
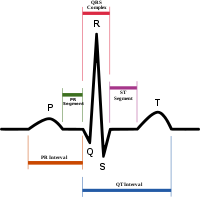
QRS complex
Encyclopedia

Depolarization
In biology, depolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential, making it more positive, or less negative. In neurons and some other cells, a large enough depolarization may result in an action potential...
of the right and left ventricles
Ventricle (heart)
In the heart, a ventricle is one of two large chambers that collect and expel blood received from an atrium towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The Atria primes the Pump...
of the human heart
Human heart
The human heart is a muscular organ that provides a continuous blood circulation through the cardiac cycle and is one of the most vital organs in the human body...
. In adults, it normally lasts 0.06 - 0.10 s; in children and during physical activity, it may be shorter.
Typically an ECG has five deflections, arbitrarily named "P" to "T" waves. The Q, R, and S waves occur in rapid succession, do not all appear in all leads, and reflect a single event, and thus are usually considered together. A Q wave is any downward deflection after the P wave
P wave (electrocardiography)
In electrocardiography, during normal atrial depolarization, the main electrical vector is directed from the SA node towards the AV node, and spreads from the right atrium to the left atrium...
. An R wave follows as an upward deflection, and the S wave is any downward deflection after the R wave. The T wave
T wave
In electrocardiography, the T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the absolute refractory period. The last half of the T wave is referred to as the relative refractory period...
follows the S wave, and in some cases an additional U wave
U wave
The U wave is a wave on an electrocardiogram that is not always seen. It is typically small, and, by definition, follows the T wave. U waves are thought to represent repolarization of the papillary muscles or Purkinje fibers.-Interpretation:...
follows the T wave.
Etiology
The HisBundle of His
The bundle of His, known as the AV bundle or atrioventricular bundle, is a collection of heart muscle cells specialized for electrical conduction that transmits the electrical impulses from the AV node to the point of the apex of the fascicular branches...
/Purkinje
Purkinje fibers
For the nervous cells, see Purkinje cellPurkinje fibers are located in the inner ventricular walls of the heart, just beneath the endocardium...
specialized muscle cells coordinate the depolarization of both ventricles, and if they are working efficiently the QRS complex is 80 to 120 ms in duration (represented by three small squares or less at the standard paper speed of 25mm/s). Any abnormality of conduction takes longer and causes "widened" QRS complexes. In bundle branch block
Bundle branch block
A bundle branch block refers to a defect of the heart's electrical conduction system.-Anatomy and physiology:The heart's electrical activity begins in the sinoatrial node , which is situated on the upper right atrium. The impulse travels next through the left and right atria and summates at the...
there can be an abnormal second upward deflection within the QRS complex, and in this case the second upward deflection is referred to as R' . This would be described as an RSR' pattern.
Ventricles contain more muscle mass than the atria; therefore the QRS complex is considerably larger than the P wave. The QRS complex is often used to determine the axis of the electrocardiogram (although it is also possible to determine a separate P wave axis).
The duration, amplitude, and morphology of the QRS complex are useful in diagnosing cardiac arrhythmias, conduction abnormalities, ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy is the enlargement of ventricles in the heart. Although left ventricular hypertrophy is more common, enlargement can also occur in the right ventricle, or both ventricles.- Physiology :...
, myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction or acute myocardial infarction , commonly known as a heart attack, results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, causing heart cells to die...
, electrolyte derangements, and other disease states.
Parameters
| Parameter | Normal value | Value comments | Clinical significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| QRS duration | 0.06 - 0.10 sec | Shorter in children and in tachycardia | Prolonged duration indicates e.g. hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia refers to the condition in which the concentration of the electrolyte potassium in the blood is elevated... . or bundle branch block Bundle branch block A bundle branch block refers to a defect of the heart's electrical conduction system.-Anatomy and physiology:The heart's electrical activity begins in the sinoatrial node , which is situated on the upper right atrium. The impulse travels next through the left and right atria and summates at the... |
| QRS amplitude |
|
Increased amplitude indicated cardiac hypertrophy | |
| Ventricular activation time (VAT) |
|
Measured in increased QRS amplitude | |
| Q wave |
|
Abnormality indicates presence of infarction |
The QRS complex is also included in estimating the QT interval
QT interval
In cardiology, the QT interval is a measure of the time between the start of the Q wave and the end of the T wave in the heart's electrical cycle. In general, the QT interval represents electrical depolarization and repolarization of the left and right ventricles...
.
Q wave
Normal Q waves, when present, represent depolarization of the interventricular septumInterventricular septum
Interventricular septum , abbreviated IVS, is the stout wall separating the lower chambers of the heart from one another....
. For this reason, they are referred to as septal Q waves and can be appreciated in the lateral leads I, aVL, V5 and V6.
R wave progression
Looking at the precordial leads, the r wave usually progresses from showing a rS-type complex in V1 with an increasing R and a decreasing S wave when moving towards the left side. There is usually an qR-type of complex in V5 and V6 with the R-wave amplitude usually taller in V5 than in V6. It is normal to have a narrow QS and rSr' patterns in V1, and so is also the case for qRs and R patterns in V5 and V6. The transition zone is where the QRS complex changes from predominately negative to predominately positive (R/S ratio becoming >1), and this usually occurs at V3 or V4. It is normal to have the transition zone at V2 (called "early transition"), and at V5 (called "delayed transition").The definition of poor R wave progression (PRWP) varies in the literature, but a common one is when the R wave is less than 2–4 mm in leads V3 or V4 and/or there is presence of a reversed R wave progression, which is defined as R in V4 < R in V3 or R in V3 < R in V2 or R in V2 < R in V1, or any combination of these. Poor R wave progression is commonly attributed to anterior myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction or acute myocardial infarction , commonly known as a heart attack, results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, causing heart cells to die...
, but it may also be caused by left bundle branch block
Left bundle branch block
Left bundle branch block is a cardiac conduction abnormality seen on the electrocardiogram . In this condition, activation of the left ventricle is delayed, which results in the left ventricle contracting later than the right ventricle....
, Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome, right and left ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy is the enlargement of ventricles in the heart. Although left ventricular hypertrophy is more common, enlargement can also occur in the right ventricle, or both ventricles.- Physiology :...
as well as
by faulty ECG recording technique.
J-point
The point at which the QRS complex meets the ST segmentST segment
In electrocardiography, the ST segment connects the QRS complex and the T wave and has a duration of 0.08 to 0.12 sec .It starts at the J point and ends at the beginning of the T wave...
is known as the J-point. The J-point is easy to identify when the ST segment is horizontal and forms a sharp angle with the last part of the QRS complex. However, when the ST segment is sloped or the QRS complex is wide, the two features do not form a sharp angle and the location of the J-point is less clear. There is no consensus on the precise location of the J-point in these circumstances. Two possible definitions are:
- The "first point of inflection of the upstroke of the S wave"
- The point at which the ECG trace becomes more horizontal than vertical.
Monomorphic or polymorphic
Monomorphic refers to all QRS waves in a single lead being similar in shape. Polymorphic means that the QRS change from complex to complex. These terms are used in the description of ventricular tachycardiaVentricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia is a tachycardia, or fast heart rhythm, that originates in one of the ventricles of the heart...
.
Terminology


