Open source software development
Encyclopedia
Open source software development is the process by which open source
software (or similar software whose source code
is publicly available) is developed. These are software products “available with its source code and under an open source license to study, change, and improve its design”. Examples of popular open source software products are Mozilla Firefox
, Google Chrome
, Android and the OpenOffice.org Suite
.
In the past, the open source software development method has been very unstructured, because no clear development tools, phases, etc., had been defined like with development methods such as Dynamic Systems Development Method
. Instead, every project had its own phases. However, more recently there has been much better progress, coordination, and communication within the open source community.
wrote The Cathedral and the Bazaar. In this book, Raymond makes the distinction between two kinds of software development. The first is the conventional closed source development. These kind of development methods are, according to Raymond, like the building of a cathedral; central planning, tight organization and one process from start to finish. The second is the progressive open source development, which is more like a “a great babbling bazaar of differing agendas and approaches out of which a coherent and stable system could seemingly emerge only by a succession of miracles.” The latter analogy points to the discussion involved in an open source development process. In some projects, anyone can submit suggestions and discuss them. The ‘coherent and stable systems’ Raymond mentions often do emerge from open source software development projects.
Differences between the two styles of development, according to Bar & Fogel, are in general the handling (and creation) of bug reports and feature requests, and the constraints under which the programmers are working. In closed source software development, the programmers are often spending a lot of time dealing with and creating bug reports, as well as handling feature requests. This time is spent on prioritizing and creation of further development plans. This leads to (part of) the development team spending a lot of time on these issues, and not on the actual development. Also, in closed source projects, the development teams must often work under management-related constraints (such as deadlines, budgets, etc.) that interfere with technical issues of the software. In open source software development, these issues are solved by integrating the users of the software in the development process, or even letting these users build the system themselves.
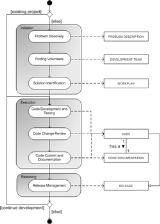
 Open source software development can be divided into several phases. The phases specified here are derived from Sharma et al.. A diagram displaying the process-data structure of open source software development is shown on the right. In this picture, the phases of open source software development are displayed, along with the corresponding data elements. This diagram is made using the meta-modeling and meta-process modeling
Open source software development can be divided into several phases. The phases specified here are derived from Sharma et al.. A diagram displaying the process-data structure of open source software development is shown on the right. In this picture, the phases of open source software development are displayed, along with the corresponding data elements. This diagram is made using the meta-modeling and meta-process modeling
techniques.
The process starts with a choice between the adopting of an existing project, or the starting of a new project. If a new project is started, the process goes to the Initiation phase. If an existing project is adopted, the process goes directly to the Execution phase.
, the Firefox web browser and the OpenOffice.org office suite of tools.
Distributions are another type of open source project. Distributions are collections of software that are published from the same source with a common purpose. The most prominent example of a "distribution" is an operating system. There are a large number of Linux
distributions (such as Debian
, Fedora Core
, Mandriva
, Slackware
, Ubuntu
etc.) which ship the Linux kernel along with many user-land components. There are also other distributions, like ActivePerl, the Perl programming language
for various operating system, and even the OpenCD and cygwin
distributions of open-source programs for Microsoft Windows
.
Other open source projects, like the BSD
derivatives, maintain the source code of an entire operating system, the kernel and all of its core components, in one revision control
system; developing the entire system together as a single team. These operating system development projects closely integrate their tools, more so than in the other distribution-based systems.
Finally, there is the book or standalone document project. These items usually do not ship as part of an open source software package. The Linux Documentation Project hosts many such projects that document various aspects of the GNU/Linux operating system. There are many other examples of this type of open source project.
Eric Raymond observed in his famous essay "The Cathedral and the Bazaar" that announcing the intent for a project is usually inferior to releasing a working project to the public.
It's a common mistake to start a project when contributing to an existing similar project would be more effective (NIH syndrome). To start a successful project it is very important to investigate what's already there.
, because in these traditional methods it is not allowed to go back to a previous phase. In open source software development requirements are rarely gathered before the start of the project; instead they are based on early releases of the software product, as Robbins describes. Besides requirements, often volunteer staff is attracted to help develop the software product based on the early releases of the software. This networking effect is essential according to Abrahamsson et al.: “if the introduced prototype gathers enough attention, it will gradually start to attract more and more developers”. However, Abrahamsson et al. also point out that the community is very harsh, much like the business world of closed source software: “if you find the customers you survive, but without customers you die”.
Alfonso Fuggetta mentions that “rapid prototyping, incremental and evolutionary development, spiral lifecycle, rapid application development, and, recently, extreme programming and the agile software process can be equally applied to proprietary and open source software”.
One open source development method mentioned by Fuggetta is an agile method
called Extreme Programming
. All the Agile methods are in essence applicable to open source software development, because of their iterative and incremental character.
Another Agile method, Internet-Speed Development
, is also suitable for open source software development in particular because of the distributed development principle it adopts. Internet-Speed Development used geographically distributed teams to ‘work around the clock’. This method is mostly adopted by large closed source firms like Microsoft
, because only big software firms are able to create distributed development centers in different time zones. Of course if software is developed by a large group of volunteers in different countries, this is being achieved naturally and without the investment needed like with closed source software development.
is one of the most common forms of communication among open source developers and users. Often, electronic mailing list
s are used to make sure e-mail messages are delivered to all interested parties at once. This ensures that at least one of the members can reply to it (in private or to the whole mailing list). In order to communicate in real time, many projects use an instant messaging
method such as IRC
(although there are many others available). Web forums have recently become a common way for users to get help with problems they encounter when using an open source product. Wiki
s have become common as a communication medium for developers and users.
Concurrent Versions System
(CVS) is a prominent example of a source code collaboration tool being used in OSS projects. CVS helps manage the files and codes of a project when several people are working on the project at the same time. CVS allows several people to work on the same file at the same time. This is done by moving the file into the users’ directories and then merging the files when the users are done. CVS also enables one to easily retrieve a previous version of a file.
The Subversion revision control system (SVN) was created to replace CVS. It is quickly gaining ground as an OSS project version control system.
Many open source projects are now using distributed revision control systems
, which scale better than centralized repositories such as SVN and CVS. Popular examples are git
, used by the Linux kernel
, and Mercurial
, used by the Python
programming language.
. Tinderbox enables participants in an OSS project to detect errors during system integration. Tinderbox runs a continuous build process and informs users about the parts of source code that have issues and on which platform(s) these issues arise. Furthermore, this tool identifies the author of the offending code. The author is then held responsible for ensuring that error is resolved. Mainly because normal testing tools are quite expensive, open source testing tools are gaining popularity.
A debugger
is a computer program that is used to debug (and sometimes test or optimize) other programs. GNU Debugger
(GDB) is an example of a debugger used in Open source software development. This debugger offers remote debugging, what makes it especially applicable to Open source software development. Also, some memory leak
detectors have been designed to work with GDB.
A memory leak tool or memory debugger
is a programming tool for finding memory leaks and buffer overflows. A memory leak is a particular kind of unnecessary memory consumption by a computer program, where the program fails to release memory that is no longer needed. Examples of memory leak detection tools used by Mozilla are the XPCOM
Memory Leak tools.
Validation tools are used to check if pieces of code conform to the specified syntax. They are most often used in the context of HTML/XML, but can also be used with programming languages. An example of a validation tool is LCLint, now called Splint
.
is a collection of tools to automate the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing software packages from a computer. The Red Hat Package Manager
(RPM) for .rpm and Advanced Packaging Tool
(APT) for .deb
file format, are package management systems used by a number of Linux distributions.
(as is often the case if the code was inherited from a previous developer), or because a proposed enhancement or extension of it cannot be cleanly implemented with the existing codebase. A final reason for wishing to revamp the code is that the code "smells bad" (to quote Martin Fowler
's Refactoring book) and does not meet the developer's
standards.
There are several kinds of revamps:
is an integral part of open source development. While many open source packages were known to be released with some glaring bugs even in some stable releases, most open source software eventually becomes very stable.
Traditionally, in most of the open source there was a general lack of awareness for automated tests, in which one writes automated test scripts and programs that run the software and try to find out if it behaves correctly. Recently, however, this awareness has been growing, possibly because of influence from Extreme Programming, and because of some high-profile software packages that incorporated such test suites.
Most open source software is either command line or alternatively APIs and as such is very easy to test automatically.
Open source
The term open source describes practices in production and development that promote access to the end product's source materials. Some consider open source a philosophy, others consider it a pragmatic methodology...
software (or similar software whose source code
Source code
In computer science, source code is text written using the format and syntax of the programming language that it is being written in. Such a language is specially designed to facilitate the work of computer programmers, who specify the actions to be performed by a computer mostly by writing source...
is publicly available) is developed. These are software products “available with its source code and under an open source license to study, change, and improve its design”. Examples of popular open source software products are Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox is a free and open source web browser descended from the Mozilla Application Suite and managed by Mozilla Corporation. , Firefox is the second most widely used browser, with approximately 25% of worldwide usage share of web browsers...
, Google Chrome
Google Chrome
Google Chrome is a web browser developed by Google that uses the WebKit layout engine. It was first released as a beta version for Microsoft Windows on September 2, 2008, and the public stable release was on December 11, 2008. The name is derived from the graphical user interface frame, or...
, Android and the OpenOffice.org Suite
OpenOffice.org
OpenOffice.org, commonly known as OOo or OpenOffice, is an open-source application suite whose main components are for word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, graphics, and databases. OpenOffice is available for a number of different computer operating systems, is distributed as free software...
.
In the past, the open source software development method has been very unstructured, because no clear development tools, phases, etc., had been defined like with development methods such as Dynamic Systems Development Method
Dynamic Systems Development Method
Dynamic systems development method is an agile project delivery framework, primarily used as a software development method. DSDM was originally based upon the rapid application development method. In 2007 DSDM became a generic approach to project management and solution delivery...
. Instead, every project had its own phases. However, more recently there has been much better progress, coordination, and communication within the open source community.
History
In 1997, Eric S. RaymondEric S. Raymond
Eric Steven Raymond , often referred to as ESR, is an American computer programmer, author and open source software advocate. After the 1997 publication of The Cathedral and the Bazaar, Raymond was for a number of years frequently quoted as an unofficial spokesman for the open source movement...
wrote The Cathedral and the Bazaar. In this book, Raymond makes the distinction between two kinds of software development. The first is the conventional closed source development. These kind of development methods are, according to Raymond, like the building of a cathedral; central planning, tight organization and one process from start to finish. The second is the progressive open source development, which is more like a “a great babbling bazaar of differing agendas and approaches out of which a coherent and stable system could seemingly emerge only by a succession of miracles.” The latter analogy points to the discussion involved in an open source development process. In some projects, anyone can submit suggestions and discuss them. The ‘coherent and stable systems’ Raymond mentions often do emerge from open source software development projects.
Differences between the two styles of development, according to Bar & Fogel, are in general the handling (and creation) of bug reports and feature requests, and the constraints under which the programmers are working. In closed source software development, the programmers are often spending a lot of time dealing with and creating bug reports, as well as handling feature requests. This time is spent on prioritizing and creation of further development plans. This leads to (part of) the development team spending a lot of time on these issues, and not on the actual development. Also, in closed source projects, the development teams must often work under management-related constraints (such as deadlines, budgets, etc.) that interfere with technical issues of the software. In open source software development, these issues are solved by integrating the users of the software in the development process, or even letting these users build the system themselves.
Open source software development phases

Meta-Process Modeling
Meta-process modeling is a type of metamodeling used in software engineering and systems engineering for the analysis and construction of models applicable and useful to some predefined problems....
techniques.
The process starts with a choice between the adopting of an existing project, or the starting of a new project. If a new project is started, the process goes to the Initiation phase. If an existing project is adopted, the process goes directly to the Execution phase.
Types of open source projects
One can distinguish several different types of open source projects. First, there is the garden variety of software programs and libraries. They are standalone pieces of code. Some might even be dependent on other open source projects. These projects serve a specified purpose and fill a definite need. Examples of this type of project include the Linux kernelLinux kernel
The Linux kernel is an operating system kernel used by the Linux family of Unix-like operating systems. It is one of the most prominent examples of free and open source software....
, the Firefox web browser and the OpenOffice.org office suite of tools.
Distributions are another type of open source project. Distributions are collections of software that are published from the same source with a common purpose. The most prominent example of a "distribution" is an operating system. There are a large number of Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
distributions (such as Debian
Debian
Debian is a computer operating system composed of software packages released as free and open source software primarily under the GNU General Public License along with other free software licenses. Debian GNU/Linux, which includes the GNU OS tools and Linux kernel, is a popular and influential...
, Fedora Core
Fedora (operating system)
Fedora is a RPM-based, general purpose collection of software, including an operating system based on the Linux kernel, developed by the community-supported Fedora Project and sponsored by Red Hat...
, Mandriva
Mandriva
Mandriva S.A. is a publicly traded Linux and open source software company with its headquarters in Paris, France and development center in Curitiba, Brazil. Mandriva, S.A...
, Slackware
Slackware
Slackware is a free and open source Linux-based operating system. It was one of the earliest operating systems to be built on top of the Linux kernel and is the oldest currently being maintained. Slackware was created by Patrick Volkerding of Slackware Linux, Inc. in 1993...
, Ubuntu
Ubuntu (operating system)
Ubuntu is a computer operating system based on the Debian Linux distribution and distributed as free and open source software. It is named after the Southern African philosophy of Ubuntu...
etc.) which ship the Linux kernel along with many user-land components. There are also other distributions, like ActivePerl, the Perl programming language
Perl
Perl is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. Perl was originally developed by Larry Wall in 1987 as a general-purpose Unix scripting language to make report processing easier. Since then, it has undergone many changes and revisions and become widely popular...
for various operating system, and even the OpenCD and cygwin
Cygwin
Cygwin is a Unix-like environment and command-line interface for Microsoft Windows. Cygwin provides native integration of Windows-based applications, data, and other system resources with applications, software tools, and data of the Unix-like environment...
distributions of open-source programs for Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
.
Other open source projects, like the BSD
Berkeley Software Distribution
Berkeley Software Distribution is a Unix operating system derivative developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group of the University of California, Berkeley, from 1977 to 1995...
derivatives, maintain the source code of an entire operating system, the kernel and all of its core components, in one revision control
Revision control
Revision control, also known as version control and source control , is the management of changes to documents, programs, and other information stored as computer files. It is most commonly used in software development, where a team of people may change the same files...
system; developing the entire system together as a single team. These operating system development projects closely integrate their tools, more so than in the other distribution-based systems.
Finally, there is the book or standalone document project. These items usually do not ship as part of an open source software package. The Linux Documentation Project hosts many such projects that document various aspects of the GNU/Linux operating system. There are many other examples of this type of open source project.
Starting an open source project
There are several ways in which work on an open source project can start:- An individual who senses the need for a project announces the intent to develop the project in public. The individual may receive offers of help from others. The group may then proceed to work on the code.
- A developer working on a limited but working codebaseCodebaseThe term codebase, or code base, is used in software development to mean the whole collection of source code used to build a particular application or component. Typically, the codebase includes only human-written source code files, and not, e.g., source code files generated by other tools or...
, releases it to the public as the first version of an open-source program. The developer continues to work on improving it, and possibly is joined by other developers. - The source code of a mature project is released to the public, after being developed as proprietary softwareProprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...
or in-house software. - A well-established open-source project can be forkedFork (software development)In software engineering, a project fork happens when developers take a legal copy of source code from one software package and start independent development on it, creating a distinct piece of software...
by an interested outside party. Several developers can then start a new project, whose source code then diverges from the original.
Eric Raymond observed in his famous essay "The Cathedral and the Bazaar" that announcing the intent for a project is usually inferior to releasing a working project to the public.
It's a common mistake to start a project when contributing to an existing similar project would be more effective (NIH syndrome). To start a successful project it is very important to investigate what's already there.
Open source software development methods
It is hard to run an open source project following a more traditional software development method like the waterfall modelWaterfall model
The waterfall model is a sequential design process, often used in software development processes, in which progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards through the phases of Conception, Initiation, Analysis, Design, Construction, Testing, Production/Implementation and Maintenance.The waterfall...
, because in these traditional methods it is not allowed to go back to a previous phase. In open source software development requirements are rarely gathered before the start of the project; instead they are based on early releases of the software product, as Robbins describes. Besides requirements, often volunteer staff is attracted to help develop the software product based on the early releases of the software. This networking effect is essential according to Abrahamsson et al.: “if the introduced prototype gathers enough attention, it will gradually start to attract more and more developers”. However, Abrahamsson et al. also point out that the community is very harsh, much like the business world of closed source software: “if you find the customers you survive, but without customers you die”.
Alfonso Fuggetta mentions that “rapid prototyping, incremental and evolutionary development, spiral lifecycle, rapid application development, and, recently, extreme programming and the agile software process can be equally applied to proprietary and open source software”.
One open source development method mentioned by Fuggetta is an agile method
Agile software development
Agile software development is a group of software development methodologies based on iterative and incremental development, where requirements and solutions evolve through collaboration between self-organizing, cross-functional teams...
called Extreme Programming
Extreme Programming
Extreme programming is a software development methodology which is intended to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements...
. All the Agile methods are in essence applicable to open source software development, because of their iterative and incremental character.
Another Agile method, Internet-Speed Development
Internet-Speed Development
Internet-Speed Development is an Agile Software Development development method using a combined spiral model/waterfall model with daily builds aimed at developing a product with high speed....
, is also suitable for open source software development in particular because of the distributed development principle it adopts. Internet-Speed Development used geographically distributed teams to ‘work around the clock’. This method is mostly adopted by large closed source firms like Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
, because only big software firms are able to create distributed development centers in different time zones. Of course if software is developed by a large group of volunteers in different countries, this is being achieved naturally and without the investment needed like with closed source software development.
Communication channels
Developers and users of an open source project are not all necessarily working on the project in proximity. They require some electronic means of communications. E-mailE-mail
Electronic mail, commonly known as email or e-mail, is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more recipients. Modern email operates across the Internet or other computer networks. Some early email systems required that the author and the recipient both be online at the...
is one of the most common forms of communication among open source developers and users. Often, electronic mailing list
Electronic mailing list
An electronic mailing list is a special usage of email that allows for widespread distribution of information to many Internet users. It is similar to a traditional mailing list — a list of names and addresses — as might be kept by an organization for sending publications to...
s are used to make sure e-mail messages are delivered to all interested parties at once. This ensures that at least one of the members can reply to it (in private or to the whole mailing list). In order to communicate in real time, many projects use an instant messaging
Instant messaging
Instant Messaging is a form of real-time direct text-based chatting communication in push mode between two or more people using personal computers or other devices, along with shared clients. The user's text is conveyed over a network, such as the Internet...
method such as IRC
Internet Relay Chat
Internet Relay Chat is a protocol for real-time Internet text messaging or synchronous conferencing. It is mainly designed for group communication in discussion forums, called channels, but also allows one-to-one communication via private message as well as chat and data transfer, including file...
(although there are many others available). Web forums have recently become a common way for users to get help with problems they encounter when using an open source product. Wiki
Wiki
A wiki is a website that allows the creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language or a WYSIWYG text editor. Wikis are typically powered by wiki software and are often used collaboratively by multiple users. Examples include...
s have become common as a communication medium for developers and users.
Version control systems
In OSS development the participants, who are mostly volunteers, are distributed amongst different geographic regions so there is need for tools to aid participants to collaborate in the development of source code.Concurrent Versions System
Concurrent Versions System
The Concurrent Versions System , also known as the Concurrent Versioning System, is a client-server free software revision control system in the field of software development. Version control system software keeps track of all work and all changes in a set of files, and allows several developers ...
(CVS) is a prominent example of a source code collaboration tool being used in OSS projects. CVS helps manage the files and codes of a project when several people are working on the project at the same time. CVS allows several people to work on the same file at the same time. This is done by moving the file into the users’ directories and then merging the files when the users are done. CVS also enables one to easily retrieve a previous version of a file.
The Subversion revision control system (SVN) was created to replace CVS. It is quickly gaining ground as an OSS project version control system.
Many open source projects are now using distributed revision control systems
Distributed revision control
A distributed revision control system , distributed version control or decentralized version control keeps track of software revisions and allows many developers to work on a given project without necessarily being connected to a common network.-Distributed vs...
, which scale better than centralized repositories such as SVN and CVS. Popular examples are git
Git (software)
Git is a distributed revision control system with an emphasis on speed. Git was initially designed and developed by Linus Torvalds for Linux kernel development. Every Git working directory is a full-fledged repository with complete history and full revision tracking capabilities, not dependent on...
, used by the Linux kernel
Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is an operating system kernel used by the Linux family of Unix-like operating systems. It is one of the most prominent examples of free and open source software....
, and Mercurial
Mercurial
Mercurial is a cross-platform, distributed revision control tool for software developers. It is mainly implemented using the Python programming language, but includes a binary diff implementation written in C. It is supported on Windows and Unix-like systems, such as FreeBSD, Mac OS X and Linux...
, used by the Python
Python (programming language)
Python is a general-purpose, high-level programming language whose design philosophy emphasizes code readability. Python claims to "[combine] remarkable power with very clear syntax", and its standard library is large and comprehensive...
programming language.
Bug trackers and task lists
Most large-scale projects require a bug tracking system (usually web or otherwise Internet based) to keep track of the status of various issues in the development of the project. A simple text file is not sufficient, because they have many such bugs, and because they wish to facilitate reporting and maintenance of bugs by users and secondary developers. Some popular bug trackers include:- BugzillaBugzillaBugzilla is a Web-based general-purpose bugtracker and testing tool originally developed and used by the Mozilla project, and licensed under the Mozilla Public License....
- a sophisticated web-based bug tracker from the MozillaMozillaMozilla is a term used in a number of ways in relation to the Mozilla.org project and the Mozilla Foundation, their defunct commercial predecessor Netscape Communications Corporation, and their related application software....
house. - Mantis Bug Tracker - a web-based PHP/MySQL bug tracker.
- TracTracTrac is an open source, web-based project management and bug-tracking tool. The program is inspired by CVSTrac, and was originally named svntrac due to its ability to interface with Subversion. It is developed and maintained by Edgewall Software....
- integrating a bug tracker with a wiki, and an interface to the Subversion version control system. - Request trackerRequest TrackerRequest Tracker, commonly abbreviated to RT, is a ticket-tracking system written in Perl used to coordinate tasks and manage requests among a community of users. RT's first release in 1996 was written by Jesse Vincent, who later formed Best Practical Solutions LLC to distribute, develop, and...
- written in Perl. Given as a default to CPANCPANCPAN, the Comprehensive Perl Archive Network, is an archive of nearly 100,000 modules of software written in Perl, as well as documentation for it. It has a presence on the World Wide Web at and is mirrored worldwide at more than 200 locations...
modules - see rt.cpan.org. - GNATS - The GNU Bugtracking system.
- SourceForgeSourceForgeSourceForge Enterprise Edition is a collaborative revision control and software development management system. It provides a front-end to a range of software development lifecycle services and integrates with a number of free software / open source software applications .While originally itself...
and its forks provide a bug tracker as part of its services. As a result many projects hosted at SourceForge.net and similar services default to using it. - LibreSourceLibreSourceLibreSource is a collaborative development platform for open-source software, groupware, community interaction, electronic archiving and Web publishing....
- SharpForge includes forums, work item tracking, release management, wiki and version control management
- JIRAJIRAJira may refer to:* JIRA, software-engineering package* Journal of Iranian Research and Analysis* Jira, also known as Zilla, fictional character* Jira * Jira...
- Atlassian's project management and issue tracking tool.
Testing tools
Since OSS projects undergo frequent integration, tools that help automate testing during system integration are used. An example of such tool is TinderboxTinderbox (software)
Tinderbox is a software suite that provides continuous integration capability. Tinderbox allows developers to manage software builds and to correlate build failures on various platforms and configurations with particular code changes....
. Tinderbox enables participants in an OSS project to detect errors during system integration. Tinderbox runs a continuous build process and informs users about the parts of source code that have issues and on which platform(s) these issues arise. Furthermore, this tool identifies the author of the offending code. The author is then held responsible for ensuring that error is resolved. Mainly because normal testing tools are quite expensive, open source testing tools are gaining popularity.
A debugger
Debugger
A debugger or debugging tool is a computer program that is used to test and debug other programs . The code to be examined might alternatively be running on an instruction set simulator , a technique that allows great power in its ability to halt when specific conditions are encountered but which...
is a computer program that is used to debug (and sometimes test or optimize) other programs. GNU Debugger
GNU Debugger
The GNU Debugger, usually called just GDB and named gdb as an executable file, is the standard debugger for the GNU software system. It is a portable debugger that runs on many Unix-like systems and works for many programming languages, including Ada, C, C++, Objective-C, Free Pascal, Fortran, Java...
(GDB) is an example of a debugger used in Open source software development. This debugger offers remote debugging, what makes it especially applicable to Open source software development. Also, some memory leak
Memory leak
A memory leak, in computer science , occurs when a computer program consumes memory but is unable to release it back to the operating system. In object-oriented programming, a memory leak happens when an object is stored in memory but cannot be accessed by the running code...
detectors have been designed to work with GDB.
A memory leak tool or memory debugger
Memory debugger
A memory debugger is a programming tool for finding memory leaks and buffer overflows. These are due to bugs related to the allocation and deallocation of dynamic memory. Programs written in languages that have garbage collection, such as managed code, might also need memory debuggers, e.g...
is a programming tool for finding memory leaks and buffer overflows. A memory leak is a particular kind of unnecessary memory consumption by a computer program, where the program fails to release memory that is no longer needed. Examples of memory leak detection tools used by Mozilla are the XPCOM
XPCOM
XPCOM is a cross-platform component model from Mozilla. It is similar to Microsoft COM and CORBA. It has multiple language bindings and IDL descriptions so programmers can plug their custom functionality into the framework and connect it with other components.-The model:XPCOM is one of the main...
Memory Leak tools.
Validation tools are used to check if pieces of code conform to the specified syntax. They are most often used in the context of HTML/XML, but can also be used with programming languages. An example of a validation tool is LCLint, now called Splint
Splint (programming tool)
Splint, short for Secure Programming Lint, is a programming tool for statically checking C programs for security vulnerabilities and coding mistakes...
.
Package management
A package management systemPackage management system
In software, a package management system, also called package manager, is a collection of software tools to automate the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing software packages for a computer's operating system in a consistent manner...
is a collection of tools to automate the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing software packages from a computer. The Red Hat Package Manager
RPM Package Manager
RPM Package Manager is a package management system. The name RPM variously refers to the .rpm file format, files in this format, software packaged in such files, and the package manager itself...
(RPM) for .rpm and Advanced Packaging Tool
Advanced Packaging Tool
The Advanced Packaging Tool, or APT, is a free user interface that works with core libraries to handle the installation and removal of software on the Debian GNU/Linux distribution and its variants...
(APT) for .deb
Deb (file format)
deb is the extension of the Debian software package format and the most often used name for such binary packages. Like the "Deb" part of the term Debian, it originates from the name of Debra, erstwhile girlfriend and now ex-wife of Debian's founder Ian Murdock.Debian packages are also used in...
file format, are package management systems used by a number of Linux distributions.
Refactoring, rewrites and other revamps
Often open source developers feel that their code requires a revamp. This can be either because the code was written or maintained without proper refactoringRefactoring
Code refactoring is "disciplined technique for restructuring an existing body of code, altering its internal structure without changing its external behavior", undertaken in order to improve some of the nonfunctional attributes of the software....
(as is often the case if the code was inherited from a previous developer), or because a proposed enhancement or extension of it cannot be cleanly implemented with the existing codebase. A final reason for wishing to revamp the code is that the code "smells bad" (to quote Martin Fowler
Martin Fowler
-Online presentations:* at RailsConf 2006* at JAOO 2006* at QCon London 2007 * at QCon London 2008 * at ThoughtWorks Quarterly Technology Briefing, October 2008...
's Refactoring book) and does not meet the developer's
standards.
There are several kinds of revamps:
- Refactoring implies that the code is moved from one place to another, methods, functions or classes are extracted, duplicate code is eliminated and so forth - all while maintaining an integrity of the code. Such refactoring can be done in small amounts (so-called "continuous refactoring") to justify a certain change, or one can decide on large amounts of refactoring to an existing code that last for several days or weeks.
- "Partial rewrites" involve rewriting a certain part of the code from scratch, while keeping the rest of the code. Such partial rewrites have been common in the Linux kernel development, where several subsystems were rewritten or re-implemented from scratch, while keeping the rest of the code intact.
- Complete rewrites involve starting the project from scratchRewrite (programming)A rewrite in computer programming is the act or result of re-implementing a large portion of existing functionality without re-use of its source code. When the rewrite is not using existing code at all, it is common to speak of a rewrite from scratch...
, while possibly still making use of some old code. A good example of a complete rewrite was the Subversion version control system, whose developers started from scratch: they believed the codebase of CVS (an older attempt at creating a version control system), was useless and needed to be completely scrapped. Another good example of such a rewrite was the Apache web serverApache HTTP ServerThe Apache HTTP Server, commonly referred to as Apache , is web server software notable for playing a key role in the initial growth of the World Wide Web. In 2009 it became the first web server software to surpass the 100 million website milestone...
, which was almost completely re-written between version 1.3.x and version 2.0.x.
Automated tests
Software testingSoftware testing
Software testing is an investigation conducted to provide stakeholders with information about the quality of the product or service under test. Software testing can also provide an objective, independent view of the software to allow the business to appreciate and understand the risks of software...
is an integral part of open source development. While many open source packages were known to be released with some glaring bugs even in some stable releases, most open source software eventually becomes very stable.
Traditionally, in most of the open source there was a general lack of awareness for automated tests, in which one writes automated test scripts and programs that run the software and try to find out if it behaves correctly. Recently, however, this awareness has been growing, possibly because of influence from Extreme Programming, and because of some high-profile software packages that incorporated such test suites.
Most open source software is either command line or alternatively APIs and as such is very easy to test automatically.
See also
- Open-source softwareOpen-source softwareOpen-source software is computer software that is available in source code form: the source code and certain other rights normally reserved for copyright holders are provided under a software license that permits users to study, change, improve and at times also to distribute the software.Open...
- Open source software securityOpen source software securityOpen source software security is the measure of assurance or guarantee in the freedom from danger and risk inherent to an open source software system.-The debate:...
- Software development processSoftware development processA software development process, also known as a software development life cycle , is a structure imposed on the development of a software product. Similar terms include software life cycle and software process. It is often considered a subset of systems development life cycle...
- Release ManagementRelease managementThe release management process is a relatively new but rapidly growing discipline within software engineering of managing software releases....
- Software engineeringSoftware engineeringSoftware Engineering is the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software, and the study of these approaches; that is, the application of engineering to software...
- Meta-Modeling
- Meta-Process ModelingMeta-Process ModelingMeta-process modeling is a type of metamodeling used in software engineering and systems engineering for the analysis and construction of models applicable and useful to some predefined problems....
External links
- Software Release Practice HOWTO by Eric Raymond

