
Wiggers diagram
Encyclopedia
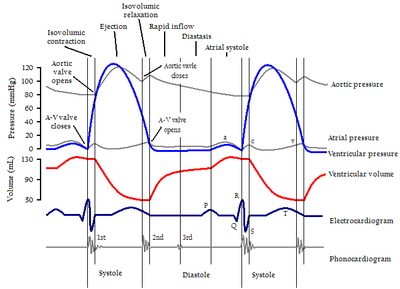
The X axis is used to plot time, while the Y axis contains all of the following on a single grid:
- Blood pressureBlood pressureBlood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies...
- Aortic pressure
- VentricularVentricle (heart)In the heart, a ventricle is one of two large chambers that collect and expel blood received from an atrium towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The Atria primes the Pump...
pressure - Atrial pressure
- Ventricular volume
- ElectrocardiogramElectrocardiogramElectrocardiography is a transthoracic interpretation of the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time, as detected by electrodes attached to the outer surface of the skin and recorded by a device external to the body...
- Arterial flow (optional)
- Heart soundsHeart soundsHeart sounds, or heartbeats, are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it...
(optional)
By illustrating the coordinated variation of these values, it becomes easier to illustrate the relationship between these values in the cardiac cycle
Cardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is a term referring to all or any of the events related to the flow or blood pressure that occurs from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. The frequency of the cardiac cycle is described by the heart rate. Each beat of the heart involves five major stages...
.
Etymology
It is named after Dr. Carl J. Wiggers, M.D.Carl J. Wiggers
Carl J. Wiggers was an eminent cardiovascular physiologist and was the 21st president of the American Physiological Society. He is the author of the Wiggers diagram, a diagram commonly used in the teaching of cardiovascular physiology...
. The diagram is frequently called a "Wigger's diagram", but this is incorrect.
Events
| >
Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiography is a transthoracic interpretation of the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time, as detected by electrodes attached to the outer surface of the skin and recorded by a device external to the body...
Heart sounds
Heart sounds, or heartbeats, are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it...
Aortic valve
The aortic valve is one of the valves of the heart. It is normally tricuspid , although in 1% of the population it is found to be congenitally bicuspid . It lies between the left ventricle and the aorta....
Mitral valve
The mitral valve is a dual-flap valve in the heart that lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle...
>-
| A
Systole (medicine)
Systole is the contraction of the heart. Used alone, it usually means the contraction of the left ventricle.In all mammals, the heart has 4 chambers. The left and right ventricles pump together. The atria and ventricles pump in sequence...
| B
Ventricle (heart)
In the heart, a ventricle is one of two large chambers that collect and expel blood received from an atrium towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The Atria primes the Pump...
systole - Isovolumetric/isovolumic contraction
QRS complex
The QRS complex is a name for the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram . It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles of the human heart...
| C1
| C2
| D
Diastole
Diastole is the period of time when the heart fills with blood after systole . Ventricular diastole is the period during which the ventricles are relaxing, while atrial diastole is the period during which the atria are relaxing...
- Isovolumetric/isovolumic relaxation
| E1
| E2
Note that during isovolumetric/isovolumic contraction and relaxation, all the heart valves are closed. At no time are all the heart valves open.
- S3 and S4 heart sounds are associated with pathologies and are not routinely heard.

