Skull fracture
Encyclopedia
Human skull
The human skull is a bony structure, skeleton, that is in the human head and which supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.In humans, the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones...
usually occurring as a result of blunt force trauma. If the force of the impact is excessive the bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
may fracture at or near the site of the impact. The force of direct impact may cause damage to the underlying physical structures contained within the skull such as the membranes
Meninges
The meninges is the system of membranes which envelopes the central nervous system. The meninges consist of three layers: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges and of the cerebrospinal fluid is to protect the central nervous system.-Dura...
, blood vessels, and brain
Human brain
The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
, even in the absence of a fracture. While an uncomplicated skull fracture can occur without associated physical or neurological damage and is in itself usually not clinically significant, a fracture in healthy bone indicates that a substantial amount of force has been applied and increases the possibility of associated injury
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury , also known as intracranial injury, occurs when an external force traumatically injures the brain. TBI can be classified based on severity, mechanism , or other features...
. Any significant blow to the head results in a concussion, with or without loss of consciousness
Consciousness
Consciousness is a term that refers to the relationship between the mind and the world with which it interacts. It has been defined as: subjectivity, awareness, the ability to experience or to feel, wakefulness, having a sense of selfhood, and the executive control system of the mind...
.
A fracture which occurs in conjunction with an overlying laceration which tears the epidermis and the meninges
Meninges
The meninges is the system of membranes which envelopes the central nervous system. The meninges consist of three layers: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges and of the cerebrospinal fluid is to protect the central nervous system.-Dura...
or runs through the paranasal sinuses and the middle ear
Middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear internal to the eardrum, and external to the oval window of the cochlea. The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles, which couple vibration of the eardrum into waves in the fluid and membranes of the inner ear. The hollow space of the middle ear has...
structures, resulting in the outside environment being in contact with the cranial cavity is termed a compound fracture. Compound fractures may either be clean or contaminated.
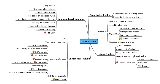
There are four major types of skull fractures; linear fractures which are the most common and usually require no intervention for the fracture itself, depressed fractures which are usually comminuted
Bone fracture
A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a break in the continuity of the bone...
with broken portions of bone displaced inward may require surgical intervention if there is underlying tissue damage, diastatic fractures in which the sutures of the skull widen usually affects children under three, and basilar fractures which occur in the bones at the base of the skull.
Linear fracture
Linear skull fractures are breaks in the bone that transverse the full thickness of the skull from the outer to inner table, are usually fairly straight and involve no displacement of the bone. The common method of injury is blunt force trauma in which the energy from the blow is transferred over a wide surface area of the skull.Linear fractures of the skull are usually of little clinical significance unless they parallel in close proximity or transverse a suture, or they involve a venous sinus groove or vascular channel. The resulting complications may include suture diastasis
Diastasis (pathology)
In pathology, diastasis is the separation of parts of the body that are normally joined together, such as the separation of certain abdominal muscles during pregnancy, or of adjacent bones without fracture.-See also:* Diastasis recti...
, venous sinus thrombosis, and epidural hematoma
Epidural hematoma
Epidural or extradural hematoma is a type of traumatic brain injury in which a buildup of blood occurs between the dura mater and the skull. The dura mater also covers the spine, so epidural bleeds may also occur in the spinal column...
. In young children although rare the possibility exists of developing a growing skull fracture especially if the fracture occurs in the parietal bone
Parietal bone
The parietal bones are bones in the human skull which, when joined together, form the sides and roof of the cranium. Each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four borders, and four angles. It is named from the Latin pariet-, wall....
.
Depressed skull fracture
A depressed skull fracture is a type of fracture usually resulting from blunt force trauma, such as getting struck with a hammer, rock or getting kicked in the head. These types of fractures, which occur in 11% of severe head injuries, are comminuted fractures in which broken bones are displaced inward. Depressed skull fractures carry a high risk of increased pressure on the brainIntracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
, crushing the delicate tissue.
Compound depressed skull fractures occur when there is a laceration over the fracture, resulting in the internal cranial cavity being in contact with the outside environment increasing the risk of contamination and infection. Complex depressed fractures are those in which the dura mater
Dura mater
The dura mater , or dura, is the outermost of the three layers of the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is derived from Mesoderm. The other two meningeal layers are the pia mater and the arachnoid mater. The dura surrounds the brain and the spinal cord and is responsible for...
is torn. Depressed skull fractures may require surgery
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery is the medical specialty concerned with the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spine, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and extra-cranial cerebrovascular system.-In the United States:In...
to lift the bones off the brain if they are placing pressure on it.
Diastatic skull fracture
Diastatic fractures occur when the fracture line transversesone or more sutures of the skull causing a widening of the suture. While this type of fracture is usually seen in infants and young children as the sutures are not yet fused it can also occur in adults. When a diastatic fracture occurs in adults it usually affects the lamboidal suture as this suture does not fully fuse in adults until about the age of 60.
Diastatic fractures can occur with different types of fractures and it is also possible for diastasis of the cranial sutures to occur without a concomitant fracture. Sutural diastasis may also occur in various congenital disorders such as cleidocranial dysplasia and osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta is a genetic bone disorder. People with OI are born with defective connective tissue, or without the ability to make it, usually because of a deficiency of Type-I collagen...
.
Basilar skull fracture
Basilar skull fractureBasilar skull fracture
A basilar skull fracture is a fracture of the base of the skull, typically involving the temporal bone, occipital bone, sphenoid bone, and/or ethmoid bone....
s, breaks in bones at the base of the skull, require more force to cause than cranial vault fractures. Thus they are rare, occurring as the only fracture in only 4% of severe head injury patients.
Basilar fractures have characteristic signs: blood in the sinuses
Paranasal sinus
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity , above and between the eyes , and behind the ethmoids...
; a clear fluid called cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid , Liquor cerebrospinalis, is a clear, colorless, bodily fluid, that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord...
(CSF) leaking from the nose (rhinorrhea
Rhinorrhea
Rhinorrhea or rhinorrhoea is a condition where the nasal cavity is filled with a significant amount of mucous fluid. The condition, commonly known as "runny nose", occurs relatively frequently and is not usually considered dangerous. Rhinorrhea is a common symptom of allergies or certain diseases,...
) or ears (otorrhea); periorbital ecchymosis
Ecchymosis
An ecchymosis is the medical term for a subcutaneous purpura larger than 1 centimeter or a hematoma, commonly called a bruise. It can be located in the skin or in a mucous membrane.-Presentation:...
or "raccoon eyes
Raccoon eyes
Raccoon eyes or periorbital ecchymosis is a sign of basal skull fracture, a craniotomy that ruptured the meninges, or certain cancers. Bilateral subconjunctival hemorrhage occurs when damage at the time of a facial fracture tears the meninges and causes the venous sinuses to bleed into the...
" (bruising of the orbits of the eyes that result from blood collecting there as it leaks from the fracture site); and retroauricular
Ear
The ear is the organ that detects sound. It not only receives sound, but also aids in balance and body position. The ear is part of the auditory system....
ecchymosis or "Battle's sign
Battle's sign
In medical terminology, Battle's sign, also mastoid ecchymosis, is an indication of fracture of middle cranial fossa of the skull, and may suggest underlying brain trauma. Battle's sign consists of bruising over the mastoid process, as a result of extravasation of blood along the path of the...
" (caused when blood collects behind the ears and causes bruising).
Growing skull fracture
A growing skull fracture (GSF) also known as a craniocerebral erosion or leptomeningeal cyst due to the usual development of a cystic mass filled with cerebral spinal fluid is a rare complication of head injury usually associated with linear skull fractures of the parietal bone in children under 3. It has been reported in older children in atypical regions of the skull such as the basiooccipital and the base of the skull base and in association with other types of skull fractures. It is characterized by a diastatic enlargement of the fracture.There are various factors associated with the development of a GSF with the primary causitive factor being a tear in the dura mater
Dura mater
The dura mater , or dura, is the outermost of the three layers of the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is derived from Mesoderm. The other two meningeal layers are the pia mater and the arachnoid mater. The dura surrounds the brain and the spinal cord and is responsible for...
. The skull fracture enlarges due in part to the rapid physiologic growth of the brain which occurs in young children and brain cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid , Liquor cerebrospinalis, is a clear, colorless, bodily fluid, that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord...
(CSF) pulsations in the underlying leptomenigeal
Leptomeninges
In medicine, leptomeninges is a term used to refer to the pia mater and arachnoid mater, two of the membranes that surround the brain and the spinal cord....
cyst
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct membrane and division on the nearby tissue. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst could go away on its own or may have to be removed through surgery.- Locations :* Acne...
ic mass.
Cranial burst skull fracture
A cranial burst skull fracture usually occurring with severe injuries in infants less than 1 year of age is a closed, diastatic skull fracture with cerebral extrusion beyond the outer table of the skull under the intact scalpScalp
The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the face anteriorly and the neck to the sides and posteriorly.-Layers:It is usually described as having five layers, which can conveniently be remembered as a mnemonic:...
.
Acute scalp swelling is associated with this type of fracture. In equivacal cases without immediate scalp swelling the diagnosis may be made via the use of Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
thus insuring more prompt treatment and avoiding the development of a "growing skull fracture".
Compound skull fracture
A fracture which occurs in conjunction with an overlying laceration which tears the epidermis and the meningesMeninges
The meninges is the system of membranes which envelopes the central nervous system. The meninges consist of three layers: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges and of the cerebrospinal fluid is to protect the central nervous system.-Dura...
or runs through the paranasal sinuses and the middle ear
Middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear internal to the eardrum, and external to the oval window of the cochlea. The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles, which couple vibration of the eardrum into waves in the fluid and membranes of the inner ear. The hollow space of the middle ear has...
structures, resulting in the outside environment being in contact with the cranial cavity is termed a compound fracture.
Compound fractures may either be clean or contaminated. Intracranial air (pneumocephalus
Pneumocephalus
Pneumocephalus is the presence of air or gas within the cranial cavity. It is usually associated with disruption of the skull: after head and facial trauma, tumors of the skull base, after neurosurgery or otorhinolaryngology, and rarely, spontaneously...
) may occur in compound skull fractures.
The most serious complication of compound skull fractures is infection. Increased risk factors for infection include visible contamination, meningeal tear, loose bone fragments and presenting for treatment more than eight hours after initial injury.
Compound elevated skull fracture
case of blunt force trauma, a rotation of the skull while striking an inanimate object as in a fall or it may occur during transfer of a patient after the initial compound head injury.Neurological deficits in skull fractures
The presence of a concussion or skull fracture in trauma patients without intracranial hemorrhage or focal neurologic deficitsFocal neurologic signs
Focal neurologic signs also known as focal neurological deficits or focal CNS signs are impairments of nerve, spinal cord, or brain function that affects a specific region of the body, e.g...
was indicated in long term cognitive impairments and emotional lability at nearly double the rate as those patients without either complication.
In a study of emergency room patients suspected of having suffered closed head injuries, neuropsychological testing and computerized tomography (CT) scans came back with normal results. The patients did not differ in Closed head injury
Closed head injury
Closed head injuries are a type of Traumatic Brain Injury in which the skull and dura mater remain intact. Closed head injuries are the leading cause of death in children under 4 years old and the most common cause of physical disability and cognitive impairment in young people...
(CHI) scores as measured by the Glasgow Coma Scale
Glasgow Coma Scale
Glasgow Coma Scale or GCS is a neurological scale that aims to give a reliable, objective way of recording the conscious state of a person for initial as well as subsequent assessment...
(GCS).
Those with a skull fracture were shown to have "neuropsychological dysfunction, even in the absence of intracranial pathology or more severe disturbance of consciousness on the GCS".
See also
- Le Fort facial fracture
- Facial fractureFacial traumaFacial trauma, also called maxillofacial trauma, is any physical trauma to the face. Facial trauma can involve soft tissue injuries such as burns, lacerations and bruises, or fractures of the facial bones such as nasal fractures and fractures of the jaw, as well as trauma such as eye injuries...
- Mandibular fractureMandibular fractureMandibular fracture also known as fractures of the jaw are breaks though the mandibular bone. They usually occur due to trauma and are often associated with other facial trauma....

