
Sailcloth
Encyclopedia

Flax
Flax is a member of the genus Linum in the family Linaceae. It is native to the region extending from the eastern Mediterranean to India and was probably first domesticated in the Fertile Crescent...
(linen
Linen
Linen is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant, Linum usitatissimum. Linen is labor-intensive to manufacture, but when it is made into garments, it is valued for its exceptional coolness and freshness in hot weather....
), hemp
Hemp
Hemp is mostly used as a name for low tetrahydrocannabinol strains of the plant Cannabis sativa, of fiber and/or oilseed varieties. In modern times, hemp has been used for industrial purposes including paper, textiles, biodegradable plastics, construction, health food and fuel with modest...
or cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
in various forms including canvas
Canvas
Canvas is an extremely heavy-duty plain-woven fabric used for making sails, tents, marquees, backpacks, and other items for which sturdiness is required. It is also popularly used by artists as a painting surface, typically stretched across a wooden frame...
. However, modern sails are rarely made from natural fibers. Most sails are made from synthetic fibers ranging from low-cost nylon
Nylon
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers known generically as polyamides, first produced on February 28, 1935, by Wallace Carothers at DuPont's research facility at the DuPont Experimental Station...
or polyester
Polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers which contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Although there are many polyesters, the term "polyester" as a specific material most commonly refers to polyethylene terephthalate...
to expensive aramids or carbon fiber
Carbon fiber
Carbon fiber, alternatively graphite fiber, carbon graphite or CF, is a material consisting of fibers about 5–10 μm in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded together in crystals that are more or less aligned parallel to the long axis of the fiber...
s. Recent strides in technology now offer many options for the sailmaker.
History

Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
for cloth, which was evolved into the English word “duck” in reference to sail canvas. Duck
Cotton duck
Cotton duck , also simply duck, sometimes duck cloth or duck canvas, commonly called "canvas" outside the textile industry, is a heavy, plain woven cotton fabric...
was typically made from cotton or linen (flax), with some use of hemp. These natural fibers have poor resistance to rot, UV light and water absorption. Linen is stronger, but cotton is lighter. Linen was the traditional fiber of sails until it was supplanted by cotton during the 19th century. At first cotton was used as a matter of necessity in the United States as it was indigenous and the supply of flax was periodically interrupted by wars such as the War of 1812
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
, during which demand for sailcloth for military use was high. As sail size grew linen was too heavy to be practical so cotton became more popular. Cotton did not substantially replace linen worldwide until the end of the age of sail; however, in some cases the strength of linen was preferred for some types of sails. It was not until the late 20th century that natural fibers were replaced by synthetics in mainstream use. Cotton sailcloth is still used for sportswear, upholstery and draperies. The traditional width for carded cotton sailcloth in the US was 23 inches (58 cm) while the British standard was 24 inches (61 cm).
Modern Fibers
The characteristics of a sail are due to design, construction and the attributes of the fibers, which are woven together to make the sail cloth. The following sections discuss the attributes of fibers assuming a good design and careful construction. There are six key factors in evaluating a fiber for suitability in weaving a sail-cloth:- Modulus (of elasticity)Elastic modulusAn elastic modulus, or modulus of elasticity, is the mathematical description of an object or substance's tendency to be deformed elastically when a force is applied to it...
: elastic stretch resistance per cross sectional area of fibre, analogous to the stiffness in a spring. Higher is better for upwind sails. - Tensile strengthTensile strengthUltimate tensile strength , often shortened to tensile strength or ultimate strength, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before necking, which is when the specimen's cross-section starts to significantly contract...
or tenacity: breaking strength, measured as a force per cross sectional area of fibre. Higher is better for sails. - Creep, which describes the long term stretch of a fiber or fabric. A material with creep may have a superior modulus, but lose its shape over time.
- UV (ultra violet) Resistance: strength loss from exposure to the Sun’s UV rays measured by a standardized exposure test.
- Flex Loss: Strength lost due to bending, folding, or flogging, which is frequently measured with an industry standard 50 fold test.
- Cost of the material
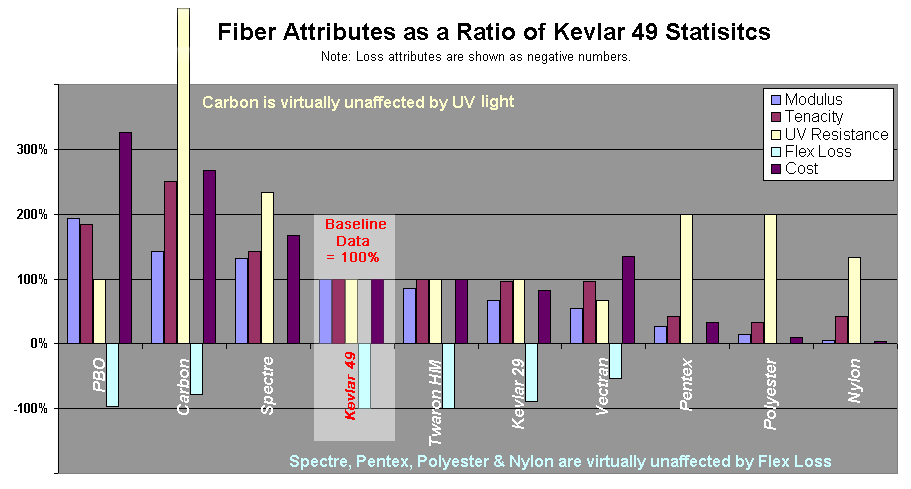
There is no perfect solution since in most cases the increase of one attribute generally results in the decreased attractiveness of another. Reduced stretch generally also reduces the flexibility causing a trade-off of performance for durability. Solving both problems generally sends the price out of range for most sailors.
Nylon

Nylon
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers known generically as polyamides, first produced on February 28, 1935, by Wallace Carothers at DuPont's research facility at the DuPont Experimental Station...
is used in spinnaker
Spinnaker
A spinnaker is a special type of sail that is designed specifically for sailing off the wind from a reaching course to a downwind, i.e. with the wind 90°–180° off the bow. The spinnaker fills with wind and balloons out in front of the boat when it is deployed, called flying. It is constructed of...
s because of its light weight, high tensile strength, superior abrasion resistance and flexibility. However, it has a low modulus allowing too much stretch to be suitable for upwind sails. Nylon is more susceptible to UV and chemical degradation than polyesters and its physical properties can change due to moisture absorption.
Polyester (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalatePolyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate , commonly abbreviated PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P, is a thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in synthetic fibers; beverage, food and other liquid containers; thermoforming applications; and engineering resins often in combination...
, the most common type of polyester
Polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers which contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Although there are many polyesters, the term "polyester" as a specific material most commonly refers to polyethylene terephthalate...
, is the most common fiber used in sailcloth; it is also commonly referred to by the brand name Dacron. PET has excellent resiliency, high abrasion resistance, high UV resistance, high flex strength and low cost. Low absorbency allows the fiber to dry quickly. PET has been replaced by stronger fibers for most serious racing applications, but remains the most popular sail cloth due to lower price and high durability. Dacron is the brand name of Dupont’s Type 52 high modulus fiber made specifically for sailcloth. Allied Signal has produced a fiber called 1W70 polyester that has a 27% higher tenacity than Dacron. Other trade names include Terylene, Tetoron, Trevira and Diolen.
PEN fiber (Pentex)
PEN (Polyethylene naphthalatePolyethylene naphthalate
Polyethylene naphthalate Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) (Poly(ethylene 2,6-naphthalate) is a polyester with good barrier properties (even better than Polyethylene terephthalate). Because it provides a very good oxygen barrier, it is particularly well-suited for...
), commonly known by Honeywell's trade name "Pentex", is another kind of polyester fiber, which stretches only 40% as much as standard PET fibers, but about twice as much as Kevlar 29. Because it only shrinks about a third as much as a good PET, PEN can not be woven as tightly; thus, woven PEN must be impregnated with resin making sails prone to damage from improper use and handling. PEN is better suited for making laminated sailcloth, where the fibers are laid straight for strength and are bonded to sheets of film for stability (e.g., PET film
PET film (biaxially oriented)
BoPET is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties and electrical insulation.A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other...
often called by one of its trade names Mylar), or as a taffeta
Taffeta
Taffeta is a crisp, smooth plain woven fabric made from silk or synthetic fibers. The word is Persian in origin, and means "twisted woven." It is considered to be a "high end" fabric, suitable for use in ball gowns, wedding dresses, and in interiors for curtains or wallcovering. There are two...
outer layer of a laminate, protecting a PET film. PEN laminates are an economical alternative for higher performance sail.
Kevlar

Kevlar
Kevlar is the registered trademark for a para-aramid synthetic fiber, related to other aramids such as Nomex and Technora. Developed at DuPont in 1965, this high strength material was first commercially used in the early 1970s as a replacement for steel in racing tires...
, an aramid
Aramid
Aramid fibers are a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers. They are used in aerospace and military applications, for ballistic rated body armor fabric and ballistic composites, in bicycle tires, and as an asbestos substitute. The name is a portmanteau of "aromatic polyamide"...
fiber, has become the predominant fiber for racing sails, since it was introduced by DuPont in 1971. It is stronger, has a higher strength to weight ratio than steel, and has a modulus that is five times greater than PET, and about twice as high as PEN. There are two popular types of Kevlar: Type 29 and Type 49, the latter having a 50% higher initial modulus than Type 29 but a lower flex loss. DuPont
DuPont
E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company , commonly referred to as DuPont, is an American chemical company that was founded in July 1802 as a gunpowder mill by Eleuthère Irénée du Pont. DuPont was the world's third largest chemical company based on market capitalization and ninth based on revenue in 2009...
has developed higher modulus Types 129, 149 and 159, but these have seen little use in sails, since generally as the modulus increases the flex strength decreases. DuPont has recently introduced Kevlar Edge, a fiber developed specifically for sails with 25% higher flex strength and a higher modulus than Kevlar 49.
Kevlar, along with other aramid fibers, have poor UV resistance (Kevlar loses strength roughly twice as quickly in sunlight as PET) and rapid loss of strength with flexing, folding and flogging. Minimal flogging and careful handling can greatly extend the life of a Kevlar sail.
Technora
TechnoraTechnora
Technora is an Aramid that is useful for a variety of applications that require high strength or chemical resistance. It is a brandname of the company Teijin.-Production:...
is an aramid, which is produced in Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
by Teijin
Teijin
is a Japanese chemical and pharmaceutical company. It is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange with a market capitalisation of USD 3.9 billion. It operates in five main business segments: synthetic fibres; films and plastics; pharmaceuticals and home health care; trading and retail; and IT and new...
, has a slightly lower modulus strength than Kevlar 29 but a slightly higher resistance to flex fatigue. The fiber’s lower UV resistance is enhanced by dying the naturally gold fiber black. Technora is most often used as bias support (X-ply) in laminate sailcloth.
Twaron
TwaronTwaron
Twaron is the brandname of Teijin Aramid for a para-aramid. It is a heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibre developed in the early 1970s by the Dutch company AKZO, division Enka, later Akzo Industrial Fibers. The research name of the para-aramid fibre was originally Fiber X, but it was soon...
is an aramid, which is produced in The Netherlands by Teijin, is chemically and physically similar to DuPont’s Kevlar. Twaron HM (High modulus) has similar stretch properties to Kevlar 49, greater tensile strength and better UV resistance. Twaron SM is similar to Kevlar 29. Like Kevlar, the fiber is a bright gold color.
Spectra
SpectraUltra high molecular weight polyethylene
Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene , also known as high-modulus polyethylene or high-performance polyethylene , is a subset of the thermoplastic polyethylene. It has extremely long chains, with molecular weight numbering in the millions, usually between 2 and 6 million...
is an ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) made by Honeywell
Honeywell
Honeywell International, Inc. is a major conglomerate company that produces a variety of consumer products, engineering services, and aerospace systems for a wide variety of customers, from private consumers to major corporations and governments....
, which offers superior UV resistance (on par with PET), very high initial modulus numbers (second only to high modulus Carbon Fiber), superior breaking strength, and high flex strength. However, it also exhibits permanent and continuous elongation under a sustained load (AKA: creep). This results in a change in shape as the sail ages. Because of this Spectra is only used in spinnakers on high performance boats where the sails are replaced regularly.
Dyneema
Equivalent to Spectra, Dyneema is the world's strongest fiber produced by the DutchNetherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
company DSM
DSM (company)
DSM is a multinational life sciences and materials sciences-based company. DSM's global end markets include food and dietary supplements, personal care, feed, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, automotive, paints, electrical and electronics, life protection, alternative energy and bio-based materials...
. It is often used by European sailcloth manufacturers, is available in a wider variety of yarn sizes than Spectra, and is growing in popularity. Dyneema DSK78 set a new standard combining the typical high strength to weight ratio, excellent low stretch, abrasion and UV resistance but added three times better creep performance compared to Dyneema SK75, and nearly two times better than Dyneema SK90.
Certran
Hoechst CelaneseCelanese
Celanese Corporation is a Fortune 500 global technology and specialty materials company with its headquarters in Dallas, Texas. The company is a leading producer of acetyl products, which are intermediate chemicals for nearly all major industries, and is the world's largest producer of vinyl...
produces Certran polyethylene
Polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene is the most widely used plastic, with an annual production of approximately 80 million metric tons...
similar to Spectra, with about one half the modulus rating of Spectra. It has similar properties to Spectra including superior resistance to flex fatigue and UV degradation but also exhibits creep.
Zylon (PBO)
PBO (Poly (p-phenylene-2, 6-benzobisoxazole)) is liquid crystal polymer developed by Japan-based Toyobo under the trade name ZylonZylon
Zylon is a trademarked name for a range of thermoset liquid crystalline polyoxazole...
. It is a gold fiber with an initial modulus that is significantly higher than other high modulus yarns, including aramids. Among PBO’s desirable properties are high thermal stability, low creep, high chemical resistance, high cut and abrasion resistance, and excellent resistance to stretch after repeated folding. PBO is also quite flexible and has a soft feel. But PBO’s has poor resistance to both UV and visible light.
Vectran

Vectran
Vectran is a manufactured fibre, spun from a liquid crystal polymer created by Celanese Acetate LLC and now manufactured by Kuraray Co., Ltd. Chemically it is an aromatic polyester produced by the polycondensation of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and 6-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxylic acid.- Properties...
is a polyester-based high performance LCP (liquid crystal polymer
Liquid crystal polymer
Liquid-crystal polymers are a class of aromatic polyester polymers. They are extremely unreactive and inert, and highly resistant to fire.-Background:...
) produced by Ticona. It is naturally gold in color and has a modulus similar to Kevlar 29, but has less strength loss with flex. This is a benefit in endurance applications and for cruising sails where durability is key. Additional advantages of Vectran fiber has a .02% creep at 30% of max load after 10000hrs, high chemical and abrasion resistance and high tensile strength. The UV endurance is inferior to PET and PEN, but the degradation levels off after roughly 400 hours of exposure, while the Aramids and Spectra continue to degrade.
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiberCarbon fiber
Carbon fiber, alternatively graphite fiber, carbon graphite or CF, is a material consisting of fibers about 5–10 μm in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded together in crystals that are more or less aligned parallel to the long axis of the fiber...
is a high modulus synthetic fiber made from carbon atoms. It is virtually unaffected by UV exposure and provides exceptionally low stretch. Variants can balance along a continuum from brittle with no-stretch to extreme durability/flexibility with only slightly more stretch than aramid sails.
Weaving
Combed singles yarn sailcloth in high counts is used for spinnaker and head sails. The count often is 148 by 160 and the fabric is finished at 40 inches (102 cm) wide with a weight of about 6.5 yds./lb (13.10 m/kg). The quality and weight of the weave can be more critical than the choice of fibers, since a poor weave can lead to high stretch and poor sail form. Weight is described in ounces, for example "an 8 oz. cloth". This means that an area of 28.5 inches x 36 inches weighs 8 ounces.Sailcloth is woven in two forms: balanced and unbalanced. The yarns in balanced cloth are the same diameter and weight in lengthwise (the “warp”) and across the width of the cloth (the “fill”). Unbalanced means a heavier yarn is used in one direction. Most moderns sails are “crosscut”, which is an unbalanced technique where the heavier yarns is in the fill. This allows greater loads to radiate up from the clew (back lower corner) along the leech (back edge). This is especially true of mainsails and high aspect jibs.
Woven sail cloths have an inherent problem with stretch resistance. In a weave the warp and fill yarns pass over and under one another. As load is applied the yarns attempt to straighten out, this results in the fabric stretching, commonly referred to as ‘crimp”. Ironically, fibers which are resistant to stretching, can not be woven as tightly as more flexible fibers such as PET, thus the cloth is more affected by crimp.
Films
Films are thin sheet material extruded from synthetic polymers and are typically used along with woven cloth in a laminate (see laminates below).PET
PET filmPET film (biaxially oriented)
BoPET is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties and electrical insulation.A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other...
is the most common film used in laminated sailcloth.
It is an extruded and biaxially oriented version of PET fiber. In the US and Britain, the most well-known trade names are Mylar and Melinex.
PEN Film
PEN film is extruded and biaxially oriented version of PEN fiber. Just as PEN fiber is stronger than PET fiber, PEN film is stronger than PET film. However, PEN film is rarely used in standard sailcloth styles because it shrinks more rapidly than PET, is less resistant to abuse, and reduces the working life of the sail.Scrim & Strands
Strands are combined from fibers; these are frequently narrow flat bands or ribbons of high strength material. Scrim is a loose weave or lattice of strands, typically bonded where they cross to maintain the grid pattern. Strands and scrims are used to strengthen or reinforce sailcloth (see laminates below).Laminated sailcloth
In the 1970s sailmakers began to laminate multiple materials with different characteristics to synergize the qualities of each. Using sheets of PET or PEN reduces stretch in all directions, where weaves are most efficient in the direction of the threadlines. Lamination also allow fibers to be placed in a straight, uninterrupted paths. There are four main construction styles:Woven-Film-Woven
Film is sandwiched in between two layers of woven taffetaTaffeta
Taffeta is a crisp, smooth plain woven fabric made from silk or synthetic fibers. The word is Persian in origin, and means "twisted woven." It is considered to be a "high end" fabric, suitable for use in ball gowns, wedding dresses, and in interiors for curtains or wallcovering. There are two...
, the film provides most of the stretch resistance and the taffeta enhances tear and abrasion resistance. The high-end versions of this method use a woven Spectra or Kevlar taffeta. In some newer styles, off threadline aramid yarns, are also laid into the laminate. In some cases the second layer of taffeta is eliminated for cost and weight savings
Film-Scrim-Film or Film-Insert-Film (Film-on-Film)
In this construction, a scrim or strands (inserts) are sandwiched between layers of film. Thus load-bearing members are laid straight, which maximizes the high modulus of the fibers, where a woven material will have some inherent stretch to the weave. Laminating film to film around the strands creates a very strong and dependable bond reducing the amount of adhesive needed. In high quality cloth, the strands or scrim are tensioned during the lamination process.The drawbacks are: film is not as abrasion or flex resistant as a weave, it does not protect the structural fibers from UV rays. In some cases UV protection is added.
Woven-Film-Scrim-Film-Woven
Woven fabric with high UV and abrasion protection is added to the Film-on-Film. This combines the best of the above, but is costly, heavy, and stiff. This is an attractive method to combine high modulus fibers with poor UV resistance.Woven/Scrim/Woven
Wovens on both sides of a scrim without the film layer. The problem is getting enough high modulus yarn into the sandwich, and still being able to get a good bond, because, dissimilar fabrics don’t often bond well. This technique is more experimental than practical, but may yield results in time.See also
- Sails
- CanvasCanvasCanvas is an extremely heavy-duty plain-woven fabric used for making sails, tents, marquees, backpacks, and other items for which sturdiness is required. It is also popularly used by artists as a painting surface, typically stretched across a wooden frame...
- PolyesterPolyesterPolyester is a category of polymers which contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Although there are many polyesters, the term "polyester" as a specific material most commonly refers to polyethylene terephthalate...
- Carbon fiberCarbon fiberCarbon fiber, alternatively graphite fiber, carbon graphite or CF, is a material consisting of fibers about 5–10 μm in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded together in crystals that are more or less aligned parallel to the long axis of the fiber...
- Aramids
- PET film (biaxially oriented)PET film (biaxially oriented)BoPET is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties and electrical insulation.A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other...
- Effort on sailEffort on sailUnderstanding the forces on sails is important for the design and operation of the sails and whatever they are moving, sailboats, ice boats, sailboards, land sailing vehicles or windmill sail rotors. When air moves past a sail, aerodynamic forces develop...

