
Nickel metal hydride battery
Encyclopedia
A nickel–metal hydride cell, abbreviated NiMH, is a type of rechargeable battery
similar to the nickel–cadmium cell. The NiMH battery uses a hydrogen-absorbing alloy
for the negative electrode
instead of cadmium
. As in NiCd cells, the positive electrode is nickel oxyhydroxide (NiOOH). A NiMH battery can have two to three times the capacity of an equivalent size nickel–cadmium battery. The energy density
of a NiMH cell is similar to that of a lithium-ion cell, but the rate of self-discharge is higher. This means that a stored NiMH battery will lose charge more quickly. In 2005 a low self-discharge NiMH battery
(LSD), which stays charged for much longer, was developed.
Common AA
(penlight-size) NiMH batteries have nominal charge capacities (C) ranging from 1100 mA·h to 3100 mA·h at 1.2 V, measured at the rate that discharges the cell in five hours. Useful discharge capacity is a decreasing function of the discharge rate, but up to a rate of around 1×C (full discharge in one hour), it does not differ significantly from the nominal capacity.
The typical specific energy
for NiMH AA cells is about 100 W·h
/kg, and for other NiMH dry cells about 75 W·h/kg (270 kJ/kg), compared to 40–60 W·h/kg for Ni–Cd, or 100-160 W·h/kg for Li-ion. NiMH has a volumetric energy density of about 300 W·h/L
(1080 MJ/m³), significantly better than nickel–cadmium at 50–150 W·h/L, and about the same as Li-ion at 250-360 W·h/L.
About 22% of portable rechargeable batteries sold in Japan in 2010 were nickel–metal hydride. In Switzerland in 2009, the equivalent statistic was approximately 60%. This percentage has fallen over time due to the increase in manufacture of lithium ion batteries: in 2000, almost half of all portable rechargeable batteries sold in Japan were nickel–metal hydride.
Because non-LSDs do not have an LSD separator, they are cheaper to manufacture than LSDs, yet most are offered at about the same price as LSDs and are marketed as "high capacity" or "ultra high capacity" NiMH batteries. While "high capacity" versions may have an extra 20% in initial capacity (compared to LSDs), this is negated by much higher internal resistance (especially in high drain situations) than LSDs and much higher self discharge rates (20% or more in first 24 hours, plus 4% per day thereafter). This energy wasted on heat and self discharge means these batteries require significant extra recharging which reduces overall battery life. Consequently, with consumer size batteries (AAA, AA, C, D, 9v), the low self-discharge NiMH battery
has all but replaced the "high capacity" or "ultra high capacity" non-LSD type.
The earliest pioneering work on NiMH batteries — essentially based on sintered
Ti2Ni+TiNi+x alloys for the negative electrode and NiOOH-electrodes for the positives — was performed at the Battelle
-Geneva Research Center starting after its invention in 1967. The development work was sponsored over nearly two decades by Daimler-Benz
in Stuttgart, Germany, and by Volkswagen AG within the framework of Deutsche Automobilgesellschaft, now a subsidiary of Daimler AG. The batteries showed high specific energy up to 50 W·h/kg (180 kJ/kg), power density up to 1000 W/kg and a reasonable life of 500 charge cycle
s (at 100% depth of discharge
). Patent applications were filed in European countries (priority: Switzerland), United States and Japan and the patents transferred to Daimler-Benz.
Interest grew in the 1970s with the commercialisation of the Nickel–hydrogen battery for satellite applications. Hydride technology promised an alternative much less bulky way to store the hydrogen. Research carried out by Philips Laboratories
and France's CNRS developed new high-energy hybrid alloys incorporating rare earth metals for the negative electrode. However, these suffered from the instability of the alloys in alkaline electrolyte and consequently insufficient cycle life. In 1987, Willems and Buschow demonstrated a successful battery based on this approach (using a mixture of La0.8Nd0.2Ni2.5Co2.4Si0.1) which kept 84% of its charge capacity after 4000 charge-discharge cycles. More economically viable alloys using mischmetal
instead of lanthanum
were soon developed and modern NiMH cells are based on this design.
Ovonic Battery Co. in Michigan
altered and improved the Ti-Ni alloy structure and composition according to their patent and licensed NiMH batteries to over 50 companies worldwide. Ovonic's NiMH variation consisted of special alloys with disordered alloy structure and specific multicomponent alloy compositions. Unfortunately, linked to their composition, the calendar and cycle life of such alloys always remains very low, and all NiMH batteries manufactured at the present time consist of AB5-type rare earth metal alloys.
Positive electrode development was done by Dr. Masahiko Oshitani from GS Yuasa Company, who was the first to develop high-energy paste electrode technology. The association of this high-energy electrode with high-energy hybrid alloys for the negative electrode led to the new environmentally friendly high-energy NiMH cell.
Currently, more than 2 million hybrid cars worldwide are running with NiMH batteries, e.g., Prius, Lexus (Toyota), Civic, Insight (Honda), Fusion (Ford), and others. Many of these batteries are manufactured by PEVE (Panasonic) and Sanyo.

 Applications of NiMH electric vehicle batteries
Applications of NiMH electric vehicle batteries
includes all-electric plug-in vehicles such as the General Motors EV1
, Honda EV Plus
, Ford Ranger EV
and Vectrix
scooter. Hybrid vehicle
s such as the Toyota Prius, Honda Insight
, Ford Escape Hybrid, Chevrolet Malibu Hybrid, and Honda Civic Hybrid
also use them. NiMH technology is used extensively in rechargeable batteries for consumer electronics
, and it will also be used on the Alstom
Citadis
low floor tram
ordered for Nice
, France
; as well as the humanoid prototype robot ASIMO
designed by Honda
. NiMH batteries are also commonly used in remote control cars.
reaction occurring in a NiMH cell is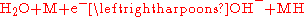
The charge reaction is read left-to-right and the discharge reaction is read right-to-left.
On the positive electrode, nickel oxyhydroxide (NiOOH) is formed,
The "metal" M in the negative electrode of a NiMH cell is actually an intermetallic compound. Many different compounds have been developed for this application, but those in current use fall into two classes. The most common is AB5, where A is a rare earth
mixture of lanthanum
, cerium
, neodymium
, praseodymium
and B is nickel
, cobalt
, manganese
, and/or aluminium
. Very few cells use higher-capacity negative material electrodes based on AB2 compounds, where A is titanium and/or vanadium
and B is zirconium
or nickel, modified with chromium
, cobalt, iron
, and/or manganese, due to the reduced life performances. Any of these compounds serve the same role, reversibly forming a mixture of metal hydride compounds.
When overcharged at low rates, oxygen produced at the positive electrode passes through the separator and recombines at the surface of the negative. Hydrogen evolution is suppressed and the charging energy is converted to heat. This process allows NiMH cells to remain sealed in normal operation and to be maintenance-free.
NiMH cells have an alkaline electrolyte
, usually potassium hydroxide
. For separation hydrophilic polyolefin
nonwovens are used.
is in the range of 1.4–1.6 V/cell. In general, a constant-voltage charging method cannot be used for automatic charging. When fast-charging, it is advisable to charge the NiMH cells with a smart battery charger
to avoid overcharging
, which can damage cells and even be dangerous. A NiCd charger should not be used as an automatic substitute for a NiMH charger.
NiMH charging manual warns that overcharging for long enough can damage a battery and suggests limiting the total charging time to 10 to 20 hours.
Duracell further suggests that, for applications where the battery must be kept in a fully charged state, a trickle charge at 0.0033 C can be used. Some chargers do this after the charge cycle, to offset the natural self-discharge rate of the battery. Panasonic's handbook, however, recommends that such batteries are kept charged by a lower duty cycle
approach, where a pulse of a higher current is used whenever the battery's voltage drops below 1.3 V. This can extend battery life and use less energy.
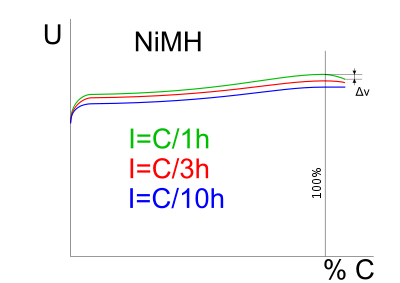 In order to charge a NiMH battery faster than the trickle method suggested above, a charger must know when to stop charging in order to avoid damaging the battery. One method is to monitor the change of voltage across the battery with time. As can be seen in the charge curve diagram, when the battery is fully charged the voltage across its terminals drops slightly. The charger can detect this and stop charging. This method is often used with Nickel-Cadmium cells which have a large drop in voltage at full charge but the voltage drop is much less pronounced for NiMH and can be non-existent at high charge rates, which can make the approach unreliable. Another option is to monitor the change of voltage with respect to time and stop when this becomes zero, but this runs the risk of premature cutoffs.
In order to charge a NiMH battery faster than the trickle method suggested above, a charger must know when to stop charging in order to avoid damaging the battery. One method is to monitor the change of voltage across the battery with time. As can be seen in the charge curve diagram, when the battery is fully charged the voltage across its terminals drops slightly. The charger can detect this and stop charging. This method is often used with Nickel-Cadmium cells which have a large drop in voltage at full charge but the voltage drop is much less pronounced for NiMH and can be non-existent at high charge rates, which can make the approach unreliable. Another option is to monitor the change of voltage with respect to time and stop when this becomes zero, but this runs the risk of premature cutoffs.
With this method, a much higher charging rate can be used than with a trickle charge, up to 1 C. At this charge rate, ΔV is approximately 5–10mV per cell. Since this method measures the voltage across the battery, a constant current (rather than a constant voltage) charging circuit must be used. This is unlike a lead–acid cell for example, which can, in theory, be more easily charged at a suitably chosen constant voltage.
. Both Panasonic and Duracell suggest a maximum rate of temperature increase of 1°C per minute. Using a temperature sensor also allows an absolute temperature cutoff, which Duracell suggests at 60°C.
With both the ΔT and the ΔV charging methods, both manufacturers recommend a further period of trickle charging to follow the initial rapid charge.
in series with the cell, particularly of the bimetallic strip type. This fuse will open if either the current or the temperature goes too high.
Modern NiMH cells contain catalysts to immediately deal with gases developed as a result of over-charging without being harmed (2 H2 + O2 ---catalyst → 2 H2O). However, this only works with overcharging
currents of up to 0.1C (nominal capacity divided by 10 hours). As a result of this reaction, the batteries will heat up considerably, marking the end of the charging process. Some quick chargers have a fan to keep the batteries cool.
A method for very rapid charging called in-cell charge control involves an internal pressure switch in the cell, which disconnects the charging current in the event of overpressure.
There is an inherent risk with NiMH chemistry that overcharging will cause a buildup of hydrogen, causing the cell to rupture. Therefore, cells have a vent. Hydrogen will be emitted from the vent in the event of serious overcharging.
Under a light load (0.5 ampere), the starting voltage of a freshly charged AA NiMH cell in good condition is about 1.4 volts;
This voltage falls rapidly to about 1.25 volts at 10% depth of discharge (DOD) and then remains almost constant until the cell is over 80% discharged. The voltage then falls rapidly from about 1.2 volts down to 0.8–1.0 volts at which the cell is considered "flat" in most devices. Mid-discharge at a load of 1 ampere, the output is about 1.2 volts; at 2 amperes, about 1.15 volts; the total effective differential internal resistance is about 0.05 ohms. Nickel metal hydride batteries provide a relatively constant voltage for most of the discharge cycle, unlike a standard alkaline where the voltage falls steadily during discharge.
cells in series in a digital camera
, where one will be completely discharged before the others due to small differences in capacity among the cells. When this happens, the good cells will start to drive the discharged cell in reverse, which can cause permanent damage to that cell. Some cameras, GPS receivers
and PDAs
detect the safe end-of-discharge voltage of the series cells and auto-shutdown, but devices like flashlights and some toys do not. A single cell driving a load can't suffer from polarity reversal, because there are no other cells to reverse-charge it when it becomes discharged.
Irreversible damage from polarity reversal is a particular danger in systems, even when a low voltage threshold cutout is employed, where cells in the battery are of different temperatures. This is because the capacity of NiMH cells significantly declines as the cells are cooled. This results in a lower voltage under load of the colder cells.
rate (equivalent to internal leakage) than NiCd cells. The self-discharge is 5–10% on the first day and stabilizes around 0.5–1% per day at room temperature
.
This is not a problem in the short term but makes them unsuitable for many light-duty uses, such as clocks, remote controls, or safety devices, where the battery would normally be expected to last many months or years. The rate is strongly affected by the temperature at which the batteries are stored with cooler storage temperatures leading to slower discharge rate and longer battery life. The highest capacity cells on the market (>8000 mA·h) are reported to have the highest self-discharge rates.
Low self-discharge cells have lower capacity than some standard NiMH cells due to the larger area of the separator. The highest capacity low-self-discharge cells have 2000–2500 mA·h and 1000 mA·h capacities for AA and AAA cells respectively, compared to 2800 mA·h and 1300 mA·h for standard AA and AAA cells. C types are typically higher than their usual NiMH cousins, with 4000 mA·h and the D type being 8000 mA·h.
After only a few weeks of storage, the retained capacity of low-self-discharge batteries often exceeds that of traditional NiMH batteries of higher capacity.
. However, mining and processing the various alternate metals that form the negative electrode may pose other types of environmental impact, depending on the metal, mining method, and environmental practices of the mine.
Most industrial nickel is recycled, due to the relatively easy retrieval of the magnetic element from scrap using electromagnet
s, and due to its high value.
and AA
. Adapter sleeves are available to use the more common AA size in C and D applications. The sizes C
and D
cells are somewhat available, but are often just a AA core hidden in an outer shell, with a rating of about 2500 mA·h, much less than ordinary alkaline C and D batteries. Real NiMH C and D batteries are expensive (and the chargers are uncommon); they should be rated at least 5000 mA·h for C and 10,000 mA·h for D sizes.
PP3
(nine volt) NiMH batteries are available; these usually have an output voltage of 8.4 V (1.2 × 7) and a capacity of roughly 200 mA·h. Also available are eight-cell nine volt batteries with a nominal output voltage of 9.6 V (1.2 × 8).
NiMH cells are not expensive, and the voltage and performance is similar to primary alkaline cells
in those sizes; they can be substituted for most purposes. Although alkaline cells are rated at 1.5 volts and NiMH cells at 1.2 volts, during discharge the alkaline voltage eventually drops below that of NiMH. NiMH batteries offer a flatter discharge curve, particularly at higher current draw.
NiMH cells are often used in digital cameras and other high drain devices, where over the duration of single charge use they outperform primary (such as alkaline) batteries. Applications that require frequent replacement of the battery, such as toys or video game controllers, also benefit from use of rechargeable batteries. With the development of low self-discharge NiMHs (see section above), many occasional-use and very low-power applications are now candidates for NiMH cells.
NiMH cells are particularly advantageous for high current drain applications, due in large part to their low internal resistance. Alkaline batteries, which might have approximately 3000 mA·h capacity at low current demand (200 mA), will have about 700 mA·h capacity with a 1000 mA load. Digital cameras with LCDs and flashlights can draw over 1000 mA, quickly depleting alkaline batteries. NiMH cells can deliver these current levels and maintain their full capacity.
Certain devices that were designed to operate using primary alkaline chemistry (or zinc–carbon/chloride) cells will not function when one uses NiMH cells as substitutes. However, this is rare, as most devices compensate for the voltage drop of an alkaline as it discharges down to about 1 volt. Low internal resistance allows NiMH cells to deliver a near-constant voltage until they are almost completely discharged. This will cause a battery level indicator to overstate the remaining charge if it was designed to read only the voltage curve of alkaline cells. The voltage of alkaline cells decreases steadily during most of the discharge cycle.
Lithium ion batteries have a higher specific energy than nickel–metal hydride batteries, but they are significantly more expensive to produce. In October 2009, ECD Ovonics announced that their next-generation NiMH batteries will provide specific energy and power that are comparable to those of lithium ion batteries at a cost that is significantly lower than the cost of lithium ion batteries.
purchased the patent from Ovonics in 1994. By the late 1990s, NiMH batteries were being used successfully in many fully electric vehicles, such as the General Motors EV1
and Dodge Caravan EPIC minivan. In October 2000, the patent was sold to Texaco and a week later Texaco was acquired by Chevron. Chevron's Cobasys
subsidiary will only provide these batteries to large OEM orders. General Motors shut down production of the EV1 citing lack of battery availability as one of their chief obstacles. The Cobasys control of NiMH batteries has created a patent encumbrance of large automotive NiMH batteries.
Rechargeable battery
A rechargeable battery or storage battery is a group of one or more electrochemical cells. They are known as secondary cells because their electrochemical reactions are electrically reversible. Rechargeable batteries come in many different shapes and sizes, ranging anything from a button cell to...
similar to the nickel–cadmium cell. The NiMH battery uses a hydrogen-absorbing alloy
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture or metallic solid solution composed of two or more elements. Complete solid solution alloys give single solid phase microstructure, while partial solutions give two or more phases that may or may not be homogeneous in distribution, depending on thermal history...
for the negative electrode
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
instead of cadmium
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
. As in NiCd cells, the positive electrode is nickel oxyhydroxide (NiOOH). A NiMH battery can have two to three times the capacity of an equivalent size nickel–cadmium battery. The energy density
Energy density
Energy density is a term used for the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Often only the useful or extractable energy is quantified, which is to say that chemically inaccessible energy such as rest mass energy is ignored...
of a NiMH cell is similar to that of a lithium-ion cell, but the rate of self-discharge is higher. This means that a stored NiMH battery will lose charge more quickly. In 2005 a low self-discharge NiMH battery
Low self-discharge NiMH battery
The low self-discharge nickel-metal hydride battery was introduced in November 2005. These batteries were developed by Sanyo, who called them "eneloop". Subsequently, other manufacturers also offered LSD NiMH....
(LSD), which stays charged for much longer, was developed.
Common AA
AA battery
An AA battery is a standard size of battery. Batteries of this size are the most commonly used type of in portable electronic devices. An AA battery is composed of a single electrochemical cell...
(penlight-size) NiMH batteries have nominal charge capacities (C) ranging from 1100 mA·h to 3100 mA·h at 1.2 V, measured at the rate that discharges the cell in five hours. Useful discharge capacity is a decreasing function of the discharge rate, but up to a rate of around 1×C (full discharge in one hour), it does not differ significantly from the nominal capacity.
The typical specific energy
Specific energy
Specific energy is defined as the energy per unit mass. Common metric units are J/kg. It is an intensive property. Contrast this with energy, which is an extensive property. There are two main types of specific energy: potential energy and specific kinetic energy. Others are the gray and sievert,...
for NiMH AA cells is about 100 W·h
Watt-hour
The kilowatt hour, or kilowatt-hour, is a unit of energy equal to 1000 watt hours or 3.6 megajoules.For constant power, energy in watt hours is the product of power in watts and time in hours...
/kg, and for other NiMH dry cells about 75 W·h/kg (270 kJ/kg), compared to 40–60 W·h/kg for Ni–Cd, or 100-160 W·h/kg for Li-ion. NiMH has a volumetric energy density of about 300 W·h/L
Litér
- External links :*...
(1080 MJ/m³), significantly better than nickel–cadmium at 50–150 W·h/L, and about the same as Li-ion at 250-360 W·h/L.
About 22% of portable rechargeable batteries sold in Japan in 2010 were nickel–metal hydride. In Switzerland in 2009, the equivalent statistic was approximately 60%. This percentage has fallen over time due to the increase in manufacture of lithium ion batteries: in 2000, almost half of all portable rechargeable batteries sold in Japan were nickel–metal hydride.
Because non-LSDs do not have an LSD separator, they are cheaper to manufacture than LSDs, yet most are offered at about the same price as LSDs and are marketed as "high capacity" or "ultra high capacity" NiMH batteries. While "high capacity" versions may have an extra 20% in initial capacity (compared to LSDs), this is negated by much higher internal resistance (especially in high drain situations) than LSDs and much higher self discharge rates (20% or more in first 24 hours, plus 4% per day thereafter). This energy wasted on heat and self discharge means these batteries require significant extra recharging which reduces overall battery life. Consequently, with consumer size batteries (AAA, AA, C, D, 9v), the low self-discharge NiMH battery
Low self-discharge NiMH battery
The low self-discharge nickel-metal hydride battery was introduced in November 2005. These batteries were developed by Sanyo, who called them "eneloop". Subsequently, other manufacturers also offered LSD NiMH....
has all but replaced the "high capacity" or "ultra high capacity" non-LSD type.
History
The first consumer grade NiMH cells for smaller applications appeared on the market in 1989, the culmination of over two decades of research and development.The earliest pioneering work on NiMH batteries — essentially based on sintered
Sintering
Sintering is a method used to create objects from powders. It is based on atomic diffusion. Diffusion occurs in any material above absolute zero, but it occurs much faster at higher temperatures. In most sintering processes, the powdered material is held in a mold and then heated to a temperature...
Ti2Ni+TiNi+x alloys for the negative electrode and NiOOH-electrodes for the positives — was performed at the Battelle
Battelle Memorial Institute
Battelle Memorial Institute is a private nonprofit applied science and technology development company headquartered in Columbus, Ohio. Battelle is a charitable trust organized as a nonprofit corporation under the laws of the State of Ohio and is exempt from taxation under Section 501 of the...
-Geneva Research Center starting after its invention in 1967. The development work was sponsored over nearly two decades by Daimler-Benz
Daimler-Benz
Daimler-Benz AG was a German manufacturer of automobiles, motor vehicles, and internal combustion engines; founded in 1926. An Agreement of Mutual Interest - which was valid until year 2000 - was signed on 1 May 1924 between Karl Benz's Benz & Cie., and Daimler Motoren Gesellschaft, which had...
in Stuttgart, Germany, and by Volkswagen AG within the framework of Deutsche Automobilgesellschaft, now a subsidiary of Daimler AG. The batteries showed high specific energy up to 50 W·h/kg (180 kJ/kg), power density up to 1000 W/kg and a reasonable life of 500 charge cycle
Charge cycle
A charge cycle is the process of charging a rechargeable battery and discharging it as required into a load. The term is typically used to specify a battery's expected life, as the number of charge cycles affects life more than the mere passage of time...
s (at 100% depth of discharge
Depth of discharge
Depth of discharge is an alternate method to indicate a battery's state of charge . The DOD is the inverse of SOC: as one increases, the other decreases. While the SOC units are percent points , the units for DOD can be Ah or percent points...
). Patent applications were filed in European countries (priority: Switzerland), United States and Japan and the patents transferred to Daimler-Benz.
Interest grew in the 1970s with the commercialisation of the Nickel–hydrogen battery for satellite applications. Hydride technology promised an alternative much less bulky way to store the hydrogen. Research carried out by Philips Laboratories
Philips
Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company....
and France's CNRS developed new high-energy hybrid alloys incorporating rare earth metals for the negative electrode. However, these suffered from the instability of the alloys in alkaline electrolyte and consequently insufficient cycle life. In 1987, Willems and Buschow demonstrated a successful battery based on this approach (using a mixture of La0.8Nd0.2Ni2.5Co2.4Si0.1) which kept 84% of its charge capacity after 4000 charge-discharge cycles. More economically viable alloys using mischmetal
Mischmetal
Mischmetal is an alloy of rare earth elements in various naturally occurring proportions. It is also called cerium mischmetal, rare earth mischmetal or misch metal. A typical composition includes approximately 50% cerium and 25% lanthanum, with small amounts of neodymium and praseodymium...
instead of lanthanum
Lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and...
were soon developed and modern NiMH cells are based on this design.
Ovonic Battery Co. in Michigan
Michigan
Michigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
altered and improved the Ti-Ni alloy structure and composition according to their patent and licensed NiMH batteries to over 50 companies worldwide. Ovonic's NiMH variation consisted of special alloys with disordered alloy structure and specific multicomponent alloy compositions. Unfortunately, linked to their composition, the calendar and cycle life of such alloys always remains very low, and all NiMH batteries manufactured at the present time consist of AB5-type rare earth metal alloys.
Positive electrode development was done by Dr. Masahiko Oshitani from GS Yuasa Company, who was the first to develop high-energy paste electrode technology. The association of this high-energy electrode with high-energy hybrid alloys for the negative electrode led to the new environmentally friendly high-energy NiMH cell.
Currently, more than 2 million hybrid cars worldwide are running with NiMH batteries, e.g., Prius, Lexus (Toyota), Civic, Insight (Honda), Fusion (Ford), and others. Many of these batteries are manufactured by PEVE (Panasonic) and Sanyo.
Applications


Electric vehicle battery
An electric vehicle battery or traction battery is a rechargeable battery used for propulsion of battery electric vehicles...
includes all-electric plug-in vehicles such as the General Motors EV1
General Motors EV1
The General Motors EV1 was an electric car produced and leased by the General Motors Corporation from 1996 to 1999. It was the first mass-produced and purpose-designed electric vehicle of the modern era from a major automaker, and the first GM car designed to be an electric vehicle from the...
, Honda EV Plus
Honda EV Plus
The Honda EV Plus was the first battery electric vehicle from a major automaker with non-lead acid batteries. Roughly 340 EV Plus models were produced and released. The EV Plus was taken out of production in 1999 when Honda announced the release of its first hybrid electric vehicle, the Honda Insight...
, Ford Ranger EV
Ford Ranger EV
The Ford Ranger EV is a battery electric vehicle produced by Ford Motor Company. It was produced starting in the 1998 model year through 2002 and is no longer in production. It is built upon a light truck chassis used in the Ford Ranger. A few vehicles with lead-acid batteries were sold, but most...
and Vectrix
Vectrix
Vectrix is an electric vehicle company based in Middletown, Rhode Island, United States, with research and development facilities in New Bedford, Massachusetts...
scooter. Hybrid vehicle
Hybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is a vehicle that uses two or more distinct power sources to move the vehicle. The term most commonly refers to hybrid electric vehicles , which combine an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors.-Power:...
s such as the Toyota Prius, Honda Insight
Honda Insight
The Honda Insight is a hybrid electric vehicle manufactured by Honda and the first production vehicle to feature Honda's Integrated Motor Assist system. The first-generation Insight was produced from 1999 to 2006 as a three-door hatchback...
, Ford Escape Hybrid, Chevrolet Malibu Hybrid, and Honda Civic Hybrid
Honda Civic Hybrid
The Civic hybrid, based on the seventh generation Civic, was first introduced to the Japanese market in December 2001. Honda claimed it was the most fuel efficient 5-passenger gasoline-powered production vehicle in the world at the time. It was introduced to the U.S. in spring 2002 as a 2003 model...
also use them. NiMH technology is used extensively in rechargeable batteries for consumer electronics
Consumer electronics
Consumer electronics are electronic equipment intended for everyday use, most often in entertainment, communications and office productivity. Radio broadcasting in the early 20th century brought the first major consumer product, the broadcast receiver...
, and it will also be used on the Alstom
Alstom
Alstom is a large multinational conglomerate which holds interests in the power generation and transport markets. According to the company website, in the years 2010-2011 Alstom had annual sales of over €20.9 billion, and employed more than 85,000 people in 70 countries. Alstom's headquarters are...
Citadis
Citadis
The Citadis is a low-floor tram built by Alstom in La Rochelle, France, and Barcelona, Spain. 1,140 Citadis are currently in use in 28 cities, among others: Bordeaux, Grenoble, Lyon, Montpellier, Orléans, the Paris area, and Barcelona, Dublin, Gdańsk, Katowice, Adelaide, Melbourne, Jerusalem and...
low floor tram
Tram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
ordered for Nice
Nice
Nice is the fifth most populous city in France, after Paris, Marseille, Lyon and Toulouse, with a population of 348,721 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Nice extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of more than 955,000 on an area of...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
; as well as the humanoid prototype robot ASIMO
ASIMO
is a humanoid robot created by Honda. Introduced in 2000, ASIMO, which is an acronym for "Advanced Step in Innovative MObility", was created to be a helper to people. With aspirations of helping people who lack full mobility, ASIMO is used to encourage young people to study science and mathematics...
designed by Honda
Honda
is a Japanese public multinational corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles.Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than...
. NiMH batteries are also commonly used in remote control cars.
Electrochemistry
The negative electrodeElectrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
reaction occurring in a NiMH cell is
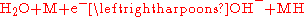
The charge reaction is read left-to-right and the discharge reaction is read right-to-left.
On the positive electrode, nickel oxyhydroxide (NiOOH) is formed,

The "metal" M in the negative electrode of a NiMH cell is actually an intermetallic compound. Many different compounds have been developed for this application, but those in current use fall into two classes. The most common is AB5, where A is a rare earth
Rare earth element
As defined by IUPAC, rare earth elements or rare earth metals are a set of seventeen chemical elements in the periodic table, specifically the fifteen lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium...
mixture of lanthanum
Lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and...
, cerium
Cerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, silvery, ductile metal which easily oxidizes in air. Cerium was named after the dwarf planet . Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth elements, making up about 0.0046% of the Earth's crust by weight...
, neodymium
Neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is a soft silvery metal that tarnishes in air. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach. It is present in significant quantities in the ore minerals monazite and bastnäsite...
, praseodymium
Praseodymium
Praseodymium is a chemical element that has the symbol Pr and atomic number 59. Praseodymium is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile metal in the lanthanide group. It is too reactive to be found in native form, and when artificially prepared, it slowly develops a green oxide coating.The element...
and B is nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
, cobalt
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal....
, manganese
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals...
, and/or aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
. Very few cells use higher-capacity negative material electrodes based on AB2 compounds, where A is titanium and/or vanadium
Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature...
and B is zirconium
Zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name of zirconium is taken from the mineral zircon. Its atomic mass is 91.224. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that resembles titanium...
or nickel, modified with chromium
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable...
, cobalt, iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
, and/or manganese, due to the reduced life performances. Any of these compounds serve the same role, reversibly forming a mixture of metal hydride compounds.
When overcharged at low rates, oxygen produced at the positive electrode passes through the separator and recombines at the surface of the negative. Hydrogen evolution is suppressed and the charging energy is converted to heat. This process allows NiMH cells to remain sealed in normal operation and to be maintenance-free.
NiMH cells have an alkaline electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
, usually potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, commonly called caustic potash.Along with sodium hydroxide , this colorless solid is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications. Most applications exploit its reactivity toward acids and its corrosive...
. For separation hydrophilic polyolefin
Polyolefin
A polyolefin is a polymer produced from a simple olefin as a monomer. For example, polyethylene is the polyolefin produced by polymerizing the olefin ethylene. An equivalent term is polyalkene; this is a more modern term, although polyolefin is still used in the petrochemical industry...
nonwovens are used.
Charging
The charging voltageVoltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
is in the range of 1.4–1.6 V/cell. In general, a constant-voltage charging method cannot be used for automatic charging. When fast-charging, it is advisable to charge the NiMH cells with a smart battery charger
Battery charger
A battery charger is a device used to put energy into a secondary cell or rechargeable battery by forcing an electric current through it.The charge current depends upon the technology and capacity of the battery being charged...
to avoid overcharging
Overcharging
Overcharging can refer to:*Overcharging , a prosecutorial practice*Charging a battery too much*Charging a customer too much...
, which can damage cells and even be dangerous. A NiCd charger should not be used as an automatic substitute for a NiMH charger.
Trickle charging
The simplest way to safely charge a NiMH cell is with a fixed low current, with or without a timer. Most manufacturers claim that overcharging is safe at very low currents, below 0.1 C (where C is the current equivalent to the capacity of the battery divided by one hour). The PanasonicPanasonic
Panasonic is an international brand name for Japanese electric products manufacturer Panasonic Corporation, which was formerly known as Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd...
NiMH charging manual warns that overcharging for long enough can damage a battery and suggests limiting the total charging time to 10 to 20 hours.
Duracell further suggests that, for applications where the battery must be kept in a fully charged state, a trickle charge at 0.0033 C can be used. Some chargers do this after the charge cycle, to offset the natural self-discharge rate of the battery. Panasonic's handbook, however, recommends that such batteries are kept charged by a lower duty cycle
Duty cycle
In engineering, the duty cycle of a machine or system is the time that it spends in an active state as a fraction of the total time under consideration....
approach, where a pulse of a higher current is used whenever the battery's voltage drops below 1.3 V. This can extend battery life and use less energy.
ΔV charging method

With this method, a much higher charging rate can be used than with a trickle charge, up to 1 C. At this charge rate, ΔV is approximately 5–10mV per cell. Since this method measures the voltage across the battery, a constant current (rather than a constant voltage) charging circuit must be used. This is unlike a lead–acid cell for example, which can, in theory, be more easily charged at a suitably chosen constant voltage.
ΔT temperature charging method
The ΔT temperature change method is similar in principle to the ΔV method. Because the charging voltage is nearly constant, constant-current charging delivers energy at a near-constant rate. When the cell is not fully charged, most of this energy is converted to chemical energy. However, when the cell reaches full charge, most of the charging energy is converted to heat. This increases the rate of change of battery temperature, which can be detected by a sensor such as a thermistorThermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word is a portmanteau of thermal and resistor...
. Both Panasonic and Duracell suggest a maximum rate of temperature increase of 1°C per minute. Using a temperature sensor also allows an absolute temperature cutoff, which Duracell suggests at 60°C.
With both the ΔT and the ΔV charging methods, both manufacturers recommend a further period of trickle charging to follow the initial rapid charge.
Safety
A good safety feature of a custom-built charger is to use a resettable fuseResettable fuse
A polymeric positive temperature coefficient device is a passive electronic component used to protect against overcurrent faults in electronic circuits...
in series with the cell, particularly of the bimetallic strip type. This fuse will open if either the current or the temperature goes too high.
Modern NiMH cells contain catalysts to immediately deal with gases developed as a result of over-charging without being harmed (2 H2 + O2 ---catalyst → 2 H2O). However, this only works with overcharging
Overcharging
Overcharging can refer to:*Overcharging , a prosecutorial practice*Charging a battery too much*Charging a customer too much...
currents of up to 0.1C (nominal capacity divided by 10 hours). As a result of this reaction, the batteries will heat up considerably, marking the end of the charging process. Some quick chargers have a fan to keep the batteries cool.
A method for very rapid charging called in-cell charge control involves an internal pressure switch in the cell, which disconnects the charging current in the event of overpressure.
There is an inherent risk with NiMH chemistry that overcharging will cause a buildup of hydrogen, causing the cell to rupture. Therefore, cells have a vent. Hydrogen will be emitted from the vent in the event of serious overcharging.
Discharging
A fully charged cell supplies an average 1.25 V/cell during discharge, down to about 1.0–1.1 V/cell (further discharge may cause permanent damage in the case of multi-cell packs, due to polarity reversal).Under a light load (0.5 ampere), the starting voltage of a freshly charged AA NiMH cell in good condition is about 1.4 volts;
This voltage falls rapidly to about 1.25 volts at 10% depth of discharge (DOD) and then remains almost constant until the cell is over 80% discharged. The voltage then falls rapidly from about 1.2 volts down to 0.8–1.0 volts at which the cell is considered "flat" in most devices. Mid-discharge at a load of 1 ampere, the output is about 1.2 volts; at 2 amperes, about 1.15 volts; the total effective differential internal resistance is about 0.05 ohms. Nickel metal hydride batteries provide a relatively constant voltage for most of the discharge cycle, unlike a standard alkaline where the voltage falls steadily during discharge.
Over-discharging
A complete discharge of a cell until it goes into polarity reversal can cause permanent damage to the cell. This situation can occur in the common arrangement of four AAAA battery
An AA battery is a standard size of battery. Batteries of this size are the most commonly used type of in portable electronic devices. An AA battery is composed of a single electrochemical cell...
cells in series in a digital camera
Digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that takes video or still photographs, or both, digitally by recording images via an electronic image sensor. It is the main device used in the field of digital photography...
, where one will be completely discharged before the others due to small differences in capacity among the cells. When this happens, the good cells will start to drive the discharged cell in reverse, which can cause permanent damage to that cell. Some cameras, GPS receivers
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System is a space-based global navigation satellite system that provides location and time information in all weather, anywhere on or near the Earth, where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites...
and PDAs
Personal digital assistant
A personal digital assistant , also known as a palmtop computer, or personal data assistant, is a mobile device that functions as a personal information manager. Current PDAs often have the ability to connect to the Internet...
detect the safe end-of-discharge voltage of the series cells and auto-shutdown, but devices like flashlights and some toys do not. A single cell driving a load can't suffer from polarity reversal, because there are no other cells to reverse-charge it when it becomes discharged.
Irreversible damage from polarity reversal is a particular danger in systems, even when a low voltage threshold cutout is employed, where cells in the battery are of different temperatures. This is because the capacity of NiMH cells significantly declines as the cells are cooled. This results in a lower voltage under load of the colder cells.
Self-discharge
NiMH cells historically had a somewhat higher self-dischargeSelf-discharge
Self-discharge is a phenomenon in batteries in which internal chemical reactions reduce the stored charge of the battery without any connection between the electrodes...
rate (equivalent to internal leakage) than NiCd cells. The self-discharge is 5–10% on the first day and stabilizes around 0.5–1% per day at room temperature
Room temperature
-Comfort levels:The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers has listings for suggested temperatures and air flow rates in different types of buildings and different environmental circumstances. For example, a single office in a building has an occupancy ratio per...
.
This is not a problem in the short term but makes them unsuitable for many light-duty uses, such as clocks, remote controls, or safety devices, where the battery would normally be expected to last many months or years. The rate is strongly affected by the temperature at which the batteries are stored with cooler storage temperatures leading to slower discharge rate and longer battery life. The highest capacity cells on the market (>8000 mA·h) are reported to have the highest self-discharge rates.
Low self-discharge cells
A new type of nickel–metal hydride cell was introduced in 2005 that reduces self-discharge and therefore lengthens shelf life. By using a new separator, manufacturers claim the cells retain 70% to 85% of their capacity after one year when stored at 20 °C (68 °F). These cells are marketed as "hybrid", "ready-to-use" or "pre-charged" rechargeables. Besides the longer shelf life, they are otherwise similar to normal NiMH batteries of equivalent capacity and can be charged in typical NiMH chargers.Low self-discharge cells have lower capacity than some standard NiMH cells due to the larger area of the separator. The highest capacity low-self-discharge cells have 2000–2500 mA·h and 1000 mA·h capacities for AA and AAA cells respectively, compared to 2800 mA·h and 1300 mA·h for standard AA and AAA cells. C types are typically higher than their usual NiMH cousins, with 4000 mA·h and the D type being 8000 mA·h.
After only a few weeks of storage, the retained capacity of low-self-discharge batteries often exceeds that of traditional NiMH batteries of higher capacity.
Environmental impact
Improper disposal of NiMH batteries poses less environmental hazard than that of NiCd because of the absence of toxic cadmiumCadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
. However, mining and processing the various alternate metals that form the negative electrode may pose other types of environmental impact, depending on the metal, mining method, and environmental practices of the mine.
Most industrial nickel is recycled, due to the relatively easy retrieval of the magnetic element from scrap using electromagnet
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by the flow of electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off...
s, and due to its high value.
Comparison with other battery types
NiMH cells and chargers are readily available in retail stores in the common sizes AAAAAA battery
A triple A or AAA battery is a standard size of dry cell battery commonly used in portable electronic devices. A carbon-zinc battery in this size is designated by IEC as "R03", by ANSI C18.1 as "24", by old JIS standard as "UM 4", and by other manufacturer and national standard designations that...
and AA
AA battery
An AA battery is a standard size of battery. Batteries of this size are the most commonly used type of in portable electronic devices. An AA battery is composed of a single electrochemical cell...
. Adapter sleeves are available to use the more common AA size in C and D applications. The sizes C
C battery
The C battery is a standard size of battery typically used in medium-drain applications such as toys and musical instruments.As of 2007, C batteries accounted for 4% of alkaline primary battery sales in the US...
and D
D battery
A D battery is a size of dry cell. A D cell is cylindrical with electrical contacts at each end; the positive end having a nub or bump...
cells are somewhat available, but are often just a AA core hidden in an outer shell, with a rating of about 2500 mA·h, much less than ordinary alkaline C and D batteries. Real NiMH C and D batteries are expensive (and the chargers are uncommon); they should be rated at least 5000 mA·h for C and 10,000 mA·h for D sizes.
PP3
PP3 battery
A nine-volt battery, the most common of which is designated a PP3 battery, is shaped as a rounded rectangular prism. 9-volt batteries are commonly used in pocket transistor radios, smoke detectors, carbon monoxide alarms, guitar effect units, and radio-controlled vehicle controllers...
(nine volt) NiMH batteries are available; these usually have an output voltage of 8.4 V (1.2 × 7) and a capacity of roughly 200 mA·h. Also available are eight-cell nine volt batteries with a nominal output voltage of 9.6 V (1.2 × 8).
NiMH cells are not expensive, and the voltage and performance is similar to primary alkaline cells
Alkaline battery
Alkaline batteries are a type of primary batteries dependent upon the reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide . A rechargeable alkaline battery allows reuse of specially designed cells....
in those sizes; they can be substituted for most purposes. Although alkaline cells are rated at 1.5 volts and NiMH cells at 1.2 volts, during discharge the alkaline voltage eventually drops below that of NiMH. NiMH batteries offer a flatter discharge curve, particularly at higher current draw.
NiMH cells are often used in digital cameras and other high drain devices, where over the duration of single charge use they outperform primary (such as alkaline) batteries. Applications that require frequent replacement of the battery, such as toys or video game controllers, also benefit from use of rechargeable batteries. With the development of low self-discharge NiMHs (see section above), many occasional-use and very low-power applications are now candidates for NiMH cells.
NiMH cells are particularly advantageous for high current drain applications, due in large part to their low internal resistance. Alkaline batteries, which might have approximately 3000 mA·h capacity at low current demand (200 mA), will have about 700 mA·h capacity with a 1000 mA load. Digital cameras with LCDs and flashlights can draw over 1000 mA, quickly depleting alkaline batteries. NiMH cells can deliver these current levels and maintain their full capacity.
Certain devices that were designed to operate using primary alkaline chemistry (or zinc–carbon/chloride) cells will not function when one uses NiMH cells as substitutes. However, this is rare, as most devices compensate for the voltage drop of an alkaline as it discharges down to about 1 volt. Low internal resistance allows NiMH cells to deliver a near-constant voltage until they are almost completely discharged. This will cause a battery level indicator to overstate the remaining charge if it was designed to read only the voltage curve of alkaline cells. The voltage of alkaline cells decreases steadily during most of the discharge cycle.
Lithium ion batteries have a higher specific energy than nickel–metal hydride batteries, but they are significantly more expensive to produce. In October 2009, ECD Ovonics announced that their next-generation NiMH batteries will provide specific energy and power that are comparable to those of lithium ion batteries at a cost that is significantly lower than the cost of lithium ion batteries.
Patent encumbrance in electric vehicles
Stanford R. Ovshinsky invented and patented ( a popular improvement of ) the NiMH battery and founded Ovonic Battery Company in 1982. General MotorsGeneral Motors
General Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
purchased the patent from Ovonics in 1994. By the late 1990s, NiMH batteries were being used successfully in many fully electric vehicles, such as the General Motors EV1
General Motors EV1
The General Motors EV1 was an electric car produced and leased by the General Motors Corporation from 1996 to 1999. It was the first mass-produced and purpose-designed electric vehicle of the modern era from a major automaker, and the first GM car designed to be an electric vehicle from the...
and Dodge Caravan EPIC minivan. In October 2000, the patent was sold to Texaco and a week later Texaco was acquired by Chevron. Chevron's Cobasys
Cobasys
Cobasys LLC supplies nickel metal hydride batteries, battery control systems, and packaged solutions for automotive applications, uninterruptable power supplies, telecommunications applications, and distributed power generation...
subsidiary will only provide these batteries to large OEM orders. General Motors shut down production of the EV1 citing lack of battery availability as one of their chief obstacles. The Cobasys control of NiMH batteries has created a patent encumbrance of large automotive NiMH batteries.
See also
- Nickel–cadmium battery
- Nickel–hydrogen battery
- Chevron CorporationChevron CorporationChevron Corporation is an American multinational energy corporation headquartered in San Ramon, California, United States and active in more than 180 countries. It is engaged in every aspect of the oil, gas, and geothermal energy industries, including exploration and production; refining,...
- Low self-discharge NiMH batteryLow self-discharge NiMH batteryThe low self-discharge nickel-metal hydride battery was introduced in November 2005. These batteries were developed by Sanyo, who called them "eneloop". Subsequently, other manufacturers also offered LSD NiMH....
- Gas diffusion electrodeGas diffusion electrodeGas diffusion electrodes are electrodes with a conjunction of a solid, liquid and gaseous interface, and an electrical conducting catalyst supporting an electrochemical reaction between the liquid and the gaseous phase...
- Nickel(II) hydroxideNickel(II) hydroxideNickel hydroxide Ni2 is an insoluble compound commonly used in rechargeable battery electrodes. When charged these electrodes form nickel oxide-hydroxide. Nickel hydroxide is a precipitate formed when the hexaaquanickel ion is mixed with aqueous alkali...
- Nickel(III) oxideNickel(III) oxideNickel oxide has been referred to in the literature but is not a well characterised compound. The substance black nickel oxide is sometimes described as being Ni2O3 however the composition quoted by suppliers has a nickel content of around 77% by weight whereas Ni2O3 would have 70.98% Ni by...
- Electric CarElectric carAn electric car is an automobile which is propelled by electric motor, using electrical energy stored in batteries or another energy storage device. Electric cars were popular in the late-19th century and early 20th century, until advances in internal combustion engine technology and mass...
- Patent encumbrance of large automotive NiMH batteriesPatent encumbrance of large automotive NiMH batteriesThe patent encumbrance of large automotive NiMH batteries is the encumbrance of the commercialization of nickel metal hydride battery technology by corporate interests...
- Power-to-weight ratioPower-to-weight ratioPower-to-weight ratio is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement of actual performance of any engine or power sources...
- Battery recyclingBattery recyclingBattery recycling is a recycling activity that aims to reduce the number of batteries being disposed as municipal solid waste. Batteries contain a number of heavy metals and toxic chemicals, their dumping has raised concern over risks of soil contamination and water pollution.-Battery recycling by...
External links
- "Bipolar Nickel Metal Hydride Battery" by Martin G. Klein, Michael Eskra, Robert Plivelich and Paula Ralston
- BatteryUniversity.com
- Sanyo Eneloop NiMH Rechargeable Batteries Review
- Choosing and Using NiMH Rechargeable Batteries
- Duracell Ni-MH Technical Bulletin
- Energizer Ni-MH Battery Datasheets
- Rayovac battery Specifications and Product Guides
- Brand Neutral Drawings of Nickel Metal Hydride Batteries
- Chevron/Texaco's patent on the NiMH battery

