
Tafel equation
Encyclopedia
The Tafel equation is an equation in electrochemical kinetics
relating the rate of an electrochemical
reaction to the overpotential
. The Tafel equation was first deduced experimentally and was later shown to have a theoretical justification. The equation is named after German chemist Julius Tafel
(1862-1918).
On a single electrode the Tafel equation can be stated as
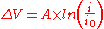
where
The Tafel slope is measured experimentally. It, however, can be shown theoretically that when the dominant reaction mechanism involves the transfer of a single electron that
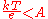
where A is defined as
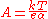
where
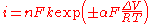
where
s, the Tafel equation is applied to each electrode separately.
The Tafel equation assumes that the reverse reaction rate is negligible compared to the forward reaction rate.
The Tafel equation is applicable to the region where the values of polarization are high. At low values of polarization, the dependence of current on polarization is usually linear (not logarithmic):
 .
.
This linear region is called "polarization resistance" due to its formal similarity to the Ohm's law
.
Electrochemical kinetics
Electrochemical kinetics is a field of electrochemistry studying the rate of electrochemical processes. Due to electrochemical phenomena unfolding at the interface between an electrode and an electrolyte, there are accompanying phenomena to electrochemical reaction which contribute to the overall...
relating the rate of an electrochemical
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place in a solution at the interface of an electron conductor and an ionic conductor , and which involve electron transfer between the electrode and the electrolyte or species in solution.If a chemical reaction is...
reaction to the overpotential
Overpotential
Overpotential is an electrochemical term which refers to the potential difference between a half-reaction's thermodynamically determined reduction potential and the potential at which the redox event is experimentally observed. The term is directly related to a cell's voltage efficiency...
. The Tafel equation was first deduced experimentally and was later shown to have a theoretical justification. The equation is named after German chemist Julius Tafel
Julius Tafel
Julius Tafel was an Swiss chemist.-Work:He worked first with Hermann Emil Fischer on the field of organic chemistry, but changed to electrochemistry after his work with Wilhelm Ostwald...
(1862-1918).
On a single electrode the Tafel equation can be stated as
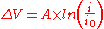
where
-
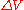 is the overpotential, V
is the overpotential, V -
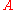 is the so called "Tafel slope", V
is the so called "Tafel slope", V -
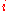 is the current densityCurrent densityCurrent density is a measure of the density of flow of a conserved charge. Usually the charge is the electric charge, in which case the associated current density is the electric current per unit area of cross section, but the term current density can also be applied to other conserved...
is the current densityCurrent densityCurrent density is a measure of the density of flow of a conserved charge. Usually the charge is the electric charge, in which case the associated current density is the electric current per unit area of cross section, but the term current density can also be applied to other conserved...
, A/m2 and -
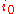 is the so called "exchange current densityExchange current densityIn electrochemistry, exchange current density is a parameter used in the Tafel equation, Butler-Volmer equation and other expressions. The Tafel equation describes the dependence of current for an electrolytic process to overpotential....
is the so called "exchange current densityExchange current densityIn electrochemistry, exchange current density is a parameter used in the Tafel equation, Butler-Volmer equation and other expressions. The Tafel equation describes the dependence of current for an electrolytic process to overpotential....
", A/m2.
Overview of the terms
The exchange current is the current at equilibrium, i.e. the rate at which oxidized and reduced species transfer electrons with the electrode. In other words, the exchange current density is the rate of reaction at the reversible potential (when the overpotential is zero by definition). At the reversible potential, the reaction is in equilibrium meaning that the forward and reverse reactions progress at the same rates. This rate is the exchange current density.The Tafel slope is measured experimentally. It, however, can be shown theoretically that when the dominant reaction mechanism involves the transfer of a single electron that
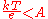
where A is defined as
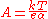
where
-
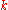 is Boltzmann's constant,
is Boltzmann's constant, -
 is the absolute temperature,
is the absolute temperature, -
 is the electron charge, and
is the electron charge, and -
 is the so called "charge transfer coefficientCharge transfer coefficientCharge transfer coefficient, and symmetry factor are two related parameters used in description of the kinetics of electrochemical reactions...
is the so called "charge transfer coefficientCharge transfer coefficientCharge transfer coefficient, and symmetry factor are two related parameters used in description of the kinetics of electrochemical reactions...
", the value of which must be between 0 and 1.
An alternative form
The Tafel equation can be also written as: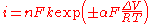
where
- the plus sign under the exponent refers to an anodic reaction, and a minus sign to a cathodic reaction,
- n is the number of electrons involved in the electrode reaction
- k is the rate constant for the electrode reaction,
- R is the universal gas constant,
- F is the Faraday constant.
Applicability
Where an electrochemical reaction occurs in two "half reactions" on separate electrodeElectrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
s, the Tafel equation is applied to each electrode separately.
The Tafel equation assumes that the reverse reaction rate is negligible compared to the forward reaction rate.
The Tafel equation is applicable to the region where the values of polarization are high. At low values of polarization, the dependence of current on polarization is usually linear (not logarithmic):
 .
.This linear region is called "polarization resistance" due to its formal similarity to the Ohm's law
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
.

