
Transition dipole moment
Encyclopedia
The Transition dipole moment or Transition moment, usually denoted  for a transition between an initial state,
for a transition between an initial state, 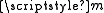 , and a final state,
, and a final state, 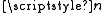 , is the electric dipole moment
, is the electric dipole moment
associated with the transition between the two states. In general the transition dipole moment is a complex
vector quantity that includes the phase factors associated with the two states. Its direction gives the polarization of the transition, which determines how the system will interact with an electromagnetic wave of a given polarization, while the square of the magnitude gives the strength of the interaction due to the distribution of charge within the system. The SI unit
of the transition dipole moment is the Coulomb meter (Cm); a more conveniently sized unit is the Debye
(D).
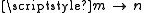 transition is given by the relevant off-diagonal element of the dipole matrix, which can be calculated from an integral taken over the product of the wavefunctions of the initial and final states of the transition, and the dipole moment operator,
transition is given by the relevant off-diagonal element of the dipole matrix, which can be calculated from an integral taken over the product of the wavefunctions of the initial and final states of the transition, and the dipole moment operator,
 ,
,
where the summation
s are over the positions of the electron
s in the system. Giving the transition dipole moment:
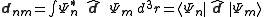 ,
,
where the integral is in principle over all space, but it can be restricted to the region in which the initial and final state wavefunctions are non-negligible.
In the case of two classical point charges,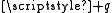 and
and  , with a displacement vector
, with a displacement vector
,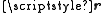 , pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge, the electric dipole moment is given by
, pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge, the electric dipole moment is given by
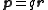 .
.
In the presence of an electric field
, such as that due to an electromagnetic wave, the two charges will experience a force in opposite directions, leading to a net torque
on the dipole. The magnitude of the torque is proportional
to both the magnitude of the charges and the separation between them, and varies with the relative angles of the field and the dipole:
 .
.
Similarly, the coupling between an electromagnetic wave and an atomic transition with transition dipole moment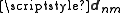 , depends on the charge distribution within the atom, the strength of the electric field, and the relative polarizations of the field and the transition. In addition, the transition dipole moment depends on the geometries and relative phases of the initial and final states.
, depends on the charge distribution within the atom, the strength of the electric field, and the relative polarizations of the field and the transition. In addition, the transition dipole moment depends on the geometries and relative phases of the initial and final states.
 , it can undergo a transition from an initial to a final state of energy difference
, it can undergo a transition from an initial to a final state of energy difference 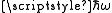 through the coupling of the electromagnetic field to the transition dipole moment. When this transition is from a lower energy state to a higher energy state, this results in the absorption
through the coupling of the electromagnetic field to the transition dipole moment. When this transition is from a lower energy state to a higher energy state, this results in the absorption
of a photon
. A transition from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, results in the emission of a photon. If the charge, , is omitted from the electric dipole operator during this calculation, one obtains
, is omitted from the electric dipole operator during this calculation, one obtains 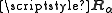 as used in oscillator strength
as used in oscillator strength
.
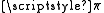 orbital to an antibonding
orbital to an antibonding 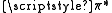 orbital is allowed because the integral
orbital is allowed because the integral
defining the transition dipole moment is nonzero. Such a transition occurs between an even and an odd orbital; the dipole operator is an odd function of , hence the integrand is an even function. The integral of an odd function over symmetric limits returns a value of zero, while for an even function this is not necessarily the case. This result is reflected in the parity
, hence the integrand is an even function. The integral of an odd function over symmetric limits returns a value of zero, while for an even function this is not necessarily the case. This result is reflected in the parity
selection rule
for electric dipole transitions.
 for a transition between an initial state,
for a transition between an initial state, 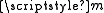 , and a final state,
, and a final state, 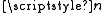 , is the electric dipole moment
, is the electric dipole momentElectric dipole moment
In physics, the electric dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative electrical charges in a system of charges, that is, a measure of the charge system's overall polarity with SI units of Coulomb-meter...
associated with the transition between the two states. In general the transition dipole moment is a complex
Complex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
vector quantity that includes the phase factors associated with the two states. Its direction gives the polarization of the transition, which determines how the system will interact with an electromagnetic wave of a given polarization, while the square of the magnitude gives the strength of the interaction due to the distribution of charge within the system. The SI unit
International System of Units
The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system and is generally a system of units of measurement devised around seven base units and the convenience of the number ten. The older metric system included several groups of units...
of the transition dipole moment is the Coulomb meter (Cm); a more conveniently sized unit is the Debye
Debye
The debye is a CGS unit of electric dipole momentElectric dipole moment is defined as charge times displacement: Historically the debye was defined as the dipole moment resulting from two charges of opposite sign but an equal magnitude of 10-10 statcoulomb10-10 statcoulomb is approximately 0.2083...
(D).
Definition
The transition dipole moment for the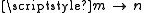 transition is given by the relevant off-diagonal element of the dipole matrix, which can be calculated from an integral taken over the product of the wavefunctions of the initial and final states of the transition, and the dipole moment operator,
transition is given by the relevant off-diagonal element of the dipole matrix, which can be calculated from an integral taken over the product of the wavefunctions of the initial and final states of the transition, and the dipole moment operator, ,
,where the summation
Summation
Summation is the operation of adding a sequence of numbers; the result is their sum or total. If numbers are added sequentially from left to right, any intermediate result is a partial sum, prefix sum, or running total of the summation. The numbers to be summed may be integers, rational numbers,...
s are over the positions of the electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s in the system. Giving the transition dipole moment:
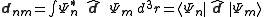 ,
,where the integral is in principle over all space, but it can be restricted to the region in which the initial and final state wavefunctions are non-negligible.
Analogy with a classical dipole
A basic, phenomenological understanding of the transition dipole moment can be obtained by analogy with a classical dipole. While the comparison can be very useful, care must be taken to ensure that one does not fall into the trap of assuming they are the same.In the case of two classical point charges,
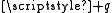 and
and  , with a displacement vector
, with a displacement vectorDisplacement (vector)
A displacement is the shortest distance from the initial to the final position of a point P. Thus, it is the length of an imaginary straight path, typically distinct from the path actually travelled by P...
,
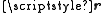 , pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge, the electric dipole moment is given by
, pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge, the electric dipole moment is given by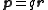 .
.In the presence of an electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
, such as that due to an electromagnetic wave, the two charges will experience a force in opposite directions, leading to a net torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
on the dipole. The magnitude of the torque is proportional
Proportionality (mathematics)
In mathematics, two variable quantities are proportional if one of them is always the product of the other and a constant quantity, called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant. In other words, are proportional if the ratio \tfrac yx is constant. We also say that one...
to both the magnitude of the charges and the separation between them, and varies with the relative angles of the field and the dipole:
 .
.Similarly, the coupling between an electromagnetic wave and an atomic transition with transition dipole moment
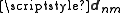 , depends on the charge distribution within the atom, the strength of the electric field, and the relative polarizations of the field and the transition. In addition, the transition dipole moment depends on the geometries and relative phases of the initial and final states.
, depends on the charge distribution within the atom, the strength of the electric field, and the relative polarizations of the field and the transition. In addition, the transition dipole moment depends on the geometries and relative phases of the initial and final states.Origin
When an atom or molecule interacts with an electromagnetic wave of frequency , it can undergo a transition from an initial to a final state of energy difference
, it can undergo a transition from an initial to a final state of energy difference 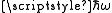 through the coupling of the electromagnetic field to the transition dipole moment. When this transition is from a lower energy state to a higher energy state, this results in the absorption
through the coupling of the electromagnetic field to the transition dipole moment. When this transition is from a lower energy state to a higher energy state, this results in the absorptionAbsorption (electromagnetic radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way by which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed to other forms of energy for example, to heat. The absorption of light during wave propagation is...
of a photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
. A transition from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, results in the emission of a photon. If the charge,
 , is omitted from the electric dipole operator during this calculation, one obtains
, is omitted from the electric dipole operator during this calculation, one obtains 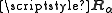 as used in oscillator strength
as used in oscillator strengthOscillator strength
An atom or a molecule can absorb light and undergo a transition fromone quantum state to another. The oscillator strength is a dimensionlessquantity to express the strength of the transition....
.
Applications
The transition dipole moment is useful for determining if transitions are allowed under the electric dipole interaction. For example, the transition from a bonding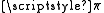 orbital to an antibonding
orbital to an antibonding 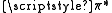 orbital is allowed because the integral
orbital is allowed because the integralIntegral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
defining the transition dipole moment is nonzero. Such a transition occurs between an even and an odd orbital; the dipole operator is an odd function of
 , hence the integrand is an even function. The integral of an odd function over symmetric limits returns a value of zero, while for an even function this is not necessarily the case. This result is reflected in the parity
, hence the integrand is an even function. The integral of an odd function over symmetric limits returns a value of zero, while for an even function this is not necessarily the case. This result is reflected in the parityParity (physics)
In physics, a parity transformation is the flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate. In three dimensions, it is also commonly described by the simultaneous flip in the sign of all three spatial coordinates:...
selection rule
Selection rule
In physics and chemistry a selection rule, or transition rule, formally constrains the possible transitions of a system from one state to another. Selection rules have been derived for electronic, vibrational, and rotational transitions...
for electric dipole transitions.

