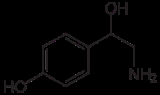
Octopamine
Encyclopedia
Octopamine is an endogenous
biogenic amine
that is closely related to norepinephrine
, and has effects on the adrenergic
and dopaminergic
systems. It is also found naturally in numerous plants, including bitter orange
. Biosynthesis
of the D-(—)-enantiomer
of octopamine is by β-hydroxylation
of tyramine
via the enzyme
dopamine β-hydroxylase. Under the trade names Epirenor, Norden, and Norfen, octopamine is also used clinically
as a sympathomimetic agent
.
in 1948 in the salivary glands of the octopus
and has since been found to act as neurotransmitter
, neurohormone
and neuromodulator in invertebrate
s. It is widely used in energy-demanding behaviors by all insects, crustaceans (crabs, lobsters, crayfish), and spiders. Such behaviors include flying, egg-laying, and jumping.
The best-understood role for octopamine is in the locust
jump. Here it modulates muscle activity, making the leg muscles contract more effectively. This is at least in part due to an increase in the rate of contraction and of relaxation.
In the honey bee
and fruit fly
, octopamine has a major role in learning and memory. In the firefly
, octopamine release leads to light production in the lantern.
Octopamine also plays a role in mollusks, though the role of octopamine has been examined only in the central nervous system
of the model organism, the pond snail
.
Heberlein et al. have conducted studies of alcohol tolerance in fruit flies; they found that a mutation that caused octopamine deficiency also caused lower alcohol tolerance.
The emerald cockroach wasp
stings the host for its larvae (a cockroach) in the head ganglion (brain). The venom blocks octopamine receptors and the cockroach fails to show normal escape responses, grooming itself excessively. It becomes docile and the wasp leads it to the wasp's den by pulling its antenna like a leash.
s, octopamine replaces norepinephrine
in sympathetic
neuron
s with chronic use of monoamine oxidase inhibitor
s. It may be responsible for the common side effect
of orthostatic hypotension
with these agents, though there is also evidence that it is actually mediated by increased levels of N-acetylserotonin.
In mammal
s, octopamine may mobilize the release of fat
from adipocytes (fat cells), which has led to its promotion on the internet
as a slimming aid. However, the released fat is likely to be promptly taken up into other cells, and there is no evidence that octopamine facilitates weight loss. Octopamine may also increase blood pressure
significantly when combined with other stimulant
s, as in some weight loss supplement
s.
Owing to lack of research, much is not known about octopamine or its role in humans.
Endogenous
Endogenous substances are those that originate from within an organism, tissue, or cell. Endogenous retroviruses are caused by ancient infections of germ cells in humans, mammals and other vertebrates...
biogenic amine
Biogenic amine
-Examples:Some prominent examples of biogenic amines include:* Histamine - a substance derived from the amino acid histidine that acts as a neurotransmitter mediating arousal and attention, as well as a pro-inflammatory signal released from mast cells in response to allergic reactions or tissue...
that is closely related to norepinephrine
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is the US name for noradrenaline , a catecholamine with multiple roles including as a hormone and a neurotransmitter...
, and has effects on the adrenergic
Adrenergic
An adrenergic agent is a drug, or other substance, which has effects similar to, or the same as, epinephrine . Thus, it is a kind of sympathomimetic agent...
and dopaminergic
Dopaminergic
Dopaminergic means related to the neurotransmitter dopamine. For example, certain proteins such as the dopamine transporter , vesicular monoamine transporter 2 , and dopamine receptors can be classified as dopaminergic, and neurons which synthesize or contain dopamine and synapses with dopamine...
systems. It is also found naturally in numerous plants, including bitter orange
Bitter orange
The name "bitter orange", also known as Seville orange, sour orange, bigarade orange, and marmalade orange, refers to a citrus tree and its fruit. Many varieties of bitter orange are used for their essential oil, which is used in perfume and as a flavoring...
. Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
of the D-(—)-enantiomer
Enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer is one of two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other that are non-superposable , much as one's left and right hands are the same except for opposite orientation. It can be clearly understood if you try to place your hands one over the other without...
of octopamine is by β-hydroxylation
Hydroxylation
Hydroxylation is a chemical process that introduces a hydroxyl group into an organic compound. In biochemistry, hydroxylation reactions are often facilitated by enzymes called hydroxylases. Hydroxylation is the first step in the oxidative degradation of organic compounds in air...
of tyramine
Tyramine
Tyramine is a naturally occurring monoamine compound and trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent...
via the enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
dopamine β-hydroxylase. Under the trade names Epirenor, Norden, and Norfen, octopamine is also used clinically
Clinic
A clinic is a health care facility that is primarily devoted to the care of outpatients...
as a sympathomimetic agent
Drug
A drug, broadly speaking, is any substance that, when absorbed into the body of a living organism, alters normal bodily function. There is no single, precise definition, as there are different meanings in drug control law, government regulations, medicine, and colloquial usage.In pharmacology, a...
.
Role in invertebrates
Octopamine was first discovered by Italian scientist Vittorio ErspamerVittorio Erspamer
Vittorio Erspamer was an Italian pharmacologist and chemist, known for the identification, synthesis and pharmacological studies of more than sixty new chemical compounds, most notably serotonin and octopamine.-Biography:...
in 1948 in the salivary glands of the octopus
Octopus
The octopus is a cephalopod mollusc of the order Octopoda. Octopuses have two eyes and four pairs of arms, and like other cephalopods they are bilaterally symmetric. An octopus has a hard beak, with its mouth at the center point of the arms...
and has since been found to act as neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
, neurohormone
Neurohormone
A neurohormone is any hormone produced and released by neurons.Examples include:*Thyrotropin-releasing hormone *Gonadotropin-releasing hormone *Adrenocorticotropin-releasing hormone*Oxytocin*Antidiuretic hormone *Epinephrine...
and neuromodulator in invertebrate
Invertebrate
An invertebrate is an animal without a backbone. The group includes 97% of all animal species – all animals except those in the chordate subphylum Vertebrata .Invertebrates form a paraphyletic group...
s. It is widely used in energy-demanding behaviors by all insects, crustaceans (crabs, lobsters, crayfish), and spiders. Such behaviors include flying, egg-laying, and jumping.
The best-understood role for octopamine is in the locust
Locust
Locusts are the swarming phase of short-horned grasshoppers of the family Acrididae. These are species that can breed rapidly under suitable conditions and subsequently become gregarious and migratory...
jump. Here it modulates muscle activity, making the leg muscles contract more effectively. This is at least in part due to an increase in the rate of contraction and of relaxation.
In the honey bee
Honey bee
Honey bees are a subset of bees in the genus Apis, primarily distinguished by the production and storage of honey and the construction of perennial, colonial nests out of wax. Honey bees are the only extant members of the tribe Apini, all in the genus Apis...
and fruit fly
Drosophila melanogaster
Drosophila melanogaster is a species of Diptera, or the order of flies, in the family Drosophilidae. The species is known generally as the common fruit fly or vinegar fly. Starting from Charles W...
, octopamine has a major role in learning and memory. In the firefly
Firefly
Lampyridae is a family of insects in the beetle order Coleoptera. They are winged beetles, and commonly called fireflies or lightning bugs for their conspicuous crepuscular use of bioluminescence to attract mates or prey. Fireflies produce a "cold light", with no infrared or ultraviolet frequencies...
, octopamine release leads to light production in the lantern.
Octopamine also plays a role in mollusks, though the role of octopamine has been examined only in the central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
of the model organism, the pond snail
Snail
Snail is a common name applied to most of the members of the molluscan class Gastropoda that have coiled shells in the adult stage. When the word is used in its most general sense, it includes sea snails, land snails and freshwater snails. The word snail without any qualifier is however more often...
.
Heberlein et al. have conducted studies of alcohol tolerance in fruit flies; they found that a mutation that caused octopamine deficiency also caused lower alcohol tolerance.
The emerald cockroach wasp
Emerald cockroach wasp
The emerald cockroach wasp or jewel wasp is a solitary wasp of the family Ampulicidae. It is known for its unusual reproductive behavior, which involves stinging a cockroach and using it as a host for its larvae...
stings the host for its larvae (a cockroach) in the head ganglion (brain). The venom blocks octopamine receptors and the cockroach fails to show normal escape responses, grooming itself excessively. It becomes docile and the wasp leads it to the wasp's den by pulling its antenna like a leash.
Role in vertebrates
In vertebrateVertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
s, octopamine replaces norepinephrine
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is the US name for noradrenaline , a catecholamine with multiple roles including as a hormone and a neurotransmitter...
in sympathetic
Sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system is one of the three parts of the autonomic nervous system, along with the enteric and parasympathetic systems. Its general action is to mobilize the body's nervous system fight-or-flight response...
neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s with chronic use of monoamine oxidase inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors are a class of antidepressant drugs prescribed for the treatment of depression. They are particularly effective in treating atypical depression....
s. It may be responsible for the common side effect
Side effect
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequences of the use of a drug.Occasionally, drugs are...
of orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, orthostasis, and colloquially as head rush or dizzy spell, is a form of hypotension in which a person's blood pressure suddenly falls when the person stands up or stretches. The decrease is typically greater than 20/10 mm Hg, and may be...
with these agents, though there is also evidence that it is actually mediated by increased levels of N-acetylserotonin.
In mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s, octopamine may mobilize the release of fat
Fat
Fats consist of a wide group of compounds that are generally soluble in organic solvents and generally insoluble in water. Chemically, fats are triglycerides, triesters of glycerol and any of several fatty acids. Fats may be either solid or liquid at room temperature, depending on their structure...
from adipocytes (fat cells), which has led to its promotion on the internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
as a slimming aid. However, the released fat is likely to be promptly taken up into other cells, and there is no evidence that octopamine facilitates weight loss. Octopamine may also increase blood pressure
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies...
significantly when combined with other stimulant
Stimulant
Stimulants are psychoactive drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both. Examples of these kinds of effects may include enhanced alertness, wakefulness, and locomotion, among others...
s, as in some weight loss supplement
Anorectic
An anorectic or anorexic , also known as anorexigenic or appetite suppressant, is a dietary supplement and/or drug which reduces appetite, food consumption, and as a result, causes weight loss to occur.-List of anorectics:Numerous pharmaceutical compounds are marketed as appetite suppressants.The...
s.
Owing to lack of research, much is not known about octopamine or its role in humans.
Further reading
- P.D. Evans, "Octopamine", in Comprehensive Insect Physiology, 11, 499, Oxford University Press 1985.

