese: 阿奇木伯克), who were given ranks in the Qing civil service and were ultimately accountable to the imperial agent.
Baita icihiyara amban; Chinese: Bànshì dàchén 辦事大臣), who were sent to most important cities in the region, where they ruled in conjunction with the local officials (hakim beg, Chinese: 阿奇木伯克), who were given ranks in the Qing civil service and were ultimately accountable to the imperial agent.Urga
In the holy city of Urga, an amban (Chinese: Kùlún bànshì dàchén 庫倫辦事大臣) was stationed in order to assert Qing control over the MongolMongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest...
dependencies. He controlled all temporal matters, and was specially charged with the control of the frontier town of Kiakhta and the trade conducted there with the Russians. Urga was also the residence of the Jebtsundamba Khutuktu, who was the spiritual head
Buddhism in Mongolia
Buddhism in Mongolia derives much of its recent characteristics from Tibetan Buddhism of the Gelugpa school. Traditionally, Mongols worshiped heaven and their ancestors, and they followed ancient northern Asian practices of shamanism, in which human intermediaries went into trance and spoke to...
of the Mongol Khalkha
Khalkha
Khalkha is the largest subgroup of Mongol people in Mongolia since 15th century. The Khalkha together with Tsahar, Ordos and Tumed, were directly ruled by the Altan Urag Khans until the 20th century; unlike the Oirat people who were ruled by the Dzungar nobles or the Khorchins who were ruled by...
tribes. The Khutuktu ranked third in degree of veneration among the dignitaries in the Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism is the body of Buddhist religious doctrine and institutions characteristic of Tibet and certain regions of the Himalayas, including northern Nepal, Bhutan, and India . It is the state religion of Bhutan...
, after the Dalai Lama
Dalai Lama
The Dalai Lama is a high lama in the Gelug or "Yellow Hat" branch of Tibetan Buddhism. The name is a combination of the Mongolian word далай meaning "Ocean" and the Tibetan word bla-ma meaning "teacher"...
and Panchen Lama
Panchen Lama
The Panchen Lama , or Bainqên Erdê'ni , is the highest ranking Lama after the Dalai Lama in the Gelugpa lineage of Tibetan Buddhism...
. He resided in a sacred quarter on the western side of the town and acted as a spiritual counterpart of the Qing amban.
After the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1912, the Manchu amban was expelled by Mongol forces, fleeing to China proper
China proper
China proper or Eighteen Provinces was a term used by Western writers on the Qing Dynasty to express a distinction between the core and frontier regions of China. There is no fixed extent for China proper, as many administrative, cultural, and linguistic shifts have occurred in Chinese history...
via Russia.
Manchuria
In the early Qing, the word amban was also used in the title of the military governors (昂邦章京, angbang-zhangjing, which is a transcription of the Manchu amban-jianggin; R.L. Edmonds translates the title in English as "military deputy-lieutenant governor") in the northeastern provinces of the Qing Empire, viz. JilinJilin
Jilin , is a province of the People's Republic of China located in the northeastern part of the country. Jilin borders North Korea and Russia to the east, Heilongjiang to the north, Liaoning to the south, and Inner Mongolia to the west...
and Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang
For the river known in Mandarin as Heilong Jiang, see Amur River' is a province of the People's Republic of China located in the northeastern part of the country. "Heilongjiang" literally means Black Dragon River, which is the Chinese name for the Amur. The one-character abbreviation is 黑...
. The first amban-jianggin appointed in the region was the Ninguta garrison commander Sarhuda
Sarhuda
Šarhūda, known also under the Chinese transcription of his name, Shaerhuda , was a Manchu military commander during the early Qing Dynasty, active both before and after the Manchus' seizing control of the entire China....
, who became the amban-jianggin of Ninguta in June 1653.
Sources and references
- Ho, Dahpon David. "The Men Who Would Not Be Amban and the One Who Would: Four Frontline Officials and Qing Tibet Policy, 1905-1911." Modern China 34, no. 2 (2008): 210-46.
- Kolmaš, Josef. The Ambans and Assistant Ambans of Tibet, Archiv Orientální. Supplementa 7. Prague: The Oriental Institute, 1994.
- Mayers, William Frederick. The Chinese Government: A Manual of Chinese Titles, Categorically Arranged and Explained, with an Appendix. 3rd edition revised by G.M.H. Playfair ed. Shanghai: Kelly & Walsh, 1897; reprint, Taibei: Ch'eng-Wen Pub. Co., 1966.
- Newby, Laura J. The Empire and the Khanate: A Political History of Qing Relations with Khoqand C. 1760-1860. Leiden; Boston: Brill, 2005.
- Norman, Jerry. A Concise Manchu-English Lexicon. Seattle: University of Washington Press, 1978.
- Shakya, Tsering. The Dragon In The Land Of Snows (1999) Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-11814-7

