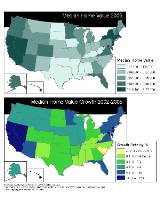
Affordable housing
Encyclopedia
Affordable housing is a term used to describe dwelling units whose total housing
costs are deemed "affordable" to those that have a median income. Although the term is often applied to rental housing that is within the financial means of those in the lower income ranges of a geographical area, the concept is applicable to both renters and purchasers in all income ranges. This article focuses on the affordability of owner-occupied and private rental housing as social housing
is a specialised tenure.
In the United States
and Canada, a commonly accepted guideline for housing affordability is a housing cost that does not exceed 30% of a household's gross income
. Housing costs considered in this guideline generally include tax
es and insurance
for owners, and usually include utility costs. When the monthly carrying costs of a home exceed 30–35% of household income, then the housing is considered unaffordable for that household.
In India
,70% of the population lives below the poverty line and there is huge demand for affordable housing.A lot of developers are developing low cost and affordable housing
for these population and leading the pack is Tata Housing Development Company
,they are developing affordable and low cost housing under the brand name Shubh Griha and New Haven Vasind.
The Government of India has taken up various initiatives for developing properties in low cost and affordable segment.They have also looked at PPP model for development of these properties.
Another method of studying affordability looks at the regular hourly wage of full-time workers who are paid only the minimum wage (as set by their local, regional, or national government). The hope is that a full-time worker will be able to afford at least a small apartment in the area that he or she works in.
Other countries look at those living in relative poverty, which is usually defined as making less than 60% of the median household income
. In their policy reports, they consider the presence or absence of housing for people making 60% of the median income.
Some organization and agencies consider the cost of purchasing a single-family home; others look exclusively at the cost of renting an apartment.
Many U.S. studies, for example, focus primarily on the median cost of renting a two-bedroom apartment in a large apartment complex for a new tenant. These studies often lump together luxury apartments and slums, as well as desirable and undesirable neighborhoods. While this practice is known to distort the true costs, it is difficult to provide accurate information for the wide variety of situations without the report being unwieldy.
Normally, only legal, permitted, separate housing is considered when calculating the cost of housing. The low rent costs for a room in a single family home, or an illegal garage
conversion, or a college dormitory are generally excluded from the calculation, no matter how many people in an area live in such situations. Because of this study methodology, median housing costs tend to be slightly inflated.
Costs are generally considered on a cash (not accrual
) basis. Thus a person making the last payment on a large home mortgage might live in officially unaffordable housing one month, and very affordable housing the following month, when the mortgage is paid off. This distortion can be significant in areas where real estate costs are high, even if incomes are similarly high, because a high income allows a higher proportion of the income to be dedicated towards buying an expensive home without endangering the household's ability to buy food or other basic necessities.
Furthermore, the absolute availability of housing is not generally considered in the calculation of affordable housing. In a depressed or sparsely settled rural area, for example, the predicted price of the canonical median two-bedroom apartment may be quite easily affordable even to a minimum-wage worker – if only any apartments had ever been built.
can afford. For example, in a perfectly balanced housing market, the median household (and the half of the households which are wealthier) could officially afford the median housing option, while those poorer than the median home could not afford the median home. 50% affordability for the median home indicates a balanced market.
A community might track the percentage of its housing that is affordable to households earning 60% of median income. In addition to the distress it causes families who cannot easily find a place to live, lack of affordable housing is considered by many urban planners
to have negative effects on a community's overall health. For example, lack of affordable housing can make low-cost labor more scarce, and increase demands on transportation systems (as workers travel longer distances between jobs and affordable housing). Housing cost increases in U.S. cities have been linked to declines in enrollment at local schools.
, and land banking
are three prominent tools, as well as tax and fiscal policies that result in reducing the cost of mortgages and the cost of borrowing. Other more recently promoted policy tools include relaxation of prohibitions against accessory dwelling units
, and reduction of the amount of parking
that must be built for a new structure.
Affordable housing is a controversial reality of contemporary life, for gains in affordability often result from expanding land available for housing or increasing the density of housing units in a given area. Ensuring a steady supply of affordable housing means ensuring that communities weigh real and perceived livability impacts against the sheer necessity of affordability. The process of weighing the impacts of locating affordable housing is quite contentious, and is laden with race and class implications
.
Under this definition, most people in the United States have secured affordable housing arrangements. In 2001, the median household paid $658 per month in total housing costs. A total of 20% of households are deemed to be living in unaffordable housing: Nine percent of all households are renters in unaffordable housing, and eleven percent of all households are homeowners with high housing costs.
In the 2000 U.S. Census, the median homeowner with a mortgage (70% of homeowners and 48% of census respondents) spent $1,088 each month, or 21.7% of household income, on housing costs. The median homeowner without a mortgage (30% of all homeowners (80% of elderly homeowners) and 20% of respondents) spent $295 per month, or 10.5% of household income, on housing costs. Renters in 2001 (32% of respondents) spent $633 each month, or 29% of household income, on housing costs.
who rent housing from a private landlord are eligible for rent assistance. Rent assistance is a subsidy paid directly to the tenant in addition to the basic Centrelink benefit such as the Age Pension or the Disability Pension. The amount of rent assistance paid depends on the amount of rent payable, whether the tenant has dependents and how many dependents there are. Tenants who live in public housing in Australia
are not eligible for rent assistance.
Australians buying a home for the first time are eligible for a first home owner grant. These grants were introduced on 1 July 2000 and are jointly funded by the Commonwealth government and the state and territory governments
. First home buyers are currently eligible for a grant of A$
7000 to alleviate the costs of entering the housing market.
The Commonwealth government in 2008 introduced first home saver account
s, whereby those saving for a new home are eligible for government contributions to their savings account, subject to conditions.
has a long tradition of promoting affordable social rented housing. This may be owned by local councils
or housing association
s.
There are also a range of affordable home ownership options, including shared ownership (where a tenant rents part share in the property from a social landlord, and owns the remainder). The government has also attempted to promote the supply of owner occupied affordable stock for purchase, principally by using the land-use planning system
to require that housing developers provide a proportion of lower cost housing within new developments. This approach is commonly known as inclusionary zoning
and the current mechanism for securing the provision of affordable housing as part of a planning application for new housing development is through the use of a S.106 Agreement. In Scotland the equivalent is a Section 75 planning agreement (Section 75 of the Town and Country Planning (Scotland) Act 1997).
A high proportion of homes in the UK were previously council-owned
, but the numbers have been reduced since the early 1980s due to initiatives of the Thatcher government
that restricted council housing construction and provided financial and policy support to other forms social housing. In 1980, the Conservative
government of Margaret Thatcher
introduced the Right to Buy
scheme, offering council tenants the opportunity to purchase their housing at a discount of up to 60% (70% on leasehold homes such as flats). Alongside Right to Buy, council-owned stock was further diminished as properties were transferred to housing associations. Council Tenants in some instances have chosen to transfer management of the properties to arms-length non-profit organisations
. The tenants still remained Council tenants, and the housing stock still remained the property of the Council. This change in management was encouraged by extra funding from central government to invest in the housing stock under the Decent Homes Programme. The program required council housing to be brought up to a set standard was combined with restrictions on the amounts that councils could borrow and led to an increase in such arms length management organisations being set up. In some areas, significant numbers of council houses were demolished as part of urban regeneration programmes, due to the poor quality of stock, low levels of demand and social problems.
In rural areas where local wages are low and house prices are higher (especially in regions with holiday homes) there are special problems. Planning restrictions severely limit rural development. but if there is evidence of need then Exception sites can be used for people with a local connection. This evidence is normally provided by a housing Needs survey carried out by a Rural Housing Enabler working for the local Rural Community Council.
Housing associations are not-for-profit organisations with a history that goes back before the start of the 20th century. The number of homes under their ownership grew significantly from the 1980s as successive governments sought to make them the principal form of social housing, in preference to local authorities. Many of the homes previously under the ownership of local authorities have been transferred to newly established housing associations, including some of the largest in the country. Despite being not-for-profit organisations, housing association rents are typically higher than for council housing. Renting a home through a housing association can in some circumstances prove costlier than purchasing a similar property through a mortgage.
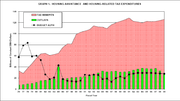 The federal government in the U.S. provides subsidies to make housing more affordable. Financial assistance is provided for homeowners through the mortgage interest tax deduction and for lower income households through housing subsidy programs. In the 1970s the federal government spent similar amounts on tax reductions for homeowners as it did on subsidies for low-income housing. However, by 2005, tax reductions had risen to $120 billion per year, representing nearly 80 percent of all federal housing assistance. The Advisory Panel on Federal Tax Reform for President Bush
The federal government in the U.S. provides subsidies to make housing more affordable. Financial assistance is provided for homeowners through the mortgage interest tax deduction and for lower income households through housing subsidy programs. In the 1970s the federal government spent similar amounts on tax reductions for homeowners as it did on subsidies for low-income housing. However, by 2005, tax reductions had risen to $120 billion per year, representing nearly 80 percent of all federal housing assistance. The Advisory Panel on Federal Tax Reform for President Bush
proposed reducing the home mortgage interest deduction
in a 2005 report.
Housing assistance from the federal government for lower income households can be divided into three parts:
“Project based” subsidies are also known by their section of the U.S. Housing Act or the Housing Act of 1949
, and include Section 8, Section 236, Section 221(d)(3), Section 202 for elderly households, Section 515 for rural renters, Section 514/516 for farmworkers and Section 811 for people with disabilities. There are also housing subsidies through the Section 8 program that are project based. The United States Department of Housing and Urban Development
(HUD) and USDA Rural Development
administer these programs. HUD and USDA Rural Development programs have ceased to produce large numbers of units since the 1980s. Since 1986, the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit
program has been the primary federal program to produce affordable units; however, the housing produced in this program is less affordable than the former HUD programs.
One of the most unique US public housing initiatives was the development of subsidized middle-class housing during the late New Deal
(1940–42) under the auspices of the Mutual Ownership Defense Housing Division
of the Federal Works Agency
under the direction of Colonel Lawrence Westbrook. These eight projects were purchased by the residents after the Second World War and as of 2009 seven of the projects continue to operate as mutual housing corporations owned by their residents. These projects are among the very few definitive success stories in the history of the US public housing effort.
In the U.S., households are commonly defined in terms of the amount of realized income they earn relative to the Area Median Income
or AMI. Localized AMI figures are calculated annually based on a survey of comparably-sized households within geographic ranges known as metropolitan statistical areas, as defined by the US Office of Management and Budget. For U.S. housing subsidies, households are categorized by federal law as follows:
Some states and cities in the United States operate a variety of affordable housing programs, including supportive housing programs, transitional housing programs and rent subsidies as part of public assistance programs. Local and state governments can adapt these income limits when administering local affordable housing programs; however, U.S. federal programs must adhere to the definitions above. For the Section 8 voucher program, the maximum household contribution to rent can be as high as 40% gross income.
With an annual budget of $4.5 million, SHSC and its two subsidiaries, SOHO and SHSC Financial Inc. offers a dedicated insurance program for social housing providers, bulk gas purchasing and an innovative energy efficiency retrofit program which coordinates energy audits, expertise, funding, bulk purchasing of energy-efficient goods, training and education, and data evaluation. SHSC manages and provides investment advice to housing providers on capital reserves valued at more than $390 million. Working closely with other housing sector organizations and non-governmental organizations, SHSC also supports and develops independent housing-related research, including a new Housing Internship program for graduate-level researchers.
Recently there has been a move toward the integration of affordable social housing with market housing and other uses, such as the 2006-10 redevelopment of the Woodward's building
site in Vancouver.
Zoning changes in some areas of Canada to permit laneway house
s has been part of the EcoDensity movement to permit home owners to create small affordable rental units in their backyards.
, the Federal Home Loan Bank, Fannie Mae, and Freddie Mac. Important private sector institutions worth consulting are the National Association of Home Builders
, the National Affordable Housing Management Association (NAHMA), the Council for Affordable and Rural Housing (CARH) and the National Association of Realtors
. Valuable research institutions with staff dedicated to the analysis of "affordable housing" includes: The Center for Housing Policy
, Brookings Institution
, the Urban Institute
and the Joint Center for Housing Studies at Harvard University
and the Furman Center for Real Estate and Urban Policy
at New York University
, and the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities
. Several of these institutions (the Fannie Mae Foundation, Urban Institute, Brookings Institution Metropolitan Policy Program, Enterprise Community Partners, LISC, the Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies, and others) partnered to create KnowledgePlex, an online information resource devoted to affordable housing and community development issues.
s are registered with the Tenant Services Authority which regulates them. The TSA is to be merged with the Homes and Communities Agency
, which provides grants for development. Housing associations that are registered with the TSA were known as Registered Social Landlords from 1996, but in the Housing And Regeneration Act 2008 the official legal term became Registered Providers; the latter also covers council housing
as well as developers and other bodies which may receive grant.
The Department for Communities and Local Government
has responsibility for housing in England.
In Scotland the task falls to the Scottish Housing Regulator.
Social housing in Northern Ireland
is regulated by the Northern Ireland Housing Executive, which was established to take on ownership of former council stock and prevent sectarian allocation of housing to people from one religion.
House
A house is a building or structure that has the ability to be occupied for dwelling by human beings or other creatures. The term house includes many kinds of different dwellings ranging from rudimentary huts of nomadic tribes to free standing individual structures...
costs are deemed "affordable" to those that have a median income. Although the term is often applied to rental housing that is within the financial means of those in the lower income ranges of a geographical area, the concept is applicable to both renters and purchasers in all income ranges. This article focuses on the affordability of owner-occupied and private rental housing as social housing
Public housing
Public housing is a form of housing tenure in which the property is owned by a government authority, which may be central or local. Social housing is an umbrella term referring to rental housing which may be owned and managed by the state, by non-profit organizations, or by a combination of the...
is a specialised tenure.
In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and Canada, a commonly accepted guideline for housing affordability is a housing cost that does not exceed 30% of a household's gross income
Gross income
Gross income in United States tax law is receipts and gains from all sources less cost of goods sold. Gross income is the starting point for determining Federal and state income tax of individuals, corporations, estates and trusts, whether resident or nonresident."Except as otherwise provided" by...
. Housing costs considered in this guideline generally include tax
Tax
To tax is to impose a financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or the functional equivalent of a state such that failure to pay is punishable by law. Taxes are also imposed by many subnational entities...
es and insurance
Insurance
In law and economics, insurance is a form of risk management primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent, uncertain loss. Insurance is defined as the equitable transfer of the risk of a loss, from one entity to another, in exchange for payment. An insurer is a company selling the...
for owners, and usually include utility costs. When the monthly carrying costs of a home exceed 30–35% of household income, then the housing is considered unaffordable for that household.
In India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
,70% of the population lives below the poverty line and there is huge demand for affordable housing.A lot of developers are developing low cost and affordable housing
Affordable housing
Affordable housing is a term used to describe dwelling units whose total housing costs are deemed "affordable" to those that have a median income. Although the term is often applied to rental housing that is within the financial means of those in the lower income ranges of a geographical area, the...
for these population and leading the pack is Tata Housing Development Company
Tata Housing Development Company
Tata Housing Development Company is a fully owned subsidiary of Tata Sons, a holding company of the Tata Group. Established in the year 1984 by the late JRD Tata. The company was revived in 2006 under the leadership of Brotin Banerjee, MD & CEO of Tata Housing Development Company Limited...
,they are developing affordable and low cost housing under the brand name Shubh Griha and New Haven Vasind.
The Government of India has taken up various initiatives for developing properties in low cost and affordable segment.They have also looked at PPP model for development of these properties.
Supply and demand
In the United States, a key element in determining affordable housing is acceptable commuting time/distance. In Southern California, for example, a household's inhabitants must decide whether to pay more for housing to keep commuting time and expense low, or to accept a long and/or expensive commute in order to obtain "better" housing.Household income
A primary factor in housing affordability is household income. The most common approach is to consider the percentage of income that a household is spending on housing costs.Another method of studying affordability looks at the regular hourly wage of full-time workers who are paid only the minimum wage (as set by their local, regional, or national government). The hope is that a full-time worker will be able to afford at least a small apartment in the area that he or she works in.
Other countries look at those living in relative poverty, which is usually defined as making less than 60% of the median household income
Median household income
The median household income is commonly used to generate data about geographic areas and divides households into two equal segments with the first half of households earning less than the median household income and the other half earning more...
. In their policy reports, they consider the presence or absence of housing for people making 60% of the median income.
Costs
The other major factor is the measurement of housing costs.Some organization and agencies consider the cost of purchasing a single-family home; others look exclusively at the cost of renting an apartment.
Many U.S. studies, for example, focus primarily on the median cost of renting a two-bedroom apartment in a large apartment complex for a new tenant. These studies often lump together luxury apartments and slums, as well as desirable and undesirable neighborhoods. While this practice is known to distort the true costs, it is difficult to provide accurate information for the wide variety of situations without the report being unwieldy.
Normally, only legal, permitted, separate housing is considered when calculating the cost of housing. The low rent costs for a room in a single family home, or an illegal garage
Garage (house)
A residential garage is part of a home, or an associated building, designed or used for storing a vehicle or vehicles. In some places the term is used synonymously with "carport", though that term normally describes a structure that is not completely enclosed.- British residential garages:Those...
conversion, or a college dormitory are generally excluded from the calculation, no matter how many people in an area live in such situations. Because of this study methodology, median housing costs tend to be slightly inflated.
Costs are generally considered on a cash (not accrual
Accrual
Accrual of something is, in finance, the adding together of interest or different investments over a period of time. It holds specific meanings in accounting, where it can refer to accounts on a balance sheet that represent liabilities and non-cash-based assets used in accrual-based accounting...
) basis. Thus a person making the last payment on a large home mortgage might live in officially unaffordable housing one month, and very affordable housing the following month, when the mortgage is paid off. This distortion can be significant in areas where real estate costs are high, even if incomes are similarly high, because a high income allows a higher proportion of the income to be dedicated towards buying an expensive home without endangering the household's ability to buy food or other basic necessities.
Furthermore, the absolute availability of housing is not generally considered in the calculation of affordable housing. In a depressed or sparsely settled rural area, for example, the predicted price of the canonical median two-bedroom apartment may be quite easily affordable even to a minimum-wage worker – if only any apartments had ever been built.
Right to build
An article in the November 2007 issue of Atlantic Monthly reported on a study of the cost of obtaining the "right to build" (i.e. a building permit, red tape, bureaucracy, etc.) in different U.S. cities. The "right to build" cost does not include the cost of the land or the cost of constructing the house. The study was conducted by Harvard economists Edward Glaeser and Kristina Tobio. According to the chart accompanying the article, the cost of obtaining the "right to build" adds approximately $600,000 to the cost of each new house that is built in San Francisco.Consequences of shortages
A common measure of community-wide affordability is the number of homes that a household with a certain percentage of median incomeMedian household income
The median household income is commonly used to generate data about geographic areas and divides households into two equal segments with the first half of households earning less than the median household income and the other half earning more...
can afford. For example, in a perfectly balanced housing market, the median household (and the half of the households which are wealthier) could officially afford the median housing option, while those poorer than the median home could not afford the median home. 50% affordability for the median home indicates a balanced market.
A community might track the percentage of its housing that is affordable to households earning 60% of median income. In addition to the distress it causes families who cannot easily find a place to live, lack of affordable housing is considered by many urban planners
Urban planning
Urban planning incorporates areas such as economics, design, ecology, sociology, geography, law, political science, and statistics to guide and ensure the orderly development of settlements and communities....
to have negative effects on a community's overall health. For example, lack of affordable housing can make low-cost labor more scarce, and increase demands on transportation systems (as workers travel longer distances between jobs and affordable housing). Housing cost increases in U.S. cities have been linked to declines in enrollment at local schools.
Policy tools
Numerous policies in the U.S. and abroad have been designed to address the problem of inadequate supplies of affordable housing. Sophisticated secondary market mechanisms, inclusionary zoningZoning
Zoning is a device of land use planning used by local governments in most developed countries. The word is derived from the practice of designating permitted uses of land based on mapped zones which separate one set of land uses from another...
, and land banking
Land banking
Land banking is the practice of purchasing raw land with the intent to hold on to it until such a time as it is profitable to sell it on to others for more than was initially paid...
are three prominent tools, as well as tax and fiscal policies that result in reducing the cost of mortgages and the cost of borrowing. Other more recently promoted policy tools include relaxation of prohibitions against accessory dwelling units
Garage apartment
A garage apartment is an apartment built within the walls of, or on top of, the garage of a house. The garage may be attached or a separate building from the main house, but will have a separate entrance and may or may not have a communicating door to the main house...
, and reduction of the amount of parking
Parking
Parking is the act of stopping a vehicle and leaving it unoccupied for more than a brief time. Parking on one or both sides of a road is commonly permitted, though often with restrictions...
that must be built for a new structure.
Affordable housing is a controversial reality of contemporary life, for gains in affordability often result from expanding land available for housing or increasing the density of housing units in a given area. Ensuring a steady supply of affordable housing means ensuring that communities weigh real and perceived livability impacts against the sheer necessity of affordability. The process of weighing the impacts of locating affordable housing is quite contentious, and is laden with race and class implications
Gentrification
Gentrification and urban gentrification refer to the changes that result when wealthier people acquire or rent property in low income and working class communities. Urban gentrification is associated with movement. Consequent to gentrification, the average income increases and average family size...
.
United States
Comprehensive data for the most affordable and least affordable places in the U.S. is published each year by an affordable housing non-profit organization, the National Low Income Housing Coalition. The NLIHC promotes a guideline of 30% of household income as the upper limit of affordability.Under this definition, most people in the United States have secured affordable housing arrangements. In 2001, the median household paid $658 per month in total housing costs. A total of 20% of households are deemed to be living in unaffordable housing: Nine percent of all households are renters in unaffordable housing, and eleven percent of all households are homeowners with high housing costs.
In the 2000 U.S. Census, the median homeowner with a mortgage (70% of homeowners and 48% of census respondents) spent $1,088 each month, or 21.7% of household income, on housing costs. The median homeowner without a mortgage (30% of all homeowners (80% of elderly homeowners) and 20% of respondents) spent $295 per month, or 10.5% of household income, on housing costs. Renters in 2001 (32% of respondents) spent $633 each month, or 29% of household income, on housing costs.
Australia
Australians in receipt of many social security benefits from CentrelinkCentrelink
Centrelink is the trading name of the Commonwealth Service Delivery Agency , a statutory authority responsible for delivering human services on behalf of agencies of the Commonwealth Government of Australia. The majority of Centrelink's services are the disbursement of social security payments...
who rent housing from a private landlord are eligible for rent assistance. Rent assistance is a subsidy paid directly to the tenant in addition to the basic Centrelink benefit such as the Age Pension or the Disability Pension. The amount of rent assistance paid depends on the amount of rent payable, whether the tenant has dependents and how many dependents there are. Tenants who live in public housing in Australia
Public housing in Australia
Public housing in Australia is usually provided by departments of state and territory governments. Australian public housing operates within the framework of the Commonwealth-State Housing Agreement, by which funding for public housing is provided by both federal and state governments...
are not eligible for rent assistance.
Australians buying a home for the first time are eligible for a first home owner grant. These grants were introduced on 1 July 2000 and are jointly funded by the Commonwealth government and the state and territory governments
States and territories of Australia
The Commonwealth of Australia is a union of six states and various territories. The Australian mainland is made up of five states and three territories, with the sixth state of Tasmania being made up of islands. In addition there are six island territories, known as external territories, and a...
. First home buyers are currently eligible for a grant of A$
Australian dollar
The Australian dollar is the currency of the Commonwealth of Australia, including Christmas Island, Cocos Islands, and Norfolk Island, as well as the independent Pacific Island states of Kiribati, Nauru and Tuvalu...
7000 to alleviate the costs of entering the housing market.
The Commonwealth government in 2008 introduced first home saver account
First home saver account
First Home Saver Accounts were a 2007 election policy of the Australian Labor Party. FHSAs were offered from 1 October 2008 after a consultation period and passage of the First Home Saver Account Act 2008 through the Australian Parliament....
s, whereby those saving for a new home are eligible for government contributions to their savings account, subject to conditions.
United Kingdom
The United KingdomUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
has a long tradition of promoting affordable social rented housing. This may be owned by local councils
Local government in the United Kingdom
The pattern of local government in England is complex, with the distribution of functions varying according to the local arrangements. Legislation concerning local government in England is decided by the Parliament and Government of the United Kingdom, because England does not have a devolved...
or housing association
Housing association
Housing associations in the United Kingdom are independent not-for-profit bodies that provide low-cost "social housing" for people in housing need. Any trading surplus is used to maintain existing homes and to help finance new ones...
s.
There are also a range of affordable home ownership options, including shared ownership (where a tenant rents part share in the property from a social landlord, and owns the remainder). The government has also attempted to promote the supply of owner occupied affordable stock for purchase, principally by using the land-use planning system
Town and country planning in the United Kingdom
Town and Country Planning is the land use planning system governments use to balance economic development and environmental quality. Each country of the United Kingdom has its own planning system that is responsible for town and country planning devolved to the Northern Ireland Assembly, the...
to require that housing developers provide a proportion of lower cost housing within new developments. This approach is commonly known as inclusionary zoning
Inclusionary zoning
Inclusionary zoning, also known as inclusionary housing, is an American term which refers to municipal and county planning ordinances that require a given share of new construction to be affordable by people with low to moderate incomes...
and the current mechanism for securing the provision of affordable housing as part of a planning application for new housing development is through the use of a S.106 Agreement. In Scotland the equivalent is a Section 75 planning agreement (Section 75 of the Town and Country Planning (Scotland) Act 1997).
A high proportion of homes in the UK were previously council-owned
Council house
A council house, otherwise known as a local authority house, is a form of public or social housing. The term is used primarily in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland. Council houses were built and operated by local councils to supply uncrowded, well-built homes on secure tenancies at...
, but the numbers have been reduced since the early 1980s due to initiatives of the Thatcher government
Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher, was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990...
that restricted council housing construction and provided financial and policy support to other forms social housing. In 1980, the Conservative
Conservative Party (UK)
The Conservative Party, formally the Conservative and Unionist Party, is a centre-right political party in the United Kingdom that adheres to the philosophies of conservatism and British unionism. It is the largest political party in the UK, and is currently the largest single party in the House...
government of Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher, was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990...
introduced the Right to Buy
Right to buy scheme
The Right to buy scheme is a policy in the United Kingdom which gives tenants of council housing the right to buy the home they are living in. Currently, there is also a right to acquire for the tenants of housing associations...
scheme, offering council tenants the opportunity to purchase their housing at a discount of up to 60% (70% on leasehold homes such as flats). Alongside Right to Buy, council-owned stock was further diminished as properties were transferred to housing associations. Council Tenants in some instances have chosen to transfer management of the properties to arms-length non-profit organisations
Arms Length Management Organisation
Arms Length Management Organisations or arm's length management organisations are UK not-for-profit companies set up by a local authorities primarily to manage and improve all or part of their housing stock. Ownership of the housing stock itself normally stays with the local authority...
. The tenants still remained Council tenants, and the housing stock still remained the property of the Council. This change in management was encouraged by extra funding from central government to invest in the housing stock under the Decent Homes Programme. The program required council housing to be brought up to a set standard was combined with restrictions on the amounts that councils could borrow and led to an increase in such arms length management organisations being set up. In some areas, significant numbers of council houses were demolished as part of urban regeneration programmes, due to the poor quality of stock, low levels of demand and social problems.
In rural areas where local wages are low and house prices are higher (especially in regions with holiday homes) there are special problems. Planning restrictions severely limit rural development. but if there is evidence of need then Exception sites can be used for people with a local connection. This evidence is normally provided by a housing Needs survey carried out by a Rural Housing Enabler working for the local Rural Community Council.
Housing associations are not-for-profit organisations with a history that goes back before the start of the 20th century. The number of homes under their ownership grew significantly from the 1980s as successive governments sought to make them the principal form of social housing, in preference to local authorities. Many of the homes previously under the ownership of local authorities have been transferred to newly established housing associations, including some of the largest in the country. Despite being not-for-profit organisations, housing association rents are typically higher than for council housing. Renting a home through a housing association can in some circumstances prove costlier than purchasing a similar property through a mortgage.
United States

George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
proposed reducing the home mortgage interest deduction
Home mortgage interest deduction
A home mortgage interest deduction allows taxpayers who own their homes to reduce their taxable income by the amount of interest paid on the loan which is secured by their principal residence...
in a 2005 report.
Housing assistance from the federal government for lower income households can be divided into three parts:
- “Tenant based” subsidies given to an individual household, known as the Section 8Section 8 (housing)Section 8 of the United States Housing Act of 1937 , as repeatedly amended, authorizes the payment of rental housing assistance to private landlords on behalf of approximately 3.1 million low-income households...
program - “Project based” subsidies given to the owner of housing units that must be rented to lower income households at affordable rates, and
- Public Housing, which is usually owned and operated by the government. (Some public housing projects are managed by subcontracted private agencies.)
“Project based” subsidies are also known by their section of the U.S. Housing Act or the Housing Act of 1949
Housing Act of 1949
The American Housing Act of 1949 was a landmark, sweeping expansion of the federal role in mortgage insurance and issuance and the construction of public housing...
, and include Section 8, Section 236, Section 221(d)(3), Section 202 for elderly households, Section 515 for rural renters, Section 514/516 for farmworkers and Section 811 for people with disabilities. There are also housing subsidies through the Section 8 program that are project based. The United States Department of Housing and Urban Development
United States Department of Housing and Urban Development
The United States Department of Housing and Urban Development, also known as HUD, is a Cabinet department in the Executive branch of the United States federal government...
(HUD) and USDA Rural Development
Rural Development
USDA Office of Rural Development is an agency with the United States Department of Agriculture which runs programs intended to improve the economy and quality of life in rural America....
administer these programs. HUD and USDA Rural Development programs have ceased to produce large numbers of units since the 1980s. Since 1986, the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit
Low-Income Housing Tax Credit
The Low Income Housing Tax Credit is a dollar-for-dollar tax credit in the United States for affordable housing investments. It was created under the Tax Reform Act of 1986 that gives incentives for the utilization of private equity in the development of affordable housing aimed at low-income...
program has been the primary federal program to produce affordable units; however, the housing produced in this program is less affordable than the former HUD programs.
One of the most unique US public housing initiatives was the development of subsidized middle-class housing during the late New Deal
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of economic programs implemented in the United States between 1933 and 1936. They were passed by the U.S. Congress during the first term of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The programs were Roosevelt's responses to the Great Depression, and focused on what historians call...
(1940–42) under the auspices of the Mutual Ownership Defense Housing Division
Mutual Ownership Defense Housing Division
The Mutual Ownership Defense Housing Division of the Federal Works Agency part of the United States government, operating from about 1940 to 1942 under the leadership of Colonel Lawrence Westbrook, was an attempt by the United States Government, late in the New Deal, to respond to the housing needs...
of the Federal Works Agency
Federal Works Agency
The Federal Works Agency was an independent agency of the Federal government of the United States which administered a number of public construction, building maintenance, and public works relief functions and laws from 1939 to 1949...
under the direction of Colonel Lawrence Westbrook. These eight projects were purchased by the residents after the Second World War and as of 2009 seven of the projects continue to operate as mutual housing corporations owned by their residents. These projects are among the very few definitive success stories in the history of the US public housing effort.
In the U.S., households are commonly defined in terms of the amount of realized income they earn relative to the Area Median Income
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
or AMI. Localized AMI figures are calculated annually based on a survey of comparably-sized households within geographic ranges known as metropolitan statistical areas, as defined by the US Office of Management and Budget. For U.S. housing subsidies, households are categorized by federal law as follows:
- Moderate income households earn between 80% and 120% of AMI.
- Low income households earn between 50% and 80% of AMI.
- Very low income households earn no more than 50% of AMI.
Some states and cities in the United States operate a variety of affordable housing programs, including supportive housing programs, transitional housing programs and rent subsidies as part of public assistance programs. Local and state governments can adapt these income limits when administering local affordable housing programs; however, U.S. federal programs must adhere to the definitions above. For the Section 8 voucher program, the maximum household contribution to rent can be as high as 40% gross income.
Canada
In Canada, housing schemes are administered by provincial governments. Ontario became the only jurisdiction in North America to have no social housing during the Harris government of the 1990s. This aberration was corrected by the creation of the Social Housing Services Corporation (SHSC). SHSC was created by Ontario in 2002 to provide group services for social housing providers (public, non-profit and co-op housing) following the downloading of responsibility for over 270,000 social housing units to local municipalities. It is a non-profit corporation governed by a board of municipal, non-profit and co-op housing representatives. Its mandate is to provide Ontario housing providers and service managers with bulk purchasing, insurance, investment and information services that add significant value to their operations.With an annual budget of $4.5 million, SHSC and its two subsidiaries, SOHO and SHSC Financial Inc. offers a dedicated insurance program for social housing providers, bulk gas purchasing and an innovative energy efficiency retrofit program which coordinates energy audits, expertise, funding, bulk purchasing of energy-efficient goods, training and education, and data evaluation. SHSC manages and provides investment advice to housing providers on capital reserves valued at more than $390 million. Working closely with other housing sector organizations and non-governmental organizations, SHSC also supports and develops independent housing-related research, including a new Housing Internship program for graduate-level researchers.
Recently there has been a move toward the integration of affordable social housing with market housing and other uses, such as the 2006-10 redevelopment of the Woodward's building
Woodward's building
The Woodward's building was a historic building in the Downtown Eastside of Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. The original portion of the building was constructed in 1903 for the Woodward's Department Store when that area of Cordova Street was the heart of Vancouver's retail shopping district. ...
site in Vancouver.
Zoning changes in some areas of Canada to permit laneway house
Laneway house
A laneway house is a form of housing that is gaining popularity on the west coast of Canada, especially in the Metro Vancouver area. These homes are typically built into pre-existing lots, usually in the backyard and opening onto the back lane...
s has been part of the EcoDensity movement to permit home owners to create small affordable rental units in their backyards.
United States
Governmental and quasi-governmental agencies that contribute to the work of ensuring the existence of a steady supply of affordable housing in the United States are the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), USDA Rural DevelopmentRural Development
USDA Office of Rural Development is an agency with the United States Department of Agriculture which runs programs intended to improve the economy and quality of life in rural America....
, the Federal Home Loan Bank, Fannie Mae, and Freddie Mac. Important private sector institutions worth consulting are the National Association of Home Builders
National Association of Home Builders
The National Association of Home Builders is one of the largest trade associations in the United States. Headquartered in Washington, DC, NAHB's mission is "to enhance the climate for housing and the building industry...
, the National Affordable Housing Management Association (NAHMA), the Council for Affordable and Rural Housing (CARH) and the National Association of Realtors
National Association of Realtors
The National Association of Realtors , whose members are known as Realtors, is North America's largest trade association. representing over 1.2 million members , including NAR's institutes, societies, and councils, involved in all aspects of the residential and commercial real estate industries...
. Valuable research institutions with staff dedicated to the analysis of "affordable housing" includes: The Center for Housing Policy
Center for Housing Policy
The Center for Housing Policy, the research affiliate of the National Housing Conference , works to broaden understanding of the nation’s housing challenges and to examine the impact of policies and programs developed to address these needs...
, Brookings Institution
Brookings Institution
The Brookings Institution is a nonprofit public policy organization based in Washington, D.C., in the United States. One of Washington's oldest think tanks, Brookings conducts research and education in the social sciences, primarily in economics, metropolitan policy, governance, foreign policy, and...
, the Urban Institute
Urban Institute
The Urban Institute is a Washington, D.C.-based think tank that carries out nonpartisan economic and social policy research, collects data, evaluates social programs, educates the public on key domestic issues, and provides advice and technical assistance to developing governments abroad...
and the Joint Center for Housing Studies at Harvard University
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, established in 1636 by the Massachusetts legislature. Harvard is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and the first corporation chartered in the country...
and the Furman Center for Real Estate and Urban Policy
Furman Center for Real Estate and Urban Policy
The Furman Center for Real Estate and Urban Policy is a joint center at New York University School of Law and the NYU Wagner School of Public Service. The Furman Center was established in 1994 to create a place where people interested in affordable housing and land use issues could turn to for...
at New York University
New York University
New York University is a private, nonsectarian research university based in New York City. NYU's main campus is situated in the Greenwich Village section of Manhattan...
, and the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities
Center on Budget and Policy Priorities
The Center on Budget and Policy Priorities is a non-profit think tank that describes itself as a "policy organization ... working at the federal and state levels on fiscal policy and public programs that affect low- and moderate-income families and individuals."The Center examines the short- and...
. Several of these institutions (the Fannie Mae Foundation, Urban Institute, Brookings Institution Metropolitan Policy Program, Enterprise Community Partners, LISC, the Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies, and others) partnered to create KnowledgePlex, an online information resource devoted to affordable housing and community development issues.
United Kingdom
All major housing associationHousing association
Housing associations in the United Kingdom are independent not-for-profit bodies that provide low-cost "social housing" for people in housing need. Any trading surplus is used to maintain existing homes and to help finance new ones...
s are registered with the Tenant Services Authority which regulates them. The TSA is to be merged with the Homes and Communities Agency
Homes and Communities Agency
The Homes and Communities Agency is the non-departmental public body that funds new affordable housing in England. It was established by the Housing and Regeneration Act 2008 as one of the successor bodies to the Housing Corporation, and became operational on 1 December 2008.-Background:On 17...
, which provides grants for development. Housing associations that are registered with the TSA were known as Registered Social Landlords from 1996, but in the Housing And Regeneration Act 2008 the official legal term became Registered Providers; the latter also covers council housing
Council house
A council house, otherwise known as a local authority house, is a form of public or social housing. The term is used primarily in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland. Council houses were built and operated by local councils to supply uncrowded, well-built homes on secure tenancies at...
as well as developers and other bodies which may receive grant.
The Department for Communities and Local Government
Department for Communities and Local Government
The Department for Communities and Local Government is the UK Government department for communities and local government in England. It was established in May 2006 and is the successor to the Office of the Deputy Prime Minister, established in 2001...
has responsibility for housing in England.
In Scotland the task falls to the Scottish Housing Regulator.
Social housing in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland is one of the four countries of the United Kingdom. Situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, it shares a border with the Republic of Ireland to the south and west...
is regulated by the Northern Ireland Housing Executive, which was established to take on ownership of former council stock and prevent sectarian allocation of housing to people from one religion.
See also
- Abahlali baseMjondoloAbahlali baseMjondoloAbahlali baseMjondolo , also known as AbM or the red shirts is a shack-dwellers' movement in South Africa which is well known for its campaigning for public housing. The movement grew out of a road blockade organized from the Kennedy Road shack settlement in the city of Durban in early 2005 and now...
, South African Shack Dwellers' Movement - Community land trustCommunity land trustA community land trust is a nonprofit corporation which acquires and manages land on behalf of the residents of a place-based community, while preserving affordability and preventing foreclosures for any housing located upon its land.-Key features:...
, a way of preserving land for reduced cost housing - Exclusionary zoningExclusionary zoningExclusionary zoning is a term that, in the United States, has come to be applied to local zoning measures that appear to impose unnecessary or unjustifiable costs or requirements facially or by execution excluding various groups of ‘undesirables.'...
, zoning practices that raise the cost of housing above an affordable level - Inclusionary zoningInclusionary zoningInclusionary zoning, also known as inclusionary housing, is an American term which refers to municipal and county planning ordinances that require a given share of new construction to be affordable by people with low to moderate incomes...
, zoning that requires the inclusion of affordable housing - Housing associationHousing associationHousing associations in the United Kingdom are independent not-for-profit bodies that provide low-cost "social housing" for people in housing need. Any trading surplus is used to maintain existing homes and to help finance new ones...
, UK charities that rent low-cost housing - Housing cooperativeHousing cooperativeA housing cooperative is a legal entity—usually a corporation—that owns real estate, consisting of one or more residential buildings. Each shareholder in the legal entity is granted the right to occupy one housing unit, sometimes subject to an occupancy agreement, which is similar to a lease. ...
, a housing organization that is owned jointly by its resident-members - HUD USERHUD USERIn 1978, the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development's Office of Policy Development and Research established HUD USER, an information source for housing and community development researchers, academics, policymakers, and the American public.-Background on HUD USER:HUD USER is the primary...
, national agency for housing in the USA - Migration of the disadvantaged, in which disadvantaged people are priced out of desirable areasGentrificationGentrification and urban gentrification refer to the changes that result when wealthier people acquire or rent property in low income and working class communities. Urban gentrification is associated with movement. Consequent to gentrification, the average income increases and average family size...
- National Housing ConferenceNational Housing ConferenceThe National Housing Conference is an American non-profit organization based in Washington, D.C. established in 1931. Its stated goal is "ensuring safe, decent and affordable housing for all Americans."...
- Public housingPublic housingPublic housing is a form of housing tenure in which the property is owned by a government authority, which may be central or local. Social housing is an umbrella term referring to rental housing which may be owned and managed by the state, by non-profit organizations, or by a combination of the...
, or social housing, housing owned directly by a government agency - Subsidized housing, in which part of the cost of housing is paid by a third party, such as a government
- Sweat equitySweat equitySweat equity is a term that refers to a party's contribution to a project in the form of effort --- as opposed to financial equity, which is a contribution in the form of capital....
, a recent term for a landowner's choice to reduce his cash costs by providing his own labor
Further reading
The authors study the effect of rent subsidies in England on mobility and unemployment.- von Hoffman, Alexander, "Let Us Continue: Housing Policy in the Great Society, Part One", Joint Center for Housing Studies, Harvard University, April 2009
- UK Housing Review, University of York, England.
- "America's Rental Housing: The Key to a Balanced National Policy", Joint Center for Housing Studies, Harvard University, 2007
External links
- United States Council for Affordable and Rural Housing
- HUD Low Income Housing News Alert
- Low-Cost Housing in South America
- The Tyee Article Stop Gap Housing in Canada
- "The Ethics of Housing and NIMBYism" by Debra Stein
- Affordable housing crisis casts a shadow over the American Dream, City Mayors Society, 20 January 2007
- Canadian affordable housing 1980s-2006, editorial article by Canadian Architect magazine editor Ian Chodikoff. Retrieved March 8, 2007.
- UK government planning document: Delivering Affordable Housing

