Space charge
Encyclopedia
Space charge is a concept in which excess electric charge
is treated as a continuum
of charge distributed over a region of space (either a volume or an area) rather than distinct point-like charges. This model typically applies when charge carriers have been emitted from some region of a solid—the cloud of emitted carriers can form a space charge region if they are sufficiently spread out, or the charged atoms or molecules left behind in the solid can form a space charge region. Space charge usually only occurs in dielectric
media (including vacuum
) because in a conductive medium the charge tends to be rapidly neutralized or screened
. The sign of the space charge can be either negative or positive. This situation is perhaps most familiar in the area near a metal
object when it is heated to incandescence
in a vacuum
. This effect was first observed by Thomas Edison
in light bulb filaments, where it is sometimes called the Edison effect, but space charge is a significant phenomenon in many vacuum and solid-state electronic devices.
s to "boil" away from the surface atom
s and surround the metal object in a cloud of free electrons. This is called thermionic emission
. The resulting cloud is negatively charged, and can be attracted to any nearby positively charged object, thus producing an electrical current which passes through the vacuum.
Space charge can result from a range of phenomena, but the most important are:
It has been suggested that in AC
most carriers injected at electrodes during a half of cycle
are ejected during the next half cycle, so the net balance of charge on a cycle is practically
zero. However, a small fraction of the carriers can be trapped at levels deep enough to
retain them when the field is inverted. The amount of charge in AC should increase slower
than in DC
and become observable after longer periods of time.
opposite to that of neighboring electrode, and homo charge is the reverse situation.
Under high voltage application, a hetero charge near the electrode is expected to reduce the
breakdown voltage, whereas a homo charge will increase it. After polarity reversal under ac
conditions, the homo charge is converted to hetero space charge.
" has a pressure
of 10-6 mmHg or less, the main vehicle
of conduction is electron
s. The emission current density (J) from the cathode
, as a function
of its thermodynamic temperature
T, in the absence of space-charge, is given by:
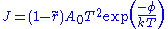
where
The reflection coefficient can be as low as 0.105 but is usually near 0.5. For Tungsten
, (1 - ř)A0 = 0.6 to 1.0 × 106 A m-2 K-2, and φ = 4.52 eV. At 2500 °C, the emission is 3000 A/m2.
The emission current as given above is many times greater than that normally collected by the electrodes, except in some pulse
d valves such as the cavity magnetron
. Most of the electrons emitted by the cathode are driven back to it by the repulsion
of the cloud
of electrons in its neighborhood. This is called the space charge effect. In the limit of large current densities, J is given by the Child-Langmuir equation below, rather than by the thermionic emission equation above.
s. This has at times made life harder or easier for electrical engineers who used tubes in their designs. For example, space charge significantly limited the practical application of triode
amplifier
s which led to further innovations such as the vacuum tube tetrode
.
On the other hand, space charge was useful in some tube applications because it generates a negative EMF
within the tube's envelope, which could be used to create a negative bias on the tube's grid. Grid bias could also be achieved by using an applied grid voltage in addition to the control voltage. This could improve the engineer's control and fidelity of amplification.
Space charges can also occur within dielectric
s. For example, when gas near a high voltage electrode begins to undergo dielectric breakdown, electrical charges are injected into the region near the electrode, forming space charge regions in the surrounding gas. Space charges can also occur within solid or liquid dielectrics that are stressed by high electric fields. Trapped space charges within solid dielectrics are often a contributing factor leading to dielectric failure within high voltage power cables and capacitors.
 Also known as the Child-Langmuir Law or the Three-Halves Power Law, Child's Law states that the space-charge limited current in a plane-parallel diode varies directly as the three-halves power of the anode voltage
Also known as the Child-Langmuir Law or the Three-Halves Power Law, Child's Law states that the space-charge limited current in a plane-parallel diode varies directly as the three-halves power of the anode voltage  and inversely as the square of the distance
and inversely as the square of the distance 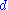 separating the cathode and the anode. That is,
separating the cathode and the anode. That is,
 .
.
Where is the anode current,
is the anode current,  the current density, and
the current density, and  the anode surface inner area. This assumes the following:
the anode surface inner area. This assumes the following:
The assumption of no scattering (ballistic transport) is what makes the predictions of Child-Langmuir Law different from those of Mott-Gurney Law. The latter assumes steady-state drift transport and therefore strong scattering.
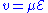
Where is the applied electric field,
is the applied electric field,  is the carrier mobility, and
is the carrier mobility, and  is the carrier velocity. If the current is limited by the drift component of inject carriers, the space-charge-limited conduction current density
is the carrier velocity. If the current is limited by the drift component of inject carriers, the space-charge-limited conduction current density  can be written as
can be written as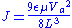
where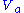 is the applied voltage, and
is the applied voltage, and 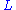 is the length of the plane-parallel sample. This expression is known as the Mott-Gurney law.
is the length of the plane-parallel sample. This expression is known as the Mott-Gurney law.
In the velocity-saturation regime, this equation takes the following form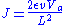
Note the different dependence of on
on  in each of the two cases. Interestingly, in the ballistic case (assuming no collisions), the Mott-Gurney equation takes the form of the more familiar Child-Langmuir law.
in each of the two cases. Interestingly, in the ballistic case (assuming no collisions), the Mott-Gurney equation takes the form of the more familiar Child-Langmuir law.
It should be noted that the above derivations make the following assumptions:
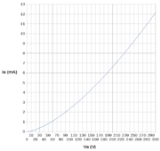
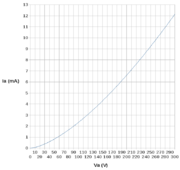
As an application example, the steady-state space-charge-limited current across a piece of silicon with a charge carrier mobility of 1500 cm2/V-s, a dielectric constant of 11.9, an area of 10-8cm2 and a thickness of 10-4cm can be calculated by an on line calculator as 126.4mA at voltage 3V.
. Electrons (and positive charge
carriers) come with their own built-in negative feedback
.
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
is treated as a continuum
Continuum mechanics
Continuum mechanics is a branch of mechanics that deals with the analysis of the kinematics and the mechanical behavior of materials modelled as a continuous mass rather than as discrete particles...
of charge distributed over a region of space (either a volume or an area) rather than distinct point-like charges. This model typically applies when charge carriers have been emitted from some region of a solid—the cloud of emitted carriers can form a space charge region if they are sufficiently spread out, or the charged atoms or molecules left behind in the solid can form a space charge region. Space charge usually only occurs in dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
media (including vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
) because in a conductive medium the charge tends to be rapidly neutralized or screened
Electric field screening
Screening is the damping of electric fields caused by the presence of mobile charge carriers. It is an important part of the behavior of charge-carrying fluids, such as ionized gases and conduction electrons in semiconductors and metals....
. The sign of the space charge can be either negative or positive. This situation is perhaps most familiar in the area near a metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
object when it is heated to incandescence
Incandescence
Incandescence is the emission of light from a hot body as a result of its temperature. The term derives from the Latin verb incandescere, to glow white....
in a vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
. This effect was first observed by Thomas Edison
Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices that greatly influenced life around the world, including the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and a long-lasting, practical electric light bulb. In addition, he created the world’s first industrial...
in light bulb filaments, where it is sometimes called the Edison effect, but space charge is a significant phenomenon in many vacuum and solid-state electronic devices.
Physical explanation
When a metal object is placed in a vacuum and is heated to incandescence, the energy is sufficient to cause electronElectron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s to "boil" away from the surface atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s and surround the metal object in a cloud of free electrons. This is called thermionic emission
Thermionic emission
Thermionic emission is the heat-induced flow of charge carriers from a surface or over a potential-energy barrier. This occurs because the thermal energy given to the carrier overcomes the binding potential, also known as work function of the metal. The charge carriers can be electrons or ions, and...
. The resulting cloud is negatively charged, and can be attracted to any nearby positively charged object, thus producing an electrical current which passes through the vacuum.
Space charge can result from a range of phenomena, but the most important are:
- Combination of the current density and spatially inhomogeneous resistance
- Ionization of species within the dielectric to form heterocharge
- Charge injection from electrodes and from a stress enhancement
- Polarization in structures such as water trees
It has been suggested that in AC
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
most carriers injected at electrodes during a half of cycle
are ejected during the next half cycle, so the net balance of charge on a cycle is practically
zero. However, a small fraction of the carriers can be trapped at levels deep enough to
retain them when the field is inverted. The amount of charge in AC should increase slower
than in DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
and become observable after longer periods of time.
Hetero and Homo Charge
Hetero charge means that the polarity of the space charge isopposite to that of neighboring electrode, and homo charge is the reverse situation.
Under high voltage application, a hetero charge near the electrode is expected to reduce the
breakdown voltage, whereas a homo charge will increase it. After polarity reversal under ac
conditions, the homo charge is converted to hetero space charge.
Mathematical explanation
If the "vacuumVacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
" has a pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
of 10-6 mmHg or less, the main vehicle
Vehicle
A vehicle is a device that is designed or used to transport people or cargo. Most often vehicles are manufactured, such as bicycles, cars, motorcycles, trains, ships, boats, and aircraft....
of conduction is electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s. The emission current density (J) from the cathode
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
, as a function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
of its thermodynamic temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
T, in the absence of space-charge, is given by:
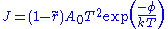
where
- A0 =
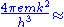 1.2 × 106 A m-2 K-2
1.2 × 106 A m-2 K-2 - e = elementary positive charge (i.e., magnitude of electron charge),
- m = electron mass,
- k = Boltzmann's constant = 1.38 x 10-23J/K,
- h = Planck's constant = 6.55 x 10-34 J s,
- φ = work functionWork functionIn solid-state physics, the work function is the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point immediately outside the solid surface...
of the cathode, - ř = mean electron reflection coefficient.
The reflection coefficient can be as low as 0.105 but is usually near 0.5. For Tungsten
Tungsten
Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as...
, (1 - ř)A0 = 0.6 to 1.0 × 106 A m-2 K-2, and φ = 4.52 eV. At 2500 °C, the emission is 3000 A/m2.
The emission current as given above is many times greater than that normally collected by the electrodes, except in some pulse
Pulse
In medicine, one's pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the heartbeat by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed against a bone, such as at the neck , at the wrist , behind the knee , on the inside of the elbow , and near the...
d valves such as the cavity magnetron
Cavity magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube that generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field. The 'resonant' cavity magnetron variant of the earlier magnetron tube was invented by John Randall and Harry Boot in 1940 at the University of...
. Most of the electrons emitted by the cathode are driven back to it by the repulsion
Repulsion
Repulsion is a 1965 British psychological thriller film directed by Roman Polanski, based on a scenario by Gérard Brach and Roman Polanski. It was Polanski's first English language film, and was shot in Britain, as such being his second film made outside his native Poland. The cast includes...
of the cloud
Cloud
A cloud is a visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals made of water and/or various chemicals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of a planetary body. They are also known as aerosols. Clouds in Earth's atmosphere are studied in the cloud physics branch of meteorology...
of electrons in its neighborhood. This is called the space charge effect. In the limit of large current densities, J is given by the Child-Langmuir equation below, rather than by the thermionic emission equation above.
Occurrence
Space charge is an inherent property of all vacuum tubeVacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
s. This has at times made life harder or easier for electrical engineers who used tubes in their designs. For example, space charge significantly limited the practical application of triode
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplification device having three active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a vacuum tube with three elements: the filament or cathode, the grid, and the plate or anode. The triode vacuum tube was the first electronic amplification device...
amplifier
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
s which led to further innovations such as the vacuum tube tetrode
Tetrode
A tetrode is an electronic device having four active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a two-grid vacuum tube. It has the three electrodes of a triode and an additional screen grid which significantly changes its behaviour.-Control grid:...
.
On the other hand, space charge was useful in some tube applications because it generates a negative EMF
Electromotive force
In physics, electromotive force, emf , or electromotance refers to voltage generated by a battery or by the magnetic force according to Faraday's Law, which states that a time varying magnetic field will induce an electric current.It is important to note that the electromotive "force" is not a...
within the tube's envelope, which could be used to create a negative bias on the tube's grid. Grid bias could also be achieved by using an applied grid voltage in addition to the control voltage. This could improve the engineer's control and fidelity of amplification.
Space charges can also occur within dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
s. For example, when gas near a high voltage electrode begins to undergo dielectric breakdown, electrical charges are injected into the region near the electrode, forming space charge regions in the surrounding gas. Space charges can also occur within solid or liquid dielectrics that are stressed by high electric fields. Trapped space charges within solid dielectrics are often a contributing factor leading to dielectric failure within high voltage power cables and capacitors.
Child's Law

 and inversely as the square of the distance
and inversely as the square of the distance 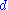 separating the cathode and the anode. That is,
separating the cathode and the anode. That is, .
.Where
 is the anode current,
is the anode current,  the current density, and
the current density, and  the anode surface inner area. This assumes the following:
the anode surface inner area. This assumes the following:
- The electrodes are planar, parallel, equipotential surfaces of infinite dimensions.
- Electrons travel ballistically between electrodes (i.e., no scattering).
- The electrons have zero velocity at the cathode surface.
- In the interelectrode region, only electrons are present.
- The current is space-charge limited.
- The anode voltage remains constant for a sufficiently long time so that the anode current is steady.
The assumption of no scattering (ballistic transport) is what makes the predictions of Child-Langmuir Law different from those of Mott-Gurney Law. The latter assumes steady-state drift transport and therefore strong scattering.
Mott-Gurney Law
In the low-field regime, velocity of injected carriers can be represented by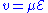
Where
 is the applied electric field,
is the applied electric field,  is the carrier mobility, and
is the carrier mobility, and  is the carrier velocity. If the current is limited by the drift component of inject carriers, the space-charge-limited conduction current density
is the carrier velocity. If the current is limited by the drift component of inject carriers, the space-charge-limited conduction current density  can be written as
can be written as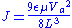
where
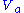 is the applied voltage, and
is the applied voltage, and 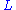 is the length of the plane-parallel sample. This expression is known as the Mott-Gurney law.
is the length of the plane-parallel sample. This expression is known as the Mott-Gurney law.In the velocity-saturation regime, this equation takes the following form
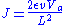
Note the different dependence of
 on
on  in each of the two cases. Interestingly, in the ballistic case (assuming no collisions), the Mott-Gurney equation takes the form of the more familiar Child-Langmuir law.
in each of the two cases. Interestingly, in the ballistic case (assuming no collisions), the Mott-Gurney equation takes the form of the more familiar Child-Langmuir law.It should be noted that the above derivations make the following assumptions:
- There is only one type of charge carrier present.
- The material has no intrinsic conductivity, but charges are injected into it from one electrode and captured by the other.
- The carrier mobility
 and the dielectric permittivity
and the dielectric permittivity  are constant throughout the sample.
are constant throughout the sample. - The electric field at the charge-injecting cathode is zero.
As an application example, the steady-state space-charge-limited current across a piece of silicon with a charge carrier mobility of 1500 cm2/V-s, a dielectric constant of 11.9, an area of 10-8cm2 and a thickness of 10-4cm can be calculated by an on line calculator as 126.4mA at voltage 3V.
Shot noise
Space charge tends to reduce shot noiseShot noise
Shot noise is a type of electronic noise that may be dominant when the finite number of particles that carry energy is sufficiently small so that uncertainties due to the Poisson distribution, which describes the occurrence of independent random events, are of significance...
. Electrons (and positive charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
carriers) come with their own built-in negative feedback
Feedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
.

