Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian languages
Encyclopedia
The Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian languages are a branch of the Austronesian family
, proposed by Wouk & Ross (2002), that are thought to have dispersed from a possible homeland in Sulawesi
. They are called nuclear
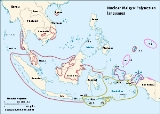
because they are the conceptual core of the Malayo-Polynesian family, including both Malay and Polynesian. Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian is found throughout Indonesia
, apart from central Borneo
, Sabah
, and the north of Sulawesi
, and into Melanesia
and the Pacific.
Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian languages are those that have abandoned the Austronesian alignment
inherited from proto-Malayo-Polynesian syntax
. These include the traditional geographic groupings of Central Malayo-Polynesian
, Eastern Malayo-Polynesian
, and part of Western Malayo-Polynesian
, a part Wouk and Ross call Inner Western Malayo-Polynesian.
Inner Western Malayo-Polynesian (Sunda–Sulawesi) is therefore defined negatively, those languages of Sunda
and Sulawesi
not included in Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian. Central–Eastern is an areal group, divergent from the rest of Malayo-Polynesian due to non-Austronesian (Papuan
) substrata
rather than due to any genealogical relationship.
Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian (75%)
Austronesian languages
The Austronesian languages are a language family widely dispersed throughout the islands of Southeast Asia and the Pacific, with a few members spoken on continental Asia that are spoken by about 386 million people. It is on par with Indo-European, Niger-Congo, Afroasiatic and Uralic as one of the...
, proposed by Wouk & Ross (2002), that are thought to have dispersed from a possible homeland in Sulawesi
Sulawesi
Sulawesi is one of the four larger Sunda Islands of Indonesia and is situated between Borneo and the Maluku Islands. In Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra have larger Indonesian populations.- Etymology :The Portuguese were the first to...
. They are called nuclear
Nuclear family
Nuclear family is a term used to define a family group consisting of a father and mother and their children. This is in contrast to the smaller single-parent family, and to the larger extended family. Nuclear families typically center on a married couple, but not always; the nuclear family may have...
because they are the conceptual core of the Malayo-Polynesian family, including both Malay and Polynesian. Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian is found throughout Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
, apart from central Borneo
Borneo
Borneo is the third largest island in the world and is located north of Java Island, Indonesia, at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia....
, Sabah
Sabah
Sabah is one of 13 member states of Malaysia. It is located on the northern portion of the island of Borneo. It is the second largest state in the country after Sarawak, which it borders on its southwest. It also shares a border with the province of East Kalimantan of Indonesia in the south...
, and the north of Sulawesi
Sulawesi
Sulawesi is one of the four larger Sunda Islands of Indonesia and is situated between Borneo and the Maluku Islands. In Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra have larger Indonesian populations.- Etymology :The Portuguese were the first to...
, and into Melanesia
Melanesia
Melanesia is a subregion of Oceania extending from the western end of the Pacific Ocean to the Arafura Sea, and eastward to Fiji. The region comprises most of the islands immediately north and northeast of Australia...
and the Pacific.
Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian languages are those that have abandoned the Austronesian alignment
Austronesian alignment
Austronesian alignment, commonly known as the Philippine- or Austronesian-type voice system, is a typologically unusual morphosyntactic alignment that combines features of ergative and accusative languages...
inherited from proto-Malayo-Polynesian syntax
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax is the study of the principles and rules for constructing phrases and sentences in natural languages....
. These include the traditional geographic groupings of Central Malayo-Polynesian
Central Malayo-Polynesian languages
The Central Malayo-Polynesian linkage is an erstwhile branch of Austronesian languages. The languages are spoken in the Lesser Sunda and Maluku Islands of the Banda Sea, in an area corresponding closely to the Indonesian provinces of East Nusa Tenggara and Maluku and the nation of East Timor , but...
, Eastern Malayo-Polynesian
Eastern Malayo-Polynesian languages
The Eastern Malayo-Polynesian languages form a putative subgroup of the Malayo-Polynesian languages consisting of over 500 languages. Their relationship is not supported by much linguistic data: per Malcolm Ross, there is "essentially no evidence" that the Halmahera–Cenderawasih and Oceanic...
, and part of Western Malayo-Polynesian
Western Malayo-Polynesian languages
The Western Malayo-Polynesian languages, also known as the Hesperonesian languages, are those Malayo-Polynesian languages which are not in the Central–Eastern branch. Since there are no features which define these languages positively as a group, recent classifications have abandoned it...
, a part Wouk and Ross call Inner Western Malayo-Polynesian.
Inner Western Malayo-Polynesian (Sunda–Sulawesi) is therefore defined negatively, those languages of Sunda
Greater Sunda Islands
The Greater Sunda Islands are a group of large islands within the Malay archipelago. Jawa , smallest but by far the most populous and important; Sumatera in the west, directly across the Strait of Malacca from Malaysia; Kalimantan, the Indonesian sector of large, compact, minicontinent Borneo; and...
and Sulawesi
Sulawesi
Sulawesi is one of the four larger Sunda Islands of Indonesia and is situated between Borneo and the Maluku Islands. In Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra have larger Indonesian populations.- Etymology :The Portuguese were the first to...
not included in Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian. Central–Eastern is an areal group, divergent from the rest of Malayo-Polynesian due to non-Austronesian (Papuan
Papuan languages
The Papuan languages are those languages of the western Pacific which are neither Austronesian nor Australian. The term does not presuppose a genetic relationship. The concept of Papuan peoples as distinct from Melanesians was first suggested and named by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1892.-The...
) substrata
Substratum
In linguistics, a stratum or strate is a language that influences, or is influenced by another through contact. A substratum is a language which has lower power or prestige than another, while a superstratum is the language that has higher power or prestige. Both substratum and superstratum...
rather than due to any genealogical relationship.
Languages
Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian is composed of a large number of smaller clades of uncertain affiliation. The following are largely uncontroversial as units:- ChamorroChamorro languageChamorro is a Malayo-Polynesian language, spoken on the Mariana Islands by about 47,000 people Chamorro (Chamorro: Fino' Chamoru or simply Chamoru) is a Malayo-Polynesian (Austronesian) language, spoken on the Mariana Islands (Guam, Rota, Tinian, and Saipan) by about 47,000 people Chamorro...
- PalauanPalauan languagePalauan is one of the two nationally recognized official languages spoken in the Republic of Palau...
- TamanicTamanic languagesThe Tamanic languages are a small group of languages of Indonesian Borneo:The classification of the Tamanic languages, usually represented by Mbalo alone, is unclear. Long left unclassified, Adelaar and Himmelmann took the view that it was especially close to Buginese...
(Mbaloh) - South SulawesiSouth Sulawesi languagesThe South Sulawesi languages are a group of languages spoken by the Bugis and related peoples of South Sulawesi province, Indonesia.-Languages:*Bugis**Buginese: Buginese, Campalagian**? Tamanic: Mbalo, Taman...
- CelebicCelebic languagesThe Celebic languages are a proposed group of Malayo-Polynesian languages spoken on the island of Sulawesi, formerly spelled Celebes. It would be the largest family of languages on that island.-Classification:...
- MoklenMoklen languagesThe Moklen languages are a pair of closely related languages spoken by the Moklen, of coastal Thailand, and the Moken "Sea Gypsies" off the coast of Burma. They are somewhat divergent from other Austronesian languages.-References:...
- ChamicChamic languagesThe Chamic languages, also known as Aceh–Chamic and Achinese–Chamic, are a group of ten languages spoken in parts of Cambodia, Vietnam, and Hainan, classified as Malayic languages in the Austronesian language family....
- Batak languagesBatak languagesThe Batak languages are spoken by Batak and Alas people of North Sumatra, Indonesia.Historically they were written using Batak script but the Latin alphabet is now used for most writing....
- GayoGayo languageGayo Language is the spoken language of about 180,000 people in the mountain region of North Sumatra around Takengon, Gayo Lues, Bener Meriah, Southeast Aceh, Genteng, and Lokop. It is classified as belonging to the Western Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian languages, but is not closely...
- EngganoEnggano languageThe Enggano language, or Engganese, is the language of Enggano Island off the southwestern coast of Sumatra.Although adjacent to Austronesian languages, Enggano has not been established as Austronesian; it may instead be a language isolate with Austronesian borrowing. Much of the basic vocabulary...
(not Austronesian?) - MentawaiMentawai languageThe Mentawai language is an Austronesian language, spoken by the Mentawai-people of the Mentawai Islands, West Sumatra. The dialects of the language include: – Silabu, Sipura – Simalegi, Sakalagan, Saumanganja – North Siberut, South Siberut – Taikaku – Pagai....
- NiasNias languageThe Nias language is an Austronesian language spoken on Nias Island and the Batu Islands off the west coast of Sumatra in Indonesia. It belongs to the Northwest Sumatran subgroup which also includes Mentawai and the Batak languages. It had about 770,000 speakers in 2000...
- Sikule
- Simeulue
- RejangRejang languageRejang is spoken by the Rejang people in Bengkulu, Indonesia. It is a Malayo-Polynesian language but has not been further classified. It has five major dialects...
- LampungicLampungic languagesThe Lampungic languages are a pair of dialect clusters at the southern tip of the Indonesian island of Sumatra. They are:-External links:*...
- JavaneseJavanese languageJavanese language is the language of the Javanese people from the central and eastern parts of the island of Java, in Indonesia. In addition, there are also some pockets of Javanese speakers in the northern coast of western Java...
- SundaneseSundanese languageSundanese is the language of about 27 million people from the western third of Java or about 15% of the Indonesian population....
- MadureseMadurese languageMadurese is a language of the Madurese people of Madura Island and eastern Java, Indonesia; it is also spoken on the neighbouring small Kangean Islands and Sapudi Islands, as well as from migrants to other parts of Indonesia, namely the Tapal Kuda area comprising Pasuruan, Surabaya, Malang until...
- BanjarBanjar languageBanjar language is the native language used by the Banjarese people of South Kalimantan, Indonesia. As many Banjarese are travelling merchants, they brought their language wherever they went all over Indonesia, even all over the world....
- MalayicMalayic languagesThe Malayic languages are a branch of the Sunda–Sulawesi languages of the Austronesian family. They include Malay, the national language of Malaysia, Indonesia, and Brunei; Minangkabau in central Sumatra; and Iban in northern Borneo....
- Bali–Sasak
- Sumba–Flores
- IrarutuIrarutu languageIrarutu, or Kasira, is an Austronesian language of most of the interior of the Bomberai Peninsula of New Guinea....
(Kasira) - SelaruSelaru languagesThe Selaru languages are a pair of Austronesian languages spoken in the Tanimbar Islands of Indonesia. They are not closely related, being 56% lexically similar ....
- Yamdena
- Kei–Tanimbar
- North BomberaiNorth Bomberai languagesThe North Bomberai languages are a small group of Austronesian languages spoken by a thousand people off the coast of the Bomberai Peninsula.The languages are Arguni, Onin, Sekar, Uruangnirin....
- Kowiai (S. Bomberai)
- East Central MalukuEast Central Maluku languagesThe East Central Maluku languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken on and around the islands of Seram and Aru in the eastern Moluccas...
- Sula–Buru
- Timor–Babar
- West DamarWest Damar languageWest Damar, or North Damar, is an Austronesian language of the Maluku Islands of Indonesia....
- Teor–Kur
- South HalmaheraSouth Halmahera languagesThe South Halmahera languages are the branch of Austronesian languages found along the southeast coast of the island of Halmahera in the Indonesian province of North Maluku...
- Raja AmpatRaja Ampat languagesThe Raja Ampat languages are the branch of Malayo-Polynesian languages spoken on the Raja Ampat Islands of the western tip of New Guinea.The languages are As, Biga, Gebe , Kawe, Legenyem, Ma'ya, Waigeo, Wauyai, Matbat , Maden....
- Northwest BomberaiNorthwest Bomberai languagesThe Northwest Bomberai languages are a pair of minor Austronesian languages spoken on the northern coast of the Bomberai Peninsula of Indonesian Papua. They are:...
- BiakicBiakic languagesThe Biakic languages are a branch of Austronesian languages spoken on Biak Island and nearby isles of Cenderawasih Bay, Indonesian Papua.They are:...
(Cenderawasih) - YapenYapen languagesThe Yapen languages are the branch of Malayo-Polynesian languages spoken on Yapen Island and nearby isle of Cenderawasih Bay, Indonesian Papua. They share Yapen Ιsland with the Papuan Yawa languages.They are:*East: Kurudu, Wabo...
–WaropenWaropen languageWaropen is an Austronesian language in the putative Cenderawasih of Indonesian Papua. It is fairly closely related to the Yapen languages....
(Cenderawasih) - MorMor language (Austronesian)Mor is a tonal Austronesian language in the putative Cenderawasih of Indonesian Papua. It is not closely related to other languages....
(Cenderawasih) - IresimIresim languageIresim is an Austronesian language in the putative Cenderawasih of Indonesian Papua. It is not closely related to other languages....
(with other Cenderawasih languages?) - TandiaTandia languageTandia is a possibly extinct Austronesian language in the putative Cenderawasih of Indonesian Papua. It is not closely related to other languages. Speakers have shifted to Wandamen....
(with other Cenderawasih languages?) - YaurYaur languageThe Yaur language, or Jaur, is a language in the putative Cenderawasih branch of the Austronesian family spoken in Irian Jaya. It has about 300 speakers.-Sources:...
(with other Cenderawasih languages?) - YeretuarYeretuar languageYeretuar, or Goni, is an Austronesian language in the putative Cenderawasih of Indonesian Papua. It is not closely related to other languages....
(with other Cenderawasih languages?) - Oceanic
ABVD (2008)
A 2008 analysis of the Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database found moderate lexical support for the syntactically defined Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian family, with a 75% confidence, within a fully supported Indo-Melanesian family (languages of Indonesia, Melanesia, and the Pacific, apart from northern Sulawesi). The structure of the family revealed by that provisional study, including the confidences for the unity of each branch to the nearest 5%, are as follows:Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian (75%)
- Greater Malayo-SumbawanMalayo-Sumbawan languagesThe Malayo-Sumbawan languages are a group of languages identified by Adelaar that unites the Malayic and Chamic languages with the languages of Java and the western Lesser Sunda Islands, except for Javanese itself...
(60%) - TamanicTamanic languagesThe Tamanic languages are a small group of languages of Indonesian Borneo:The classification of the Tamanic languages, usually represented by Mbalo alone, is unclear. Long left unclassified, Adelaar and Himmelmann took the view that it was especially close to Buginese...
(Mbaloh) - Sulawesi–Polynesian (65%)
- SangirSangiric languagesThe Sangiric languages are a group of languages spoken in northern Sulawesi and several small islands to the north which belong to the Philippines.The languages are Sangir and a southern group of Bantik, Ratahan, Talaud....
–MinahasanMinahasan languagesThe Minahasan languages are a group of languages spoken by the Minahasa people in northern Sulawesi.-Classification:The languages are :*Tonsawang*North Minahasan**Tontemboan...
(80%) - South SulawesiSouth Sulawesi languagesThe South Sulawesi languages are a group of languages spoken by the Bugis and related peoples of South Sulawesi province, Indonesia.-Languages:*Bugis**Buginese: Buginese, Campalagian**? Tamanic: Mbalo, Taman...
(100%) - Celebo-Polynesian (80%)
- CelebicCelebic languagesThe Celebic languages are a proposed group of Malayo-Polynesian languages spoken on the island of Sulawesi, formerly spelled Celebes. It would be the largest family of languages on that island.-Classification:...
(100%) - Greater Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian (85%)
- ? Northern Sumatran – Barrier IslandsNorthwest Sumatran languagesThe Northwest Sumatran languages are a putative group of languages spoken by the Batak and related peoples in the interior of northern Sumatra, and by the Nias, Mentawai, etc. on the barrier islands off the western coast of Sumatra.-Classification:The languages normally included in North Sumatran...
(Nias) - ChamorroChamorro languageChamorro is a Malayo-Polynesian language, spoken on the Mariana Islands by about 47,000 people Chamorro (Chamorro: Fino' Chamoru or simply Chamoru) is a Malayo-Polynesian (Austronesian) language, spoken on the Mariana Islands (Guam, Rota, Tinian, and Saipan) by about 47,000 people Chamorro...
- PalauanPalauan languagePalauan is one of the two nationally recognized official languages spoken in the Republic of Palau...
- Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian (80%)
- Sumba–Flores (100%)
- Core Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian (80%)
- ? Northern Sumatran – Barrier Islands
- Celebic
- Sangir

