Rhythm Method
Encyclopedia
Calendar-based methods are various methods of estimating a woman
's likelihood of fertility
, based on a record of the length of previous menstrual cycle
s. Various systems are known as the Knaus–Ogino Method, rhythm method, and Standard Days Method. These systems may be used to achieve pregnancy
, by timing unprotected intercourse for days identified as fertile, or to avoid pregnancy
, by restricting unprotected intercourse to days identified as infertile.
The first formalized calendar-based method was developed in 1930 by John Smulders, a Roman Catholic physician from the Netherlands
. It was based on knowledge of the menstrual cycle
. This method was independently discovered by Hermann Knaus (Austria), and Kyusaku Ogino
(Japan). This system was a main form of birth control available to Catholic couples for several decades, until the popularization of symptoms-based fertility awareness
methods. A new development in calendar-based methods occurred in 1999, when Georgetown University
introduced the Standard Days Method. The Standard Days Method is promoted in conjunction with a product called CycleBeads, a ring of colored beads which are meant to help the user keep track of her fertile and non-fertile days.
is usually used as a broad term that includes tracking basal body temperature
and cervical mucus as well as cycle length. The World Health Organization
considers the rhythm method to be a specific type of calendar-based method, and calendar-based methods to be only one form of fertility awareness.
More effective than calendar-based methods, systems of fertility awareness that track basal body temperature, cervical mucus, or both, are known as symptoms-based methods. Teachers of symptoms-based methods take care to distance their systems from the poor reputation of the rhythm method. Many consider the rhythm method to have been obsolete for at least 20 years, and some even exclude calendar-based methods from their definition of fertility awareness.
Some sources may treat the terms rhythm method and natural family planning as synonymous. In the early 20th century, the calendar-based method known as the rhythm method was promoted by members of the Roman Catholic Church
as the only morally acceptable form of family planning
. Methods accepted by this church are referred to as natural family planning
(NFP): so at one time, the term "the rhythm method" was synonymous with NFP. Today, NFP is an umbrella term that includes symptoms-based fertility awareness methods and the lactational amenorrhea method
as well as calendar-based methods such as rhythm. This overlap between uses of the terms "the rhythm method" and "natural family planning" may contribute to confusion.
The term "the rhythm method" is sometimes used, in error, to describe the behavior of any people who have unprotected vaginal intercourse, yet wish to avoid pregnancy.
wrote of periodic abstinence. Addressing followers of Manichaeism
, his former religion, he said, "Is it not you who used to counsel us to observe as much as possible the time when a woman, after her purification, is most likely to conceive, and to abstain from cohabitation at that time...?" If the Manichaieans practiced something like the Jewish observances of menstruation
, then the "time... after her purification" would have indeed been when "a woman... is most likely to conceive." Over a century previously, however, the influential Greek physician Soranus had written that "the time directly before and after menstruation" was the most fertile part of a woman's cycle; this inaccuracy was repeated in the 6th century by the Byzantine
physician Aëtius
. Similarly, a Chinese
sex manual written close to the year 600 stated that only the first five days following menstruation were fertile. Some historians believe that Augustine, too, incorrectly identified the days immediately after menstruation as the time of highest fertility.
Written references to a "safe period" do not appear again for over a thousand years. Scientific advances prompted a number of secular thinkers to advocate periodic abstinence to avoid pregnancy: in the 1840s it was discovered that many animals ovulate during estrus. Because some animals (such as dog
s) have a bloody discharge during estrus, it was assumed that menstruation was the corresponding most fertile time for women. This inaccurate theory was popularized by physicians Bischoff, Félix Archimède Pouchet
, and Adam Raciborski. In 1854, an English
doctor named George Drysdale correctly taught his patients that the days near menstruation are the least fertile, but this remained the minority view for the remainder of the 19th century.
, a Dutch gynecologist, showed that women only ovulate once per menstrual cycle. In the 1920s, Kyusaku Ogino
, a Japanese gynecologist, and Hermann Knaus, from Austria, working independently, each made the discovery that ovulation occurs about fourteen days before the next menstrual period. Ogino used his discovery to develop a formula for use in aiding infertile women to time intercourse to achieve pregnancy.
In 1930, John Smulders, a Roman Catholic physician from the Netherlands, used Knaus and Ogino's discoveries to create a method for avoiding pregnancy. Smulders published his work with the Dutch Roman Catholic medical association, and this was the official rhythm method promoted over the next several decades. In 1932 a Catholic physician, Dr. Leo J Latz, published a book titled The Rhythm of Sterility and Fertility in Women describing the method, and the 1930s also saw the first U.S. Rhythm Clinic (founded by John Rock
) to teach the method to Catholic couples.
included the statement, "It is supremely desirable... that medical science should by the study of natural rhythms succeed in determining a sufficiently secure basis for the chaste limitation of offspring." This is interpreted as favoring the then-new, more reliable symptoms-based fertility awareness
methods over the rhythm method. Currently, many fertility awareness teachers consider the rhythm method to have been obsolete for at least 20 years, and calendar-based methods are not classified as NFP by the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops
.
New attention was drawn to calendar-based methods in 1999, when Georgetown University
introduced the Standard Days Method. Designed to be simpler to teach and use than the older rhythm method, the Standard Days Method is being successfully integrated into family planning
programs worldwide.
Imperfect use of calendar-based methods would consist of not correctly tracking the length of the woman's cycles, thus using the wrong numbers in the formula, or of having unprotected intercourse on an identified fertile day. The discipline required to keep accurate records of menstrual cycles, and to abstain from unprotected intercourse, makes imperfect use fairly common. The actual failure rate of calendar-based methods is 25% per year.
's Institute for Reproductive Health, the Standard Days Method has a simpler rule set and is more effective than the rhythm method. A product, called CycleBeads, was developed alongside the method to help the user keep track of estimated high and low fertility points during her menstrual cycle. The Standard Days Method may only be used by women whose cycles are always between 26 and 32 days in length. In this system:
When used to avoid pregnancy, the Standard Days Method has a perfect-use failure rate of 5% per year.
No clinical studies have been done to determine effectiveness, but the program's developers claim a perfect-use failure rate of 4% per year. The Perimon software requires a paid subscription.
Several Web-based implementations of the cycle method are known. Examples can be found at .
programs in developing countries. The method is satisfactory for many women and men who find other methods unacceptable; offering it through family planning centers results in a significant increase in contraceptive use among couples who do not want to become pregnant. The low cost of the method may also enable it to have a significant positive impact in countries that lack funding to provide other methods of birth control
.
and contraceptive sponge
have comparably high failure rates. This lower level of reliability of calendar-based methods is because their formulas make several assumptions that are not always true.
The postovulatory (luteal) phase has a normal length of 12 to 16 days, and the rhythm method formula assumes all women have luteal phase lengths within this range. However, many women have shorter luteal phases, and a few have longer luteal phases. For these women, the rhythm method formula incorrectly identifies a few fertile days as being in the infertile period.
Calendar-based methods use records of past menstrual cycles to predict the length of future cycles. However, the length of the pre-ovulatory phase can vary significantly, depending on the woman's typical cycle length, stress factors, medication, illness, menopause
, breastfeeding
, and whether she is just coming off hormonal contraception
. If a woman with previously regular cycles has a delayed ovulation due to one of these factors, she will still be fertile when the method tells her she is in the post-ovulatory infertile phase. If she has an unusually early ovulation, calendar-based methods will indicate she is still in the pre-ovulatory infertile phase when she has actually become fertile.
Finally, calendar-based methods assume that all bleeding is true menstruation. However, mid-cycle or anovulatory bleeding can be caused by a number of factors. Incorrectly identifying bleeding as menstruation will cause the method's calculations to be incorrect.
It has also been suggested that pregnancies resulting from method failures of periodic abstinence methods are at increased risk of miscarriage and birth defects due to aged gametes at the time of conception. Newer research suggests that timing of conception has no effect on miscarriage rates, low birth weight, or preterm delivery.
Woman
A woman , pl: women is a female human. The term woman is usually reserved for an adult, with the term girl being the usual term for a female child or adolescent...
's likelihood of fertility
Fertility
Fertility is the natural capability of producing offsprings. As a measure, "fertility rate" is the number of children born per couple, person or population. Fertility differs from fecundity, which is defined as the potential for reproduction...
, based on a record of the length of previous menstrual cycle
Menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is the scientific term for the physiological changes that can occur in fertile women for the purpose of sexual reproduction. This article focuses on the human menstrual cycle....
s. Various systems are known as the Knaus–Ogino Method, rhythm method, and Standard Days Method. These systems may be used to achieve pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
, by timing unprotected intercourse for days identified as fertile, or to avoid pregnancy
Birth control
Birth control is an umbrella term for several techniques and methods used to prevent fertilization or to interrupt pregnancy at various stages. Birth control techniques and methods include contraception , contragestion and abortion...
, by restricting unprotected intercourse to days identified as infertile.
The first formalized calendar-based method was developed in 1930 by John Smulders, a Roman Catholic physician from the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
. It was based on knowledge of the menstrual cycle
Menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is the scientific term for the physiological changes that can occur in fertile women for the purpose of sexual reproduction. This article focuses on the human menstrual cycle....
. This method was independently discovered by Hermann Knaus (Austria), and Kyusaku Ogino
Kyusaku Ogino
was a Japanese doctor specializing in obstetrics and gynecology.His natural father's family name was Nakamura, but Kyusaku was adopted by the Ogino family in 1901....
(Japan). This system was a main form of birth control available to Catholic couples for several decades, until the popularization of symptoms-based fertility awareness
Fertility awareness
Fertility awareness refers to a set of practices used to determine the fertile and infertile phases of a woman's menstrual cycle. Fertility awareness methods may be used to avoid pregnancy, to achieve pregnancy, or as a way to monitor gynecological health....
methods. A new development in calendar-based methods occurred in 1999, when Georgetown University
Georgetown University
Georgetown University is a private, Jesuit, research university whose main campus is in the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C. Founded in 1789, it is the oldest Catholic university in the United States...
introduced the Standard Days Method. The Standard Days Method is promoted in conjunction with a product called CycleBeads, a ring of colored beads which are meant to help the user keep track of her fertile and non-fertile days.
Terminology
Some sources may treat the terms rhythm method and fertility awareness as synonymous. However, fertility awarenessFertility awareness
Fertility awareness refers to a set of practices used to determine the fertile and infertile phases of a woman's menstrual cycle. Fertility awareness methods may be used to avoid pregnancy, to achieve pregnancy, or as a way to monitor gynecological health....
is usually used as a broad term that includes tracking basal body temperature
Basal body temperature
Basal body temperature is the lowest temperature attained by the body during rest . It is generally measured immediately after awakening and before any physical activity has been undertaken, although the temperature measured at that time is somewhat higher than the true basal body temperature...
and cervical mucus as well as cycle length. The World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
considers the rhythm method to be a specific type of calendar-based method, and calendar-based methods to be only one form of fertility awareness.
More effective than calendar-based methods, systems of fertility awareness that track basal body temperature, cervical mucus, or both, are known as symptoms-based methods. Teachers of symptoms-based methods take care to distance their systems from the poor reputation of the rhythm method. Many consider the rhythm method to have been obsolete for at least 20 years, and some even exclude calendar-based methods from their definition of fertility awareness.
Some sources may treat the terms rhythm method and natural family planning as synonymous. In the early 20th century, the calendar-based method known as the rhythm method was promoted by members of the Roman Catholic Church
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
as the only morally acceptable form of family planning
Family planning
Family planning is the planning of when to have children, and the use of birth control and other techniques to implement such plans. Other techniques commonly used include sexuality education, prevention and management of sexually transmitted infections, pre-conception counseling and...
. Methods accepted by this church are referred to as natural family planning
Natural family planning
Natural family planning is a term referring to the family planning methods approved by the Roman Catholic Church. In accordance with the Church's requirements for sexual behavior in keeping with its philosophy of the dignity of the human person, NFP excludes the use of other methods of birth...
(NFP): so at one time, the term "the rhythm method" was synonymous with NFP. Today, NFP is an umbrella term that includes symptoms-based fertility awareness methods and the lactational amenorrhea method
Lactational Amenorrhea Method
The lactational amenorrhea method is a method of avoiding pregnancies which is based on the natural postnatal infertility that occurs when a woman is amenorrheic and fully breastfeeding...
as well as calendar-based methods such as rhythm. This overlap between uses of the terms "the rhythm method" and "natural family planning" may contribute to confusion.
The term "the rhythm method" is sometimes used, in error, to describe the behavior of any people who have unprotected vaginal intercourse, yet wish to avoid pregnancy.
Early methods
It is not known if historical cultures were aware of what part of the menstrual cycle is most fertile. In the year 388, Augustine of HippoAugustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo , also known as Augustine, St. Augustine, St. Austin, St. Augoustinos, Blessed Augustine, or St. Augustine the Blessed, was Bishop of Hippo Regius . He was a Latin-speaking philosopher and theologian who lived in the Roman Africa Province...
wrote of periodic abstinence. Addressing followers of Manichaeism
Manichaeism
Manichaeism in Modern Persian Āyin e Māni; ) was one of the major Iranian Gnostic religions, originating in Sassanid Persia.Although most of the original writings of the founding prophet Mani have been lost, numerous translations and fragmentary texts have survived...
, his former religion, he said, "Is it not you who used to counsel us to observe as much as possible the time when a woman, after her purification, is most likely to conceive, and to abstain from cohabitation at that time...?" If the Manichaieans practiced something like the Jewish observances of menstruation
Niddah
Niddah is a Hebrew term describing a woman during menstruation, or a woman who has menstruated and not yet completed the associated requirement of immersion in a mikveh ....
, then the "time... after her purification" would have indeed been when "a woman... is most likely to conceive." Over a century previously, however, the influential Greek physician Soranus had written that "the time directly before and after menstruation" was the most fertile part of a woman's cycle; this inaccuracy was repeated in the 6th century by the Byzantine
Byzantine
Byzantine usually refers to the Roman Empire during the Middle Ages.Byzantine may also refer to:* A citizen of the Byzantine Empire, or native Greek during the Middle Ages...
physician Aëtius
Aëtius Amidenus
Aëtius of Amida was a Byzantine physician and medical writer, particularly distinguished by the extent of his erudition. Historians are not agreed about his exact date...
. Similarly, a Chinese
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
sex manual written close to the year 600 stated that only the first five days following menstruation were fertile. Some historians believe that Augustine, too, incorrectly identified the days immediately after menstruation as the time of highest fertility.
Written references to a "safe period" do not appear again for over a thousand years. Scientific advances prompted a number of secular thinkers to advocate periodic abstinence to avoid pregnancy: in the 1840s it was discovered that many animals ovulate during estrus. Because some animals (such as dog
Dog
The domestic dog is a domesticated form of the gray wolf, a member of the Canidae family of the order Carnivora. The term is used for both feral and pet varieties. The dog may have been the first animal to be domesticated, and has been the most widely kept working, hunting, and companion animal in...
s) have a bloody discharge during estrus, it was assumed that menstruation was the corresponding most fertile time for women. This inaccurate theory was popularized by physicians Bischoff, Félix Archimède Pouchet
Félix Archimède Pouchet
Félix-Archimède Pouchet was a French naturalist and a leading proponent of spontaneous generation of life from non-living materials, and as such an opponent of Louis Pasteur's germ theory...
, and Adam Raciborski. In 1854, an English
English people
The English are a nation and ethnic group native to England, who speak English. The English identity is of early mediaeval origin, when they were known in Old English as the Anglecynn. England is now a country of the United Kingdom, and the majority of English people in England are British Citizens...
doctor named George Drysdale correctly taught his patients that the days near menstruation are the least fertile, but this remained the minority view for the remainder of the 19th century.
Knaus–Ogino or rhythm method
In 1905 Theodoor Hendrik van de VeldeTheodoor Hendrik van de Velde
Theodoor Hendrik van de Velde was a Dutch physician and gynæcologist who served as Director at the Gynæcological Institute in Haarlem. His 1926 book Het volkomen huwelijk made him an instant international celebrity...
, a Dutch gynecologist, showed that women only ovulate once per menstrual cycle. In the 1920s, Kyusaku Ogino
Kyusaku Ogino
was a Japanese doctor specializing in obstetrics and gynecology.His natural father's family name was Nakamura, but Kyusaku was adopted by the Ogino family in 1901....
, a Japanese gynecologist, and Hermann Knaus, from Austria, working independently, each made the discovery that ovulation occurs about fourteen days before the next menstrual period. Ogino used his discovery to develop a formula for use in aiding infertile women to time intercourse to achieve pregnancy.
In 1930, John Smulders, a Roman Catholic physician from the Netherlands, used Knaus and Ogino's discoveries to create a method for avoiding pregnancy. Smulders published his work with the Dutch Roman Catholic medical association, and this was the official rhythm method promoted over the next several decades. In 1932 a Catholic physician, Dr. Leo J Latz, published a book titled The Rhythm of Sterility and Fertility in Women describing the method, and the 1930s also saw the first U.S. Rhythm Clinic (founded by John Rock
John Rock (American scientist)
John Rock was an American obstetrician and gynecologist. He is best known for the major role he played in the development of the first hormonal contraceptive, colloquially called "the pill".-Early life and career:...
) to teach the method to Catholic couples.
Later 20th century to present
In the first half of the 20th century, most users of the rhythm method were Catholic, they were following their church's teaching that all other methods of birth control were sinful. In 1968 the encyclical Humanae VitaeHumanae Vitae
Humanae Vitae is an encyclical written by Pope Paul VI and issued on 25 July 1968. Subtitled On the Regulation of Birth, it re-affirms the traditional teaching of the Catholic Church regarding married love, responsible parenthood, and the continuing proscription of most forms of birth...
included the statement, "It is supremely desirable... that medical science should by the study of natural rhythms succeed in determining a sufficiently secure basis for the chaste limitation of offspring." This is interpreted as favoring the then-new, more reliable symptoms-based fertility awareness
Fertility awareness
Fertility awareness refers to a set of practices used to determine the fertile and infertile phases of a woman's menstrual cycle. Fertility awareness methods may be used to avoid pregnancy, to achieve pregnancy, or as a way to monitor gynecological health....
methods over the rhythm method. Currently, many fertility awareness teachers consider the rhythm method to have been obsolete for at least 20 years, and calendar-based methods are not classified as NFP by the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops
United States Conference of Catholic Bishops
The United States Conference of Catholic Bishops is the episcopal conference of the Catholic Church in the United States. Founded in 1966 as the joint National Conference of Catholic Bishops and United States Catholic Conference, it is composed of all active and retired members of the Catholic...
.
New attention was drawn to calendar-based methods in 1999, when Georgetown University
Georgetown University
Georgetown University is a private, Jesuit, research university whose main campus is in the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C. Founded in 1789, it is the oldest Catholic university in the United States...
introduced the Standard Days Method. Designed to be simpler to teach and use than the older rhythm method, the Standard Days Method is being successfully integrated into family planning
Family planning
Family planning is the planning of when to have children, and the use of birth control and other techniques to implement such plans. Other techniques commonly used include sexuality education, prevention and management of sexually transmitted infections, pre-conception counseling and...
programs worldwide.
Types and effectiveness
Most menstrual cycles have several days at the beginning that are infertile (pre-ovulatory infertility), a period of fertility, and then several days just before the next menstruation that are infertile (post-ovulatory infertility). The first day of red bleeding is considered day one of the menstrual cycle. To use these methods, a woman is required to know the length of her menstrual cycles.Imperfect use of calendar-based methods would consist of not correctly tracking the length of the woman's cycles, thus using the wrong numbers in the formula, or of having unprotected intercourse on an identified fertile day. The discipline required to keep accurate records of menstrual cycles, and to abstain from unprotected intercourse, makes imperfect use fairly common. The actual failure rate of calendar-based methods is 25% per year.
Rhythm method (Knaus–Ogino method)
To find the estimated length of the pre-ovulatory infertile phase, nineteen (19) is subtracted from the length of the woman's shortest cycle. To find the estimated start of the post-ovulatory infertile phase, ten (10) is subtracted from the length of the woman's longest cycle. A woman whose menstrual cycles ranged in length from 30 to 36 days would be estimated to be infertile for the first 11 days of her cycle (30-19=11), to be fertile on days 12-25, and to resume infertility on day 26 (36-10=26). When used to avoid pregnancy, the rhythm method has a perfect-use failure rate of up to 9% per year.Standard Days Method
Developed by Georgetown UniversityGeorgetown University
Georgetown University is a private, Jesuit, research university whose main campus is in the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C. Founded in 1789, it is the oldest Catholic university in the United States...
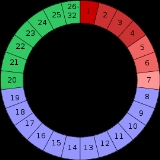
's Institute for Reproductive Health, the Standard Days Method has a simpler rule set and is more effective than the rhythm method. A product, called CycleBeads, was developed alongside the method to help the user keep track of estimated high and low fertility points during her menstrual cycle. The Standard Days Method may only be used by women whose cycles are always between 26 and 32 days in length. In this system:
- Days 1-7 of a woman's menstrual cycle are considered infertile
- Days 8-19 are considered fertile; considered unsafe for unprotected intercourse
- From Day 20, infertility is considered to resume
When used to avoid pregnancy, the Standard Days Method has a perfect-use failure rate of 5% per year.
Software-based systems
A software program developed in Germany from 1995 to 2001, Perimon is a stricter variant of the rhythm method. It requires a greater period where unprotected sex is not allowed when used to avoid pregnancy, designating a maximum of 10.5 days each cycle as infertile. If 7 of those infertile days occur when a woman's is menstruating, this means there are only 3.5 days of non-menstrual infertile days per cycle.No clinical studies have been done to determine effectiveness, but the program's developers claim a perfect-use failure rate of 4% per year. The Perimon software requires a paid subscription.
Several Web-based implementations of the cycle method are known. Examples can be found at .
Advantages
The Standard Days method (SDM) is increasingly being introduced as part of family planningFamily planning
Family planning is the planning of when to have children, and the use of birth control and other techniques to implement such plans. Other techniques commonly used include sexuality education, prevention and management of sexually transmitted infections, pre-conception counseling and...
programs in developing countries. The method is satisfactory for many women and men who find other methods unacceptable; offering it through family planning centers results in a significant increase in contraceptive use among couples who do not want to become pregnant. The low cost of the method may also enable it to have a significant positive impact in countries that lack funding to provide other methods of birth control
Birth control
Birth control is an umbrella term for several techniques and methods used to prevent fertilization or to interrupt pregnancy at various stages. Birth control techniques and methods include contraception , contragestion and abortion...
.
Failure rate
One concern related to the use of calendar-based methods is their relatively high failure rate, compared to other methods of birth control. Even when used perfectly, calendar-based methods, especially the rhythm method, result in a high pregnancy rate among couples intending to avoid pregnancy. Of commonly known methods of birth control, only the cervical capCervical cap
The cervical cap is a form of barrier contraception. A cervical cap fits over the cervix and blocks sperm from entering the uterus through the external orifice of the uterus, called the os.-Terminology:...
and contraceptive sponge
Contraceptive sponge
The contraceptive sponge combines barrier and spermicidal methods to prevent conception. Three brands are marketed: Pharmatex, Protectaid and Today. Pharmatex is marketed in France and the province of Quebec; Protectaid in the rest of Canada and Europe; and Today in the United States.Sponges work...
have comparably high failure rates. This lower level of reliability of calendar-based methods is because their formulas make several assumptions that are not always true.
The postovulatory (luteal) phase has a normal length of 12 to 16 days, and the rhythm method formula assumes all women have luteal phase lengths within this range. However, many women have shorter luteal phases, and a few have longer luteal phases. For these women, the rhythm method formula incorrectly identifies a few fertile days as being in the infertile period.
Calendar-based methods use records of past menstrual cycles to predict the length of future cycles. However, the length of the pre-ovulatory phase can vary significantly, depending on the woman's typical cycle length, stress factors, medication, illness, menopause
Menopause
Menopause is a term used to describe the permanent cessation of the primary functions of the human ovaries: the ripening and release of ova and the release of hormones that cause both the creation of the uterine lining and the subsequent shedding of the uterine lining...
, breastfeeding
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is the feeding of an infant or young child with breast milk directly from female human breasts rather than from a baby bottle or other container. Babies have a sucking reflex that enables them to suck and swallow milk. It is recommended that mothers breastfeed for six months or...
, and whether she is just coming off hormonal contraception
Hormonal contraception
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The original hormonal method—the combined oral contraceptive...
. If a woman with previously regular cycles has a delayed ovulation due to one of these factors, she will still be fertile when the method tells her she is in the post-ovulatory infertile phase. If she has an unusually early ovulation, calendar-based methods will indicate she is still in the pre-ovulatory infertile phase when she has actually become fertile.
Finally, calendar-based methods assume that all bleeding is true menstruation. However, mid-cycle or anovulatory bleeding can be caused by a number of factors. Incorrectly identifying bleeding as menstruation will cause the method's calculations to be incorrect.
Embryonic health
It has been suggested that unprotected intercourse in the infertile periods of the menstrual cycle may still result in conceptions, but create embryos incapable of implanting.It has also been suggested that pregnancies resulting from method failures of periodic abstinence methods are at increased risk of miscarriage and birth defects due to aged gametes at the time of conception. Newer research suggests that timing of conception has no effect on miscarriage rates, low birth weight, or preterm delivery.

