
Poisson random measure
Encyclopedia
Let 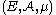 be some measure space with
be some measure space with  -finite measure
-finite measure 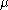 . The Poisson random measure with intensity measure
. The Poisson random measure with intensity measure
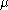 is a family of random variables
is a family of random variables 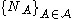 defined on some probability space
defined on some probability space
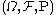 such that
such that
i)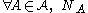 is a Poisson random variable
is a Poisson random variable
with rate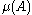 .
.
ii) If sets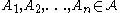 don't intersect then the corresponding random variables from i) are mutually independent
don't intersect then the corresponding random variables from i) are mutually independent
.
iii)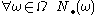 is a measure on
is a measure on 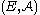
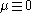 then
then 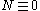 satisfies the conditions i)–iii). Otherwise, in the case of finite measure
satisfies the conditions i)–iii). Otherwise, in the case of finite measure 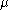 given
given 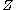 – Poisson random variable
– Poisson random variable
with rate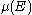 and
and 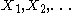 – mutually independent
– mutually independent
random variable
s with distribution
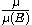 define
define 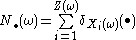 where
where 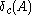 is a degenerate measure located in
is a degenerate measure located in  . Then
. Then 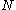 will be a Poisson random measure. In the case
will be a Poisson random measure. In the case 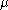 is not finite the measure
is not finite the measure
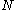 can be obtained from the measures constructed above on parts of
can be obtained from the measures constructed above on parts of 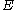 where
where 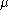 is finite.
is finite.
es, in particular in Lévy–Itō decomposition of the Lévy process
es.
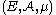 be some measure space with
be some measure space with  -finite measure
-finite measure 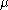 . The Poisson random measure with intensity measure
. The Poisson random measure with intensity measureMeasure (mathematics)
In mathematical analysis, a measure on a set is a systematic way to assign to each suitable subset a number, intuitively interpreted as the size of the subset. In this sense, a measure is a generalization of the concepts of length, area, and volume...
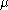 is a family of random variables
is a family of random variables 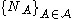 defined on some probability space
defined on some probability spaceProbability space
In probability theory, a probability space or a probability triple is a mathematical construct that models a real-world process consisting of states that occur randomly. A probability space is constructed with a specific kind of situation or experiment in mind...
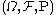 such that
such thati)
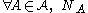 is a Poisson random variable
is a Poisson random variablePoisson distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
with rate
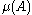 .
.ii) If sets
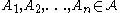 don't intersect then the corresponding random variables from i) are mutually independent
don't intersect then the corresponding random variables from i) are mutually independentStatistical independence
In probability theory, to say that two events are independent intuitively means that the occurrence of one event makes it neither more nor less probable that the other occurs...
.
iii)
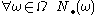 is a measure on
is a measure on 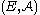
Existence
If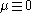 then
then 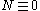 satisfies the conditions i)–iii). Otherwise, in the case of finite measure
satisfies the conditions i)–iii). Otherwise, in the case of finite measure 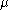 given
given 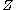 – Poisson random variable
– Poisson random variablePoisson distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
with rate
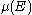 and
and 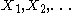 – mutually independent
– mutually independentStatistical independence
In probability theory, to say that two events are independent intuitively means that the occurrence of one event makes it neither more nor less probable that the other occurs...
random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s with distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
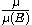 define
define 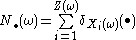 where
where 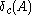 is a degenerate measure located in
is a degenerate measure located in  . Then
. Then  will be a Poisson random measure. In the case
will be a Poisson random measure. In the case 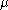 is not finite the measure
is not finite the measureMeasure (mathematics)
In mathematical analysis, a measure on a set is a systematic way to assign to each suitable subset a number, intuitively interpreted as the size of the subset. In this sense, a measure is a generalization of the concepts of length, area, and volume...
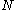 can be obtained from the measures constructed above on parts of
can be obtained from the measures constructed above on parts of 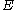 where
where 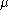 is finite.
is finite.Applications
This kind of random measure is often used when describing jumps of stochastic processStochastic process
In probability theory, a stochastic process , or sometimes random process, is the counterpart to a deterministic process...
es, in particular in Lévy–Itō decomposition of the Lévy process
Lévy process
In probability theory, a Lévy process, named after the French mathematician Paul Lévy, is any continuous-time stochastic process that starts at 0, admits càdlàg modification and has "stationary independent increments" — this phrase will be explained below...
es.

