
Sundanese language
Encyclopedia
Sundanese
Sundanese (Bahasa Sunda, in Sundanese script
ᮘᮞ ᮞᮥᮔ᮪ᮓ, literally "language of Sunda
") is the language
of about 27 million people from the western third of Java or about 15% of the Indonesia
n population.
It appears to be most closely related to Madurese
and Malay
, and more distantly related to Javanese
. It has several types, conventionally described according to the locations of the people:
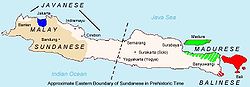
Priangan, which covers the largest area of Sundaland (Tatar Pasundan in Sundanese), is the most widely spoken type of Sundanese language, taught in elementary till junior-high schools (equivalent to ninth-year school grade) in West Java and Banten Province.
s, the Sundanese script
(Aksara Sunda) and Pegon
in historical times, and in modern times the Latin alphabet
.
). There are five pure vowel sounds: a /ɑ/, é /ɛ/, i /i/, o /ɔ/, u /ʊ/, and two neutral vowels; e /ə/, and eu /ɤ/. The consonantal phonemes (18—but see below) are transcribed with the letters p, b, t, d, k, g, c , j, h, ng (/ŋ/, occurs initially), ny /ɳ/, m, n, s /s/, w, l, r (trilled or flapped), and y /j/.
Other consonants that originally appear in Indonesian loanwords are mostly transferred into native consonants: f → p, v → p, sy → s, sh → s, z -> j, and kh /x/ → h.
Definition of Sundanese Phonology, according to Yayat Sudaryat (1985:26):
"Fonologi nyaeta bagean tina elmu basa anu maluruh jeung medar sora-sora basa, prosesna, selang surupna, jeung parobahanana".
There are 16 consonants in Sundanese phonology, according to Yayat Sudaryat (1991,35):
"fonem konsonan (contoid) nya eta sora omongan (fonem) anu kawangun ku hawa anu kaluar tina bayah sarta waktu liwat tikoro aya nu ngahalangan. konsonan nu aya dina basa sunda, nyaeta:
/b/, /ts/, /d/, /g/, /h/, /dʒ/, /k/, /l/, /m/, /n/, /p/, /r/, /s/, /n/, /t/, /n'/, kuayana pangaruh basa kosta sok kapanggih konsonan /f/, /v/, /z/ mangrupa fomem nu asalna pangaruh basa kosta, saperti dina kecap: fonem, qur'an, xerox, zakat".
Based on the statement above, it is clear that the Sundanese language has only 16 consonants, there are three consonants /f, v, z/ which exist in Sundanese as a result of borrowing words, but naturally they are not Sundanese consonants.
Furthermore, Sudaryat does not mention the phonemes /w, j/ as semi vowels, although as vowels, /w, j/ function as a glide sound between two different vowels, as in the words:
Phonemes /w/ and /j/ function as glide sounds between two different vowels as in the words:
"Abdi henteu acan neda". (I have not eaten yet.)
Explanation: From the above example, "henteu" is used for negative term.
"Buku abdi mah sanes nu ieu". (My book is not this one.)
Explanation: From the above example, "sanes" is used for negative term.
Dupi -(question)
example:
Polite-
"Buku dibantun ku abdi". (The book is brought by me.)
Explanation: "dibantun" (to be brought/passive) and "ngabantun" (active)
The other examples:
"Pulpen ditambut ku abdi". (The pen is borrowed by me.)
"Soal ieu dikerjakeun ku abdi". (This problem is done by me.)
example:
teuas (hard), tiis (cool), hipu (soft), lada (hot, usually for foods), haneut (warm), etc.
Sundanese (Bahasa Sunda, in Sundanese script
Sundanese script
Sundanese script Sundanese script Sundanese script (Aksara Sunda, is a writing system which is used by some Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (Aksara Sunda Kuna) which was used by ancientSundanese between 14th and 18th centuries....
ᮘᮞ ᮞᮥᮔ᮪ᮓ, literally "language of Sunda
Sundanese people
The Sundanese are an ethnic group native to the western part of the Indonesian island of Java. They number approximately 31 million, and are the second most populous of all the nation's ethncities. The Sundanese are predominantly Muslim...
") is the language
Language
Language may refer either to the specifically human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, or to a specific instance of such a system of complex communication...
of about 27 million people from the western third of Java or about 15% of the Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
n population.
It appears to be most closely related to Madurese
Madurese language
Madurese is a language of the Madurese people of Madura Island and eastern Java, Indonesia; it is also spoken on the neighbouring small Kangean Islands and Sapudi Islands, as well as from migrants to other parts of Indonesia, namely the Tapal Kuda area comprising Pasuruan, Surabaya, Malang until...
and Malay
Malay language
Malay is a major language of the Austronesian family. It is the official language of Malaysia , Indonesia , Brunei and Singapore...
, and more distantly related to Javanese
Javanese language
Javanese language is the language of the Javanese people from the central and eastern parts of the island of Java, in Indonesia. In addition, there are also some pockets of Javanese speakers in the northern coast of western Java...
. It has several types, conventionally described according to the locations of the people:
- BantenBantenBanten is a province of Indonesia in Java. Formerly part of the Province of West Java, it was made a separate province in 2000.The administrative center is Serang. Preliminary results from the 2010 census counted some 10.6 million people.-Geography:...
, - BogorBogorBogor is a city on the island of Java in the West Java province of Indonesia. The city is located in the center of the Bogor Regency , 60 kilometers south of the Indonesian capital Jakarta...
, - Priangan (BandungBandungBandung is the capital of West Java province in Indonesia, and the country's third largest city, and 2nd largest metropolitan area in Indonesia, with a population of 7.4 million in 2007. Located 768 metres above sea level, approximately 140 km southeast of Jakarta, Bandung has cooler...
and its surroundings), - CiamisCiamisCiamis is the capital of the Ciamis Regency in West Java, Indonesia....
, - KuninganKuninganKuningan is a city in eastern West Java, Indonesia, between Cirebon and Tasikmalaya, about 200 km east of Jakarta. The area is near Mount Cereme/Ciremai , the highest mountain in West Java. The mountain is located in the western part of the region. The eastern part is a valley...
, and - CirebonCirebonCirebon is a port city on the north coast of the Indonesian island of Java. It is located in the province of West Java near the provincial border with Central Java, approximately 297 km east of Jakarta, at .The seat of a former Sultanate, the city's West and Central Java border location have...
.
Priangan, which covers the largest area of Sundaland (Tatar Pasundan in Sundanese), is the most widely spoken type of Sundanese language, taught in elementary till junior-high schools (equivalent to ninth-year school grade) in West Java and Banten Province.
Writing
Sundanese can be written in different writing systemWriting system
A writing system is a symbolic system used to represent elements or statements expressible in language.-General properties:Writing systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communication systems in that the reader must usually understand something of the associated spoken language to...
s, the Sundanese script
Sundanese script
Sundanese script Sundanese script Sundanese script (Aksara Sunda, is a writing system which is used by some Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (Aksara Sunda Kuna) which was used by ancientSundanese between 14th and 18th centuries....
(Aksara Sunda) and Pegon
Pegon (language)
Pegon is an Arabic alphabet used to write the Javanese and Sundanese languages, as an alternative to the Roman alphabet or the pre-colonial Javanese script and the old Sundanese script. In particular, it was used for religious writing and poetry from the fifteenth century, particularly in writing...
in historical times, and in modern times the Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
.
Phonology
Sundanese orthography is highly phonetic (see also Sundanese scriptSundanese script
Sundanese script Sundanese script Sundanese script (Aksara Sunda, is a writing system which is used by some Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (Aksara Sunda Kuna) which was used by ancientSundanese between 14th and 18th centuries....
). There are five pure vowel sounds: a /ɑ/, é /ɛ/, i /i/, o /ɔ/, u /ʊ/, and two neutral vowels; e /ə/, and eu /ɤ/. The consonantal phonemes (18—but see below) are transcribed with the letters p, b, t, d, k, g, c , j, h, ng (/ŋ/, occurs initially), ny /ɳ/, m, n, s /s/, w, l, r (trilled or flapped), and y /j/.
Other consonants that originally appear in Indonesian loanwords are mostly transferred into native consonants: f → p, v → p, sy → s, sh → s, z -> j, and kh /x/ → h.
Definition of Sundanese Phonology, according to Yayat Sudaryat (1985:26):
"Fonologi nyaeta bagean tina elmu basa anu maluruh jeung medar sora-sora basa, prosesna, selang surupna, jeung parobahanana".
There are 16 consonants in Sundanese phonology, according to Yayat Sudaryat (1991,35):
"fonem konsonan (contoid) nya eta sora omongan (fonem) anu kawangun ku hawa anu kaluar tina bayah sarta waktu liwat tikoro aya nu ngahalangan. konsonan nu aya dina basa sunda, nyaeta:
/b/, /ts/, /d/, /g/, /h/, /dʒ/, /k/, /l/, /m/, /n/, /p/, /r/, /s/, /n/, /t/, /n'/, kuayana pangaruh basa kosta sok kapanggih konsonan /f/, /v/, /z/ mangrupa fomem nu asalna pangaruh basa kosta, saperti dina kecap: fonem, qur'an, xerox, zakat".
Based on the statement above, it is clear that the Sundanese language has only 16 consonants, there are three consonants /f, v, z/ which exist in Sundanese as a result of borrowing words, but naturally they are not Sundanese consonants.
Furthermore, Sudaryat does not mention the phonemes /w, j/ as semi vowels, although as vowels, /w, j/ function as a glide sound between two different vowels, as in the words:
- Kueh - /kuweh/
- Muih - /muwih/
- Bear - /beAar/
- Miang - /mijan/
Phonemes /w/ and /j/ function as glide sounds between two different vowels as in the words:
- wa - rung
- wa - yang
- ba - wang
- ha - yang
- ku - ya
Root verb
| English | Sundanese (normal) | Sundanese (polite) |
|---|---|---|
| eat .. | dahar .. | tuang ..(for other) neda ..(for myself) |
| drink .. | inum .. | leueut .. |
| write .. | tulis .. | serat .. |
| read .. | maca .. | maos .. |
| forget .. | poho .. | hilap .. |
| remember .. | inget .. | emut .. |
| sit .. | diuk .. | calik .. |
| stand .. | tangtung .. | adeg .. |
| walk .. | leumpang .. | papah .. |
Active form
Most of active form in sundanese verb are in their root verb like 'diuk' or 'dahar'. Some other depend on first phonem in root verb:- first phoneme in 'd' is eliminated and changed to prefix 'nga' like in 'ngadahar'
- first phoneme in 'i' is eliminated and changed to prefix 'ng' like in 'nginum'
- first phoneme in 'b' is eliminated and changed to prefix 'm' like in 'maca'
Negation
(to be written)."Abdi henteu acan neda". (I have not eaten yet.)
Explanation: From the above example, "henteu" is used for negative term.
"Buku abdi mah sanes nu ieu". (My book is not this one.)
Explanation: From the above example, "sanes" is used for negative term.
Question
(to be written).Dupi -(question)
example:
Polite-
- Dupi Bapa aya di bumi? (is your father at home?)
- Dupi bumi di palih mana? (where do you live?)
Passive form
(to be written.)"Buku dibantun ku abdi". (The book is brought by me.)
Explanation: "dibantun" (to be brought/passive) and "ngabantun" (active)
The other examples:
"Pulpen ditambut ku abdi". (The pen is borrowed by me.)
"Soal ieu dikerjakeun ku abdi". (This problem is done by me.)
Adjectives
(to be written).example:
teuas (hard), tiis (cool), hipu (soft), lada (hot, usually for foods), haneut (warm), etc.
Place
| English | Sundanese (normal) | Sundanese (polite) |
|---|---|---|
| above .. | diluhureun .. | diluhureun .. |
| behind .. | ditukangeun .. | dipengkereun .. |
| under .. | dihandapeun .. | dihandapeun .. |
| inside .. | di jero .. | di lebet .. |
| outside .. | di luar .. | di luar .. |
| between .. and .. |
di antara .. jeung .. |
di antawis .. sareng .. |
| front .. | hareup .. | payun .. |
| back .. | tukang .. | pengker .. |
Time
| English | Sundanese (normal) | Sundanese (polite) |
|---|---|---|
| before | saacan | sateuacan |
| after | sanggeus | saparantos |
| during | basa | nalika |
| past | baheula | kapungkur |
Miscellaneous
| English | Sundanese (normal) | Sundanese (polite) |
|---|---|---|
| from | tina | tina |
| for | jang | kanggo |


