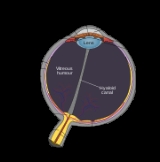
Optic disc
Encyclopedia
The optic disc or optic nerve head is the location where ganglion cell
axons exit the eye
to form the optic nerve
. There are no light sensitive rods or cones to respond to a light
stimulus at this point. This causes a break in the visual field
called "the blind spot
" or the "physiological blind spot". The optic disc represents the beginning of the optic nerve (second cranial nerve) and is the point where the axons of retinal ganglion
cells come together. The optic disc is also the entry point for the major blood vessels that supply the retina. The optic nerve head in a normal human eye carries from 1 to 1.2 million neuron
s from the eye towards the brain.
. It is a vertical oval, with average dimensions of 1.76mm horizontally by 1.92mm vertically. There is a central depression, of variable size, called the optic cup
.
examination
along with an appropriate aspheric focusing lens (+66D, +78D or +90D) is required for a detailed stereoscopic view of the optic disc and structures inside the eye.
A biomicroscopic exam can give an indication of the health of the optic nerve. In particular, the eye care physician notes the colour, cupping size (as a cup-to-disc ratio
), sharpness of edge, swelling, hemorrhages, notching in the optic disc and any other unusual anomalies. It is useful for finding evidence corroborating the diagnosis of glaucoma
and other optic neuropathies, optic neuritis
, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
or papilledema
(i.e. optic disc swelling produced by raised intracranial pressure
), and optic disc drusen
.
Women in advanced stage of pregnancy with pre-eclampsia
should be screened by an ophthalmoscopic examination of the optic disc for early evidence of rise in intracranial pressure
.
(Stratus-OCT 3) are the currently available computerised techniques for imaging various structures of the eyes, including the optic disc. They quantify the nerve fiber layer of disc and surrounding retina and statistically correlate the findings with a database of previously screened population of normals. They are useful for baseline and serial follow-up to monitor minute changes in optic disc morphology
.
Imaging will not provide conclusive evidence for clinical diagnosis however, and the evidence needs to be supplanted by serial physiological testing for functional changes. Such tests may include visual field charting, and final clinical interpretation of the complete eye examination
by an eye care physician. Ophthalmologists and Optometrists are able to provide this service.
Ganglion cell
A retinal ganglion cell is a type of neuron located near the inner surface of the retina of the eye. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: bipolar cells and amacrine cells...
axons exit the eye
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
to form the optic nerve
Optic nerve
The optic nerve, also called cranial nerve 2, transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. Derived from the embryonic retinal ganglion cell, a diverticulum located in the diencephalon, the optic nerve doesn't regenerate after transection.-Anatomy:The optic nerve is the second of...
. There are no light sensitive rods or cones to respond to a light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
stimulus at this point. This causes a break in the visual field
Visual field
The term visual field is sometimes used as a synonym to field of view, though they do not designate the same thing. The visual field is the "spatial array of visual sensations available to observation in introspectionist psychological experiments", while 'field of view' "refers to the physical...
called "the blind spot
Blind spot (vision)
A blind spot, also known as a scotoma, is an obscuration of the visual field. A particular blind spot known as the blindspot, or physiological blind spot, or punctum caecum in medical literature, is the place in the visual field that corresponds to the lack of light-detecting photoreceptor cells on...
" or the "physiological blind spot". The optic disc represents the beginning of the optic nerve (second cranial nerve) and is the point where the axons of retinal ganglion
Ganglion
In anatomy, a ganglion is a biological tissue mass, most commonly a mass of nerve cell bodies. Cells found in a ganglion are called ganglion cells, though this term is also sometimes used to refer specifically to retinal ganglion cells....
cells come together. The optic disc is also the entry point for the major blood vessels that supply the retina. The optic nerve head in a normal human eye carries from 1 to 1.2 million neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s from the eye towards the brain.
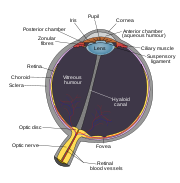
Anatomy
The optic disc is placed 3 to 4 mm to the nasal side of the foveaFovea
The fovea centralis, also generally known as the fovea , is a part of the eye, located in the center of the macula region of the retina....
. It is a vertical oval, with average dimensions of 1.76mm horizontally by 1.92mm vertically. There is a central depression, of variable size, called the optic cup
Optic cup (ophthalmology)
The optic cup is the white, cup-like area in the center of the optic disc.The ratio of the size of the optic cup to the optic disc is measured to diagnose glaucoma....
.
Clinical examination
The eye is unique because of the transparency of its optical media. Almost all eye structures can be examined with appropriate optical equipment and lenses. Using a modern direct ophthalmoscope gives a view of the optic disc using the principle of reversibility of light. A slit lamp biomicroscopicSlit lamp
The slit lamp is an instrument consisting of a high-intensity light source that can be focused to shine a thin sheet of light into the eye. It is used in conjunction with a biomicroscope...
examination
Eye examination
An eye examination is a battery of tests performed by an ophthalmologist, optometrist, or orthoptist assessing vision and ability to focus on and discern objects, as well as other tests and examinations pertaining to the eyes....
along with an appropriate aspheric focusing lens (+66D, +78D or +90D) is required for a detailed stereoscopic view of the optic disc and structures inside the eye.
A biomicroscopic exam can give an indication of the health of the optic nerve. In particular, the eye care physician notes the colour, cupping size (as a cup-to-disc ratio
Cup-to-disc ratio
The cup-to-disc ratio is a measurement used in ophthalmology and optometry to assess the progression of glaucoma. The optic disc is the anatomical location of the eye's "blind spot", the area where the optic nerve and blood vessels enter the retina. The optic disc can be flat or it can have a...
), sharpness of edge, swelling, hemorrhages, notching in the optic disc and any other unusual anomalies. It is useful for finding evidence corroborating the diagnosis of glaucoma
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye disorder in which the optic nerve suffers damage, permanently damaging vision in the affected eye and progressing to complete blindness if untreated. It is often, but not always, associated with increased pressure of the fluid in the eye...
and other optic neuropathies, optic neuritis
Optic neuritis
Optic neuritis is the inflammation of the optic nerve that may cause a complete or partial loss of vision.-Causes:The optic nerve comprises axons that emerge from the retina of the eye and carry visual information to the primary visual nuclei, most of which is relayed to the occipital cortex of the...
, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy is a medical condition involving loss of vision due to damage to the optic nerve from insufficient blood supply. AION is generally divided into two types: arteritic AION and non-arteritic AION...
or papilledema
Papilledema
Papilledema is optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure. The swelling is usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks. Unilateral presentation is extremely rare....
(i.e. optic disc swelling produced by raised intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
), and optic disc drusen
Optic disc drusen
Optic disc drusen or optic nerve head drusen are globules of mucoproteins and mucopolysaccharides that progressively calcify in the optic disc...
.
Women in advanced stage of pregnancy with pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia or preeclampsia is a medical condition in which hypertension arises in pregnancy in association with significant amounts of protein in the urine....
should be screened by an ophthalmoscopic examination of the optic disc for early evidence of rise in intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
.

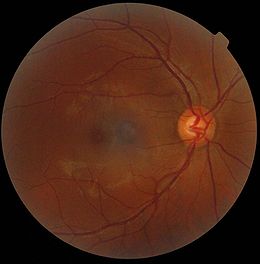
Pale disc
A normal optic disc is orange to pink in colour. A pale disc is an optic disc which varies in colour from a pale pink or orange colour to white. A pale disc is an indication of a disease condition.Imaging of the optic disc
Traditional colour-film camera images are the gold standard in imaging, requiring an expert ophthalmic photographer, ophthalmic technician, optometrist or an ophthalmologist for taking standardised pictures of the optic disc. Stereoscopic images offer an excellent investigative tool for serial follow-up of suspected changes in the hands of an expert optometrist or ophthalmologist. Automated techniques have also been developed to allow for more efficient and less expensive imaging. Heidelberg Retinal Tomography (HRT-II), GDx-VCC and optical coherence tomographyOptical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography is an optical signal acquisition and processing method. It captures micrometer-resolution, three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media . Optical coherence tomography is an interferometric technique, typically employing near-infrared light...
(Stratus-OCT 3) are the currently available computerised techniques for imaging various structures of the eyes, including the optic disc. They quantify the nerve fiber layer of disc and surrounding retina and statistically correlate the findings with a database of previously screened population of normals. They are useful for baseline and serial follow-up to monitor minute changes in optic disc morphology
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
.
Imaging will not provide conclusive evidence for clinical diagnosis however, and the evidence needs to be supplanted by serial physiological testing for functional changes. Such tests may include visual field charting, and final clinical interpretation of the complete eye examination
Eye examination
An eye examination is a battery of tests performed by an ophthalmologist, optometrist, or orthoptist assessing vision and ability to focus on and discern objects, as well as other tests and examinations pertaining to the eyes....
by an eye care physician. Ophthalmologists and Optometrists are able to provide this service.


