
Birth rate
Encyclopedia
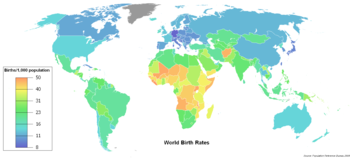
Crude birth rate is the nativity or childbirths per 1,000 people per year (in estimation review points). Another word used interchangeably with "birth rate" is "natality". When the crude birth rate is subtracted from the crude death rate, it reveals the rate of natural increase. This number is equal to the rate of population change (not factoring in migration).
It is important to distinguish between a total or crude birth rate, which uses all births, typically indicated as births per 1000, versus an age-specific rate which is typically indicated as the number of births per 1 000 persons in this age group. The first known use of the term "birth rate" in the English language was in 1859. The birth rate is typically the main variable in assessing the rate of population growth.
According to the United Nations' World Population Prospects: The 2008 Revision Population Database, crude birth rate is the number of births over a given period divided by the person-years lived by the population over that period. It is expressed as number of births per 1,000 population. CBR = (births in a period / population of person-years over that period).
Another indicator of fertility that is frequently used is the total fertility rate
Total Fertility Rate
The total fertility rate of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates through her lifetime, and she...
, which is the average number of children born to each woman over the course of her life. In general, the total fertility rate is a better indicator of (current) fertility rates because, unlike the crude birth rate, it is not affected by the age distribution of the population. Fertility rates tend to be higher in less economically developed countries and lower in more economically developed countries.
The birth rate is an item of concern and policy for a number of national governments. Some, including those of Italy and Malaysia, seek to increase the national birth rate using measures such as financial incentives or provision of support services to new mothers. Conversely, other countries have policies to reduce the birth rate, for example, China's one child policy. Measures such as improved information about and availability of birth control
Birth control
Birth control is an umbrella term for several techniques and methods used to prevent fertilization or to interrupt pregnancy at various stages. Birth control techniques and methods include contraception , contragestion and abortion...
have achieved similar results in countries such as Iran
Family planning in Iran
The Republic of Iran has a comprehensive and effective program of family planning. While Iran's population grew at a rate of more than 3%/year between 1956 and 1986, the growth rate began to decline in the late 1980s and early 1990s after the government initiated a major population control program...
.
There has also been discussion on whether bringing women into the forefront of development initiatives will lead to a decline in birth rates. In some places, government policies have been focused on reducing birth rates through improving women's sexual and reproductive health and rights. Typically, high birth rates have been associated with health impairments and low life expectancy, low living standards, low status of women, and low levels of education. There are claims that as countries go through economic development and social change, population growth such as birth rate declines.
In 1974, at the World Population Conference in Bucharest, women's issues gained considerable attention. Family programmes were seriously discussed and 137 countries drafted a World Population Plan of Action. In the discussion, many countries accepted modern birth control, such as the pill and the condom, but opposed abortion. In 1994, another action plan was drafted in Cairo under the United Nations. They discussed the concern on population and the need to incorporate women into the discourse. They agreed that improvements in women's status, and initiatives in defense of reproductive health and freedom, the environment, and sustainable socio-economic development were needed.
Generally, birth rate is calculated using live birth counts from a universal system of registration of births, deaths, and marriages, and population counts from a census or using estimation through specialized demographic techniques. Birth rate is also commonly used to calculate population growth. It is combined with death rates and migration rates to calculate population growth.
As of 2009, the average birth rate for the whole world is 19.95 per year per 1000 total population, a 0.48% decline from 2003's world birth rate of 20.43 per 1000 total population.
Per U.S. federal government data released in March 2011, births fell 4% from 2007 to 2009, the largest drop in the U.S. for any two-year period since the 1970s.
Births have declined for three consecutive years, and are now 7% below the peak in 2007. This drop has continued through 2010, according to data released by the U.S. National Center for Health Statistics in June 2011. Numerous experts have suggested that this decline is largely a reflection of unfavorable uneconomic conditions. This connection between birth rates and economic downturns partly stems from the fact that American birth rates have now fallen to levels that are comparable to the Great Depression of the 1930's. Teen birth rates in the U.S. are at the lowest level in U.S. history. In fact, teen birth rates in the U.S. have consistently decreased since 1991 through 2011, except for a brief increase between 2005 and 2007. The other aberration from this otherwise steady decline in teen birth rates is the 6% decrease in birth rates for 15–19 year olds between 2008 and 2009. Despite these years of decrease, U.S. teen birth rates are still higher than in other developed nations. Racial differences prevail with teen birth and pregnancy rates as well. The American Indian/Alaska Native, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic black teen pregnancy rates are more than double the non-Hispanic white teen birth rate.
According to the CIA – The World Factbook
The World Factbook
The World Factbook is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency of the United States with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official paper copy version is available from the National Technical Information Service and the Government Printing Office...
, the country with the highest birth rate currently is Niger at 51.26 births per 1000 people. The country with the lowest birth rate is Japan at 7.64 births per 1000 people. (Hong Kong, a Special Administrative Region of China, is at 7.42 births per 1000 people.) As compared to the 1950s (birth rate was at 36 births per 1000 in the 1950s), birth rate has declined by 16 births per 1000 people. In July, 2011, the U.S. National Institutes of Health announced that the adolescent birth rate continues to decline. Birth rates vary even within the same geographic areas. In Europe, as of July 2011, Ireland's birth rate is 16.5 per cent, which is 3.5 per cent higher than the next-ranked country, the UK. France has a birth rate of 12.8 per cent while Sweden is at 12.3 per cent. In July, 2011, the UK's Office for National Statistics (ONS) announced a 2.4% increase in live births in the UK in 2010 alone. This is the highest birth rate in the UK in 40 years. By contrast, the birth rate in Germany is only 8.3 per 1,000, which is so low that both the UK and France, which have significantly smaller populations, produced more births in the last year. Birth rates also vary within the same geographic area, based on different demographic groups. For example, in April 2011, the U.S. CDC announced that the birth rate for women over the age of 40 in the U.S. rose between 2007 and 2009, while it fell among every other age group during the same time span. In August 2011, Taiwan's government announced that its birth rate declined in the previous year, despite the fact that it implemented a host of approaches to encourage its citizens to have babies.
Birth rates ranging from 10–20 births per 1000 are considered low, while rates from 40–50 births per 1000 are considered high. There are problems associated with both an extremely high birth rate and an extremely low birth rate. High birth rates can cause stress on the government welfare and family programs to support a youthful population. Additional problems faced by a country with a high birth rate include educating a growing number of children, creating jobs for these children when they enter the workforce, and dealing with the environmental effects that a large population can produce. Low birth rates can put stress on the government to provide adequate senior welfare systems and also the stress on families to support the elders themselves. There will be less children or working age population to support the constantly growing aging population.
Methods of measuring birth rate
The crude birth rate is the number of births in a given population during a given time period (such as 1 January – December 31) divided by the total population and multiplied by one thousand.Birth rate and the Demographic Transition Model
The Demographic Transition Model describes how population mortality and fertility decline as social and economic development occurs through time. The two major factors in the Demographic Transition Model are Crude Birth Rate (CBR) and Crude Death Rate (CDR). There are four stages to the Demographic Model. In the first and second stages, CBR remains high because people are still in agrarian cultures and need more labour to work on farms. In addition, the chances of children dying are high because medicine is not as advanced during that phase. In the third stage, CBR starts to decline due to women's increasing participation in society and the reduced need for families to have many children to work on farms. In the fourth stage, CBR is sustained at a very low level, with some countries having rates that are below replacement levels in other countries.See also
- Death rate
- Population ageingPopulation ageingPopulation ageing or population aging occurs when the median age of a country or region rises. This happens because of rising life expectancy or declining birth rates. Excepting 18 countries termed 'demographic outliers' by the UN) this process is taking place in every country and region across...
- Population controlPopulation controlHuman population control is the practice of artificially altering the rate of growth of a human population.Historically, human population control has been implemented by limiting the population's birth rate, usually by government mandate, and has been undertaken as a response to factors including...
- Total fertility rateTotal Fertility RateThe total fertility rate of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates through her lifetime, and she...
Case studies:
- Aging of EuropeAging of EuropeThe Ageing of Europe, also known as the greying of Europe, is a demographic phenomenon in Europe characterized by a decrease in fertility, a decrease in mortality rate, and a higher life expectancy among Europeans.-Overall trends:...
- Aging of JapanAging of JapanThe ageing of Japan outweighs all other nations with the highest proportion of elderly citizens, 21% over the age of 65. In 1989, only 11.6% of the population was 65 years or older, but projections were that 25.6% would be in that age category by 2030...
Lists:
Organisations:
- Population Matters, (formerly known as the Optimum Population Trust)

