
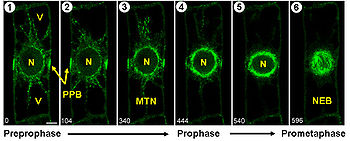
Preprophase
Encyclopedia
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
in plant cell
Plant cell
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that differ in several key respects from the cells of other eukaryotic organisms. Their distinctive features include:...
s that does not occur in other eukaryote
Eukaryote
A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
s such as animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s or fungi
Fungus
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds , as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, and bacteria...
. It precedes prophase
Prophase
Prophase, from the ancient Greek πρό and φάσις , is a stage of mitosis in which the chromatin condenses into a highly ordered structure called a chromosome in which the chromatin becomes visible. This process, called chromatin condensation, is mediated by the condensin complex...
and is characterized by two distinct events:
- The formation of the preprophase bandPreprophase bandThe preprophase band is a microtubule array found in plant cells that are about to undergo cell division and enter the preprophase stage of the plant cell cycle. Besides the phragmosome, it is the first microscopically visible sign that a plant cell is about to enter mitosis...
, a dense microtubuleMicrotubuleMicrotubules are a component of the cytoskeleton. These rope-like polymers of tubulin can grow as long as 25 micrometers and are highly dynamic. The outer diameter of microtubule is about 25 nm. Microtubules are important for maintaining cell structure, providing platforms for intracellular...
ring underneath the plasma membrane. - The initiation of microtubule nucleationMicrotubule nucleationMicrotubules are filaments of the cytoskeleton. They typically form through the polymerization of α- and β-tubulin dimers elongating existing microtubules...
at the nuclear envelopeNuclear envelopeA nuclear envelope is a double lipid bilayer that encloses the genetic material in eukaryotic cells. The nuclear envelope also serves as the physical barrier, separating the contents of the nucleus from the cytosol...
.
Function of preprophase in the cell cycle
Plant cells are fixed with regards to their neighbor cells within the tissueTissue (biology)
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
s they are growing in. In contrast to animals where certain cells can migrate within the embryo
Embryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
to form new tissues, the seedlings of higher plants grow entirely based on the orientation of cell division
Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells . Cell division is usually a small segment of a larger cell cycle. This type of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis, and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again. The corresponding sort...
and subsequent elongation and differentiation of cells within their cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
s. Therefore, the accurate control of cell division planes and placement of the future cell wall in plant cells is crucial for the correct architecture of plant tissues and organs.
The preprophase stage of somatic
Somatic
The term somatic means 'of the body',, relating to the body. In medicine, somatic illness is bodily, not mental, illness. The term is often used in biology to refer to the cells of the body in contrast to the germ line cells which usually give rise to the gametes...
plant cell mitosis serves to establish the precise location of the division plane and future cell wall before the cell enters prophase
Prophase
Prophase, from the ancient Greek πρό and φάσις , is a stage of mitosis in which the chromatin condenses into a highly ordered structure called a chromosome in which the chromatin becomes visible. This process, called chromatin condensation, is mediated by the condensin complex...
. This is achieved through the formation of a transient microtubule structure, the preprophase band, and a so far unknown mechanism by which the cell is able to "memorize" the position of the preprophase band to guide the new cell wall growing during cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the late stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a binucleate cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation...
to the correct location. In gametophyte
Gametophyte
A gametophyte is the haploid, multicellular phase of plants and algae that undergo alternation of generations, with each of its cells containing only a single set of chromosomes....
tissues during the reproductive phase of the plant life cycle
Biological life cycle
A life cycle is a period involving all different generations of a species succeeding each other through means of reproduction, whether through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction...
, cell division planes may be established without the use of a preprophase band.
In highly vacuolated plant cells, preprophase may be preceded by the formation of a phragmosome
Phragmosome
The phragmosome is a sheet of cytoplasm forming in highly vacuolated plant cells in preparation for mitosis. In contrast to animal cells, plant cells often contain large central vacuoles occupying up to 90% of the total cell volume and pushing the nucleus against the cell wall. In order for mitosis...
. The function of the phragmosome is to suspend the cell nucleus
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
in the center of the cell in preparation for mitosis. If a phragmosome is visible, the preprophase band will appear at its outer edge.
Preprophase band formation
At the beginning of preprophase, the corticalCortex (anatomy)
In anatomy and zoology the cortex is the outermost layer of an organ. Organs with well-defined cortical layers include kidneys, adrenal glands, ovaries, the thymus, and portions of the brain, including the cerebral cortex, the most well-known of all cortices.The cerebellar cortex is the thin gray...
microtubules of a plant cell disappear and aggregate into a dense ring underneath the plasma membrane. This preprophase band runs around the equatorial plane of the future mitotic spindle
Mitotic spindle
In cell biology, the spindle fibers are the structure that separates the chromosomes into the daughter cells during cell division. It is part of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells...
and marks the plane of cell division and future fusion site for the cell plate
Cell plate
thumb|300px|Phragmoplast and cell plate formation in a plant cell during cytokinesis. Left side: Phragmoplast forms and cell plate starts to assemble in the center of the cell. Toawards the right: Phragmoplast enlarges in a donut-shape towards the outside of the cell, leaving behind mature cell...
. It consists of microtubules and microfilament
Microfilament
Microfilaments are the thinnest filaments of the cytoskeleton, a structure found in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. These linear polymers of actin subunits are flexible and relatively strong, resisting buckling by multi-piconewton compressive forces and filament fracture by nanonewton...
s (actin
Actin
Actin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
) and persists into prophase. Spindle formation occurs during prophase with the axis perpendicular to the plane surrounded by the preprophase band.
Microtubule nucleation
In contrast to animal cells, plant cells do not possess centrosomeCentrosome
In cell biology, the centrosome is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center of the animal cell as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression. It was discovered by Edouard Van Beneden in 1883...
s to organize their mitotic spindles. Instead, the nuclear envelope acts as a microtubule organizing center
Microtubule organizing center
The microtubule-organizing center is a structure found in eukaryotic cells from which microtubules emerge. MTOCs have two main functions: the organization of eukaryotic flagella and cilia and the organization of the mitotic and meiotic spindle apparatus, which separate the chromosomes during cell...
(MTOC) for spindle formation during preprophase. The first sign is a clear, actin-free zone appearing around the nuclear envelope. This zone fills with microtubules nucleating on the surface of the nucleus. The preprophase spindle forms by self-assembly of these microtubules in the cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
surrounding the nuclear envelope. It is reinforced through chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
(kinetochore
Kinetochore
The kinetochore is the protein structure on chromatids where the spindle fibers attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart....
)-mediated spindle assembly after the nuclear envelope breaks down at the end of prophase.
Transition into prophase
During progression from preprophase into prophase, the randomly oriented microtubules align parallel along the nuclear surface according to the spindle axis. This structure is called the prophase spindle. Triggered by nuclear envelope breakdown at the end of prophase, the preprophase band disappears and the prophase spindle matures into the metaphaseMetaphase
Metaphase, from the ancient Greek μετά and φάσις , is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which condensed & highly coiled chromosomes, carrying genetic information, align in the middle of the cell before being separated into each of the two daughter cells...
spindle occupying the space of the former nucleus. Experiments with drugs destroying microfilaments indicate that actin may play a role in keeping the cellular "memory" of the position of the division plane after the preprophase band breaks down to direct cytokinesis in telophase
Telophase
Telophase from the ancient Greek "τελος" and "φασις" , is a stage in both meiosis and mitosis in a eukaryotic cell. During telophase, the effects of prophase and prometaphase events are reversed. Two daughter nuclei form in the cell. The nuclear envelopes of the daughter cells are formed from the...
.

