Weak gravitational lensing
Encyclopedia
While the presence of any mass bends the path of light passing near it, this effect rarely produces the giant arcs and multiple images associated with strong gravitational lensing
. Most lines of sight in the universe are thoroughly in the weak lensing regime, in which the deflection is impossible to detect in a single background source. However, even in these cases, the presence of the foreground mass can be detected, by way of a systematic alignment of background sources around the lensing mass. Weak gravitational lensing is thus an intrinsically statistical measurement, but it provides a way to measure the masses of astronomical objects without requiring assumptions about their composition or dynamical state.
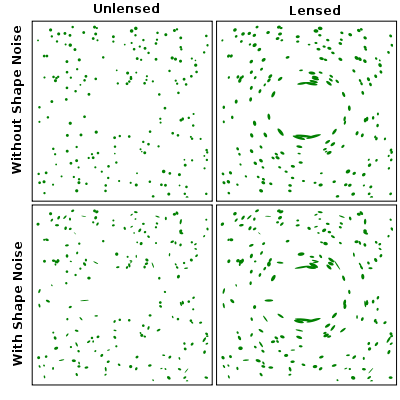 Gravitational lensing acts as a coordinate transformation that distorts the images of background objects (usually galaxies) near a foreground mass. The transformation can be split into two terms, the convergence and shear. The convergence term magnifies the background objects by increasing their size, and the shear term stretches them tangentially around the foreground mass.
Gravitational lensing acts as a coordinate transformation that distorts the images of background objects (usually galaxies) near a foreground mass. The transformation can be split into two terms, the convergence and shear. The convergence term magnifies the background objects by increasing their size, and the shear term stretches them tangentially around the foreground mass.
To measure this tangential alignment, it is necessary to measure the ellipticities of the background galaxies and construct a statistical estimate of their systematic alignment. The fundamental problem is that galaxies are not intrinsically circular, so their measured ellipticity is a combination of their intrinsic ellipticity and the gravitational lensing shear. Typically, the intrinsic ellipticity is much greater than the shear (by a factor of 3-300, depending on the foreground mass). The measurements of many background galaxies must be combined to average down this "shape noise". The orientation of intrinsic ellipticities of galaxies should be almost entirely random, so any systematic alignment between multiple galaxies can generally be assumed to be caused by lensing.
Another major challenge for weak lensing is correction for the point spread function
(PSF) due to instrumental and atmospheric effects, which causes the observed images to be smeared relative to the "true sky". This smearing tends to make small objects more round, destroying some of the information about their true ellipticity. As a further complication, the PSF typically adds a small level of ellipticity to objects in the image, which is not at all random, and can in fact mimic a true lensing signal. Even for the most modern telescopes, this effect is usually at least the same order of magnitude as the gravitational lensing shear, and is often much larger. Correcting for the PSF requires building a model for how it varies across the field. Stars in our own galaxy provide a direct measurement of the PSF, and these can be used to construct such a model, usually by interpolating between the points where stars appear on the image. This model can then be used to reconstruct the "true" ellipticities from the smeared ones. Ground-based and space-based data typically undergo distinct reduction procedures due to the differences in instruments and observing conditions.
Angular diameter distances to the lenses and background sources are important for converting the lensing observables to physically meaningful quantities. These distances are often estimated using photometric redshift
s when spectroscopic redshifts
are unavailable. Redshift information is also important in separating the background source population from other galaxies in the foreground, or those associated with the mass responsible for the lensing. With no redshift information, the foreground and background populations can be split by an apparent magnitude
or a color
cut, but this is much less accurate.
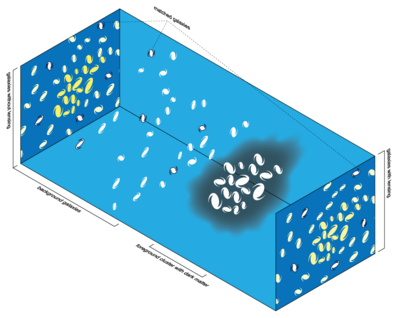 Galaxy clusters are among the largest gravitation
Galaxy clusters are among the largest gravitation
ally bound structures in the Universe
, surpassed only by superclusters, with approximately 80% of cluster content in the form of dark matter
. The gravitational fields of these clusters deflect light-rays traveling near them. As seen from Earth
, this effect can cause dramatic distortions of a background source object detectable by eye such as multiple images, arcs, and rings (cluster strong lensing). More generally, the effect causes small, but statistically coherent, distortions of background sources on the order of 10% (cluster weak lensing). Abell 1689
, CL0024+17
, and the Bullet Cluster
are among the most prominent examples of lensing clusters.
and Vahe Petrosian of Stanford University
who discovered giant luminous arcs in a survey of galaxy clusters in the late 1970s. Lynds and Petrosian published their findings in 1986 without knowing the origin of the arcs. In 1987, Genevieve Soucail of the Toulouse Observatory
and her collaborators presented data of a blue ring-like structure in Abell 370 and proposed a gravitational lensing interpretation. The first cluster weak lensing analysis was conducted in 1990 by J. Anthony Tyson of Bell Laboratories and collaborators. Tyson et al. detected a coherent alignment of the ellipticities
of the faint blue galaxies behind both Abell 1689
and CL 1409+52. Lensing has been used as a tool to investigate a tiny fraction of the thousands of known galaxy clusters.
Historically, lensing analyses were conducted on galaxy clusters detected via their baryon
content (e.g. from optical
or X-ray
surveys). The sample of galaxy clusters studied with lensing was thus subject to various selection effects; for example, only the most luminous
clusters were investigated. In 2006, David Wittman of the University of California at Davis and collaborators published the first sample of galaxy clusters detected via their lensing signals, completely independent of their baryon content. Clusters discovered through lensing are subject to mass selection effects because the more massive clusters produce lensing signals with higher signal-to-noise.
can be recovered from the measurement of the ellipticities of the lensed background galaxies through techniques that can be classifed into two types: direct reconstruction and inversion
. However, a mass distribution
reconstructed without knowledge of the magnification suffers from a limitation known as the mass sheet degeneracy
, where the cluster surface mass density κ can be determined only up to a transformation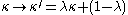 where λ is an arbitrary constant. This degeneracy can be broken if an independent measurement of the magnification is available because the magnification is not invariant
where λ is an arbitrary constant. This degeneracy can be broken if an independent measurement of the magnification is available because the magnification is not invariant
under the aforementioned degeneracy transformation.
Given a centroid
for the cluster, which can be determined by using a reconstructed mass distribution or optical or X-ray data, a model can be fit to the shear profile as a function of clustrocentric radius. For example, the singular isothermal sphere (SIS) profile and the Navarro-Frenk-White (NFW) profile
are two commonly used parametric model
s. Knowledge of the lensing cluster redshift
and the redshift distribution of the background galaxies is also necessary for estimation of the mass and size from a model fit; these redshifts can be measured precisely using spectroscopy
or estimated using photometry
. Individual mass estimates from weak lensing can only be derived for the most massive clusters, and the accuracy of these mass estimates are limited by projections along the line of sight.
 Cluster mass estimates determined by lensing are valuable because the method requires no assumption about the dynamical state or star formation history
Cluster mass estimates determined by lensing are valuable because the method requires no assumption about the dynamical state or star formation history
of the cluster in question. Lensing mass maps can also potentially reveal "dark clusters," clusters containing overdense concentrations of dark matter but relatively insignificant amounts of baryonic matter. Comparison of the dark matter distribution mapped using lensing with the distribution of the baryons using optical and X-ray data reveals the interplay of the dark matter with the stellar
and gas
components. A notable example of such a joint analysis is the so-called Bullet Cluster
. The Bullet Cluster data provide constraints on models relating light, gas, and dark matter distributions such as Modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND)
and Λ-Cold Dark Matter (Λ-CDM)
.
In principle, since the number density of clusters as a function of mass and redshift is sensitive to the underlying cosmology
, cluster counts derived from large weak lensing surveys should be able to constrain cosmological parameters. In practice, however, projections along the line of sight cause many false positives. Weak lensing can also be used to calibrate the mass-observable relation via a stacked weak lensing signal around an ensemble of clusters, although this relation is expected to have an intrinsic scatter
. In order for lensing clusters to be a precision probe of cosmology in the future, the projection effects and the scatter in the lensing mass-observable relation need to be thoroughly characterized and modeled.
(as opposed to a galaxy cluster
or the large-scale structure of the cosmos). Of the three typical mass regimes in weak lensing, galaxy-galaxy lensing produces a “mid-range” signal (shear correlations of ~1%) that is weaker than the signal due to cluster lensing, but stronger than the signal due to cosmic shear.
have greatly increased the observed number density of both background source and foreground lens galaxies, allowing for a much more robust statistical sample of galaxies, making the lensing signal much easier to detect. Today, measuring the shear signal due to galaxy-galaxy lensing is a widely used technique in observational astronomy
and cosmology
, often used in parallel with other measurements in determining physical characteristics of foreground galaxies.
ratio will improve, allowing one to determine a statistically significant signal, averaged over the entire lens set.
:
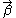 to the lensed position
to the lensed position  . The Jacobian
. The Jacobian
of the transform can be written as an integral over the gravitational potential along the line of sight
along the line of sight
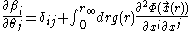
where is the comoving distance
is the comoving distance
,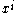 are the transverse distances, and
are the transverse distances, and
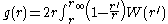
is the lensing kernel, which defines the efficiency of lensing for a distribution of sources .
.
As in the thin-lens approximation, the Jacobian can be decomposed into shear and convergence terms.
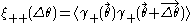

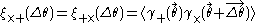
where is the component along or perpendicular to
is the component along or perpendicular to 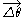 , and
, and 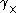 is the component at 45°. These correlation functions are typically computed by averaging over many pairs of galaxies. The last correlation function,
is the component at 45°. These correlation functions are typically computed by averaging over many pairs of galaxies. The last correlation function, 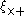 , is not affected at all by lensing, so measuring a value for this function that is inconsistent with zero is often interpreted as a sign of systematic error
, is not affected at all by lensing, so measuring a value for this function that is inconsistent with zero is often interpreted as a sign of systematic error
.
The functions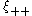 and
and 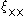 can be related to projections (integrals with certain weight functions) of the dark matter density correlation function, which can be predicted from theory for a cosmological model through its Fourier transform, the matter power spectrum
can be related to projections (integrals with certain weight functions) of the dark matter density correlation function, which can be predicted from theory for a cosmological model through its Fourier transform, the matter power spectrum
.
Because they both depend on a single scalar density field, and
and 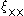 are not independent, and they can be decomposed further into E-mode and B-mode correlation functions. In analogy with electric and magnetic fields, the E-mode field is curl-free and the B-mode field is divergence-free. Because gravitational lensing can only produce an E-mode field, the B-mode provides yet another test for systematic errors.
are not independent, and they can be decomposed further into E-mode and B-mode correlation functions. In analogy with electric and magnetic fields, the E-mode field is curl-free and the B-mode field is divergence-free. Because gravitational lensing can only produce an E-mode field, the B-mode provides yet another test for systematic errors.
The E-mode correlation function is also known as the aperture mass variance
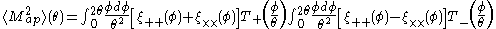
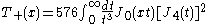
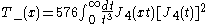
where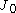 and
and  are Bessel Functions.
are Bessel Functions.
An exact decomposition thus requires knowledge of the shear correlation functions at zero separation, but an approximate decomposition is fairly insensitive to these values because the filters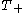 and
and  are small near
are small near  .
.
makes it a potentially powerful probe of cosmological parameters, especially when combined with other observations such as the cosmic microwave background, supernovae
, and galaxy surveys
. Detecting the extremely faint cosmic shear signal requires averaging over many background galaxies, so surveys must be both deep and wide, and because these background galaxies are small, the image quality must be very good. Measuring the shear correlations at small scales also requires a high density of background objects (again requiring deep, high quality data), while measurements at large scales push for wider surveys.
While weak lensing of large-scale structure was discussed as early as 1967, due to the challenges mentioned above, it was not detected until more than 30 years later when large CCD
cameras enabled surveys of the necessary size and quality. In 2000, four independent groups published the first detections of cosmic shear, and subsequent observations have started to put constraints on cosmological parameters (particularly the dark matter density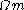 and power spectrum amplitude
and power spectrum amplitude 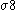
) that are competitive with other cosmological probes.
For current and future surveys, one goal is to use the redshifts of the background galaxies (often approximated using photometric redshift
s) to divide the survey into multiple redshift bins. The low-redshift bins will only be lensed by structures very near to us, while the high-redshift bins will be lensed by structures over a wide range of redshift. This technique, dubbed "cosmic tomography
", makes it possible to map out the 3D distribution of mass. Because the third dimension involves not only distance but cosmic time, tomographic weak lensing is sensitive not only to the matter power spectrum today, but also to its evolution over the history of the universe, and the expansion history of the universe during that time. This is a much more valuable cosmological probe, and many proposed experiments to measure the properties of dark energy
and dark matter
have focused on weak lensing, such as the Dark Energy Survey
, Pan-STARRS
, and LSST.
Weak lensing also has an important effect on the Cosmic Microwave Background and diffuse 21cm line radiation
. Even though there are no distinct resolved sources, perturbations on the origining surface are sheared in a similar way to galaxy weak lensing, resulting in changes to the power spectrum and statistics of the observed signal. Since the source plane for the CMB and high-redshift diffuse 21cm are at higher redshift that resolved galaxies, the lensing effect probes cosmology at higher redshifts than galaxy lensing.
Gravitational lens
A gravitational lens refers to a distribution of matter between a distant source and an observer, that is capable of bending the light from the source, as it travels towards the observer...
. Most lines of sight in the universe are thoroughly in the weak lensing regime, in which the deflection is impossible to detect in a single background source. However, even in these cases, the presence of the foreground mass can be detected, by way of a systematic alignment of background sources around the lensing mass. Weak gravitational lensing is thus an intrinsically statistical measurement, but it provides a way to measure the masses of astronomical objects without requiring assumptions about their composition or dynamical state.
Methodology

To measure this tangential alignment, it is necessary to measure the ellipticities of the background galaxies and construct a statistical estimate of their systematic alignment. The fundamental problem is that galaxies are not intrinsically circular, so their measured ellipticity is a combination of their intrinsic ellipticity and the gravitational lensing shear. Typically, the intrinsic ellipticity is much greater than the shear (by a factor of 3-300, depending on the foreground mass). The measurements of many background galaxies must be combined to average down this "shape noise". The orientation of intrinsic ellipticities of galaxies should be almost entirely random, so any systematic alignment between multiple galaxies can generally be assumed to be caused by lensing.
Another major challenge for weak lensing is correction for the point spread function
Point spread function
The point spread function describes the response of an imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is a system's impulse response, the PSF being the impulse response of a focused optical system. The PSF in many contexts can be thought of as the extended blob...
(PSF) due to instrumental and atmospheric effects, which causes the observed images to be smeared relative to the "true sky". This smearing tends to make small objects more round, destroying some of the information about their true ellipticity. As a further complication, the PSF typically adds a small level of ellipticity to objects in the image, which is not at all random, and can in fact mimic a true lensing signal. Even for the most modern telescopes, this effect is usually at least the same order of magnitude as the gravitational lensing shear, and is often much larger. Correcting for the PSF requires building a model for how it varies across the field. Stars in our own galaxy provide a direct measurement of the PSF, and these can be used to construct such a model, usually by interpolating between the points where stars appear on the image. This model can then be used to reconstruct the "true" ellipticities from the smeared ones. Ground-based and space-based data typically undergo distinct reduction procedures due to the differences in instruments and observing conditions.
Angular diameter distances to the lenses and background sources are important for converting the lensing observables to physically meaningful quantities. These distances are often estimated using photometric redshift
Photometric redshift
A photometric redshift is an estimate for the distance of an astronomical object, such as a galaxy or quasar. The technique uses photometry to determine the redshift, and hence, through Hubble's...
s when spectroscopic redshifts
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
are unavailable. Redshift information is also important in separating the background source population from other galaxies in the foreground, or those associated with the mass responsible for the lensing. With no redshift information, the foreground and background populations can be split by an apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
or a color
Color index
In astronomy, the color index is a simple numerical expression that determines the color of an object, which in the case of a star gives its temperature...
cut, but this is much less accurate.
Weak lensing by clusters of galaxies

Gravitation
Gravitation, or gravity, is a natural phenomenon by which physical bodies attract with a force proportional to their mass. Gravitation is most familiar as the agent that gives weight to objects with mass and causes them to fall to the ground when dropped...
ally bound structures in the Universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
, surpassed only by superclusters, with approximately 80% of cluster content in the form of dark matter
Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
. The gravitational fields of these clusters deflect light-rays traveling near them. As seen from Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, this effect can cause dramatic distortions of a background source object detectable by eye such as multiple images, arcs, and rings (cluster strong lensing). More generally, the effect causes small, but statistically coherent, distortions of background sources on the order of 10% (cluster weak lensing). Abell 1689
Abell 1689
Abell 1689 is a galaxy cluster in the constellation Virgo. It is one of the biggest and most massive galaxy clusters known and acts as a gravitational lens, distorting the images of galaxies that lie behind it...
, CL0024+17
CL0024+17
The cluster CL0024+17 is a cluster of galaxies located in Pisces. Cl 0024+17, is allowing astronomers to probe the distribution of dark matter in space. The blue streaks near the center of the image are the smeared images of very distant galaxies that are not part of the cluster...
, and the Bullet Cluster
Bullet cluster
The Bullet cluster consists of two colliding clusters of galaxies. Studies of the Bullet cluster, announced in August 2006, provide the best evidence to date for the existence of dark matter...
are among the most prominent examples of lensing clusters.
History
The effects of cluster strong lensing were first detected by Roger Lynds of the National Optical Astronomy ObservatoriesNational Optical Astronomy Observatory
The National Optical Astronomy Observatory is the United States national observatory for ground based nighttime ultraviolet-optical-infrared astronomy. The National Science Foundation funds NOAO to provide forefront astronomical research facilities for US astronomers...
and Vahe Petrosian of Stanford University
Stanford University
The Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University or Stanford, is a private research university on an campus located near Palo Alto, California. It is situated in the northwestern Santa Clara Valley on the San Francisco Peninsula, approximately northwest of San...
who discovered giant luminous arcs in a survey of galaxy clusters in the late 1970s. Lynds and Petrosian published their findings in 1986 without knowing the origin of the arcs. In 1987, Genevieve Soucail of the Toulouse Observatory
Toulouse Observatory
The Observatoire de Toulouse is located in Toulouse, France and was established in 1733. It was founded by l'Académie des Sciences, Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres de Toulouse . It was moved 1841 and again in 1981...
and her collaborators presented data of a blue ring-like structure in Abell 370 and proposed a gravitational lensing interpretation. The first cluster weak lensing analysis was conducted in 1990 by J. Anthony Tyson of Bell Laboratories and collaborators. Tyson et al. detected a coherent alignment of the ellipticities
Ellipse
In geometry, an ellipse is a plane curve that results from the intersection of a cone by a plane in a way that produces a closed curve. Circles are special cases of ellipses, obtained when the cutting plane is orthogonal to the cone's axis...
of the faint blue galaxies behind both Abell 1689
Abell 1689
Abell 1689 is a galaxy cluster in the constellation Virgo. It is one of the biggest and most massive galaxy clusters known and acts as a gravitational lens, distorting the images of galaxies that lie behind it...
and CL 1409+52. Lensing has been used as a tool to investigate a tiny fraction of the thousands of known galaxy clusters.
Historically, lensing analyses were conducted on galaxy clusters detected via their baryon
Baryon
A baryon is a composite particle made up of three quarks . Baryons and mesons belong to the hadron family, which are the quark-based particles...
content (e.g. from optical
Visible-light astronomy
Visible-light astronomy encompasses a wide variety of observations via telescopes that are sensitive in the range of visible light...
or X-ray
X-ray astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets, and...
surveys). The sample of galaxy clusters studied with lensing was thus subject to various selection effects; for example, only the most luminous
Luminous intensity
In photometry, luminous intensity is a measure of the wavelength-weighted power emitted by a light source in a particular direction per unit solid angle, based on the luminosity function, a standardized model of the sensitivity of the human eye...
clusters were investigated. In 2006, David Wittman of the University of California at Davis and collaborators published the first sample of galaxy clusters detected via their lensing signals, completely independent of their baryon content. Clusters discovered through lensing are subject to mass selection effects because the more massive clusters produce lensing signals with higher signal-to-noise.
Observational products
The projected mass densityDensity
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
can be recovered from the measurement of the ellipticities of the lensed background galaxies through techniques that can be classifed into two types: direct reconstruction and inversion
Inverse problem
An inverse problem is a general framework that is used to convert observed measurements into information about a physical object or system that we are interested in...
. However, a mass distribution
Mass distribution
Mass distribution is a term used in physics and mechanics and describes the spatial distribution of mass within a solid body. In principle, it is relevant also for gases or liquids, but on earth their mass distribution is almost homogeneous.-Astronomy:...
reconstructed without knowledge of the magnification suffers from a limitation known as the mass sheet degeneracy
Degeneracy
Degeneracy may refer to:* DegenerationIn science and mathematics:* Degeneracy , a property of quantum states sharing the same energy levels...
, where the cluster surface mass density κ can be determined only up to a transformation
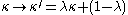 where λ is an arbitrary constant. This degeneracy can be broken if an independent measurement of the magnification is available because the magnification is not invariant
where λ is an arbitrary constant. This degeneracy can be broken if an independent measurement of the magnification is available because the magnification is not invariantInvariant (mathematics)
In mathematics, an invariant is a property of a class of mathematical objects that remains unchanged when transformations of a certain type are applied to the objects. The particular class of objects and type of transformations are usually indicated by the context in which the term is used...
under the aforementioned degeneracy transformation.
Given a centroid
Centroid
In geometry, the centroid, geometric center, or barycenter of a plane figure or two-dimensional shape X is the intersection of all straight lines that divide X into two parts of equal moment about the line. Informally, it is the "average" of all points of X...
for the cluster, which can be determined by using a reconstructed mass distribution or optical or X-ray data, a model can be fit to the shear profile as a function of clustrocentric radius. For example, the singular isothermal sphere (SIS) profile and the Navarro-Frenk-White (NFW) profile
Navarro-Frenk-White profile
The Navarro–Frenk–White profile or NFW profile is a spatial mass distribution of dark matter fitted to dark matter haloes identified in N-body simulations by Julio Navarro, Carlos Frenk and Simon White...
are two commonly used parametric model
Parametric model
In statistics, a parametric model or parametric family or finite-dimensional model is a family of distributions that can be described using a finite number of parameters...
s. Knowledge of the lensing cluster redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
and the redshift distribution of the background galaxies is also necessary for estimation of the mass and size from a model fit; these redshifts can be measured precisely using spectroscopy
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
or estimated using photometry
Photometric redshift
A photometric redshift is an estimate for the distance of an astronomical object, such as a galaxy or quasar. The technique uses photometry to determine the redshift, and hence, through Hubble's...
. Individual mass estimates from weak lensing can only be derived for the most massive clusters, and the accuracy of these mass estimates are limited by projections along the line of sight.
Scientific implications

Star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense parts of molecular clouds collapse into a ball of plasma to form a star. As a branch of astronomy star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium and giant molecular clouds as precursors to the star formation process and the study of young...
of the cluster in question. Lensing mass maps can also potentially reveal "dark clusters," clusters containing overdense concentrations of dark matter but relatively insignificant amounts of baryonic matter. Comparison of the dark matter distribution mapped using lensing with the distribution of the baryons using optical and X-ray data reveals the interplay of the dark matter with the stellar
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
and gas
Intracluster medium
In astronomy, the intracluster medium is the superheated plasma present at the center of a galaxy cluster. This is gas heated to temperatures of between roughly 10 and 100 megakelvins and consisting mainly of ionised hydrogen and helium, containing most of the baryonic material in the cluster...
components. A notable example of such a joint analysis is the so-called Bullet Cluster
Bullet cluster
The Bullet cluster consists of two colliding clusters of galaxies. Studies of the Bullet cluster, announced in August 2006, provide the best evidence to date for the existence of dark matter...
. The Bullet Cluster data provide constraints on models relating light, gas, and dark matter distributions such as Modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND)
Mond
Mond may refer to:* MOND - Modified Newtonian Dynamics. A proposed adjustment to the classical inverse-square law of gravity.* Der Mond, an opera in one act* Mond Nickel Company, a defunct mining company...
and Λ-Cold Dark Matter (Λ-CDM)
Lambda-CDM model
ΛCDM or Lambda-CDM is an abbreviation for Lambda-Cold Dark Matter, which is also known as the cold dark matter model with dark energy...
.
In principle, since the number density of clusters as a function of mass and redshift is sensitive to the underlying cosmology
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
, cluster counts derived from large weak lensing surveys should be able to constrain cosmological parameters. In practice, however, projections along the line of sight cause many false positives. Weak lensing can also be used to calibrate the mass-observable relation via a stacked weak lensing signal around an ensemble of clusters, although this relation is expected to have an intrinsic scatter
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
. In order for lensing clusters to be a precision probe of cosmology in the future, the projection effects and the scatter in the lensing mass-observable relation need to be thoroughly characterized and modeled.
Galaxy-galaxy lensing
Galaxy-galaxy lensing is a specific type of weak (and occasionally strong) gravitational lensing, in which the foreground object responsible for distorting the shapes of background galaxies is itself an individual field galaxyField galaxy
A field galaxy is a galaxy that does not belong to a larger cluster of galaxies, but is gravitationally alone. The vast majority of galaxies exist outside of clusters.Most low surface brightness galaxies are field galaxies....
(as opposed to a galaxy cluster
Galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster is a compact cluster of galaxies. Basic difference between a galaxy group and a galaxy cluster is that there are many more galaxies in a cluster than in a group. Also, galaxies in a cluster are more compact and have higher velocity dispersion. One of the key features of cluster is...
or the large-scale structure of the cosmos). Of the three typical mass regimes in weak lensing, galaxy-galaxy lensing produces a “mid-range” signal (shear correlations of ~1%) that is weaker than the signal due to cluster lensing, but stronger than the signal due to cosmic shear.
History
J.A. Tyson and collaborators first postulated the concept of galaxy-galaxy lensing in 1984, though the observational results of their study were inconclusive. It was not until 1996 that evidence of such distortion was tentatively discovered, with the first statistically significant results not published until the year 2000. Since those initial discoveries, the construction of larger, high resolution telescopes and the advent of dedicated wide field galaxy surveysRedshift survey
In astronomy, a redshift survey, or galaxy survey, is a survey of a section of the sky to measure the redshift of astronomical objects. Using Hubble's law, the redshift can be used to calculate the distance of an object from Earth. By combining redshift with angular position data, a redshift...
have greatly increased the observed number density of both background source and foreground lens galaxies, allowing for a much more robust statistical sample of galaxies, making the lensing signal much easier to detect. Today, measuring the shear signal due to galaxy-galaxy lensing is a widely used technique in observational astronomy
Observational astronomy
Observational astronomy is a division of the astronomical science that is concerned with getting data, in contrast with theoretical astrophysics which is mainly concerned with finding out the measurable implications of physical models...
and cosmology
Cosmology
Cosmology is the discipline that deals with the nature of the Universe as a whole. Cosmologists seek to understand the origin, evolution, structure, and ultimate fate of the Universe at large, as well as the natural laws that keep it in order...
, often used in parallel with other measurements in determining physical characteristics of foreground galaxies.
Stacking
Much like in cluster-scale weak lensing, detection of a galaxy-galaxy shear signal requires one to measure the shapes of background source galaxies, and then look for statistical shape correlations (specifically, source galaxy shapes should be aligned tangentially, relative to the lens center.) In principle, this signal could be measured around any individual foreground lens. In practice, however, due to the relatively low mass of field lenses and the inherent randomness in intrinsic shape of background sources (the “shape noise”), the signal is impossible to measure on a galaxy by galaxy basis. However, by combining the signals of many individual lens measurements together (a technique known as “stacking”), the signal to noiseSignal to Noise
Signal to Noise is a graphic novel written by Neil Gaiman and illustrated by Dave McKean. It was originally serialised in the UK style magazine The Face, beginning in 1989, and collected as a graphic novel in 1992, published by Victor Gollancz Ltd in the UK and by Dark Horse Comics in the US.The...
ratio will improve, allowing one to determine a statistically significant signal, averaged over the entire lens set.
Scientific applications
Galaxy-galaxy lensing (like all other types of gravitational lensing) is used to measure several quantities pertaining to massMass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
:
- Mass density profiles
- Using techniques similar to those in cluster-scale lensing, galaxy-galaxy lensing can provide information about the shape of mass density profiles, though these profiles correspond to galaxy-sized objects instead of larger clusters or groups. Given a high enough number density of background sources, a typical galaxy-galaxy mass density profile can cover a wide range of distances (from ~1 to ~100 effective radiiEffective radiusThe effective radius of a galaxy is the radius at which one half of the total light of the system is emitted interior to this radius. This assumes the galaxy is circularly symmetric...
). Since the effects of lensing are insensitive to the matter type, a galaxy-galaxy mass density profile can be used to probe a wide range of matter environments: from the central cores of galaxies where baryonBaryonA baryon is a composite particle made up of three quarks . Baryons and mesons belong to the hadron family, which are the quark-based particles...
s dominate the total mass fraction, to the outer halosDark matter haloA dark matter halo is a hypothetical component of a galaxy, which extends beyond the edge of the visible galaxy and dominates the total mass. Since they consist of dark matter, halos cannot be observed directly, but their existence is inferred through their effects on the motions of stars and gas...
where dark matterDark matterIn astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
is more prevalent.
- Using techniques similar to those in cluster-scale lensing, galaxy-galaxy lensing can provide information about the shape of mass density profiles, though these profiles correspond to galaxy-sized objects instead of larger clusters or groups. Given a high enough number density of background sources, a typical galaxy-galaxy mass density profile can cover a wide range of distances (from ~1 to ~100 effective radii
- Mass-to-light ratios
- Comparing the measured mass to the luminosityLuminosityLuminosity is a measurement of brightness.-In photometry and color imaging:In photometry, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance, which is the density of luminous intensity in a given direction. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre.The luminosity function...
(averaged over the entire galaxy stack) in a specific filterFilter (optics)Optical filters are devices which selectively transmit light of different wavelengths, usually implemented as plane glass or plastic devices in the optical path which are either dyed in the mass or have interference coatings....
, galaxy-galaxy lensing can also provide insight into the mass to light ratioMass to light ratioIn astrophysics and physical cosmology the mass to light ratio, normally designated with the symbol \Upsilon is the quotient between the total mass of a spatial volume and its luminosity...
s of field galaxies. Specifically, the quantity measured through lensing is the total (or virial) mass to light ratio – again due to the insensitivity of lensing to matter type. Assuming that luminous matter can trace dark matter, this quantity is of particular importance, since measuring the ratio of luminous (baryonic) matter to total matter can provide information regarding the overall ratio of baryonic to dark matter in the universe.
- Comparing the measured mass to the luminosity
- Galaxy mass evolution
- Since the speed of lightSpeed of lightThe speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
is finite, an observer on the Earth will see distant galaxies not as they look today, but rather as they appeared at some earlier time. By restricting the lens sample of a galaxy-galaxy lensing study to lie at only one particular redshift, it is possible to understand the mass properties of the field galaxies that existed during this earlier time. Comparing the results of several such redshift-restricted lensing studies (with each study encompassing a different redshift), one can begin to observe changes in the mass features of galaxies over a period of several epochTimeline of the Big BangThis timeline of the Big Bang describes the history of the universe according to the prevailing scientific theory of how the universe came into being, using the cosmological time parameter of comoving coordinates...
s, leading towards a better understanding of the evolution of mass on the smallest cosmological scales.
- Since the speed of light
- Other mass trends
- Lens redshift is not the only quantity of interest that can be varied when studying mass differences between galaxy populations, and often there are several parameters used when segregating objects into galaxy-galaxy lens stacks. Two widely used criteria are galaxy colorColor indexIn astronomy, the color index is a simple numerical expression that determines the color of an object, which in the case of a star gives its temperature...
and morphology, which act as tracers of (among other things) stellar population, galaxy age, and local mass environment. By separating lens galaxies based on these properties, and then further segregating samples based on redshift, it is possible to use galaxy-galaxy lensing to see how several different types of galaxies evolve through time.
- Lens redshift is not the only quantity of interest that can be varied when studying mass differences between galaxy populations, and often there are several parameters used when segregating objects into galaxy-galaxy lens stacks. Two widely used criteria are galaxy color
Cosmic shear
The gravitational lensing by large-scale structure also produces an observable pattern of alignments in background galaxies, but this distortion is only ~0.1%-1% - much more subtle than cluster or galaxy-galaxy lensing. The thin lens approximation usually used in cluster and galaxy lensing does not always work in this regime, because structures can be elongated along the line of sight. Instead, the distortion can be derived by assuming that the deflection angle is always small (see Gravitational Lensing Formalism). As in the thin lens case, the effect can be written as a mapping from the unlensed angular position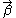 to the lensed position
to the lensed position  . The Jacobian
. The JacobianJacobian
In vector calculus, the Jacobian matrix is the matrix of all first-order partial derivatives of a vector- or scalar-valued function with respect to another vector. Suppose F : Rn → Rm is a function from Euclidean n-space to Euclidean m-space...
of the transform can be written as an integral over the gravitational potential
 along the line of sight
along the line of sight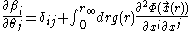
where
 is the comoving distance
is the comoving distanceComoving distance
In standard cosmology, comoving distance and proper distance are two closely related distance measures used by cosmologists to define distances between objects...
,
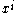 are the transverse distances, and
are the transverse distances, and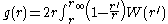
is the lensing kernel, which defines the efficiency of lensing for a distribution of sources
 .
.As in the thin-lens approximation, the Jacobian can be decomposed into shear and convergence terms.
Shear correlation functions
Because large-scale cosmological structures do not have a well-defined location, detecting cosmological gravitational lensing typically involves the computation of shear correlation functions, which measure the mean product of the shear at two points as a function of the distance between those points. Because there are two components of shear, three different correlation functions can be defined: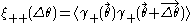

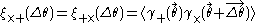
where
 is the component along or perpendicular to
is the component along or perpendicular to 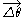 , and
, and 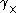 is the component at 45°. These correlation functions are typically computed by averaging over many pairs of galaxies. The last correlation function,
is the component at 45°. These correlation functions are typically computed by averaging over many pairs of galaxies. The last correlation function, 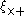 , is not affected at all by lensing, so measuring a value for this function that is inconsistent with zero is often interpreted as a sign of systematic error
, is not affected at all by lensing, so measuring a value for this function that is inconsistent with zero is often interpreted as a sign of systematic errorSystematic error
Systematic errors are biases in measurement which lead to the situation where the mean of many separate measurements differs significantly from the actual value of the measured attribute. All measurements are prone to systematic errors, often of several different types...
.
The functions
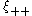 and
and 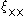 can be related to projections (integrals with certain weight functions) of the dark matter density correlation function, which can be predicted from theory for a cosmological model through its Fourier transform, the matter power spectrum
can be related to projections (integrals with certain weight functions) of the dark matter density correlation function, which can be predicted from theory for a cosmological model through its Fourier transform, the matter power spectrumMatter power spectrum
The matter power spectrum describes the density contrast of the universe as a function of scale. It is the Fourier transform of the matter correlation function. On large scales, gravity competes with cosmic expansion, and structures grow according to linear theory...
.
Because they both depend on a single scalar density field,
 and
and 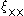 are not independent, and they can be decomposed further into E-mode and B-mode correlation functions. In analogy with electric and magnetic fields, the E-mode field is curl-free and the B-mode field is divergence-free. Because gravitational lensing can only produce an E-mode field, the B-mode provides yet another test for systematic errors.
are not independent, and they can be decomposed further into E-mode and B-mode correlation functions. In analogy with electric and magnetic fields, the E-mode field is curl-free and the B-mode field is divergence-free. Because gravitational lensing can only produce an E-mode field, the B-mode provides yet another test for systematic errors.The E-mode correlation function is also known as the aperture mass variance
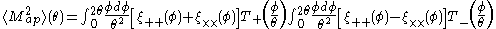
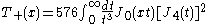
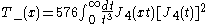
where
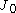 and
and  are Bessel Functions.
are Bessel Functions.An exact decomposition thus requires knowledge of the shear correlation functions at zero separation, but an approximate decomposition is fairly insensitive to these values because the filters
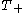 and
and  are small near
are small near  .
.Weak lensing and cosmology
The ability of weak lensing to constrain the matter power spectrumMatter power spectrum
The matter power spectrum describes the density contrast of the universe as a function of scale. It is the Fourier transform of the matter correlation function. On large scales, gravity competes with cosmic expansion, and structures grow according to linear theory...
makes it a potentially powerful probe of cosmological parameters, especially when combined with other observations such as the cosmic microwave background, supernovae
Type Ia supernova
A Type Ia supernova is a sub-category of supernovae, which in turn are a sub-category of cataclysmic variable stars, that results from the violent explosion of a white dwarf star. A white dwarf is the remnant of a star that has completed its normal life cycle and has ceased nuclear fusion...
, and galaxy surveys
Redshift survey
In astronomy, a redshift survey, or galaxy survey, is a survey of a section of the sky to measure the redshift of astronomical objects. Using Hubble's law, the redshift can be used to calculate the distance of an object from Earth. By combining redshift with angular position data, a redshift...
. Detecting the extremely faint cosmic shear signal requires averaging over many background galaxies, so surveys must be both deep and wide, and because these background galaxies are small, the image quality must be very good. Measuring the shear correlations at small scales also requires a high density of background objects (again requiring deep, high quality data), while measurements at large scales push for wider surveys.
While weak lensing of large-scale structure was discussed as early as 1967, due to the challenges mentioned above, it was not detected until more than 30 years later when large CCD
Charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time...
cameras enabled surveys of the necessary size and quality. In 2000, four independent groups published the first detections of cosmic shear, and subsequent observations have started to put constraints on cosmological parameters (particularly the dark matter density
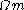 and power spectrum amplitude
and power spectrum amplitude 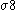
Lambda-CDM model
ΛCDM or Lambda-CDM is an abbreviation for Lambda-Cold Dark Matter, which is also known as the cold dark matter model with dark energy...
) that are competitive with other cosmological probes.
For current and future surveys, one goal is to use the redshifts of the background galaxies (often approximated using photometric redshift
Photometric redshift
A photometric redshift is an estimate for the distance of an astronomical object, such as a galaxy or quasar. The technique uses photometry to determine the redshift, and hence, through Hubble's...
s) to divide the survey into multiple redshift bins. The low-redshift bins will only be lensed by structures very near to us, while the high-redshift bins will be lensed by structures over a wide range of redshift. This technique, dubbed "cosmic tomography
Tomography
Tomography refers to imaging by sections or sectioning, through the use of any kind of penetrating wave. A device used in tomography is called a tomograph, while the image produced is a tomogram. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, geophysics, oceanography, materials science,...
", makes it possible to map out the 3D distribution of mass. Because the third dimension involves not only distance but cosmic time, tomographic weak lensing is sensitive not only to the matter power spectrum today, but also to its evolution over the history of the universe, and the expansion history of the universe during that time. This is a much more valuable cosmological probe, and many proposed experiments to measure the properties of dark energy
Dark energy
In physical cosmology, astronomy and celestial mechanics, dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Dark energy is the most accepted theory to explain recent observations that the universe appears to be expanding...
and dark matter
Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
have focused on weak lensing, such as the Dark Energy Survey
The Dark Energy Survey
The Dark Energy Survey is a survey that aims to probe the dynamics of the expansion of the universe and the growth of large scale structure. The collaboration is composed of research institutes and universities from United States, Brazil, England, Germany and Spain. The survey will use the 4-meter...
, Pan-STARRS
Pan-STARRS
The Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System is a planned array of astronomical cameras and telescopes and computing facility that will survey the sky on a continual basis, including accurate astrometry and photometry of detected objects...
, and LSST.
Weak lensing also has an important effect on the Cosmic Microwave Background and diffuse 21cm line radiation
Hydrogen line
The hydrogen line, 21 centimeter line or HI line refers to the electromagnetic radiation spectral line that is created by a change in the energy state of neutral hydrogen atoms. This electromagnetic radiation is at the precise frequency of 1420.40575177 MHz, which is equivalent to the vacuum...
. Even though there are no distinct resolved sources, perturbations on the origining surface are sheared in a similar way to galaxy weak lensing, resulting in changes to the power spectrum and statistics of the observed signal. Since the source plane for the CMB and high-redshift diffuse 21cm are at higher redshift that resolved galaxies, the lensing effect probes cosmology at higher redshifts than galaxy lensing.

