
Cell plate
Encyclopedia
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the late stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a binucleate cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation...
in terrestrial plant
Terrestrial plant
A terrestrial plant is one that grows on land. Other types of plants are aquatic , epiphytic , lithophytes and aerial ....
s occurs by cell plate formation. This process entails the delivery of Golgi
Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It was identified in 1898 by the Italian physician Camillo Golgi, after whom the Golgi apparatus is named....
-derived and endosomal vesicles carrying cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
and cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
components to the plane of cell division
Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells . Cell division is usually a small segment of a larger cell cycle. This type of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis, and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again. The corresponding sort...
and the subsequent fusion of these vesicles within this plate.
After formation of an early tubulo-vesicular network at the center of the cell, the initially labile cell plate consolidates into a tubular network and eventually a fenestrated sheet. The cell plate grows outward from the center of the cell to the parental plasma membrane with which it will fuse, thus completing cell division
Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells . Cell division is usually a small segment of a larger cell cycle. This type of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis, and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again. The corresponding sort...
. Formation and growth of the cell plate is dependent upon the phragmoplast
Phragmoplast
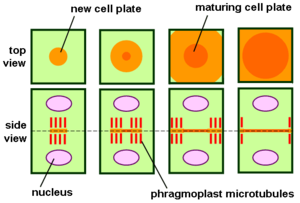
thumb|300px|Phragmoplast and cell plate formation in a plant cell during cytokinesis. Left side: Phragmoplast forms and cell plate starts to assemble in the center of the cell. Towards the right: Phragmoplast enlarges in a donut-shape towards the outside of the cell, leaving behind mature cell...
, which is required for proper targeting of Golgi
Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It was identified in 1898 by the Italian physician Camillo Golgi, after whom the Golgi apparatus is named....
-derived vesicles to the cell plate.
As the cell plate matures in the central part of the cell, the phragmoplast
Phragmoplast
thumb|300px|Phragmoplast and cell plate formation in a plant cell during cytokinesis. Left side: Phragmoplast forms and cell plate starts to assemble in the center of the cell. Towards the right: Phragmoplast enlarges in a donut-shape towards the outside of the cell, leaving behind mature cell...
disassembles in this region and new elements are added on its outside. This process leads to a steady expansion of the phragmoplast, and concomitantly, to a continuous retargeting of Golgi
Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It was identified in 1898 by the Italian physician Camillo Golgi, after whom the Golgi apparatus is named....
-derived vesicles to the growing edge of the cell plate. Once the cell plate reaches and fuses with the plasma membrane the phragmoplast
Phragmoplast
thumb|300px|Phragmoplast and cell plate formation in a plant cell during cytokinesis. Left side: Phragmoplast forms and cell plate starts to assemble in the center of the cell. Towards the right: Phragmoplast enlarges in a donut-shape towards the outside of the cell, leaving behind mature cell...
disappears. This event not only marks the separation of the two daughter cells, but also initiates a range of biochemical modifications that transform the callose
Callose
Callose is a plant polysaccharide. It is composed of glucose residues linked together through β-1,3-linkages, and is termed a β-glucan. It is thought to be manufactured at the cell wall by callose synthases and is degraded by β-1,3-glucanases. It is laid down at plasmodesmata, at the cell...
-rich, flexible cell plate into a cellulose
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β linked D-glucose units....
-rich, stiff primary cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
.
The heavy dependence of cell plate formation on active Golgi
Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It was identified in 1898 by the Italian physician Camillo Golgi, after whom the Golgi apparatus is named....
stacks explains why plant cell
Plant cell
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that differ in several key respects from the cells of other eukaryotic organisms. Their distinctive features include:...
s, unlike mammalian cells, do not disassemble their secretion machinery during cell division.

