
VIA Nano
Encyclopedia
The VIA Nano is a 64-bit
CPU for personal computer
s. The VIA Nano was released by VIA Technologies
in 2008 after five years of development by its CPU division, Centaur Technology
. This new Isaiah 64-bit architecture was designed from scratch, unveiled on 24 January 2008, and launched on May 29, including low-voltage variants and the Nano brand name. The processor supports a number of VIA-specific x86 extensions designed to boost efficiency in low-power appliances. A dual-core version is expected but has yet to ship. Via Technologies showed off a working prototype of its dual-core x86 processor, the Nano DC, at the Computex 2010 exhibition in Taiwan.
Unlike Intel and AMD, VIA uses two distinct development code names for each of its CPU cores. In this case, the codename 'CN' was used in the United States
by Centaur Technology. Biblical names are used as codes by VIA in Taiwan
, and Isaiah was the choice for this particular processor and architecture. It is expected that the VIA Isaiah will be twice as fast in integer performance and four times as fast in floating-point performance as the previous-generation VIA Esther at an equivalent clock speed. Power consumption is also expected to be on par with the previous-generation VIA CPUs, with thermal design power
ranging from 5 W to 25 W. Being a completely new design, the Isaiah architecture was built with support for features like the x86-64
instruction set and x86 virtualization
which were unavailable on its predecessors, the VIA C7
line, while retaining their encryption extensions. Several independent tests showed that the VIA Nano performs better than the single-core Intel Atom
across a variety of workloads. In a 2008 Ars Technica
test, a VIA Nano gained significant performance after its CPUID changed to Intel, hinting at the possibility that the benchmark software only checks the CPUID instead of the actual features supported by the CPU to choose a code path.
On November 3, 2009, VIA launched the Nano 3000 series. VIA claims that these models can offer a 20% performance boost and 20% more energy efficiency than the Nano 1000 and 2000 series. Benchmarks run by VIA claim that a 1.6 GHz 3000-series Nano can outperform the aging Intel Atom N270 by about 40–54%. The 3000 series adds an SSE4
instruction set, which was first completely introduced in the Intel Core i7. (A subset of the instructions called SSE4.1 was introduced in the second generation of Core 2 processors).
On January 4, 2011, VIA announced the VIA Nano X2 Dual-Core Processor. VIA Nano X2 processors samples are currently available for OEMs and motherboard vendors, with systems featuring the processors expected to arrive in Q1 2011.
64-bit
64-bit is a word size that defines certain classes of computer architecture, buses, memory and CPUs, and by extension the software that runs on them. 64-bit CPUs have existed in supercomputers since the 1970s and in RISC-based workstations and servers since the early 1990s...
CPU for personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s. The VIA Nano was released by VIA Technologies
VIA Technologies
VIA Technologies is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory, and is part of the Formosa Plastics Group. It is the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets...
in 2008 after five years of development by its CPU division, Centaur Technology
Centaur Technology
Centaur Technology is an x86 CPU design company, now a wholly owned subsidiary of VIA Technologies, a member of the Formosa Plastics Group, Taiwan's largest industrial conglomerate.-History:...
. This new Isaiah 64-bit architecture was designed from scratch, unveiled on 24 January 2008, and launched on May 29, including low-voltage variants and the Nano brand name. The processor supports a number of VIA-specific x86 extensions designed to boost efficiency in low-power appliances. A dual-core version is expected but has yet to ship. Via Technologies showed off a working prototype of its dual-core x86 processor, the Nano DC, at the Computex 2010 exhibition in Taiwan.
Unlike Intel and AMD, VIA uses two distinct development code names for each of its CPU cores. In this case, the codename 'CN' was used in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
by Centaur Technology. Biblical names are used as codes by VIA in Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
, and Isaiah was the choice for this particular processor and architecture. It is expected that the VIA Isaiah will be twice as fast in integer performance and four times as fast in floating-point performance as the previous-generation VIA Esther at an equivalent clock speed. Power consumption is also expected to be on par with the previous-generation VIA CPUs, with thermal design power
Thermal Design Power
The thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
ranging from 5 W to 25 W. Being a completely new design, the Isaiah architecture was built with support for features like the x86-64
X86-64
x86-64 is an extension of the x86 instruction set. It supports vastly larger virtual and physical address spaces than are possible on x86, thereby allowing programmers to conveniently work with much larger data sets. x86-64 also provides 64-bit general purpose registers and numerous other...
instruction set and x86 virtualization
X86 virtualization
In computing, x86 virtualization is the facility that allows multiple operating systems to simultaneously share x86 processor resources in a safe and efficient manner, a facility generically known as hardware virtualization...
which were unavailable on its predecessors, the VIA C7
VIA C7
The VIA C7 is an x86 central processing unit designed by Centaur Technology and sold by VIA Technologies.- Product history :The C7 delivers a number of improvements to the older VIA C3 cores but is nearly identical to the latest VIA C3 Nehemiah core. The C7 was officially launched in May 2005,...
line, while retaining their encryption extensions. Several independent tests showed that the VIA Nano performs better than the single-core Intel Atom
Intel Atom
Intel Atom is the brand name for a line of ultra-low-voltage x86 and x86-64 CPUs from Intel, designed in 45 nm CMOS and used mainly in netbooks, nettops, embedded application ranging from health care to advanced robotics and Mobile Internet devices...
across a variety of workloads. In a 2008 Ars Technica
Ars Technica
Ars Technica is a technology news and information website created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, science, technology policy, and video games. Ars Technica is known for its features, long articles that go...
test, a VIA Nano gained significant performance after its CPUID changed to Intel, hinting at the possibility that the benchmark software only checks the CPUID instead of the actual features supported by the CPU to choose a code path.
On November 3, 2009, VIA launched the Nano 3000 series. VIA claims that these models can offer a 20% performance boost and 20% more energy efficiency than the Nano 1000 and 2000 series. Benchmarks run by VIA claim that a 1.6 GHz 3000-series Nano can outperform the aging Intel Atom N270 by about 40–54%. The 3000 series adds an SSE4
SSE4
SSE4 is a CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 . It was announced on 27 September 2006 at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper; more precise details of 47 instructions became available at the Spring 2007 Intel Developer Forum...
instruction set, which was first completely introduced in the Intel Core i7. (A subset of the instructions called SSE4.1 was introduced in the second generation of Core 2 processors).
On January 4, 2011, VIA announced the VIA Nano X2 Dual-Core Processor. VIA Nano X2 processors samples are currently available for OEMs and motherboard vendors, with systems featuring the processors expected to arrive in Q1 2011.
Features

- x86-64X86-64x86-64 is an extension of the x86 instruction set. It supports vastly larger virtual and physical address spaces than are possible on x86, thereby allowing programmers to conveniently work with much larger data sets. x86-64 also provides 64-bit general purpose registers and numerous other...
instruction set - SuperscalarSuperscalarA superscalar CPU architecture implements a form of parallelism called instruction level parallelism within a single processor. It therefore allows faster CPU throughput than would otherwise be possible at a given clock rate...
out-of-order instruction execution - 65 nmNanometreA nanometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one billionth of a metre. The name combines the SI prefix nano- with the parent unit name metre .The nanometre is often used to express dimensions on the atomic scale: the diameter...
manufacturing process - Clock speed of 1 GHz to 2 GHz
- Bus speed of 533 MHz or 800 MHz
- Support for ECC
- x86 virtualizationX86 virtualizationIn computing, x86 virtualization is the facility that allows multiple operating systems to simultaneously share x86 processor resources in a safe and efficient manner, a facility generically known as hardware virtualization...
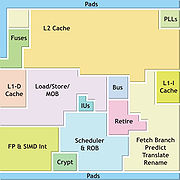
(Intel-compatible implementation), deactivated before stepping 3 - 32 KB L1 cache and 512 KB L2 cache, exclusive
- Pin-compatible with the VIA C7VIA C7The VIA C7 is an x86 central processing unit designed by Centaur Technology and sold by VIA Technologies.- Product history :The C7 delivers a number of improvements to the older VIA C3 cores but is nearly identical to the latest VIA C3 Nehemiah core. The C7 was officially launched in May 2005,...
Architecture improvements

- Out-of-orderOut-of-order executionIn computer engineering, out-of-order execution is a paradigm used in most high-performance microprocessors to make use of instruction cycles that would otherwise be wasted by a certain type of costly delay...
and superscalarSuperscalarA superscalar CPU architecture implements a form of parallelism called instruction level parallelism within a single processor. It therefore allows faster CPU throughput than would otherwise be possible at a given clock rate...
design: Providing much better performance than its predecessor, the VIA C7 processor, which was in-order. This puts the Isaiah architecture in line with current offerings from AMD and Intel, except for Intel AtomIntel AtomIntel Atom is the brand name for a line of ultra-low-voltage x86 and x86-64 CPUs from Intel, designed in 45 nm CMOS and used mainly in netbooks, nettops, embedded application ranging from health care to advanced robotics and Mobile Internet devices...
which has an in-order design. - Instructions fusion: Allows the processor to combine some instructions as a single instruction, reducing power requirements and giving higher performance (the Atom uses a similar strategy in processing x86 instructions in a more 'whole' manner, rather than breaking them into RISC-like micro-ops).
- Improved branch prediction: Uses eight predictors in two pipeline stages.
- CacheCacheIn computer engineering, a cache is a component that transparently stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster. The data that is stored within a cache might be values that have been computed earlier or duplicates of original values that are stored elsewhere...
design: An exclusive cache design means that contents of the L1 cache is not duplicated in the L2 cache, providing a larger total cache. - Data prefetch: Incorporating new mechanisms for data-prefetch, including both the loading of a special 64-line cache before loading the L2 cache and a direct load to the L1 cache.
- Fetches 4 x86 instructions per cycleInstruction cycleAn instruction cycle is the basic operation cycle of a computer. It is the process by which a computer retrieves a program instruction from its memory, determines what actions the instruction requires, and carries out those actions...
as opposed to Intel's 3-5 - Issues 3 micro-operationMicro-operationIn computer central processing units, micro-operations are detailed low-level instructions used in some designs to implement complex machine instructions .Various forms of μops have long been the basis for traditional microcode routines used to simplify the implementation of a...
s/clock to execution units
- Fetches 4 x86 instructions per cycle
- MemoryMemoryIn psychology, memory is an organism's ability to store, retain, and recall information and experiences. Traditional studies of memory began in the fields of philosophy, including techniques of artificially enhancing memory....
access: Merging of smaller stores into larger load data. - Execution units: Seven execution units are available, that allows up to seven micro-ops being executed per clock.
- 2 Integer units
- One unit (ALU1) is feature complete, while the other (ALU2) lacks some low usage instructions and therefore can be used more often for tasks like address calculations.
- 2 Store units (VIAVIA TechnologiesVIA Technologies is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory, and is part of the Formosa Plastics Group. It is the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets...
refer to this as one for Address Store and another for Data Store) - 1 Load unit
- 2 Media units with 128-bit128-bitThere are currently no mainstream general-purpose processors built to operate on 128-bit integers or addresses, though a number of processors do operate on 128-bit data. The IBM System/370 could be considered the first rudimentary 128-bit computer as it used 128-bit floating point registers...
wide datapathDatapathA datapath is a collection of functional units, such as arithmetic logic units or multipliers, that perform data processing operations. Most central processing units consist of a datapath and a control unit, with a large part of the control unit dedicated to regulating the interaction between the...
, supporting 4 single precision or 2 double-precision operations.- One unit (MEDIA-A) correspond to floating point support, 2-clock latency for single-precision and double-precision add instructions, integer SIMD, encryption, divide and square root.
- The other unit (MEDIA-B) performs single-precision multiplies, with 3-clock latency for double-precision multiplies.
- 2 Integer units
- Media computation: Refers to the use of floating point execution units.
- Using an execution unit for floating point computation and another for multiplication allows the execution of up to four floating point and four multiplies per clock.
- A new implementation of FP-addition with the lowest latency (in clocks) seen in x86 processors so far.
- Almost all integer SIMDSIMDSingle instruction, multiple data , is a class of parallel computers in Flynn's taxonomy. It describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data simultaneously...
instructions execute in one clock. - Implements MMX, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, SSSE3SSSE3Supplemental Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 is a SIMD instruction set created by Intel and is the fourth iteration of the SSE technology.- History :...
multimedia instruction sets - Implements SSE4SSE4SSE4 is a CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 . It was announced on 27 September 2006 at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper; more precise details of 47 instructions became available at the Spring 2007 Intel Developer Forum...
multimedia instruction set (VIA Nano 3000 series only)
- Power ManagementPower managementPower management is a feature of some electrical appliances, especially copiers, computers and computer peripherals such as monitors and printers, that turns off the power or switches the system to a low-power state when inactive. In computing this is known as PC power management and is built...
: Besides requiring very low power, many new features are included.- Includes a new C6 power state (Caches are flushed, internal state saved, and core voltage is turned off).
- Adaptive P-State Control: Transition between performance and voltage states without stopping execution.
- Adaptive Overclocking: Automatic overclocking if there is low temperature in the processor core.
- Adaptive Thermal Limit: Adjusting of the processor to maintain a user predefined temperature.
- EncryptionEncryptionIn cryptography, encryption is the process of transforming information using an algorithm to make it unreadable to anyone except those possessing special knowledge, usually referred to as a key. The result of the process is encrypted information...
: Includes the VIA PadLock engine- Hardware support for AESAdvanced Encryption StandardAdvanced Encryption Standard is a specification for the encryption of electronic data. It has been adopted by the U.S. government and is now used worldwide. It supersedes DES...
encryption, SHA-1 and SHA-256 hashing
- Hardware support for AES

