Alpha-Pinene
Encyclopedia
α-Pinene is an organic compound
of the terpene
class, one of two isomers of pinene
. It is an alkene
and it contains a reactive four-membered ring
. It is found in the oils of many species of many coniferous
trees, notably the pine
. It is also found in the essential oil of rosemary
(Rosmarinus officinalis). Both enantiomer
s are known in nature; (1S,5S)- or (−)-α-pinene is more common in European pines, whereas the (1R,5R)- or (+)-α-isomer is more common in North America. The racemic mixture is present in some oils such as eucalyptus
oil.
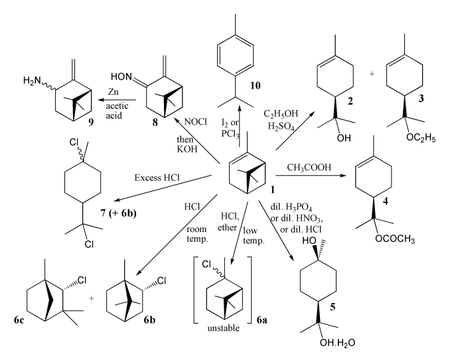
, prone to skeletal rearrangements such as the Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement
. For example, attempts to perform hydration or hydrogen halide
addition with the alkene functionality typically lead to rearranged products. With concentrated sulfuric acid
and ethanol
the major products are terpineol
2 and its ethyl ether
3, while glacial acetic acid
gives the corresponding acetate
ester
4. With dilute acids, terpin hydrate
5 becomes the major product.
With one molar equivalent of anhydrous HCl
, the simple addition product 6a can be formed at low temperature in the presence of ether
, but it is very unstable. At normal temperatures, or if no ether is present, the major product is bornyl chloride 6b, along with a small amount of fenchyl chloride 6c. For many years 6b (also called "artificial camphor") was referred to as "pinene hydrochloride", until it was confirmed as identical with bornyl chloride made from camphene
. If more HCl is used, achiral 7 (dipentene hydrochloride) is the major product along with some 6b. Nitrosyl chloride
followed by base leads to the oxime
8 which can be reduced to "pinylamine" 9. Both 8 and 9 are stable compounds containing an intact four-membered ring, and these compounds helped greatly in identifying this important component of the pinene skeleton.
A variety of reagents such as iodine
or PCl3
cause aromatisation
, leading to p-cymene 10.
Under aerobic oxidation conditions, the main oxidation products are pinene oxide, verbenyl hydroperoxide, verbenol and verbenone
.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
of the terpene
Terpene
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, though also by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies, which emit terpenes from their osmeterium. They are often strong smelling and thus may have had a protective...
class, one of two isomers of pinene
Pinene
Pinene is a bicyclic monoterpene chemical compound. There are two structural isomers of pinene found in nature: α-pinene and β-pinene. As the name suggests, both forms are important constituents of pine resin; they are also found in the resins of many other conifers, as well as in non-coniferous...
. It is an alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
and it contains a reactive four-membered ring
Cyclobutane
Cyclobutane is an organic compound with the formula 4. Cyclobutane is a colourless gas and commercially available as a liquefied gas. Derivatives of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes...
. It is found in the oils of many species of many coniferous
Pinophyta
The conifers, division Pinophyta, also known as division Coniferophyta or Coniferae, are one of 13 or 14 division level taxa within the Kingdom Plantae. Pinophytes are gymnosperms. They are cone-bearing seed plants with vascular tissue; all extant conifers are woody plants, the great majority being...
trees, notably the pine
Pine
Pines are trees in the genus Pinus ,in the family Pinaceae. They make up the monotypic subfamily Pinoideae. There are about 115 species of pine, although different authorities accept between 105 and 125 species.-Etymology:...
. It is also found in the essential oil of rosemary
Rosemary
Rosemary, , is a woody, perennial herb with fragrant, evergreen, needle-like leaves and white, pink, purple or blue flowers, native to the Mediterranean region. It is a member of the mint family Lamiaceae, which includes many other herbs, and is one of two species in the genus Rosmarinus...
(Rosmarinus officinalis). Both enantiomer
Enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer is one of two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other that are non-superposable , much as one's left and right hands are the same except for opposite orientation. It can be clearly understood if you try to place your hands one over the other without...
s are known in nature; (1S,5S)- or (−)-α-pinene is more common in European pines, whereas the (1R,5R)- or (+)-α-isomer is more common in North America. The racemic mixture is present in some oils such as eucalyptus
Eucalyptus
Eucalyptus is a diverse genus of flowering trees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Members of the genus dominate the tree flora of Australia...
oil.
Reactivity
The four-membered ring in α-pinene 1 makes it a reactive hydrocarbonHydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
, prone to skeletal rearrangements such as the Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement
Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement
A Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement is a class of carbocation 1,2-rearrangement reactions in which a hydrogen, alkyl or aryl group migrates from one carbon to a neighboring carbon.Several reviews have been published....
. For example, attempts to perform hydration or hydrogen halide
Hydrogen halide
Hydrogen halides are acids resulting from the chemical reaction of hydrogen with one of the halogen elements , which are found in Group 17 of the periodic table. Astatine is not included in the list because it is very rare, unstable and not found as the acid in substantial quantities...
addition with the alkene functionality typically lead to rearranged products. With concentrated sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
and ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
the major products are terpineol
Terpineol
Terpineol is a naturally occurring monoterpene alcohol that has been isolated from a variety of sources such as cajuput oil, pine oil, and petitgrain oil. There are three isomers, alpha-, beta-, and gamma-terpineol, the last two differing only by the location of the double bond...
2 and its ethyl ether
Ether
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula R–O–R'. A typical example is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether"...
3, while glacial acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
gives the corresponding acetate
Acetate
An acetate is a derivative of acetic acid. This term includes salts and esters, as well as the anion found in solution. Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In...
ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
4. With dilute acids, terpin hydrate
Terpin hydrate
Terpin hydrate is an expectorant, commonly used to loosen mucus in the setting of acute or chronic bronchitis, and related conditions. It is derived from sources such as oil of turpentine, oregano, thyme and eucalyptus. Though it was quite popular in the USA since the late nineteenth century, it...
5 becomes the major product.
With one molar equivalent of anhydrous HCl
Hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the formula HCl. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric humidity. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry...
, the simple addition product 6a can be formed at low temperature in the presence of ether
Diethyl ether
Diethyl ether, also known as ethyl ether, simply ether, or ethoxyethane, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula . It is a colorless, highly volatile flammable liquid with a characteristic odor...
, but it is very unstable. At normal temperatures, or if no ether is present, the major product is bornyl chloride 6b, along with a small amount of fenchyl chloride 6c. For many years 6b (also called "artificial camphor") was referred to as "pinene hydrochloride", until it was confirmed as identical with bornyl chloride made from camphene
Camphene
Camphene is bicyclic monoterpene. It is nearly insoluble in water, but very soluble in common organic solvents. It volatilizes readily at room temperature and has a pungent smell. It is a minor constituent of many essential oils such as turpentine, cypress oil, camphor oil, citronella oil,...
. If more HCl is used, achiral 7 (dipentene hydrochloride) is the major product along with some 6b. Nitrosyl chloride
Nitrosyl chloride
Nitrosyl chloride is the chemical compound NOCl. It is a yellow gas that is most commonly encountered as a decomposition product of aqua regia, a mixture of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid...
followed by base leads to the oxime
Oxime
An oxime is a chemical compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula R1R2C=NOH, where R1 is an organic side chain and R2 may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substituted oximes form a closely related family of compounds...
8 which can be reduced to "pinylamine" 9. Both 8 and 9 are stable compounds containing an intact four-membered ring, and these compounds helped greatly in identifying this important component of the pinene skeleton.
A variety of reagents such as iodine
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The name is pronounced , , or . The name is from the , meaning violet or purple, due to the color of elemental iodine vapor....
or PCl3
Phosphorus trichloride
Phosphorus trichloride is a chemical compound of phosphorus and chlorine, having chemical formula PCl3. Its shape is trigonal pyramidal. It is the most important of the three phosphorus chlorides. It is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of organophosphorus compounds...
cause aromatisation
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, Aromaticity is a chemical property in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibit a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August...
, leading to p-cymene 10.
Under aerobic oxidation conditions, the main oxidation products are pinene oxide, verbenyl hydroperoxide, verbenol and verbenone
Verbenone
Verbenone is a natural organic compound classified as a terpene which is found naturally in a variety of plants. The chemical has a pleasant characteristic odor. Besides being a natural constituent of plants, it and its analogs are insect pheromones...
.