
Valentianism
Encyclopedia
Valentinianism is a Gnostic movement that was founded by Valentinus
in the second century AD
. Valentinianism was one of the major Gnostic movements. Its influence was extremely widespread, not just within Rome, but also from Egypt through Asia Minor and Syria in the east, and Northwest Africa.
Later in the movement’s history it broke into two schools, an Eastern school and a Western school. Disciples of Valentinus continued to be active into the 4th century AD, after the Roman Empire
was declared to be Christian
.
Valentinus and the Gnostic movement that bore his name were considered threats to Christianity by church leaders and Christian scholars, not only because of their influence, but also because of their doctrine, practices and beliefs. Gnostics were condemned as heretics, and prominent Church fathers
such as Irenaeus of Lyons and Hippolytus of Rome wrote against Gnosticism. Most evidence for the Valentinian theory comes from its critics and detractors, most notably Irenaeus, since he was especially concerned with refuting Valentinianism.
was born in approximately 100 AD and died in Alexandria
in approximately AD 180. According to Epiphanius of Salamis
, a Christian scholar, he was born in Egypt
and schooled in Alexandria. Clement of Alexandria
, another Christian scholar and teacher, reports that Valentinus was taught by Theudas
, a disciple of the apostle Paul
. It is reputed that he was an extremely eloquent man who possessed a great deal of charisma and had an innate ability to attract people. He went to Rome
some time between AD 136 and 140, in the time of Pope Hyginus
, and had risen to the peak of his teaching career between AD 150 and 155, during the time of Pius
.
Valentinus is said to have been a very successful teacher, and for some time in the mid-2nd century he was even a prominent and well-respected member of the Catholic community in Rome. At one point during his career he had even hoped to attain the office of bishop, and apparently it was after he was passed over for the position that he broke from the Catholic Church. Valentinus was said to have been a prolific writer; however, the only surviving remains of his work come from quotes that have been transmitted by Clement of Alexandria, Hippolytus and Marcellus of Ancyra
. Most scholars also believe that Valentinus wrote the Gospel of Truth
, one of the Nag Hammadi text
s.
Notable Valentinians included Heracleon
, Ptolemy
, Florinus, Axionicus and Theodotus
.
The theology that Irenaeus attributed to Valentinus is extremely complicated and difficult to follow. There is some skepticism among scholars that the system actually originated with him, and many believe that the system Irenaeus was reacting against was that of the later Valentinians, and not Valentinus himself.
, also known as the ‘fullness’. At the centre of the Pleroma was the primal Father or Bythos, the beginning of all things who, after ages of silence and contemplation, projected thirty Aeon
s, heavenly archetypes representing fifteen syzygies
or sexually complementary pairs. Among them was Sophia. Sophia’s weakness, curiosity and passion led to her fall from the Pleroma and the creation of the world and man, both of which are flawed. Valentinians identified the God
of the Old Testament
as the Demiurge
, the imperfect creator of the material world. Man, the highest being in this material world, participates in both the spiritual and the material nature. The work of redemption consists in freeing the former from the latter. One needed to recognize the Father, the depth of all being, as the true source of divine power in order to achieve gnosis (knowledge). The Valentinians believed that the attainment of this knowledge by the human individual had positive consequences within the universal order and contributed to restoring that order, and that gnosis, not faith, was the key to salvation. Clement wrote that the Valentinians regarded Catholic Christians “as simple people to whom they attributed faith, while they think that gnosis is in themselves. Through the excellent seed that is to be found in them, they are by nature redeemed, and their gnosis is as far removed from faith as the spiritual from the physical”.
 Epiphanius
Epiphanius
alleges that the Valentinians “set forth their thirty aeons in mythologic fashion, thinking that they conformed to the years of Jesus”. Of the eight celestial beings of the Ogdoad, four are peculiar to the Valentinian system. The third pair of Aeons, Logos
and Zoe, occur only here, and the place of this pair of Aeons is not firmly established, and occur sometimes before and sometimes after the fourth pair of Aeons, the Anthropos and the Ekklesia. We cannot be far wrong in suspecting that Valentinus was influenced by the prologue of the fourth Gospel (we also find the probably Johannine names Monogenes and Parakletos
in the series of Aeons).
Sophia is the youngest of the Aeons. Observing the multitude of Aeons and the power of begetting them, she hurries back into the depth of the Father, and seeks to emulate him by producing offspring without conjugal intercourse, but only projects an abortion, a formless substance. Upon this she is cast out of Pleroma and into the primal sub-stratum of matter. In the Valentinian systems, the fall of Sophia appears in double guise. The higher Sophia still remains within the upper world after creating a disturbance, and after her expiation and repentance; but her premature offspring, Sophia Achamoth, is removed from the Pleroma, and becomes the heroine of the rest of the drama. This fallen Sophia becomes a world creative power.
Sophia Achamoth, or “Lower Wisdom”, the daughter of “Higher Wisdom”, becomes the mother of the Demiurge, identified with the God of the Old Testament.
The Gnostics are children of Sophia; from her the heavenly seed, the divine spark, descended into this lower world, subject to the Heimarmene
and in the power of hostile spirits and powers; and all their sacraments and mysteries, their formulae and symbols, must be in order to find the way upwards, back to the highest heaven. This idea that the Gnostics know themselves to be in a hostile and evil world reacted in the same direction upon the conception of Sophia. She became likewise a fallen Aeon, who has sunk down into the material world and seeks to free herself from it, receiving her liberation at the hands of a heavenly Redeemer, exactly like the Gnostics.
The goddess who sinks down into the material may readily be identified with Ruach (רוח), the Spirit
of God, who broods over Chaos, or even with the later Chokhmah
, who was generally conceived of as a world-creating agent.
This system was very closely followed by Valentinus, who may have come to know these doctrines in Egypt
. Irenaeus characterizes the Gnostics as the pneumatici who have a perfect knowledge of God, and have been initiated into the mysteries of Achamoth.
(i.e. the Primal Man) – of whom the myth originally relates that he has sunk into matter and then raised himself up from it again – which appears in its simple form in individual Gnostic systems, e.g. in Poimandres (in the Corpus Hermeticum) and in Manichaeism
.
According to Valentinus, the Anthropos no longer appears as the world-creative power sinking down into the material world, but as a celestial Aeon of the upper world (or even as the supreme god), who stands in a clearly defined relationship to the fallen Aeon. Adam was created in the name of Anthropos, and overawes the demons by the fear of the pre-existent man. This Anthropos is a cosmogonic element, pure mind as distinct from matter, mind conceived hypostatically as emanating from God and not yet darkened by contact with matter. This mind is considered as the reason of humanity, or humanity itself, as a personified idea, a category without corporeality, the human reason conceived as the World-Soul
. It is possible that the role of the Anthropos is here transferred to Sophia Achamoth.
It is also clear why the Ekklesia appears together with the Anthropos. With this is associated the community of the faithful and the redeemed, who are to share the same fate with him. Perfect gnosis (and thus the whole body of Gnostics) is connected with the Anthropos.
In the fully developed Ptolemaean system we find a kindred conception, but with a slight difference. Here Christ and Sophia appear as brother and sister, with Christ representing the higher and Sophia the lower element. When this world has been born from Sophia in consequence of her sin, Nous and Aletheia, two Aeons, by command of the Father, produce two new Aeons, Christ and the Holy Ghost; these restore order in the Pleroma, and in consequence all Aeons combine their best and most wonderful qualities to produce a new Aeon (Jesus, Logos, Soter, or Christ), the “First Fruits
” whom they offer to the Father. And this celestial redeemer-Aeon now enters into a marriage with the fallen Aeon; they are the “bride and bridegroom”. It is boldly stated in the exposition in Hippolytus’ Philosophumena
that they produce between them 70 celestial angels.
This myth can be connected with the historic Jesus of Nazareth by further relating that Christ, having been united to the Sophia, descends into the earthly Jesus, the son of Mary, at his baptism, and becomes the Saviour of men.
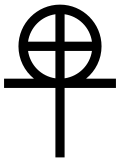 A figure entirely peculiar to Valentinian Gnosticism is that of Horos (the Limiter). The name is perhaps an echo of the Egyptian Horus
A figure entirely peculiar to Valentinian Gnosticism is that of Horos (the Limiter). The name is perhaps an echo of the Egyptian Horus
.
The task of Horos is to separate the fallen Aeons from the upper world of Aeons. At the same time he becomes a kind of world-creative power, who in this capacity helps to construct an ordered world out of Sophia and her passions. He is also called Stauros (cross
), and we frequently meet with references to the figure of Stauros. Speculations about the Stauros are older than Christianity, and a Platonic
conception may have been at work here. Plato
had already stated
that the World-Soul revealed itself in the form of the letter Chi (X)
; by which he meant that figure described in the heavens by the intersecting orbits of the sun
and the planetary ecliptic
. Since through this double orbit all the movements of the heavenly powers are determined, so all “becoming” and all life depend on it, and thus we can understand the statement that the World-Soul appears in the form of an X, or a cross.
The cross can also stand for the wondrous Aeon on whom depends the ordering and life of the world, and thus Horos-Stauros appears here as the first redeemer of Sophia from her passions, and as the orderer of the creation of the world which now begins. Naturally, then, the figure of Horos-Stauros was often assimilated to that of the Christian Redeemer. We possibly find echoes of this in the Gospel of Peter
, where the Cross
itself is depicted as speaking and even floating out of the tomb.
According to the older conception, he was an evil and malicious offspring of his mother, who has already been deprived of any particle of light. In the Valentinian systems, the Demiurge was the offspring of a union of Sophia Achamoth with matter, and appears as the fruit of Sophia’s repentance and conversion. But as Achamoth herself was only the daughter of Sophia, the last of the thirty Aeons, the Demiurge was distant by many emanations from the Supreme God. The Demiurge in creating this world out of Chaos was unconsciously influenced for good by Christ; and the universe, to the surprise even of its Maker, became almost perfect. The Demiurge regretted even its slight imperfection, and as he thought himself the Supreme God, he attempted to remedy this by sending a Messiah. To this Messiah, however, was actually united Christ the Saviour, who redeemed men.
It is significant that Valentinus himself is credited with having written a treatise upon the threefold nature of man, who is represented as at once spiritual, psychical and material. In accordance with this there also arise three classes of men, the pneumatici, the psychici and the hylici. This doctrine dates at least as far back as Plato’s Republic.
We also find ideas that emphasize the distinction between the soma psychikon and the soma pneumatikon:
). This setting free of the light sparks is the process of salvation; when all light shall have left Hyle, it will be burnt up and destroyed.
In Valentinianism the process is extraordinarily elaborate, and we find here developed particularly clearly the myth of the heavenly marriage. This myth, as we shall see more fully below, and as may be mentioned here, is of great significance for the practical piety of the Valentinian Gnostics. It is the chief idea of their pious practices mystically to repeat the experience of this celestial union of the Saviour with Sophia. In this respect, consequently, the myth underwent yet wider development. Just as the Saviour is the bridegroom of Sophia, so the heavenly angels, who sometimes appear as the sons of the Saviour and Sophia, sometimes as the escort of the Saviour, are the males betrothed to the souls of the Gnostics, which are looked upon as feminine. Thus every Gnostic had her unfallen counterpart standing in the presence of God, and the object of a pious life was to bring about and experience this inner union with the celestial abstract personage. This leads us straight to the sacramental ideas of this branch of Gnosticism (see below). And it also explains the expression used of the Gnostics in Irenaeus, that they always meditate upon the secret of the heavenly union (the Syzygia).
“The final consummation of all things will take place when all that is spiritual has been formed and perfected by gnosis.”
But this contemplation of God, as Valentinus declares, closely and deliberately following the doctrines of the Church and with him the compiler of the Gospel of John, is accomplished through the revelation of the Son. This mystic also discusses a vision which is preserved in the Philosophumena of Hippolytus:
With celestial enthusiasm Valentinus here surveys and depicts the heavenly world of Aeons, and its connection with the lower world. Exalted joy of battle and a valiant courage breathe forth in the sermon in which Valentinus addresses the faithful:
given in Irenaeus i. 13 and 20, and in the last section of Clement of Alexandria’s Excerpta ex Theodoto.
In almost all the sacramental prayers of the Gnostics handed down to us by Irenaeus, the Mother is the object of the invocation. There are moreover various figures in the fully developed system of the Valentinians who are in the Gnostic’s mind when he calls upon the Mother; sometimes it is the fallen Achamoth, sometimes the higher Sophia abiding in the celestial world, sometimes Aletheia, the consort of the supreme heavenly father, but it is always the same idea, the Mother, on whom the faith of the Gnostics is fixed. Thus a baptismal confession of faith of the Gnostics runs:
, a probable Valentinian text, reads:
As Sophia was united with the Saviour, her bridegroom, so the faithful would experience a union with their angel in the Pleroma (cf. the “Higher Self
” or “Holy Guardian Angel
”). The ritual of this sacrament is briefly indicated: “A few of them prepare a bridal chamber and in it go through a form of consecration, employing certain fixed formulae, which are repeated over the person to be initiated, and stating that a spiritual marriage is to be performed after the pattern of the higher Syzygia.” Through a fortunate chance, a liturgical formula which was used at this sacrament appears to be preserved, though in a garbled form and in an entirely different connection, the author seeming to have been uncertain as to its original meaning. It runs:
, using the same form in all essentials as that of the Christian Church. The name given to baptism, at least among certain bodies, was apolytrosis (liberation); the baptismal formulae have been mentioned above.
The Gnostics are baptized in the mysterious name which also descended upon Jesus at his baptism
. The angels of the Gnostics have also had to be baptized in this name, in order to bring about redemption for themselves and the souls belonging to them.
In the baptismal formulae the sacred name of the Redeemer is mentioned over and over again. In one of the formulae occur the words: “I would enjoy thy name, Saviour of Truth.” The concluding formula of the baptismal ceremony is: “Peace over all upon whom the Name rests.” This name pronounced at baptism over the faithful has above all the significance that the name will protect the soul in its ascent through the heavens, conduct it safely through all hostile powers to the lower heavens, and procure it access to Horos, who frightens back the lower souls by his magic
word. And for this life also baptism, in consequence of the pronouncing of the protecting name over the baptized person, accomplishes his liberation from the lower daemonic powers. Before baptism the Heimarmene is supreme, but after baptism the soul is free from her.
Another formula is appended, in which there is a distinction in the invocation between the higher and lower Sophia. Another prayer of the same style is to be found in Irenaeus i. 13, and it is expressly stated that after prayer is pronounced the Mother throws the Homeric helmet
(cf. the Tarnhelm
) over the faithful soul, and so makes him invisible to the mights and powers which surround and attack him.
Many Valentinian traditions and practices also clashed with those of the Church. They often met at unauthorized gatherings and rejected ecclesiastical authority, based on their belief that they were all equal. Members of the movement took turns administering sacraments, as well as preaching. Among the Valentinians, women were considered to be equal, or at least nearly equal to men. There were female prophets, teachers, healers, evangelists and even priests, which was very different from the Church’s view of women at the time. Valentinians held normal jobs, got married and raised children just like Christians; however they regarded these pursuits as being less important than gnosis, which was to be achieved individually. The beliefs of the Valentinians were much more oriented towards the individual than towards the group, and salvation
was not seen as being universal, as it was in the Church.
The main disagreements between the Valentinians and the Church, then, were in the notions that God and the creator were two separate entities, the idea that the creator was flawed and formed man and Earth out of ignorance and confusion, and the separation of Christ’s human form and divine form. Church authorities believed that Valentinian theology was “a wickedly casuistic way of subverting their authority and thereby threatening the ecclesiastical order with anarchy.” The practices and rituals of the Valentinians were also different from those of the Christian Church, however the Valentinians considered themselves to be Christians and not pagans or heretics. By referring to themselves as Christians they worsened their relationship with the Church, who viewed them not only as heretics, but as rivals.
Although the Valentinians publicly professed their faith in one God, “in their own private meetings they insisted on discriminating between the popular image of God – as master, king, lord, creator, and judge – and what that image represented: God understood as the ultimate source of all being.” Aside from the Church fathers, however, “the majority of Christians did not recognize the followers of Valentinus as heretics. Most could not tell the difference between Valentinian and orthodox teaching.” This was partially because Valentinus used many books that now belong to the Old and New Testaments as a basis for interpretation in his own writing. He based his work on proto-orthodox Christian canon instead of on Gnostic scripture, and his style was similar to that of early Christian works. In this way, Valentinus tried to bridge the gap between Gnostic religion and early Catholicism. By attempting to bridge this gap, however, Valentinus and his followers became the proverbial wolves in sheep’s clothing. “The apparent similarity with orthodox teaching only made this heresy more dangerous – like poison disguised as milk.” Valentinian Gnosticism was “the most influential and sophisticated form of Gnostic teaching, and by far the most threatening to the church.”
Early Christianity has been described as “a complex network of individual parties, groups, sects, or denominations.” This inconsistency made the threat of Gnostic sects such as Valentinianism even more threatening to the Church.
Valentinus (Gnostic)
Valentinus was the best known and for a time most successful early Christian gnostic theologian. He founded his school in Rome...
in the second century AD
Christianity in the 2nd century
The 2nd century of Christianity was largely the time of the Apostolic Fathers who were the students of the apostles of Jesus, though there is some overlap as John the Apostle may have survived into the 2nd century and the early Apostolic Father Clement of Rome is said to have died at the end of the...
. Valentinianism was one of the major Gnostic movements. Its influence was extremely widespread, not just within Rome, but also from Egypt through Asia Minor and Syria in the east, and Northwest Africa.
Later in the movement’s history it broke into two schools, an Eastern school and a Western school. Disciples of Valentinus continued to be active into the 4th century AD, after the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
was declared to be Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
.
Valentinus and the Gnostic movement that bore his name were considered threats to Christianity by church leaders and Christian scholars, not only because of their influence, but also because of their doctrine, practices and beliefs. Gnostics were condemned as heretics, and prominent Church fathers
Church Fathers
The Church Fathers, Early Church Fathers, Christian Fathers, or Fathers of the Church were early and influential theologians, eminent Christian teachers and great bishops. Their scholarly works were used as a precedent for centuries to come...
such as Irenaeus of Lyons and Hippolytus of Rome wrote against Gnosticism. Most evidence for the Valentinian theory comes from its critics and detractors, most notably Irenaeus, since he was especially concerned with refuting Valentinianism.
History
ValentinusValentinus (Gnostic)
Valentinus was the best known and for a time most successful early Christian gnostic theologian. He founded his school in Rome...
was born in approximately 100 AD and died in Alexandria
Alexandria
Alexandria is the second-largest city of Egypt, with a population of 4.1 million, extending about along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the north central part of the country; it is also the largest city lying directly on the Mediterranean coast. It is Egypt's largest seaport, serving...
in approximately AD 180. According to Epiphanius of Salamis
Epiphanius of Salamis
Epiphanius of Salamis was bishop of Salamis at the end of the 4th century. He is considered a saint and a Church Father by both the Eastern Orthodox and Catholic Churches. He gained a reputation as a strong defender of orthodoxy...
, a Christian scholar, he was born in Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
and schooled in Alexandria. Clement of Alexandria
Clement of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens , known as Clement of Alexandria , was a Christian theologian and the head of the noted Catechetical School of Alexandria. Clement is best remembered as the teacher of Origen...
, another Christian scholar and teacher, reports that Valentinus was taught by Theudas
Theudas (teacher of Valentinius)
Theudas was allegedly the name of a Christian Gnostic thinker, who was a follower of Paul of Tarsus. He went on to teach the Gnostic Valentinus. The only evidence of this connection is the testimony of Valentinius' followers....
, a disciple of the apostle Paul
Paul of Tarsus
Paul the Apostle , also known as Saul of Tarsus, is described in the Christian New Testament as one of the most influential early Christian missionaries, with the writings ascribed to him by the church forming a considerable portion of the New Testament...
. It is reputed that he was an extremely eloquent man who possessed a great deal of charisma and had an innate ability to attract people. He went to Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
some time between AD 136 and 140, in the time of Pope Hyginus
Pope Hyginus
Pope Saint Hyginus was bishop of Rome from about 136 or 138 to about 140 or 142. Tradition holds that during his papacy he determined the various prerogatives of the clergy and defined the grades of the ecclesiastical hierarchy...
, and had risen to the peak of his teaching career between AD 150 and 155, during the time of Pius
Pope Pius I
Pope Saint Pius I was Bishop of Rome, according to the Annuario Pontificio, from 142 or 146 to 157 or 161, respectively. Others suggest that his pontificate was perhaps from 140 to 154.-Early life:...
.
Valentinus is said to have been a very successful teacher, and for some time in the mid-2nd century he was even a prominent and well-respected member of the Catholic community in Rome. At one point during his career he had even hoped to attain the office of bishop, and apparently it was after he was passed over for the position that he broke from the Catholic Church. Valentinus was said to have been a prolific writer; however, the only surviving remains of his work come from quotes that have been transmitted by Clement of Alexandria, Hippolytus and Marcellus of Ancyra
Marcellus of Ancyra
Marcellus of Ancyra was one of the bishops present at the Councils of Ancyra and of Nicaea. He was a strong opponent of Arianism, but was accused of adopting the opposite extreme of modified Sabellianism...
. Most scholars also believe that Valentinus wrote the Gospel of Truth
Gospel of Truth
The Gospel of Truth is one of the Gnostic texts from the New Testament apocrypha found in the Nag Hammadi codices . It exists in two Coptic translations, a Subachmimic rendition surviving almost in full in the first codex and a Sahidic in fragments in the twelfth.-History:The Gospel of Truth was...
, one of the Nag Hammadi text
Nag Hammadi library
The Nag Hammadi library is a collection of early Christian Gnostic texts discovered near the Upper Egyptian town of Nag Hammadi in 1945. That year, twelve leather-bound papyrus codices buried in a sealed jar were found by a local peasant named Mohammed Ali Samman...
s.
Notable Valentinians included Heracleon
Heracleon
Heracleon was a Gnostic who flourished about AD 175, probably in the south of Italy. He is described by Clement of Alexandria as the most esteemed of the school of Valentinus; and, according to Origen Heracleon was a Gnostic who flourished about AD 175, probably in the south of Italy. He is...
, Ptolemy
Ptolemy (gnostic)
Ptolemy the Gnostic, or Ptolemaeus Gnosticus was a disciple of the Gnostic teacher Valentinius, and is known to us for an epistle he wrote to a wealthy woman named Flora, herself not a gnostic....
, Florinus, Axionicus and Theodotus
Theodotus of Byzantium
Theodotus of Byzantium was an early Christian writer from Byzantium, one of several named Theodotus whose writings were condemned as heresy in the early church.Theodotus claimed that Jesus was born of the Virgin Mary and the Holy Spirit as a mortal man, and though later "adopted" by...
.
The Valentinian System
The theology that Irenaeus attributed to Valentinus is extremely complicated and difficult to follow. There is some skepticism among scholars that the system actually originated with him, and many believe that the system Irenaeus was reacting against was that of the later Valentinians, and not Valentinus himself.
Synopsis
According to Irenaeus, the Valentinians believed that at the beginning there was a PleromaPleroma
Pleroma generally refers to the totality of divine powers. The word means fullness from comparable to πλήρης which means "full", and is used in Christian theological contexts: both in Gnosticism generally, and by Paul of Tarsus in Colossians Colossians 2:9 KJV .Gnosticism holds that the...
, also known as the ‘fullness’. At the centre of the Pleroma was the primal Father or Bythos, the beginning of all things who, after ages of silence and contemplation, projected thirty Aeon
Aeon
The word aeon, also spelled eon or æon , originally means "life", and/or "being", though it then tended to mean "age", "forever" or "for eternity". It is a Latin transliteration from the koine Greek word , from the archaic . In Homer it typically refers to life or lifespan...
s, heavenly archetypes representing fifteen syzygies
Aeon (Gnosticism)
In many Gnostic systems, the various emanations of God, who is also known by such names as the One, the Monad, Aion teleos , Bythos , Proarkhe , the Arkhe , are called Aeons...
or sexually complementary pairs. Among them was Sophia. Sophia’s weakness, curiosity and passion led to her fall from the Pleroma and the creation of the world and man, both of which are flawed. Valentinians identified the God
God
God is the English name given to a singular being in theistic and deistic religions who is either the sole deity in monotheism, or a single deity in polytheism....
of the Old Testament
Old Testament
The Old Testament, of which Christians hold different views, is a Christian term for the religious writings of ancient Israel held sacred and inspired by Christians which overlaps with the 24-book canon of the Masoretic Text of Judaism...
as the Demiurge
Demiurge
The demiurge is a concept from the Platonic, Neopythagorean, Middle Platonic, and Neoplatonic schools of philosophy for an artisan-like figure responsible for the fashioning and maintenance of the physical universe. The term was subsequently adopted by the Gnostics...
, the imperfect creator of the material world. Man, the highest being in this material world, participates in both the spiritual and the material nature. The work of redemption consists in freeing the former from the latter. One needed to recognize the Father, the depth of all being, as the true source of divine power in order to achieve gnosis (knowledge). The Valentinians believed that the attainment of this knowledge by the human individual had positive consequences within the universal order and contributed to restoring that order, and that gnosis, not faith, was the key to salvation. Clement wrote that the Valentinians regarded Catholic Christians “as simple people to whom they attributed faith, while they think that gnosis is in themselves. Through the excellent seed that is to be found in them, they are by nature redeemed, and their gnosis is as far removed from faith as the spiritual from the physical”.
Aeons
The superstructure of the celestial system, the celestial world of Aeons, is here developed in the most complicated way. These Aeons belong to the purely ideal, noumenal, intelligible, or supersensible world; they are immaterial, they are hypostatic ideas. Together with the source from which they emanate they form the Pleroma. The transition from the immaterial to the material, from the noumenal to the sensible, is brought about by a flaw, or a passion, or a sin, in the female Aeon Sophia.
Epiphanius of Salamis
Epiphanius of Salamis was bishop of Salamis at the end of the 4th century. He is considered a saint and a Church Father by both the Eastern Orthodox and Catholic Churches. He gained a reputation as a strong defender of orthodoxy...
alleges that the Valentinians “set forth their thirty aeons in mythologic fashion, thinking that they conformed to the years of Jesus”. Of the eight celestial beings of the Ogdoad, four are peculiar to the Valentinian system. The third pair of Aeons, Logos
Logos
' is an important term in philosophy, psychology, rhetoric and religion. Originally a word meaning "a ground", "a plea", "an opinion", "an expectation", "word," "speech," "account," "reason," it became a technical term in philosophy, beginning with Heraclitus ' is an important term in...
and Zoe, occur only here, and the place of this pair of Aeons is not firmly established, and occur sometimes before and sometimes after the fourth pair of Aeons, the Anthropos and the Ekklesia. We cannot be far wrong in suspecting that Valentinus was influenced by the prologue of the fourth Gospel (we also find the probably Johannine names Monogenes and Parakletos
Paraclete
Paraclete means advocate or helper. In Christianity, the term most commonly refers to the Holy Spirit.-Etymology:...
in the series of Aeons).
Sophia
In Valentinianism, Sophia always stands absolutely at the center of the system, and in some sense she seems to represent the supreme female principle.Sophia is the youngest of the Aeons. Observing the multitude of Aeons and the power of begetting them, she hurries back into the depth of the Father, and seeks to emulate him by producing offspring without conjugal intercourse, but only projects an abortion, a formless substance. Upon this she is cast out of Pleroma and into the primal sub-stratum of matter. In the Valentinian systems, the fall of Sophia appears in double guise. The higher Sophia still remains within the upper world after creating a disturbance, and after her expiation and repentance; but her premature offspring, Sophia Achamoth, is removed from the Pleroma, and becomes the heroine of the rest of the drama. This fallen Sophia becomes a world creative power.
Sophia Achamoth, or “Lower Wisdom”, the daughter of “Higher Wisdom”, becomes the mother of the Demiurge, identified with the God of the Old Testament.
The Gnostics are children of Sophia; from her the heavenly seed, the divine spark, descended into this lower world, subject to the Heimarmene
Destiny
Destiny or fate refers to a predetermined course of events. It may be conceived as a predetermined future, whether in general or of an individual...
and in the power of hostile spirits and powers; and all their sacraments and mysteries, their formulae and symbols, must be in order to find the way upwards, back to the highest heaven. This idea that the Gnostics know themselves to be in a hostile and evil world reacted in the same direction upon the conception of Sophia. She became likewise a fallen Aeon, who has sunk down into the material world and seeks to free herself from it, receiving her liberation at the hands of a heavenly Redeemer, exactly like the Gnostics.
The goddess who sinks down into the material may readily be identified with Ruach (רוח), the Spirit
Spirit
The English word spirit has many differing meanings and connotations, most of them relating to a non-corporeal substance contrasted with the material body.The spirit of a living thing usually refers to or explains its consciousness.The notions of a person's "spirit" and "soul" often also overlap,...
of God, who broods over Chaos, or even with the later Chokhmah
Chokhmah (Kabbalah)
Chokhmah in the Kabbalah of Judaism, is the uppermost of the Sephirot of the right line . It is derived from the Hebrew word chokhmah which means "wisdom". It is to the bottom right of Keter, and with Binah across it. Under it are the sephirot of Chesed and Netzach...
, who was generally conceived of as a world-creating agent.
This system was very closely followed by Valentinus, who may have come to know these doctrines in Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
. Irenaeus characterizes the Gnostics as the pneumatici who have a perfect knowledge of God, and have been initiated into the mysteries of Achamoth.
Anthropos
The chief influence at work here seems to have been the idea of the celestial AnthroposAdam Kadmon
In the religious writings of Kabbalah, Adam Kadmon is a phrase meaning "Primal Man". The oldest rabbinical source for the term "Adam ha-Ḳadmoni" is Num. R. x., where Adam is styled, not as usually, "Ha-Rishon" , "Ha-Kadmoni" ....
(i.e. the Primal Man) – of whom the myth originally relates that he has sunk into matter and then raised himself up from it again – which appears in its simple form in individual Gnostic systems, e.g. in Poimandres (in the Corpus Hermeticum) and in Manichaeism
Manichaeism
Manichaeism in Modern Persian Āyin e Māni; ) was one of the major Iranian Gnostic religions, originating in Sassanid Persia.Although most of the original writings of the founding prophet Mani have been lost, numerous translations and fragmentary texts have survived...
.
According to Valentinus, the Anthropos no longer appears as the world-creative power sinking down into the material world, but as a celestial Aeon of the upper world (or even as the supreme god), who stands in a clearly defined relationship to the fallen Aeon. Adam was created in the name of Anthropos, and overawes the demons by the fear of the pre-existent man. This Anthropos is a cosmogonic element, pure mind as distinct from matter, mind conceived hypostatically as emanating from God and not yet darkened by contact with matter. This mind is considered as the reason of humanity, or humanity itself, as a personified idea, a category without corporeality, the human reason conceived as the World-Soul
Anima mundi (spirit)
The world soul is, according to several systems of thought, an intrinsic connection between all living things on the planet, which relates to our world in much the same way as the soul is connected to the human body...
. It is possible that the role of the Anthropos is here transferred to Sophia Achamoth.
It is also clear why the Ekklesia appears together with the Anthropos. With this is associated the community of the faithful and the redeemed, who are to share the same fate with him. Perfect gnosis (and thus the whole body of Gnostics) is connected with the Anthropos.
Christ
Next to Sophia stands a male redeeming divinity. In the true Valentinian system, the Christ is the son of the fallen Sophia, who is thus conceived as an individual. Sophia conceives a passion for the First Father himself, or rather, under pretext of love she seeks to draw near to the unattainable Bythos, the Unknowable, and to comprehend his greatness. She brings forth, through her longing for that higher being, an Aeon who is higher and purer than herself, and at once rises into the celestial worlds. Christ has pity on the abortive substance born of Sophia and gives it essence and form, whereupon Sophia tries to rise again to the Father, but in vain. In the enigmatic figure of Christ we again find hidden the original conception of the Primal Man, who sinks down into matter but rises again.In the fully developed Ptolemaean system we find a kindred conception, but with a slight difference. Here Christ and Sophia appear as brother and sister, with Christ representing the higher and Sophia the lower element. When this world has been born from Sophia in consequence of her sin, Nous and Aletheia, two Aeons, by command of the Father, produce two new Aeons, Christ and the Holy Ghost; these restore order in the Pleroma, and in consequence all Aeons combine their best and most wonderful qualities to produce a new Aeon (Jesus, Logos, Soter, or Christ), the “First Fruits
First Fruits
First Fruits are a religious offering of the first agricultural produce of the harvest. In classical Greek, Roman, Hebrew and Christian religions, the first fruits were offered to the temple or church. First Fruits were often a primary source of income to maintain the religious leaders and the...
” whom they offer to the Father. And this celestial redeemer-Aeon now enters into a marriage with the fallen Aeon; they are the “bride and bridegroom”. It is boldly stated in the exposition in Hippolytus’ Philosophumena
Refutation of all Heresies
The Refutation of All Heresies or Philosophumena is a compendious Christian polemical work of the early third century, now generally attributed to Hippolytus of Rome. Most of it was recovered in 1842 in a manuscript at Mount Athos, but the complete text is not known...
that they produce between them 70 celestial angels.
This myth can be connected with the historic Jesus of Nazareth by further relating that Christ, having been united to the Sophia, descends into the earthly Jesus, the son of Mary, at his baptism, and becomes the Saviour of men.
Horos

Horus
Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
.
The task of Horos is to separate the fallen Aeons from the upper world of Aeons. At the same time he becomes a kind of world-creative power, who in this capacity helps to construct an ordered world out of Sophia and her passions. He is also called Stauros (cross
Cross
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two lines or bars perpendicular to each other, dividing one or two of the lines in half. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally; if they run obliquely, the design is technically termed a saltire, although the arms of a saltire need not meet...
), and we frequently meet with references to the figure of Stauros. Speculations about the Stauros are older than Christianity, and a Platonic
Platonism
Platonism is the philosophy of Plato or the name of other philosophical systems considered closely derived from it. In a narrower sense the term might indicate the doctrine of Platonic realism...
conception may have been at work here. Plato
Plato
Plato , was a Classical Greek philosopher, mathematician, student of Socrates, writer of philosophical dialogues, and founder of the Academy in Athens, the first institution of higher learning in the Western world. Along with his mentor, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato helped to lay the...
had already stated
Timaeus (dialogue)
Timaeus is one of Plato's dialogues, mostly in the form of a long monologue given by the title character, written circa 360 BC. The work puts forward speculation on the nature of the physical world and human beings. It is followed by the dialogue Critias.Speakers of the dialogue are Socrates,...
that the World-Soul revealed itself in the form of the letter Chi (X)
Chi (letter)
Chi is the 22nd letter of the Greek alphabet, pronounced as in English.-Greek:-Ancient Greek:Its value in Ancient Greek was an aspirated velar stop .-Koine Greek:...
; by which he meant that figure described in the heavens by the intersecting orbits of the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
and the planetary ecliptic
Ecliptic
The ecliptic is the plane of the earth's orbit around the sun. In more accurate terms, it is the intersection of the celestial sphere with the ecliptic plane, which is the geometric plane containing the mean orbit of the Earth around the Sun...
. Since through this double orbit all the movements of the heavenly powers are determined, so all “becoming” and all life depend on it, and thus we can understand the statement that the World-Soul appears in the form of an X, or a cross.
The cross can also stand for the wondrous Aeon on whom depends the ordering and life of the world, and thus Horos-Stauros appears here as the first redeemer of Sophia from her passions, and as the orderer of the creation of the world which now begins. Naturally, then, the figure of Horos-Stauros was often assimilated to that of the Christian Redeemer. We possibly find echoes of this in the Gospel of Peter
Gospel of Peter
The Gospel According to Peter , commonly called the Gospel of Peter, is one of the non-Canonical gospels which were rejected by the Church Fathers and the Catholic Church's synods of Carthage and Rome, which established the New Testament canon, as apocryphal...
, where the Cross
True Cross
The True Cross is the name for physical remnants which, by a Christian tradition, are believed to be from the cross upon which Jesus was crucified.According to post-Nicene historians, Socrates Scholasticus and others, the Empress Helena The True Cross is the name for physical remnants which, by a...
itself is depicted as speaking and even floating out of the tomb.
Monism
Peculiarly Valentinian is the above-mentioned derivation of the material world from the passions of Sophia. Whether this already formed part of the original system of Valentinus is, indeed, questionable, but at any rate it plays a prominent part in the Valentinian school, and consequently appears with the most diverse variations in the account given by Irenaeus. By it is effected the comparative monism of the Valentinian system, and the dualism of the conception of two separate worlds of light and darkness is overcome:Demiurge
This derivation of the material world from the passions of the fallen Sophia is next affected by an older theory, which probably occupied an important place in the true Valentinian system. According to this theory the son of Sophia, whom she forms on the model of the Christ who has disappeared in the Pleroma, becomes the Demiurge, and this Demiurge with his angels now appears as the real world-creative power.According to the older conception, he was an evil and malicious offspring of his mother, who has already been deprived of any particle of light. In the Valentinian systems, the Demiurge was the offspring of a union of Sophia Achamoth with matter, and appears as the fruit of Sophia’s repentance and conversion. But as Achamoth herself was only the daughter of Sophia, the last of the thirty Aeons, the Demiurge was distant by many emanations from the Supreme God. The Demiurge in creating this world out of Chaos was unconsciously influenced for good by Christ; and the universe, to the surprise even of its Maker, became almost perfect. The Demiurge regretted even its slight imperfection, and as he thought himself the Supreme God, he attempted to remedy this by sending a Messiah. To this Messiah, however, was actually united Christ the Saviour, who redeemed men.
Creation of Man
With the doctrine of the creation of the world is connected the subject of the creation of man. According to it, the world-creating angels – not one, but many – create man, but the seed of the spirit comes into their creature without their knowledge, by the agency of a higher celestial Aeon, and they are then terrified by the faculty of speech by which their creature rises above them, and try to destroy him.It is significant that Valentinus himself is credited with having written a treatise upon the threefold nature of man, who is represented as at once spiritual, psychical and material. In accordance with this there also arise three classes of men, the pneumatici, the psychici and the hylici. This doctrine dates at least as far back as Plato’s Republic.
- The first, the material, will return to the grossness of matter and finally be consumed by fire.
- The second, or psychical, together with the Demiurge as their master, will enter a middle state, neither heaven (Pleroma) nor hell (matter).
- The purely spiritual men will be completely freed from the influence of the Demiurge and together with the Saviour and Achamoth, his spouse, will enter the Pleroma divested of body and soul.
We also find ideas that emphasize the distinction between the soma psychikon and the soma pneumatikon:
Soteriology
Salvation is not merely individual redemption of each human soul; it is a cosmic process. It is the return of all things to what they were before the flaw in the sphere of the Aeons brought matter into existence and imprisoned some part of the Divine Light into the evil Hyle (matterMatter
Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects consist. Typically, matter includes atoms and other particles which have mass. A common way of defining matter is as anything that has mass and occupies volume...
). This setting free of the light sparks is the process of salvation; when all light shall have left Hyle, it will be burnt up and destroyed.
In Valentinianism the process is extraordinarily elaborate, and we find here developed particularly clearly the myth of the heavenly marriage. This myth, as we shall see more fully below, and as may be mentioned here, is of great significance for the practical piety of the Valentinian Gnostics. It is the chief idea of their pious practices mystically to repeat the experience of this celestial union of the Saviour with Sophia. In this respect, consequently, the myth underwent yet wider development. Just as the Saviour is the bridegroom of Sophia, so the heavenly angels, who sometimes appear as the sons of the Saviour and Sophia, sometimes as the escort of the Saviour, are the males betrothed to the souls of the Gnostics, which are looked upon as feminine. Thus every Gnostic had her unfallen counterpart standing in the presence of God, and the object of a pious life was to bring about and experience this inner union with the celestial abstract personage. This leads us straight to the sacramental ideas of this branch of Gnosticism (see below). And it also explains the expression used of the Gnostics in Irenaeus, that they always meditate upon the secret of the heavenly union (the Syzygia).
“The final consummation of all things will take place when all that is spiritual has been formed and perfected by gnosis.”
Gnosis
The central point of the piety of Valentinus seems to have been that mystical contemplation of God; in a letter preserved in Clement of Alexandria, he sets forth that the soul of man is like an inn, which is inhabited by many evil spirits.But this contemplation of God, as Valentinus declares, closely and deliberately following the doctrines of the Church and with him the compiler of the Gospel of John, is accomplished through the revelation of the Son. This mystic also discusses a vision which is preserved in the Philosophumena of Hippolytus:
With celestial enthusiasm Valentinus here surveys and depicts the heavenly world of Aeons, and its connection with the lower world. Exalted joy of battle and a valiant courage breathe forth in the sermon in which Valentinus addresses the faithful:
Sacraments
Our authorities for the sacramental practices of the Valentinians are preserved especially in the accounts of the MarcosiansMarcosians
The Marcosians were a Gnostic sect founded by Marcus, active in Lyons and southern Europe from the second to the 4th century. Women held special status in the Marcosian communities; they were regarded as prophetesses and participated in administering the Eucharistic rites. Irenaeus accuses Marcus...
given in Irenaeus i. 13 and 20, and in the last section of Clement of Alexandria’s Excerpta ex Theodoto.
In almost all the sacramental prayers of the Gnostics handed down to us by Irenaeus, the Mother is the object of the invocation. There are moreover various figures in the fully developed system of the Valentinians who are in the Gnostic’s mind when he calls upon the Mother; sometimes it is the fallen Achamoth, sometimes the higher Sophia abiding in the celestial world, sometimes Aletheia, the consort of the supreme heavenly father, but it is always the same idea, the Mother, on whom the faith of the Gnostics is fixed. Thus a baptismal confession of faith of the Gnostics runs:
Bridal Chamber
The chief sacrament of the Valentinians seems to have been that of the bridal chamber (nymphon). The Gospel of PhilipGospel of Philip
The Gospel of Philip is one of the Gnostic Gospels, a text of New Testament apocrypha, dating back to around the third century but lost to modern researchers until an Egyptian peasant rediscovered it by accident, buried in a cave near Nag Hammadi, in 1945...
, a probable Valentinian text, reads:
As Sophia was united with the Saviour, her bridegroom, so the faithful would experience a union with their angel in the Pleroma (cf. the “Higher Self
Higher self
Higher self is a new age term associated with multiple belief systems, but its basic premise describes an eternal, omnipotent, conscious, and intelligent being, who is one's real self. Blavatsky formally defined the higher self as "Atma the inseparable ray of the Universal and ONE SELF. It is the...
” or “Holy Guardian Angel
Holy Guardian Angel
The term Holy Guardian Angel was possibly coined either by Abraham of Würzburg, a French Cabalist who wrote a book on ceremonial magick during the 15th century or Samuel Liddell MacGregor Mathers, the founder of the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, who later translated this manuscript and...
”). The ritual of this sacrament is briefly indicated: “A few of them prepare a bridal chamber and in it go through a form of consecration, employing certain fixed formulae, which are repeated over the person to be initiated, and stating that a spiritual marriage is to be performed after the pattern of the higher Syzygia.” Through a fortunate chance, a liturgical formula which was used at this sacrament appears to be preserved, though in a garbled form and in an entirely different connection, the author seeming to have been uncertain as to its original meaning. It runs:
Baptism
Besides this the Gnostics already practiced baptismBaptism
In Christianity, baptism is for the majority the rite of admission , almost invariably with the use of water, into the Christian Church generally and also membership of a particular church tradition...
, using the same form in all essentials as that of the Christian Church. The name given to baptism, at least among certain bodies, was apolytrosis (liberation); the baptismal formulae have been mentioned above.
The Gnostics are baptized in the mysterious name which also descended upon Jesus at his baptism
Baptism of Jesus
The baptism of Jesus marks the beginning of Jesus Christ's public ministry. This event is recorded in the Canonical Gospels of Matthew, Mark and Luke. In John 1:29-33 rather than a direct narrative, the Baptist bears witness to the episode...
. The angels of the Gnostics have also had to be baptized in this name, in order to bring about redemption for themselves and the souls belonging to them.
In the baptismal formulae the sacred name of the Redeemer is mentioned over and over again. In one of the formulae occur the words: “I would enjoy thy name, Saviour of Truth.” The concluding formula of the baptismal ceremony is: “Peace over all upon whom the Name rests.” This name pronounced at baptism over the faithful has above all the significance that the name will protect the soul in its ascent through the heavens, conduct it safely through all hostile powers to the lower heavens, and procure it access to Horos, who frightens back the lower souls by his magic
Magic (paranormal)
Magic is the claimed art of manipulating aspects of reality either by supernatural means or through knowledge of occult laws unknown to science. It is in contrast to science, in that science does not accept anything not subject to either direct or indirect observation, and subject to logical...
word. And for this life also baptism, in consequence of the pronouncing of the protecting name over the baptized person, accomplishes his liberation from the lower daemonic powers. Before baptism the Heimarmene is supreme, but after baptism the soul is free from her.
Death
With baptism was also connected the anointing with oil, and hence we can also understand the death sacrament occurring among some Valentinians consisting in an anointing with a mixture of oil and water. This death sacrament has naturally the express object of assuring the soul the way to the highest heaven “so that the soul may be intangible and invisible to the higher mights and powers”. In this connection we also find a few formulae which are entrusted to the faithful, so that their souls may pronounce them on their journey upwards. One of these formulae runs:Another formula is appended, in which there is a distinction in the invocation between the higher and lower Sophia. Another prayer of the same style is to be found in Irenaeus i. 13, and it is expressly stated that after prayer is pronounced the Mother throws the Homeric helmet
Cap of invisibility
In classical mythology, the Cap of Invisibility is a helmet or cap that can turn the wearer invisible. It is also known as the Cap of Hades, Helm of Hades, or Helm of Darkness. Wearers of the cap in Greek myths include the goddess of wisdom Athena, the messenger god Hermes, and the hero Perseus...
(cf. the Tarnhelm
Tarnhelm
Tarnhelm is the name of a magic helmet in Richard Wagner's Der Ring des Nibelungen. It is used as a cloak of invisibility by Alberich in Das Rheingold...
) over the faithful soul, and so makes him invisible to the mights and powers which surround and attack him.
Reaction
On the other hand, we see how here and there a reaction took place against the sacramental rites. A pure piety, rising above mere sacramentalism, breathes in the words of the Gnostics preserved in Excerpta ex Theodoto, 78, 2:Relationship with the Church
The distinction between the human and divine Saviour was a major point of contention between the Valentinians and the Church. Valentinus separated Christ into three figures; the spiritual, the psychical and material. Each of the three Christ figures had its own meaning and purpose. They acknowledged that Christ suffered and died, but believed that “in his incarnation, Christ transcended human nature so that he could prevail over death by divine power”. These beliefs are what caused Irenaeus to say of the Valentinians, “Certainly they confess with their tongues the one Jesus Christ, but in their minds they divide him.” In one passage in the account of Irenaeus, it is directly stated that the redeemer assumed a psychical body to redeem the psychical, for the spiritual already belong by nature to the celestial world and no longer require any historical redemption, while the material is incapable of redemption, as “flesh and blood cannot inherit the kingdom of God; neither doth corruption inherit incorruption”.Many Valentinian traditions and practices also clashed with those of the Church. They often met at unauthorized gatherings and rejected ecclesiastical authority, based on their belief that they were all equal. Members of the movement took turns administering sacraments, as well as preaching. Among the Valentinians, women were considered to be equal, or at least nearly equal to men. There were female prophets, teachers, healers, evangelists and even priests, which was very different from the Church’s view of women at the time. Valentinians held normal jobs, got married and raised children just like Christians; however they regarded these pursuits as being less important than gnosis, which was to be achieved individually. The beliefs of the Valentinians were much more oriented towards the individual than towards the group, and salvation
Salvation
Within religion salvation is the phenomenon of being saved from the undesirable condition of bondage or suffering experienced by the psyche or soul that has arisen as a result of unskillful or immoral actions generically referred to as sins. Salvation may also be called "deliverance" or...
was not seen as being universal, as it was in the Church.
The main disagreements between the Valentinians and the Church, then, were in the notions that God and the creator were two separate entities, the idea that the creator was flawed and formed man and Earth out of ignorance and confusion, and the separation of Christ’s human form and divine form. Church authorities believed that Valentinian theology was “a wickedly casuistic way of subverting their authority and thereby threatening the ecclesiastical order with anarchy.” The practices and rituals of the Valentinians were also different from those of the Christian Church, however the Valentinians considered themselves to be Christians and not pagans or heretics. By referring to themselves as Christians they worsened their relationship with the Church, who viewed them not only as heretics, but as rivals.
Although the Valentinians publicly professed their faith in one God, “in their own private meetings they insisted on discriminating between the popular image of God – as master, king, lord, creator, and judge – and what that image represented: God understood as the ultimate source of all being.” Aside from the Church fathers, however, “the majority of Christians did not recognize the followers of Valentinus as heretics. Most could not tell the difference between Valentinian and orthodox teaching.” This was partially because Valentinus used many books that now belong to the Old and New Testaments as a basis for interpretation in his own writing. He based his work on proto-orthodox Christian canon instead of on Gnostic scripture, and his style was similar to that of early Christian works. In this way, Valentinus tried to bridge the gap between Gnostic religion and early Catholicism. By attempting to bridge this gap, however, Valentinus and his followers became the proverbial wolves in sheep’s clothing. “The apparent similarity with orthodox teaching only made this heresy more dangerous – like poison disguised as milk.” Valentinian Gnosticism was “the most influential and sophisticated form of Gnostic teaching, and by far the most threatening to the church.”
Early Christianity has been described as “a complex network of individual parties, groups, sects, or denominations.” This inconsistency made the threat of Gnostic sects such as Valentinianism even more threatening to the Church.
External links
- Valentinus and the Valentinian Tradition – an extremely comprehensive collection of material on Valentinian mythology, theology and tradition (from the Gnosis Archive website).
- Patristic Material on Valentinus Complete collection of patristic sources mentioning Valentinus.
- Valentinus – A Gnostic for All Seasons Excellent introductory essay by Stephan A. Hoeller (from the Gnosis Archive website).

