
Palmette
Encyclopedia

Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
with a subsequent development through the art of most of Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
, often in forms that bear relatively little resemblance to the original. In Ancient Greek
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
and Ancient Roman
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
uses it is also known as the anthemion (from the Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
ανθέμιον, a flower). It is found in most artistic media, but especially as an architectural ornament, whether carved or painted, and painted on ceramics. It is very often a component of the design of a frieze
Frieze
thumb|267px|Frieze of the [[Tower of the Winds]], AthensIn architecture the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Even when neither columns nor pilasters are expressed, on an astylar wall it lies upon...
or border. The complex evolution of the palmette was first traced by Alois Riegl
Alois Riegl
Alois Riegl was an Austrian art historian, and is considered a member of the Vienna School of Art History...
in his Stilfragen
Stilfragen
Stilfragen: Grundlegungen zu einer Geschichte der Ornamentik is a book on the history of ornament by the Austrian art historian Alois Riegl. It was published in Berlin in 1893. The English translation renders the title as Problems of style: foundations for a history of ornament, although this has...
of 1893.
Description

In the repeated border design commonly referred to as anthemion the palm fronds more closely resemble petals of the honeysuckle flower, as if designed to attract fertilizing insects. Some compare the shape to an open 'hamsa' hand – explaining the commonality and derivation of the 'palm' of the hand. In some forms of the motif the volutes or scrolls resemble a pair of eyes, like those on the harmika of the Tibetan or Nepalese stupa
Stupa
A stupa is a mound-like structure containing Buddhist relics, typically the remains of Buddha, used by Buddhists as a place of worship....
and the eyes and sun-disk at the crown of Egyptian stelae. In some variants the features of a more fully developed face become discernible in the palmette itself, while in certain architectural uses, usually at the head of pilasters or herms, the fan of palm-fronds transforms into a male or female face and the volutes sometimes appear as breasts. Common to all these forms is the pair of volutes at the base of the fan – constituting the defining characteristics of the palmette.
Evolution
It is thought that the palmette originated in ancient Greece 2,500 years B.C.,and has influenced Egyptian art. Egyptian palmettes(Greek Anthemion) were originally based on features of various flowers, including the papyrusPapyrus
Papyrus is a thick paper-like material produced from the pith of the papyrus plant, Cyperus papyrus, a wetland sedge that was once abundant in the Nile Delta of Egypt....
and the lotus
Nelumbo nucifera
Nelumbo nucifera, known by a number of names including Indian Lotus, Sacred Lotus, Bean of India, or simply Lotus, is a plant in the monogeneric family Nelumbonaceae...
or lily representing lower and upper Egypt and their fertile union, before it became associated with the palm tree. From earliest times there was a strong association with the sun and it is probably an early form of the halo
Halo (religious iconography)
A halo is a ring of light that surrounds a person in art. They have been used in the iconography of many religions to indicate holy or sacred figures, and have at various periods also been used in images of rulers or heroes...
.
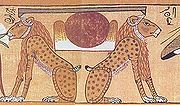
Akhet (hieroglyph and season)
The Egyptian language word Akhet is both a hieroglyph and an Ancient Egyptian season.The two uses for akhet:* In ancient Egyptian, the place where the sun rises and sets; often translated as "horizon" or "mountain of light". It is included in names like "Akhet Khufu" and Akhetaten...
' hieroglyph depicting the setting or rising sun at the point where it touches the two mountains of the horizon – 'dying', being 'reborn' and giving life to the earth. A second form, apparently evolved from this, is a more fully developed palmette similar to the forms found in Ancient Greece.

Hapy
Hapi, sometimes transliterated as Hapy, not to be confused with another god of the same name, was a deification of the annual flooding of the Nile River in Ancient Egyptian religion, which deposited rich silt on its banks, allowing the Egyptians to grow crops. His name means Running One, probably...
, the god of the crucial life-giving annual Nile inundation, who binds their stems together around an offering table in the sema-tawi motif – itself echoing the shapes of the 'akhet' of the horizon. This unification scene appeared on the base of the throne of several kings, who were thought of as preserving the union of the two lands of (upper and lower, but also physical and spiritual) Egypt and thereby mastering the forces of renewal. These 'binding' scenes, and the heliotropic swamp plants appearing in them, evoked the necessity of discerning and revealing the underlying harmony, the origin of all manifest forms, that re-connects the dispersed and separate-seeming fragments of everyday experience. The further implication is that it is from this apparently occult and magical, undivided source that fertility and new life spring.
Another variant of this motif is a single lotus bloom between two upright buds, a favourite fragrant offering. The god of fragrance, Nefertem, is represented by such a lotus, or is shown bearing a lotus as his crown
Crown (headgear)
A crown is the traditional symbolic form of headgear worn by a monarch or by a deity, for whom the crown traditionally represents power, legitimacy, immortality, righteousness, victory, triumph, resurrection, honour and glory of life after death. In art, the crown may be shown being offered to...
. The lotus in Nefertem's head dress typically incorporates twin 'menats' or necklace counterpoises (commonly said to represent fertility) hanging down from the base of the flower on either side of the stem, recalling the symmetrically drooping pair of stems in the lotus and papyrus clumps mentioned above. Curiously, when depicted on Egyptian tomb walls and in formalized garden scenes, date palms are invariably shown in a similar stylistic convention with a cluster of dates hanging down on either side below the crown in this same position. The link between these hanging clusters and the volutes of the palmette is visually clear, but remains inexplicit. Rising and setting sun and opening and closing lotus are linked by the Osiris
Osiris
Osiris is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead. He is classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and...
legend to day and night, life and death and the nightly ordeal of the setting sun to be swallowed by night-sky goddess Nut, to pass through the 'duat' or underworld and be born anew each morning. The plants depicted with this solar fan of fronds or petals and 'supported' by pairs of pendant blooms, buds or fruit clusters all seem especially to emulate and share in the sun's sacrificial cycle of death and re-birth and to point to the lessons it holds for mankind. It seems likely that the underlying model for all these fertile shapes, echoed by the curling cows-horn wig and sistrum-volutes of maternity-goddess Hathor
Hathor
Hathor , is an Ancient Egyptian goddess who personified the principles of love, beauty, music, motherhood and joy. She was one of the most important and popular deities throughout the history of Ancient Egypt...
, was the womb, with the twin egg-clusters of its ovaries
Ovary
The ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ, often found in pairs as part of the vertebrate female reproductive system. Ovaries in anatomically female individuals are analogous to testes in anatomically male individuals, in that they are both gonads and endocrine glands.-Human anatomy:Ovaries...
. When the sun is re-born in the morning it is said to be born from the womb of Nut. The stylized palmette-forms of the lotus and papyrus showing the solar rosette or daisy-wheel emerging from the volutes of the calyx are similar magical enactments of the 'akhet' – this sacred moment of enhanced creation, the act of transcending or surpassing one's mortal form and 'going forth by day' as an 'akh' or higher, winged, shining, all-encompassing and all-seeing form of life.
Most early Egyptian forms of the motif appear later in Crete, Mesopotamia, Assyria and Ancient Persia, including the daisy-wheel-style lotus and bud border. In the form of the palmette that appears most frequently on Greek pottery, often interspersed with scenes of heroic deeds, the same motif is bound within a leaf-shaped or lotus-bud shaped outer line. The outer line can be seen to have evolved from an alternating frieze of stylized lotus and palmette. This anticipates the form it often took – from renaissance sculpture through to baroque fountains – of the inside of a half scallop shell, in which the palm fronds have become the fan of the shell and the scrolls remain at the convergence of the fan. Here the shape was associated with Venus or Neptune and was typically flanked by a pair of dolphins 25.115601°N 55.132484°W or became a vehicle drawn by sea-horses. Later, this circular or oval outer line became a motif in itself, forming an open C-shape with the two in-growing scrolls at its tips. Much baroque
Baroque
The Baroque is a period and the style that used exaggerated motion and clear, easily interpreted detail to produce drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur in sculpture, painting, literature, dance, and music...
and rococo
Rococo
Rococo , also referred to as "Late Baroque", is an 18th-century style which developed as Baroque artists gave up their symmetry and became increasingly ornate, florid, and playful...
furniture, stucco ornament or wrought-iron work of gates and balconies is made up of ever-varying combinations these C-scrolls, either on their own, back to back, or in support of full palmettes.
Classical architecture
As an ornamental motif found in classical architectureClassical architecture
Classical architecture is a mode of architecture employing vocabulary derived in part from the Greek and Roman architecture of classical antiquity, enriched by classicizing architectural practice in Europe since the Renaissance...
, the palmette and anthemion take many and varied forms. Typically, the upper part of the motif consists of five or more leaves or petals fanning rhythmically upwards from a single triangular or lozenge-shaped source at the base. In some instances fruits resembling palm fruits hang down on either side above the base and below the lowest leaves. The lower part consists of a symmetrical pair of elegant 'S' scrolls or volute
Volute
A volute is a spiral scroll-like ornament that forms the basis of the Ionic order, found in the capital of the Ionic column. It was later incorporated into Corinthian order and Composite column capitals...
s curling out sideways and downwards from the base of the leaves. The upper part recalls the thrusting growth of leaves and flowers, while the volutes of the lower part seem to suggest both contributing fertile energies and resulting fruits. It is often present on the necking of the capital of ionic order
Ionic order
The Ionic order forms one of the three orders or organizational systems of classical architecture, the other two canonic orders being the Doric and the Corinthian...
columns; however in column capitals of the Corinthian order
Corinthian order
The Corinthian order is one of the three principal classical orders of ancient Greek and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric and Ionic. When classical architecture was revived during the Renaissance, two more orders were added to the canon, the Tuscan order and the Composite order...
it takes the shape of a 'fleuron' or flower resting against the abacus
Abacus (architecture)
In architecture, an abacus is a flat slab forming the uppermost member or division of the capital of a column, above the bell. Its chief function is to provide a large supporting surface to receive the weight of the arch or the architrave above...
(top-most slab) of the capital and springing out from a pair of volutes which, in some versions, give rise to the elaborate volutes
Volute
A volute is a spiral scroll-like ornament that forms the basis of the Ionic order, found in the capital of the Ionic column. It was later incorporated into Corinthian order and Composite column capitals...
and acanthus
Acanthus (ornament)
The acanthus is one of the most common plant forms to make foliage ornament and decoration.-Architecture:In architecture, an ornament is carved into stone or wood to resemble leaves from the Mediterranean species of the Acanthus genus of plants, which have deeply cut leaves with some similarity to...
ornament
Ornament (architecture)
In architecture and decorative art, ornament is a decoration used to embellish parts of a building or object. Large figurative elements such as monumental sculpture and their equivalents in decorative art are excluded from the term; most ornament does not include human figures, and if present they...
of the capital.
In classical architecture the motif had specific uses, including:
- the fronts of ante-fixaeAnte-fixaeAn antefix is a vertical block which terminates the covering tiles of the roof of a tiled roof. In grand buildings the face of each stone ante-fix was richly carved, often with the anthemion ornament...
, - acroteria
- the upper portion of the stele or vertical tombstones,
- the necking of the Ionic columns of the ErechtheumErechtheumThe Erechtheion is an ancient Greek temple on the north side of the Acropolis of Athens in Greece.-Architecture:The temple as seen today was built between 421 and 406 BC. Its architect may have been Mnesicles, and it derived its name from a shrine dedicated to the legendary Greek hero Erichthonius...
and its continuation as a decorative frieze on the walls of the same, and - the cymatiumCymatiumCymatium, a molding on the cornice of some classical buildings. Sometimes decorated with an anthemion. It is characteristic of Ionic columns and can appear as part of the entablature, the epistylium, and the capital....
of a corniceCorniceCornice molding is generally any horizontal decorative molding that crowns any building or furniture element: the cornice over a door or window, for instance, or the cornice around the edge of a pedestal. A simple cornice may be formed just with a crown molding.The function of the projecting...
.
Variants and related motifs

Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
palmette motifs existed both as a form of flower and as a stylized tree, often referred to as a Tree of Life
Tree of Life
The tree of life in the Book of Genesis is a tree planted by God in midst of the Garden of Eden , whose fruit gives everlasting life, i.e. immortality. Together with the tree of life, God planted the tree of the knowledge of good and evil . According to some scholars, however, these are in fact...
. Other examples from ancient Egypt are the alternating lotus flower and bud border designs, the winged disk with its pair of uraeus
Uraeus
The Uraeus is the stylized, upright form of an Egyptian spitting cobra , used as a symbol of sovereignty, royalty, deity, and divine authority in ancient Egypt.The Uraeus is a symbol for the goddess Wadjet, who was one of the earliest Egyptian deities and who...
serpents, the Eye of Horus
Eye of Horus
The Eye of Horus is an ancient Egyptian symbol of protection, royal power and good health. The eye is personified in the goddess Wadjet...
and curve-topped commemorative stele. In later Assyrian versions of the Tree of Life, the feathered falcon wings of the Egyptian winged disk have become associated with the frond
Frond
The term frond refers to a large, divided leaf. In both common usage and botanical nomenclature, the leaves of ferns are referred to as fronds and some botanists restrict the term to this group...
s of the palm tree. Similar lotus flower and bud borders, closely associated with palmettes and rosettes, also appeared in Mesopotamia. There appears to be an equivalence between the horns of horned creatures, the wings of winged beings including angels, griffins and sphinx
Sphinx
A sphinx is a mythical creature with a lion's body and a human head or a cat head.The sphinx, in Greek tradition, has the haunches of a lion, the wings of a great bird, and the face of a woman. She is mythicised as treacherous and merciless...
es and both the fan and the volutes of the palmette; there is also an underlying 'V' shape in each of these forms that parallels the association of the palm itself with victory, energy and optimism.

Caduceus
The caduceus is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology. The same staff was also borne by heralds in general, for example by Iris, the messenger of Hera. It is a short staff entwined by two serpents, sometimes surmounted by wings...
wand of Hermes, the ubiquitous scrolled scallop shells in the canopy of the renaissance sculptural niche
Niche (architecture)
A niche in classical architecture is an exedra or an apse that has been reduced in size, retaining the half-dome heading usual for an apse. Nero's Domus Aurea was the first semi-private dwelling that possessed rooms that were given richly varied floor plans, shaped with niches and exedras;...
, originating in Greek and Roman sarcophagi, echoed above theatrical proscenium
Proscenium
A proscenium theatre is a theatre space whose primary feature is a large frame or arch , which is located at or near the front of the stage...
arches and on the doors, windows, wrought iron gates and balconies of palaces and grand houses; the shell-like fanlight
Fanlight
A fanlight is a window, semicircular or semi-elliptical in shape, with glazing bars or tracery sets radiating out like an open fan, It is placed over another window or a doorway. and is sometimes hinged to a transom. The bars in the fixed glazed window spread out in the manner a sunburst...
over the door in Georgian and similar urban architecture, the 'gul' and 'boteh' motifs of Central Asian carpets
Persian rug
The Persian carpet is an essential part of Persian art and culture. Carpet-weaving is undoubtedly one of the most distinguished manifestations of Persian culture and art, and dates back to ancient Persia. In 2008, Iran’s exports of hand-woven carpets was $420 million or 30% of the world's market...
and textiles, the trident of Neptune/Poseidon
Trident
A trident , also called a trishul or leister or gig, is a three-pronged spear. It is used for spear fishing and was also a military weapon. Tridents are featured widely in mythical, historical and modern culture. The major Hindu god, Shiva the Destroyer and the sea god Poseidon or Neptune are...
, both the trident and lingam
Lingam
The Lingam is a representation of the Hindu deity Shiva used for worship in temples....
of Shiva
Shiva
Shiva is a major Hindu deity, and is the destroyer god or transformer among the Trimurti, the Hindu Trinity of the primary aspects of the divine. God Shiva is a yogi who has notice of everything that happens in the world and is the main aspect of life. Yet one with great power lives a life of a...
, the 'bai sema' lotus-petal-shaped boundary marker
Boundary marker
A boundary marker, boundary stone or border stone is a robust physical marker that identifies the start of a land boundary or the change in a boundary, especially a change in a direction of a boundary...
s of the Thai inner-temple, Vishnu's mount, Garuda, the vajra thunderbolt
Thunderbolt
A thunderbolt is a discharge of lightning accompanied by a loud thunderclap or its symbolic representation. In its original usage the word may also have been a description of meteors, or, as Plato suggested in Timaeus, of the consequences of a close approach between two planetary cosmic bodies,...
, diamond mace or enlightenment
Bodhi
Bodhi is both a Pāli and Sanskrit word traditionally translated into English with the word "enlightenment", but which means awakened. In Buddhism it is the knowledge possessed by a Buddha into the nature of things...
jewel-in-the-lotus
Nelumbo nucifera
Nelumbo nucifera, known by a number of names including Indian Lotus, Sacred Lotus, Bean of India, or simply Lotus, is a plant in the monogeneric family Nelumbonaceae...
of Tibet and South-East Asia, the symmetrically scrolled cloud and bat motifs and the similarly scrolled ruyi or ju-i scepter and lingzhi or fungus of longevity of the Chinese tradition. Both as a form of the lotus rising from the swamps to touch the sun and as a (palm) tree reaching from earth to heaven, the palmette carries the characteristics of the axis mundi
Axis mundi
The axis mundi , in religion or mythology, is the world center and/or the connection between heaven and Earth. As the celestial pole and geographic pole, it expresses a point of connection between sky and earth where the four compass directions meet...
or world tree. The fleur de lis, which became a potent and enigmatic emblem of the divine right of kings
Divine Right of Kings
The divine right of kings or divine-right theory of kingship is a political and religious doctrine of royal and political legitimacy. It asserts that a monarch is subject to no earthly authority, deriving his right to rule directly from the will of God...
, said to have been bestowed on early French kings by an angel, evolved in Egypt and Mesopotamia as a variant of the palmette. mage:Weltliche Schatzkammer Wienc.jpg|thumb|300px|right|The coronation mantle of the Holy Roman Emperors (Vienna; Imperial treasury
Schatzkammer (Vienna)
The Imperial Treasury in Vienna, Austria is located in the Hofburg with its entrance at the Schweizerhof , the oldest part of the palace rebuilt in a Renaissance style under Emperor Ferdinand I...
Similarly, from the early 13th century to 1806 the divine right of the Holy Roman Emperors was conferred by investiture in the imperial regalia, which included the coronation mantle displaying the twin lions (recalling the twin lions of Aker above) guarding the palm in the form of a tree of life, with its two pendant clusters of fruit.
It is believed that the Irminsul
Irminsul
An Irminsul was a kind of pillar which is attested as playing an important role in the Germanic paganism of the Saxon people. The oldest chronicle describing an Irminsul refers to it as a tree trunk erected in the open air...
, the sacred pillar of the Saxons and equivalent of the Norse Yggdrasil
Yggdrasil
In Norse mythology, Yggdrasil is an immense tree that is central in Norse cosmology. It was said to be the world tree around which the nine worlds existed...
, another version of the world tree, took on its palmette form under gallo-Roman influence.

The anthemion is also the mint mark of the Mint of Greece, and it shows in all Greek euro coins
Greek euro coins
Greek euro coins feature a unique design for each of the eight coins. They were all designed by Georgios Stamatopoulos with the minor coins depicting Greek ships, the middle ones portraying famous Greeks and the two large denominations showing images of Greek history and mythology. All designs...
destined for circulation, as well as in all Greek collectors' coins
Euro gold and silver commemorative coins (Greece)
Euro gold and silver commemorative coins are special euro coins minted and issued by member states of the Eurozone, mainly in gold and silver, although other precious metals are also used in rare occasions. Greece was one of the first twelve countries in the Eurozone that introduced the euro on...
.
See also
- Tree of lifeTree of lifeThe concept of a tree of life, a many-branched tree illustrating the idea that all life on earth is related, has been used in science , religion, philosophy, mythology, and other areas...
- Fleur-de-LysFleur-de-lisThe fleur-de-lis or fleur-de-lys is a stylized lily or iris that is used as a decorative design or symbol. It may be "at one and the same time, political, dynastic, artistic, emblematic, and symbolic", especially in heraldry...
- Lotus Flower
- Blue Egyptian Water LilyNymphaea caeruleaNymphaea caerulea, also known as the Blue Egyptian water lily or sacred blue lily, is a water-lily in the genus Nymphaea.-Distribution:Its original habitat may have been along the Nile and other locations in East Africa...

