
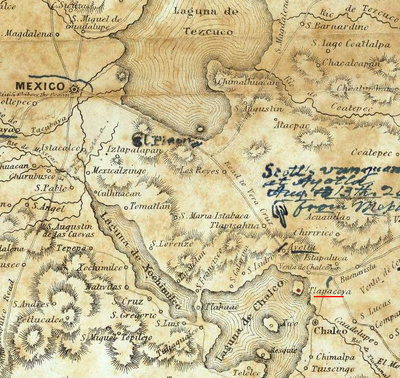
Tlapacoya (Mesoamerican site)
Encyclopedia

Archaeological site
An archaeological site is a place in which evidence of past activity is preserved , and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record.Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a 'site' can vary widely,...
in Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
, located at the foot of the Tlapacoya volcano, southeast of Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
, on the former shore of Lake Chalco
Lake Chalco
Lake Chalco was an endorheic lake formerly located in the Valley of Mexico and was important for human development in central Mexico. The lake was named after the city of Chalco on its eastern shore....
. Tlapacoya was a major site for the Tlatilco culture
Tlatilco culture
Tlatilco culture is a culture that flourished in the Valley of Mexico between the years 1250 BCE and 800 BCE, during the Mesoamerican Early Formative period...
.
Tlapacoya is known in particular for Tlapacoya figurines. These sophisticated earthware figurines were generally created between 1500 and 300 BCE
Common Era
Common Era ,abbreviated as CE, is an alternative designation for the calendar era originally introduced by Dionysius Exiguus in the 6th century, traditionally identified with Anno Domini .Dates before the year 1 CE are indicated by the usage of BCE, short for Before the Common Era Common Era...
and are representative of the Preclassic Period
Mesoamerican chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian , the Archaic , the Preclassic , the Classic , and the Postclassic...
.
Tlapacoya was also a manufacturing center for so-called "Dragon Pots" (see photo below). These flat-bottomed cylindrical bowls have white or buff surfaces incised with almost abstract Olmec
Olmec
The Olmec were the first major Pre-Columbian civilization in Mexico. They lived in the tropical lowlands of south-central Mexico, in the modern-day states of Veracruz and Tabasco....
-style drawings, generally of were-jaguars
Olmec were-jaguar
The were-jaguar was both an Olmec motif and a supernatural entity, perhaps a deity.The were-jaguar motif is characterized by almond-shaped eyes, a downturned open mouth, and a cleft head. It appears widely in the Olmec archaeological record, and in many cases, under the principle of pars pro toto,...
.
Even more ancient remains?
In addition to the figurines and other artifacts from the 1500 - 300 BCE era, human and animal remains have been found, some of which could be as much as 25,000 years old.Silvia González et al. have published research claiming that "one Tlapacoya skull is the first directly dated human in Mexico with an age of 9730 ± 65 years BP
Before Present
Before Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
" (before present). If confirmed, this would be the 2nd oldest human remain found in the Americas, after the Buhl woman
Buhl woman
Buhla is the name for a skeleton of a prehistoric woman found in a quarry near Buhl, Idaho, United States, in January 1989. The skeleton's age has been estimated by radiocarbon dating at 10,675 ± 95 BCE , which confirms this as one of the oldest human remains found in the Americas...
of Idaho.
The most controversial findings in Tlapacoya are artifacts which have been dated by some researchers to as early as 25,000 BP
Before Present
Before Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
. If verified, these would be some of the earliest dates for human habitation in the Americas and would discredit prevailing theories of the timing of settlement of the New World.
The evidence for these much-earlier dates consists of the bones of black bear and two species of deer which appeared in midden
Midden
A midden, is an old dump for domestic waste which may consist of animal bone, human excrement, botanical material, vermin, shells, sherds, lithics , and other artifacts and ecofacts associated with past human occupation...
s associated with 22,000-year-old hearth
Hearth
In common historic and modern usage, a hearth is a brick- or stone-lined fireplace or oven often used for cooking and/or heating. For centuries, the hearth was considered an integral part of a home, often its central or most important feature...
s, as well as a curved obsidian blade
Obsidian use in Mesoamerica
Obsidian is a naturally formed volcanic glass that was an important part of the material culture of Pre-Columbian Mesoamerica. Obsidian was a highly integrated part of daily and ritual life, and its widespread and varied use may be a significant contributor to Mesoamerica's lack of metallurgy...
which was found beneath a buried tree trunk. The bones were 24,000 years BP (± 4000 years) and 21,700 years BP (± 500 years) (Lorenzo and Mirambell 1999:488-489). The obsidian blade was found under a tree trunk which dated to 24,000 years BP (± 1000 years) and was itself dated, using the obsidian hydration method
Obsidian hydration dating
Obsidian hydration dating is a geochemical method of determining age in either absolute or relative terms of an artifact made of obsidian....
, to between 21,250 and 25,000 years BP.
These very early pre-Clovis
Clovis culture
The Clovis culture is a prehistoric Paleo-Indian culture that first appears 11,500 RCYBP , at the end of the last glacial period, characterized by the manufacture of "Clovis points" and distinctive bone and ivory tools...
dates have been challenged by other archaeologists.
The site was uncovered during the construction of a Mexico City-Puebla
Puebla
Puebla officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 217 municipalities and its capital city is Puebla....
freeway in the 1960s and 1970s. It has since been almost completely obliterated by freeway construction.

External links
- Anthropologist K. Kris Hirst discusses Tlapacoya at about.com
- Article en Español on Silvia González
- Discussion of the pre-Clovis dating at Tlapacoya and further links

