
Polyolefin
Encyclopedia

Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
produced from a simple olefin (also called an alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
with the general formula CnH2n) as a monomer
Monomer
A monomer is an atom or a small molecule that may bind chemically to other monomers to form a polymer; the term "monomeric protein" may also be used to describe one of the proteins making up a multiprotein complex...
. For example, polyethylene
Polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene is the most widely used plastic, with an annual production of approximately 80 million metric tons...
is the polyolefin produced by polymerizing the olefin ethylene
Ethylene
Ethylene is a gaseous organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest alkene . Because it contains a carbon-carbon double bond, ethylene is classified as an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Ethylene is widely used in industry and is also a plant hormone...
. An equivalent term is polyalkene; this is a more modern term, although polyolefin is still used in the petrochemical
Petrochemical
Petrochemicals are chemical products derived from petroleum. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as corn or sugar cane....
industry. Polypropylene
Polypropylene
Polypropylene , also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging, textiles , stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes...
is another common polyolefin which is made from the olefin propylene
Propylene
Propene, also known as propylene or methylethylene, is an unsaturated organic compound having the chemical formula C3H6. It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons, and it is also second in natural abundance.-Properties:At room temperature and...
.
Industrial polyolefins
- ThermoplasticThermoplasticThermoplastic, also known as a thermosoftening plastic, is a polymer that turns to a liquid when heated and freezes to a very glassy state when cooled sufficiently...
polyolefins: polyethylenePolyethylenePolyethylene or polythene is the most widely used plastic, with an annual production of approximately 80 million metric tons...
(PE), polypropylenePolypropylenePolypropylene , also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging, textiles , stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes...
(PP), polymethylpentenePolymethylpentenePolymethylpentene is a thermoplastic polymer of methylpentene monomer units. It is used for gas permeable packaging, autoclavable medical and laboratory equipment, microwave components, and cookware...
(PMP), polybutene-1 (PB-1); - Polyolefin elastomerElastomerAn elastomer is a polymer with the property of viscoelasticity , generally having notably low Young's modulus and high yield strain compared with other materials. The term, which is derived from elastic polymer, is often used interchangeably with the term rubber, although the latter is preferred...
s (POE): polyisobutylene (PIB), Ethylene propylene rubberEthylene propylene rubberEthylene propylene rubber is an insulation used for high voltage cables. It has improved thermal characteristics over more traditional cables, such as cross-linked polyethylene, enabling a smaller cross sectional area for the same load carrying capacity...
(EPR), ethylene propylene diene Monomer (M-class) rubber (EPDM rubberEPDM rubberEPDM rubber , a type of synthetic rubber, is an elastomer which is characterized by a wide range of applications. The E refers to ethylene, P to propylene, D to diene and M refers to its classification in ASTM standard D-1418. The M class includes rubbers having a saturated chain of the...
)…
Properties
Polyolefins are impossible to join by solvent cementing because they have excellent chemical resistance and can only be adhesively bonded after surface treatment because they have very low surface energies. They are also extremely inert chemically and exhibit decreased strength at lower temperatures.A more specific type of olefin is a poly-alpha-olefin (or poly-α-olefin, sometimes abbreviated as PAO), a polymer made by polymerizing an alpha-olefin
Alpha-olefin
Alpha-olefins are a family of organic compounds which are olefins or alkenes with a chemical formula CxH2x, distinguished by having a double bond at the primary or alpha position...
. An alpha-olefin (or α-olefin) is an alkene where the carbon-carbon double bond
Double bond
A double bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving four bonding electrons instead of the usual two. The most common double bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkenes. Many types of double bonds between two different elements exist, for example in...
starts at the α-carbon atom, i.e. the double bond is between the #1 and #2 carbons in the molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
. Common alpha-olefins used as co-monomers to give a polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
alkyl branching groups
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
are similar to 1-hexene
1-Hexene
1-Hexene is an organic compound with the formula CH2CHC4H9. It is an alkene that is classified in industry as higher olefin and an alpha-olefin, the latter term meaning that the double bond is located at the alpha position, endowing the compound with higher reactivity and thus useful chemical...
or may be longer (see chemical structure
Chemical structure
A chemical structure includes molecular geometry, electronic structure and crystal structure of molecules. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together. Molecular geometry can range from the very simple, such as...
below).
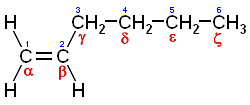
Chemical structure
A chemical structure includes molecular geometry, electronic structure and crystal structure of molecules. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together. Molecular geometry can range from the very simple, such as...
, make it very difficult for the polymer molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s to line themselves up side-by-side in an orderly way. Therefore, many poly-alpha-olefins do not crystallize or solidify easily and are able to remain oily, viscous liquids even at lower temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
s. Low molecular weight poly-alpha-olefins are useful as synthetic lubricant
Lubricant
A lubricant is a substance introduced to reduce friction between moving surfaces. It may also have the function of transporting foreign particles and of distributing heat...
s such as synthetic motor oil
Synthetic oil
Synthetic oil is a lubricant consisting of chemical compounds that are artificially made . Synthetic lubricants can be manufactured using chemically modified petroleum components rather than whole crude oil, but can also be synthesized from other raw materials...
s for vehicles used in a wide temperature range.
Even polyethylene
Polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene is the most widely used plastic, with an annual production of approximately 80 million metric tons...
s copolymerized with a small amount of alpha-olefins (such as 1-hexene
1-Hexene
1-Hexene is an organic compound with the formula CH2CHC4H9. It is an alkene that is classified in industry as higher olefin and an alpha-olefin, the latter term meaning that the double bond is located at the alpha position, endowing the compound with higher reactivity and thus useful chemical...
, 1-octene
1-Octene
1-Octene is an organic compound with a formula CH2CHC6H13. The alkene is classified as a higher olefin and alpha-olefin, meaning that the double bond is located at the alpha position, endowing this compound with higher reactivity and thus useful chemical properties. 1-Octene is one of the...
, or longer) are more flexible than simple straight chain high density polyethylene, which has no branching. The methyl branch groups on a polypropylene
Polypropylene
Polypropylene , also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging, textiles , stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes...
polymer are not long enough to make typical commercial polypropylene more flexible than polyethylene.
Uses
Polyolefin is used for blown film and heatshrink electrical insulation sleeves for crimped wire terminals, as well as rash guards or under garments for wetsuits.Polyolefin elastomer POE is used as a main ingredient in the molded flexible foam technology such as in the fabrication of self skinned footwear (for example, Crocs
Crocs
Crocs, Inc. is a shoe manufacturer founded by 3 friends - Scott Seamans, Lyndon "Duke" Hanson, and George Boedecker, Jr. - to produce and distribute a foam clog design acquired from a Quebec company called Foam Creations. The shoe had originally been developed as a spa shoe. The first model...
shoes), seat cushions, arm rests, spa pillows, etc. Hydrogenated PAO Polyalphaolefin is used as a radar coolant. Head
Head (company)
Head N.V. is a sports equipment and clothing company, known mainly for their alpine skis and tennis racquets. Founded as a ski company in Baltimore, Maryland, the company is currently headquartered in Amsterdam, Netherlands, and Kennelbach, Austria...
makes polyolefin tennis strings.

