
Mass to light ratio
Encyclopedia
In astrophysics
and physical cosmology
the mass to light ratio, normally designated with the symbol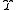 is the quotient between the total mass
is the quotient between the total mass
of a spatial volume (typically on the scales of a galaxy
or a cluster
) and its luminosity
. These ratios are often reported using the value calculated for the Sun
as a baseline ratio which is a constant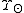 = 5133 kg
= 5133 kg
/W
equal to a solar mass
divided by a solar luminosity. The mass to light ratios of galaxies and clusters are all much greater than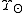 due in part to the fact that most of the matter
due in part to the fact that most of the matter
in these objects does not reside within stars and observations suggest that a large fraction is present in the form of dark matter
.
Luminosities are obtained from photometric
observations, correcting the observed brightness
of the object for the distance dimming
and extinction effects. In general, unless a complete spectrum
of the radiation
emitted by the object is obtained, a model must be extrapolated through either power law
or blackbody fits. The luminosity thus obtained is known as the bolometric luminosity.
Masses are often calculated from the dynamics of the virialized system or from gravitational lens
ing.
Typical mass to light ratios for galaxies range from 2 to 10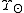 while on the largest scales, the mass to light ratio of the observable universe
while on the largest scales, the mass to light ratio of the observable universe
is approximately 100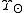 , in concordance with the current best fit cosmological model
, in concordance with the current best fit cosmological model
.
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the physics of the universe, including the physical properties of celestial objects, as well as their interactions and behavior...
and physical cosmology
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
the mass to light ratio, normally designated with the symbol
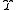 is the quotient between the total mass
is the quotient between the total massMass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
of a spatial volume (typically on the scales of a galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
or a cluster
Galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster is a compact cluster of galaxies. Basic difference between a galaxy group and a galaxy cluster is that there are many more galaxies in a cluster than in a group. Also, galaxies in a cluster are more compact and have higher velocity dispersion. One of the key features of cluster is...
) and its luminosity
Luminosity
Luminosity is a measurement of brightness.-In photometry and color imaging:In photometry, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance, which is the density of luminous intensity in a given direction. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre.The luminosity function...
. These ratios are often reported using the value calculated for the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
as a baseline ratio which is a constant
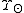 = 5133 kg
= 5133 kgKilogram
The kilogram or kilogramme , also known as the kilo, is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units and is defined as being equal to the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram , which is almost exactly equal to the mass of one liter of water...
/W
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
equal to a solar mass
Solar mass
The solar mass , , is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, used to indicate the masses of other stars and galaxies...
divided by a solar luminosity. The mass to light ratios of galaxies and clusters are all much greater than
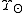 due in part to the fact that most of the matter
due in part to the fact that most of the matterMatter
Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects consist. Typically, matter includes atoms and other particles which have mass. A common way of defining matter is as anything that has mass and occupies volume...
in these objects does not reside within stars and observations suggest that a large fraction is present in the form of dark matter
Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
.
Luminosities are obtained from photometric
Photometry (astronomy)
Photometry is a technique of astronomy concerned with measuring the flux, or intensity of an astronomical object's electromagnetic radiation...
observations, correcting the observed brightness
Brightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target...
of the object for the distance dimming
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are "close enough" to Earth...
and extinction effects. In general, unless a complete spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
of the radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
emitted by the object is obtained, a model must be extrapolated through either power law
Power law
A power law is a special kind of mathematical relationship between two quantities. When the frequency of an event varies as a power of some attribute of that event , the frequency is said to follow a power law. For instance, the number of cities having a certain population size is found to vary...
or blackbody fits. The luminosity thus obtained is known as the bolometric luminosity.
Masses are often calculated from the dynamics of the virialized system or from gravitational lens
Gravitational lens
A gravitational lens refers to a distribution of matter between a distant source and an observer, that is capable of bending the light from the source, as it travels towards the observer...
ing.
Typical mass to light ratios for galaxies range from 2 to 10
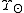 while on the largest scales, the mass to light ratio of the observable universe
while on the largest scales, the mass to light ratio of the observable universeObservable universe
In Big Bang cosmology, the observable universe consists of the galaxies and other matter that we can in principle observe from Earth in the present day, because light from those objects has had time to reach us since the beginning of the cosmological expansion...
is approximately 100
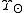 , in concordance with the current best fit cosmological model
, in concordance with the current best fit cosmological modelLambda-CDM model
ΛCDM or Lambda-CDM is an abbreviation for Lambda-Cold Dark Matter, which is also known as the cold dark matter model with dark energy...
.

