
Dark matter halo
Encyclopedia

Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
, halos cannot be observed directly, but their existence is inferred through their effects on the motions of stars and gas in galaxies. Dark matter halos play a key role in current models of galaxy formation and evolution
Galaxy formation and evolution
The study of galaxy formation and evolution is concerned with the processes that formed a heterogeneous universe from a homogeneous beginning, the formation of the first galaxies, the way galaxies change over time, and the processes that have generated the variety of structures observed in nearby...
.
.jpg)
Rotation curves as evidence of a dark matter halo
The presence of dark matter in the halo is demonstrated by its gravitational effect on a spiral galaxy's rotation curve. Without large amounts of massMass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
in the extended halo, the rotational velocity of the galaxy should decrease at large distance from the galactic core. However, observations
Observational astronomy
Observational astronomy is a division of the astronomical science that is concerned with getting data, in contrast with theoretical astrophysics which is mainly concerned with finding out the measurable implications of physical models...
of spiral galaxies, particularly radio observations
Radio astronomy
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The initial detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was made in the 1930s, when Karl Jansky observed radiation coming from the Milky Way. Subsequent observations have identified a number of...
of line emission
Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from a deficiency or excess of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies.- Types of line spectra :...
from neutral atomic hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
(known, in astronomical parlance, as HI), show that the rotation curve of most spiral galaxies remains flat far beyond the visible matter. The absence of any visible matter
Matter
Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects consist. Typically, matter includes atoms and other particles which have mass. A common way of defining matter is as anything that has mass and occupies volume...
to account for these observations implies the presence of unobserved (i.e. dark) matter. Asserting that this dark matter does not exist would mean that the accepted theory of gravitation (General Relativity
General relativity
General relativity or the general theory of relativity is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1916. It is the current description of gravitation in modern physics...
) is incomplete, and while that could be possible, most scientists would require extensive amounts of compelling evidence before seriously considering it.
The Navarro-Frenk-White profile
Navarro-Frenk-White profile
The Navarro–Frenk–White profile or NFW profile is a spatial mass distribution of dark matter fitted to dark matter haloes identified in N-body simulations by Julio Navarro, Carlos Frenk and Simon White...
:
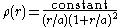
is often used to model the distribution of mass in dark matter halos. Theoretical dark matter halos produced in computer simulations are best described by the Einasto profile
Einasto profile
The Einasto profile is a mathematical function that describes how the density \rho of a spherical stellar system varies with distance r from its center...
:
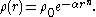
Theories about the nature of dark matter
The nature of dark matter in the galactic halo of spiral galaxies is still undetermined, but there are two popular theories: either the halo is composed of weakly interacting elementary particles known as WIMPs, or it is home to large numbers of small, dark bodies known as MACHOMacho
Macho typically refers to machismo. Other uses include:*Macho , a short-lived disco group in the late 1970s*Pique macho, Bolivian dish*Macho Man , a 1978 disco song performed by the Village People...
s. It seems unlikely that the halo is composed of large quantities of gas and dust, because both ought to be detectable through observations. Searches for gravitational microlensing
Gravitational microlensing
Gravitational microlensing is an astronomical phenomenon due to the gravitational lens effect. It can be used to detect objects ranging from the mass of a planet to the mass of a star, regardless of the light they emit. Typically, astronomers can only detect bright objects that emit lots of light ...
events in the halo of the Milky Way show that the number of MACHOs is likely not sufficient to account for the required mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
.
Milky Way dark matter halo
The dark matter halo is the single largest part of the GalaxyMilky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
as it covers the space between 100,000 light-years to 300,000 light-years from the galactic center
Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the rotational center of the Milky Way galaxy. It is located at a distance of 8.33±0.35 kpc from the Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius where the Milky Way appears brightest...
. It is also the most mysterious part of the Galaxy. It is now believed that about 95% of the Galaxy is composed of dark matter
Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
, a type of matter that does not seem to interact with the rest of the Galaxy's matter and energy in any way except through gravity. The dark matter halo is the location of nearly all of the Galaxy's dark matter, which is more than ten times as much mass as all of the visible star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s, gas, and dust in the rest of the Galaxy. The luminous matter makes up approximately 90,000,000,000 (9 x 1010) solar mass
Solar mass
The solar mass , , is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, used to indicate the masses of other stars and galaxies...
es. The dark matter halo is likely to include around 600,000,000,000 (6 x 1011) to 3,000,000,000,000 (3 x 1012) solar mass
Solar mass
The solar mass , , is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, used to indicate the masses of other stars and galaxies...
es of dark matter. The Milky Way is a large galaxy comprising an estimated 200 billion stars (some estimates range as high as 400 billion) arrayed in the form of a disk, with a central elliptical bulge (some 12,000 light-years in diameter) of closely packed stars lying in the direction of Sagittarius. It is surrounded by a flat disk marked by six spiral arms—four major and two minor—which wind out from the nucleus like a giant pinwheel. Because of these arms, the Milky Way was classified as a spiral galaxy. However, increasing evidence indicates that the Milky Way probably has a bar or barlike structure of new, bright stars in its central region. This would modify its classification to a barred spiral or an intermediate type between barred and “normal” spiral. Our sun is situated in one of the smaller arms, called the Local or Orion Arm, that connect the more substantial next inner arm and the next outer arm. The sun lies roughly two thirds of the way from the center of the disk, which is some 28,000 light-years distant, and in the galactic plane. When we look in the plane of the disk we see the combined light of its stars as the Milky Way. The diameter of the disk is c.100,000 light-years; its average thickness is 10,000 light-years, increasing to 30,000 light-years at the nucleus.
Certain features of the region near the sun suggested that our galaxy resembles the Andromeda Galaxy. In 1951 a group led by William Morgan detected evidence of spiral arms in Orion and Perseus. Another bright arm stretches from Sagittarius to Carina in the southern sky. With the development of radio astronomy, scientists have extended a nearly complete map of the spiral structure of the galaxy by tracing regions of hydrogen that dominate the spiral arms.
Surrounding the galaxy is a large spherical halo of globular star clusters that extends to a diameter of about 130,000 light-years; this is called the stellar halo. The galaxy also has a vast outer spherical region called the corona, or dark halo, which is as much as 600,000 light years in diameter and, in addition to dark matter which accounts for most of the Milky Way's mass, includes some distant globular clusters, the two nearby galaxies called the Magellanic clouds, and four smaller galaxies.
See also
- Galaxy formation and evolutionGalaxy formation and evolutionThe study of galaxy formation and evolution is concerned with the processes that formed a heterogeneous universe from a homogeneous beginning, the formation of the first galaxies, the way galaxies change over time, and the processes that have generated the variety of structures observed in nearby...
- Galactic coordinate systemGalactic coordinate systemThe galactic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system which is centered on the Sun and is aligned with the apparent center of the Milky Way galaxy. The "equator" is aligned to the galactic plane...
- Disc (galaxy)Disc (galaxy)A disc is a component of disc galaxies, such as spiral galaxies, or lenticular galaxies.The galactic disc is the plane in which the spirals, bars and discs of disc galaxies exist. Galaxy discs tend to have more gas and dust, and younger stars than galactic bulges, or galactic haloes.The galactic...
- Bulge (astronomy)Bulge (astronomy)In astronomy, a bulge is a tightly packed group of stars within a larger formation. The term almost exclusively refers to the central group of stars found in most spiral galaxies...
- Galactic haloGalactic haloThe term galactic halo is used to denote an extended, roughly spherical component of a galaxy, which extends beyond the main, visible component. It can refer to any of several distinct components which share these properties:* the galactic spheroid...
- Spiral arm
- Dark matterDark matterIn astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
- Dark galaxyDark galaxyA dark galaxy is a hypothetical galaxy composed of dark matter. Dark galaxies receive their name because they have no detectable stars and are theoretically invisible...
External links
- Rare Blob Unveiled: Evidence For Hydrogen Gas Falling Onto A Dark Matter Clump? European Southern ObservatoryEuropean Southern ObservatoryThe European Southern Observatory is an intergovernmental research organisation for astronomy, supported by fifteen countries...
(ScienceDaily) July 3, 2006 - Dark Matter Search Experiment , PICASSO Experiment

