
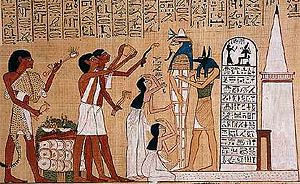
Opening of the mouth ceremony
Encyclopedia
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
ian ritual described in funerary text
Funerary text
Funerary texts or funerary literature feature in many belief systems. Its purpose is usually to provide guidance to the newly deceased or the soon-to-be-deceased about how to survive and prosper in the afterlife.-Antiquity:...
s such as the Pyramid Texts
Pyramid Texts
The Pyramid Texts are a collection of ancient Egyptian religious texts from the time of the Old Kingdom. The pyramid texts are possibly the oldest known religious texts in the world. Written in Old Egyptian, the pyramid texts were carved on the walls and sarcophagi of the pyramids at Saqqara during...
.
Funerary magic
The ritual involved the symbolic animation of a statueStatue
A statue is a sculpture in the round representing a person or persons, an animal, an idea or an event, normally full-length, as opposed to a bust, and at least close to life-size, or larger...
or mummy
Mummy
A mummy is a body, human or animal, whose skin and organs have been preserved by either intentional or incidental exposure to chemicals, extreme coldness , very low humidity, or lack of air when bodies are submerged in bogs, so that the recovered body will not decay further if kept in cool and dry...
by magically opening its mouth so that it could breathe and speak. There is evidence of this ritual from the Old Kingdom
Old Kingdom
Old Kingdom is the name given to the period in the 3rd millennium BC when Egypt attained its first continuous peak of civilization in complexity and achievement – the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods, which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley .The term itself was...
to the Roman Period. Special tools were used to perform the ceremony, such as a ritual adze
Adze
An adze is a tool used for smoothing or carving rough-cut wood in hand woodworking. Generally, the user stands astride a board or log and swings the adze downwards towards his feet, chipping off pieces of wood, moving backwards as they go and leaving a relatively smooth surface behind...
, an arm shaped ritual censer, a spooned blade known as a peseshkaf, a serpent-head blade, and a variety of other amulets. A calf's leg was also held up to the lips painted on the coffin.
The ancient Egyptians believed that in order for a person's soul to survive in the afterlife it would need to have food and water. The opening of the mouth ritual was thus performed so that the person who died could eat and drink again in the afterlife.
The ceremony involved up to 75 "episodes" and, in its most complete version, included the following stages:
- Episodes 1–9 Preliminary rites
- Episodes 10–22 Animation of the statue
- Episodes 23–42 Meat offerings aligned with upper Egypt
- Episodes 43–46 Meat offerings aligned with lower Egypt
- Episodes 47–71 Funerary meal
- Episodes 72–75 Closing rites
The Book of the Dead also contains a spell for this process, which the deceased may use on themselves:
- My mouth is opened by Ptah,
- My mouth's bonds are loosed by my city-god.
- Thoth has come fully equipped with spells,
- He looses the bonds of Seth from my mouth.
- Atum has given me my hands,
- They are placed as guardians.
- My mouth is given to me,
- My mouth is opened by Ptah,
- With that chisel of metal
- With which he opened the mouth of the gods.
- I am Sekhmet-Wadjet who dwells in the west of heaven,
- I am Sahyt among the souls of On.
Connections with Psalm 51
Parallels between the Opening of the Mouth and Psalm 51Psalm 51
Psalm 51 , traditionally referred to as the Miserere, its Latin incipit, is one of the Penitential Psalms. It begins: Have mercy on me, O God....
are pointed out in "Psalm 51 and the 'Opening of the Mouth' Ceremony," by Benjamin Urrutia
Benjamín Urrutia
Benjamin Urrutia is an author and scholar. With Guy Davenport, Urrutia edited The Logia of Yeshua, which collected what Urrutia and Davenport consider to be Jesus' authentic sayings from a variety of canonical and non-canonical sources...
, Scripta Hierosolymitana: Publications of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, volume 28, pages 222–223 (1982). The parallels include:
- Mentions of ritual washing with special herbs (Psalm 51:2,7).
- Restoration of broken bones (verse 8).
- "O Lord, open thou my lips" (verse 15).
- Sacrifices (verses 16,17, 19).
External links
- The Opening of the Mouth Ritual by Marie Parsons

