
Via Aurelia
Encyclopedia
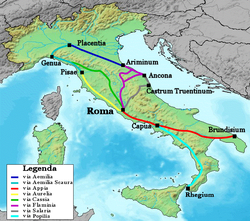
Roman road
The Roman roads were a vital part of the development of the Roman state, from about 500 BC through the expansion during the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. Roman roads enabled the Romans to move armies and trade goods and to communicate. The Roman road system spanned more than 400,000 km...
in Italy constructed around the year 241 BC
241 BC
Year 241 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Atticus and Cerco...
. The project was undertaken by C. Aurelius Cotta, who at that time was censor. Cotta had a history of building roads for Rome, as he had overseen the construction of a military road in Sicily (as consul in 252 BC
252 BC
Year 252 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cotta and Geminus...
, during the First Punic War
First Punic War
The First Punic War was the first of three wars fought between Ancient Carthage and the Roman Republic. For 23 years, the two powers struggled for supremacy in the western Mediterranean Sea, primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters but also to a lesser extent in...
) connecting Agrigentum (modern Agrigento
Agrigento
Agrigento , is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy, and capital of the province of Agrigento. It is renowned as the site of the ancient Greek city of Akragas , one of the leading cities of Magna Graecia during the golden...
) and Panormus (modern Palermo
Palermo
Palermo is a city in Southern Italy, the capital of both the autonomous region of Sicily and the Province of Palermo. The city is noted for its history, culture, architecture and gastronomy, playing an important role throughout much of its existence; it is over 2,700 years old...
).
Background
In the middle Republic, a series of roads were built throughout Italy to serve the needs of Roman expansion, including swift army movements and reasonably quick communication with Roman colonies spread throughout Italy. There was also the unintended (but beneficial) consequence of an increase in trade among Italian cities and with Rome. The roads were standardized to 15 feet (4.6 m) wide allowing two chariots to pass, and distance was marked with milestoneMilestone
A milestone is one of a series of numbered markers placed along a road or boundary at intervals of one mile or occasionally, parts of a mile. They are typically located at the side of the road or in a median. They are alternatively known as mile markers, mileposts or mile posts...
s. The Via Aurelia was constructed as a part of this road construction campaign, which began in 312 BC
312 BC
Year 312 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Corvus and Mus...
with the building of the Via Appia. Other roads included in this construction period were the Viae Amerina (ca. 241 BC), Flaminina, Clodia, Aemilia
Via Aemilia
The Via Aemilia was a trunk Roman road in the north Italian plain, running from Ariminum , on the Adriatic coast, to Placentia on the river Padus . It was completed in 187 BC...
, Cassia, Valeria (ca. 307 BC), and Caecilia (ca. 283 BC).
Route
The Via Aurelia crossed the Tiber River by way of the bridge Pons Aemilius, then exited Rome from its west side. After the Emperor AurelianAurelian
Aurelian , was Roman Emperor from 270 to 275. During his reign, he defeated the Alamanni after a devastating war. He also defeated the Goths, Vandals, Juthungi, Sarmatians, and Carpi. Aurelian restored the Empire's eastern provinces after his conquest of the Palmyrene Empire in 273. The following...
built a wall around Rome (ca. 270 -273 AD), the Via Aurelia exited from the Porta Aurelia (gates). The road then ran about 25 miles (40 km) to Alsium on the Tyrrhenian coast, north along the coast to Vada Volaterrana, Cosa
Cosa
Cosa was a Latin colonia founded under Roman influence in southwestern Tuscany in 273 BC, perhaps on land confiscated from the Etruscans...
and Pisae (modern Pisa
Pisa
Pisa is a city in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the right bank of the mouth of the River Arno on the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa...
). There the original length of the Via Aurelia terminated. This was an especially important route during the early and middle Republic because it linked Rome, Cosa and Pisae. Cosa was an important colony and military outpost in Etruria
Etruria
Etruria—usually referred to in Greek and Latin source texts as Tyrrhenia—was a region of Central Italy, an area that covered part of what now are Tuscany, Latium, Emilia-Romagna, and Umbria. A particularly noteworthy work dealing with Etruscan locations is D. H...
, and Pisae was the only port between Genua and Rome. Consequently, it was an important naval base for the Romans in their wars against the Ligurians
Ligures
The Ligures were an ancient people who gave their name to Liguria, a region of north-western Italy.-Classical sources:...
, Gauls
Gauls
The Gauls were a Celtic people living in Gaul, the region roughly corresponding to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland and Northern Italy, from the Iron Age through the Roman period. They mostly spoke the Continental Celtic language called Gaulish....
and Carthaginians.
The Via Aurelia was later extended by roughly 200 miles (321.9 km) in 109 BC
109 BC
Year 109 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Numidicus and Silanus...
by the Via Aemilia Scaura, constructed by M. Aemilius Scaurus. This road lead to Dertona (modern Tortona
Tortona
Tortona is a comune of Piemonte, in the Province of Alessandria, Italy. Tortona is sited on the right bank of the Scrivia between the plain of Marengo and the foothills of the Ligurian Apennines.-History:...
), Placentia, Cremona
Cremona
Cremona is a city and comune in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po River in the middle of the Pianura Padana . It is the capital of the province of Cremona and the seat of the local City and Province governments...
, Aquilea and Genua, from which travellers could proceed to Gallia Narbonensis (southern France) by way of the Via Postumia
Via Postumia
The Via Postumia was an ancient Roman road of northern Italy constructed in 148 BC by the consul Spurius Postumius Albinus Magnus.It ran from the coast at Genua through the mountains to Dertona, Placentia and Cremona, just east of the point where it crossed the Po River...
. This followed some rebuilding of the road by the same person during his consulship in 119 BC. By the time of the high Empire, travellers could go from Rome by way of the Via Aurelia across the Alps via the Julian-Augustan Way to either northern France or Gades (modern Cadiz
Cádiz
Cadiz is a city and port in southwestern Spain. It is the capital of the homonymous province, one of eight which make up the autonomous community of Andalusia....
, Spain).
The modern Strada Statale 1 occupies the same route, and is still referred to colloquially as La Via Aurelia.
Roman bridges
- For an overview of the location of Roman bridges, see List of Roman bridges.
There are the remains of several Roman bridge
Roman bridge
Roman bridges, built by ancient Romans, were the first large and lasting bridges built. Roman bridges were built with stone and had the arch as its basic structure....
s along the road, including the Cloaca di Porta San Clementino, Ponte del Diavolo, Primo Ponte and the Secondo Ponte (the last three in Sta Marinella).
External links
- Samuel Ball Platner, Via Aurelia, from A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome (London: Oxford University Press, 1929).
- Joshua Hammer, Via Aurelia: The Roman Empire's Lost Highway, Smithsonian magazine, June 2009.
- Omnes Viae: Via Aurelia on the Tabula Peutingeriana

