
Nitroso
Encyclopedia
Nitroso refers to a functional group
in organic chemistry
which has the general formula RNO. Nitroso compounds are a class of organic compound
s containing the nitroso functional group
, R−N=O.
Nitrosyls are molecules with the general formula RNO, where R represents an unspecified substituent
.
Nitroso and bent Nitrosyl are synonyms; nitroso is used in organic chemistry, while bent nitrosyl is used in inorganic chemistry. Neither Nitroso nor bent Nitrosyl are identical to linear Nitrosil, which possesses sp hybridization. A common example of a nitroso compound is nitrosyl chloride
, NOCl (although its structure is better represented ONCl).
Nitrosyl also refers to the discrete molecule nitric oxide
, NO. Nitric oxide is a stable radical
, having an unpaired electron.
Reduction of nitric oxide gives the hyponitrite
anion, NO−:
Oxidation of NO yields the nitrosonium
cation, NO+:
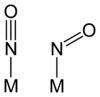
Nitric oxide can serve as a ligand
in complexes
. The resulting complexes are called metal nitrosyls, and can bond to a metal atom in two distinct modes: as NO+ and as NO−. NO+ coordinates linearly, the M−N−O angle being 180°, whereas NO− forms a bent geometry, with an M−N−O angle of approximately 120°.
s or by the oxidation of hydroxylamine
s. A good example is (CH3)3CNO, known formally as 2-methyl-2-nitrosopropane
, or t-BuNO, which is prepared by the following sequence:3CNH2 → (CH3)3CNO23CNO2 → (CH3)3CNHOH3CNHOH → (CH3)3CNO
(CH3)3CNO is blue and exists in solution in equilibrium
with its dimer, which is colorless, m.p. 80–81 °C.
In the Fischer-Hepp rearrangement
aromatic 4-nitroso-anilines are prepared from the corresponding nitrosamine
s. Another named reaction involving a nitroso compound is the Barton reaction
.
can enter two kinds of reaction, depending on the physico-chemical environment.

Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
which has the general formula RNO. Nitroso compounds are a class of organic compound
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
s containing the nitroso functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
, R−N=O.
Nitrosyls are molecules with the general formula RNO, where R represents an unspecified substituent
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
.
Nitroso and bent Nitrosyl are synonyms; nitroso is used in organic chemistry, while bent nitrosyl is used in inorganic chemistry. Neither Nitroso nor bent Nitrosyl are identical to linear Nitrosil, which possesses sp hybridization. A common example of a nitroso compound is nitrosyl chloride
Nitrosyl chloride
Nitrosyl chloride is the chemical compound NOCl. It is a yellow gas that is most commonly encountered as a decomposition product of aqua regia, a mixture of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid...
, NOCl (although its structure is better represented ONCl).
Nitrosyl also refers to the discrete molecule nitric oxide
Nitric oxide
Nitric oxide, also known as nitrogen monoxide, is a diatomic molecule with chemical formula NO. It is a free radical and is an important intermediate in the chemical industry...
, NO. Nitric oxide is a stable radical
Radical (chemistry)
Radicals are atoms, molecules, or ions with unpaired electrons on an open shell configuration. Free radicals may have positive, negative, or zero charge...
, having an unpaired electron.
Reduction of nitric oxide gives the hyponitrite
Hyponitrite
A hyponitrite refers to ionic compounds that contain the hyponitrite ion, N2O22−, or to organic hyponitrites , for example di-tert butyl hyponitrite.-Hyponitrite ion:There are cis and trans forms of the hyponitrite ion...
anion, NO−:
- NO + e− → NO−
Oxidation of NO yields the nitrosonium
Nitrosonium
The nitrosonium ion is NO+, in which the nitrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom with a bond order of 3, and the overall diatomic species bears a positive charge. This ion is usually obtained as the following salts: NOClO4, NOSO4H , and NOBF4. The ClO and BF salts are slightly soluble in CH3CN...
cation, NO+:
- NO → NO+ + e−
Nitrosyl as a ligand

Nitric oxide can serve as a ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
in complexes
Complex (chemistry)
In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex, is an atom or ion , bonded to a surrounding array of molecules or anions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents...
. The resulting complexes are called metal nitrosyls, and can bond to a metal atom in two distinct modes: as NO+ and as NO−. NO+ coordinates linearly, the M−N−O angle being 180°, whereas NO− forms a bent geometry, with an M−N−O angle of approximately 120°.
Nitroso compounds
Nitroso compounds can be prepared by the reduction of nitro compoundNitro compound
Nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups . They are often highly explosive, especially when the compound contains more than one nitro group and is impure. The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores used globally...
s or by the oxidation of hydroxylamine
Hydroxylamine
Hydroxylamine is an inorganic compound with the formula NH2OH. The pure material is a white, unstable crystalline, hygroscopic compound. However, hydroxylamine is almost always provided and used as an aqueous solution. It is used to prepare oximes, an important functional group. It is also an...
s. A good example is (CH3)3CNO, known formally as 2-methyl-2-nitrosopropane
2-Methyl-2-nitrosopropane
2-Methyl-2-nitrosopropane can be prepared by catalytic oxidation of 3CNH2 using hydrogen peroxide and sodium tungstate. Depending on the temperature and solvent, it is either dimeric and colorless or monomeric and blue. It can be used as a spin trap...
, or t-BuNO, which is prepared by the following sequence:3CNH2 → (CH3)3CNO23CNO2 → (CH3)3CNHOH3CNHOH → (CH3)3CNO
(CH3)3CNO is blue and exists in solution in equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
with its dimer, which is colorless, m.p. 80–81 °C.
In the Fischer-Hepp rearrangement
Fischer-Hepp rearrangement
The Fischer-Hepp rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction in which an aromatic N-nitroso or nitrosamine converts to a carbon nitroso compound:This organic reaction was first described by the German chemist Otto Philipp Fischer and...
aromatic 4-nitroso-anilines are prepared from the corresponding nitrosamine
Nitrosamine
Nitrosamines are chemical compounds of the chemical structure R1N-N=O, some of which are carcinogenic.-Usages:Nitrosamines are used in manufacture of some cosmetics, pesticides, and in most rubber products. -Occurrences:...
s. Another named reaction involving a nitroso compound is the Barton reaction
Barton reaction
The Barton Reaction involves the photolysis of a nitrite to form a δ-nitroso alcohol. It is named for the British chemist Sir Derek Harold Richard Barton...
.
Nitrosation vs. nitrosylation
NitriteNitrite
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula NO2−. The anion is symmetric with equal N-O bond lengths and a O-N-O bond angle of ca. 120°. On protonation the unstable weak acid nitrous acid is produced. Nitrite can be oxidised or reduced, with product somewhat dependent on the oxidizing/reducing agent...
can enter two kinds of reaction, depending on the physico-chemical environment.
- NitrosylationNitrosylationNitrosylation is a protein modification in which a nitrosyl group is post-translationally added to a protein.There is a range of enzymes that produce nitric oxide, and the frequent consequence of this production is nitrosylation....
is adding a nitrosyl ion NO− to a metal (e.g. iron) or a thiol, leading to nitrosyl iron Fe-NO (e.g., in nitrosylated heme = nitrosylheme) or S-nitrosothiols (RSNOs). - NitrosationNitrosationNitrosation is a process of converting organic compounds into nitroso derivatives, i.e. compounds containing the R-NO functionality.-C-Nitroso compounds:C-Nitroso compounds, such as nitrosobenzene, are typically prepared by oxidation of hydroxylamines:...
is adding a nitrosonium ion NO+ to an amine -NH2 leading to a nitrosamineNitrosamineNitrosamines are chemical compounds of the chemical structure R1N-N=O, some of which are carcinogenic.-Usages:Nitrosamines are used in manufacture of some cosmetics, pesticides, and in most rubber products. -Occurrences:...
. This occurs at acidic pH, particularly in the stomach, as shown in the figure below. Primary amines lead to unstable nitrosamines (that turn to alcool), but secondary amines R1-NH-R2 lead to stable nitrosamines, most of which are carcinogens in rodents.

In food
In foodstuffs and in the gastro-intestinal tract, nitrosation and nitrosylation do not have the same consequences on consumer health.- In cured meat: Meat processed by curingCuring (food preservation)Curing refers to various food preservation and flavoring processes, especially of meat or fish, by the addition of a combination of salt, nitrates, nitrite or sugar. Many curing processes also involve smoking, the process of flavoring, or cooking...
contains nitrite and has a pH of 5 approximately, where almost all nitrite is present as NO2− (99%). Cured meat is also added with sodium ascorbateSodium ascorbateSodium ascorbate is a more bioavailable form of vitamin C that is an alternative to taking ascorbic acid as a supplement. The molecular formula of this chemical compound is C6H7NaO6...
(or erythorbate or Vitamin C). As demonstrated by S. Mirvish, ascorbate inhibits nitrosation of amines to nitrosamine, because ascorbate reacts with NO2− to form NO. Ascorbate and pH 5 thus favor nitrosylation of heme iron, forming nitrosyl-heme, a red pigment when included inside myoglobin, and a pink pigment when it has been released by cooking. It participates to the "bacon flavor" of cured meat: nitrosyl-heme is thus considered a benefit for the meat industry and for consumers.
- In the stomachStomachThe stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
: secreted HCl makes an acidic environment (pH=2) and ingested nitrite (with food or saliva) leads to nitrosation of amines, that yields nitrosamineNitrosamineNitrosamines are chemical compounds of the chemical structure R1N-N=O, some of which are carcinogenic.-Usages:Nitrosamines are used in manufacture of some cosmetics, pesticides, and in most rubber products. -Occurrences:...
s (potential carcinogens). Nitrosation is low if amine concentration is low (e.g., low-protein diet, no fermented food) or if Vitamin C concentration is high (e.g., high fruit diet). Then S-nitrosothiols are formed, that are stable at pH 2.
- In the colonColon (anatomy)The colon is the last part of the digestive system in most vertebrates; it extracts water and salt from solid wastes before they are eliminated from the body, and is the site in which flora-aided fermentation of unabsorbed material occurs. Unlike the small intestine, the colon does not play a...
: neutral pH does not favour nitrosation. No nitrosamine is formed in stools, even after addition of a secondary amine or nitrite. Neutral pH favors NO− release from S-nitrosothiols, and nitrosylation of iron. The previously called NOC (N-nitroso compounds) measured by Bingham's team in stools from red meat-fed volunteers were, according to Bingham and Kuhnle, largely non-N-nitroso ATNC (Apparent Total Nitroso Compounds), e.g., S-nitrosothiols and nitrosyl iron (as nitrosyl heme).
See also
- NitrosamineNitrosamineNitrosamines are chemical compounds of the chemical structure R1N-N=O, some of which are carcinogenic.-Usages:Nitrosamines are used in manufacture of some cosmetics, pesticides, and in most rubber products. -Occurrences:...
, the functional group with the NO attached to an amine, such as R2N-NO - NitrosobenzeneNitrosobenzeneNitrosobenzene is the organic compound with the formula C6H5NO. The compound can be viewed as hybrid of singlet O2 and azobenzene. This diamagnetic species exists in equilibrium with its dimer.-Preparation:...
- Nitric oxideNitric oxideNitric oxide, also known as nitrogen monoxide, is a diatomic molecule with chemical formula NO. It is a free radical and is an important intermediate in the chemical industry...
- NitroxylNitroxylNitroxyl is the chemical compound HNO. It is well known in the gas phase . In aqueous solution it acts as an acid with the conjugate base NO−, . NO− is the reduced form of nitric oxide and is isoelectronic with dioxygen...

