
Neutron electric dipole moment
Encyclopedia
The neutron
electric dipole moment
(nEDM) is a measure for the distribution of positive and negative charge inside the neutron. A finite electric dipole moment can only exist if the centers of the negative and positive charge distribution inside the particle do not coincide. So far, no neutron EDM has been found. The current best upper limit amounts to .
(P) and time reversal symmetry
(T). This can be understood by examining the neutron with its magnetic dipole moment
and hypothetical electric dipole moment. Under time reversal, the magnetic dipole moment changes its direction, whereas the electric dipole moment stays unchanged. Under parity, the electric dipole moment changes its direction but not the magnetic dipole moment. As the resulting system under P and T is not symmetric with respect to the initial system, these symmetries are violated in the case of the existence of an EDM. Having also CPT symmetry
, the combined symmetry CP is violated as well.
CP symmetry. CP violation has been observed in weak interaction
s and is included in the Standard Model of particle physics
via the CP-violating phase in the CKM
matrix. However, the amount of CP violation is very small and therefore also the contribution to the nEDM: .
s, it is also susceptible to CP violation stemming from strong interaction
s. Quantum chromodynamics
- the theoretical description of the strong force - naturally includes a term which breaks CP-symmetry. The strength of this term is characterized by the angle θ. The current limit on the nEDM constrains this angle to be less than 10−10 rad. This fine-tuning
of the θ-angle, which is naturally expected to be of order 1, is the strong CP problem.
extensions to the Standard Model, such as the Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model
, generally lead to a large CP-violation. Typical predictions for the neutron EDM arising from the theory range between and . As in the case of the strong interaction
, the limit on the neutron EDM is already constraining the CP violating phases. The fine-tuning
is, however, not as severe yet.
of the neutron spin
in the presence of parallel and antiparallel magnetic and electric fields. The precession frequency for each of the two cases is given by
 ,
,
the addition or subtraction of the frequencies stemming from the precession of the magnetic moment
around the magnetic field
and the precession of the electric dipole moment around the electric field
. From the difference of those two frequencies one readily obtains a measure of the neutron EDM:
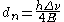
The biggest challenge of the experiment (and at the same time the source of the biggest systematic false effects) is to ensure that the magnetic field
does not change during these two measurements.
(and later cold
) neutrons to conduct the measurement. It started with the experiment by Smith, Purcell
and Ramsey
in 1951 (and published in 1957) obtaining a limit of . Beams of neutrons were used until 1977 for nEDM experiments. At this point, systematic effects related to the high velocities of the neutrons in the beam became insurmountable. The final limit obtained with a neutron beam amounts to .
After that, experiments with ultracold neutrons
took over. It started in 1980 with an experiment at the Leningrad Nuclear Physics Institute obtaining a limit of . This experiment and especially the experiment starting in 1984 at the Institut Laue-Langevin
pushed the limit down by another two orders of magnitude
yielding the above quoted best upper limit in 2006.
During these 50 years of experiments, six orders of magnitude
have been covered thereby putting stringent constraints on more theoretical models than probably any other experimental value.
extensions to the Standard Model.
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
electric dipole moment
Electric dipole moment
In physics, the electric dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative electrical charges in a system of charges, that is, a measure of the charge system's overall polarity with SI units of Coulomb-meter...
(nEDM) is a measure for the distribution of positive and negative charge inside the neutron. A finite electric dipole moment can only exist if the centers of the negative and positive charge distribution inside the particle do not coincide. So far, no neutron EDM has been found. The current best upper limit amounts to .
Theory
A permanent electric dipole moment of a fundamental particle violates both parityParity (physics)
In physics, a parity transformation is the flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate. In three dimensions, it is also commonly described by the simultaneous flip in the sign of all three spatial coordinates:...
(P) and time reversal symmetry
T-symmetry
T Symmetry is the symmetry of physical laws under a time reversal transformation: T: t \mapsto -t.Although in restricted contexts one may find this symmetry, the observable universe itself does not show symmetry under time reversal, primarily due to the second law of thermodynamics.Time asymmetries...
(T). This can be understood by examining the neutron with its magnetic dipole moment
Magnetic moment
The magnetic moment of a magnet is a quantity that determines the force that the magnet can exert on electric currents and the torque that a magnetic field will exert on it...
and hypothetical electric dipole moment. Under time reversal, the magnetic dipole moment changes its direction, whereas the electric dipole moment stays unchanged. Under parity, the electric dipole moment changes its direction but not the magnetic dipole moment. As the resulting system under P and T is not symmetric with respect to the initial system, these symmetries are violated in the case of the existence of an EDM. Having also CPT symmetry
CPT symmetry
CPT symmetry is a fundamental symmetry of physical laws under transformations that involve the inversions of charge, parity, and time simultaneously.-History:...
, the combined symmetry CP is violated as well.
Standard Model prediction
As seen above, in order to generate a finite nEDM one needs processes that violateCP violation
In particle physics, CP violation is a violation of the postulated CP-symmetry: the combination of C-symmetry and P-symmetry . CP-symmetry states that the laws of physics should be the same if a particle were interchanged with its antiparticle , and left and right were swapped...
CP symmetry. CP violation has been observed in weak interaction
Weak interaction
Weak interaction , is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, alongside the strong nuclear force, electromagnetism, and gravity. It is responsible for the radioactive decay of subatomic particles and initiates the process known as hydrogen fusion in stars...
s and is included in the Standard Model of particle physics
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, which mediate the dynamics of the known subatomic particles. Developed throughout the mid to late 20th century, the current formulation was finalized in the mid 1970s upon...
via the CP-violating phase in the CKM
Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa matrix
In the Standard Model of particle physics, the Cabibbo–Kobayashi–Maskawa matrix is a unitary matrix which contains information on the strength of flavour-changing weak decays...
matrix. However, the amount of CP violation is very small and therefore also the contribution to the nEDM: .
Matter–antimatter asymmetry
From the asymmetry between matter and antimatter in the universe, one suspects that there must be a sizeable amount of CP-violation. Measuring a neutron electric dipole moment at a much higher level than predicted by the Standard Model would therefore directly confirm this suspicion and improve our understanding of CP-violating processes.Strong CP problem
As the neutron is built up of quarkQuark
A quark is an elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. Due to a phenomenon known as color confinement, quarks are never directly...
s, it is also susceptible to CP violation stemming from strong interaction
Strong interaction
In particle physics, the strong interaction is one of the four fundamental interactions of nature, the others being electromagnetism, the weak interaction and gravitation. As with the other fundamental interactions, it is a non-contact force...
s. Quantum chromodynamics
Quantum chromodynamics
In theoretical physics, quantum chromodynamics is a theory of the strong interaction , a fundamental force describing the interactions of the quarks and gluons making up hadrons . It is the study of the SU Yang–Mills theory of color-charged fermions...
- the theoretical description of the strong force - naturally includes a term which breaks CP-symmetry. The strength of this term is characterized by the angle θ. The current limit on the nEDM constrains this angle to be less than 10−10 rad. This fine-tuning
Fine-tuning
In theoretical physics, fine-tuning refers to circumstances when the parameters of a model must be adjusted very precisely in order to agree with observations. Theories requiring fine-tuning are regarded as problematic in the absence of a known mechanism to explain why the parameters happen to...
of the θ-angle, which is naturally expected to be of order 1, is the strong CP problem.
SUSY CP problem
SupersymmetricSupersymmetry
In particle physics, supersymmetry is a symmetry that relates elementary particles of one spin to other particles that differ by half a unit of spin and are known as superpartners...
extensions to the Standard Model, such as the Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model
Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model
The Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model is the minimal extension to the Standard Model that realizes supersymmetry, although non-minimal extensions do exist. Supersymmetry pairs bosons with fermions; therefore every Standard Model particle has a partner that has yet to be discovered...
, generally lead to a large CP-violation. Typical predictions for the neutron EDM arising from the theory range between and . As in the case of the strong interaction
Strong interaction
In particle physics, the strong interaction is one of the four fundamental interactions of nature, the others being electromagnetism, the weak interaction and gravitation. As with the other fundamental interactions, it is a non-contact force...
, the limit on the neutron EDM is already constraining the CP violating phases. The fine-tuning
Fine-tuning
In theoretical physics, fine-tuning refers to circumstances when the parameters of a model must be adjusted very precisely in order to agree with observations. Theories requiring fine-tuning are regarded as problematic in the absence of a known mechanism to explain why the parameters happen to...
is, however, not as severe yet.
Experimental technique
In order to extract the neutron EDM, one measures the Larmor precessionLarmor precession
In physics, Larmor precession is the precession of the magnetic moments of electrons, atomic nuclei, and atoms about an external magnetic field...
of the neutron spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
in the presence of parallel and antiparallel magnetic and electric fields. The precession frequency for each of the two cases is given by
 ,
,the addition or subtraction of the frequencies stemming from the precession of the magnetic moment
Magnetic moment
The magnetic moment of a magnet is a quantity that determines the force that the magnet can exert on electric currents and the torque that a magnetic field will exert on it...
around the magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
and the precession of the electric dipole moment around the electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
. From the difference of those two frequencies one readily obtains a measure of the neutron EDM:
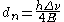
The biggest challenge of the experiment (and at the same time the source of the biggest systematic false effects) is to ensure that the magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
does not change during these two measurements.
History
The first experiments searching for the electric dipole moment of the neutron used beams of thermalNeutron temperature
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term temperature is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with a certain temperature. The neutron energy distribution is...
(and later cold
Neutron temperature
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term temperature is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with a certain temperature. The neutron energy distribution is...
) neutrons to conduct the measurement. It started with the experiment by Smith, Purcell
Edward Mills Purcell
Edward Mills Purcell was an American physicist who shared the 1952 Nobel Prize for Physics for his independent discovery of nuclear magnetic resonance in liquids and in solids. Nuclear magnetic resonance has become widely used to study the molecular structure of pure materials and the...
and Ramsey
Norman Foster Ramsey, Jr.
Norman Foster Ramsey, Jr. was an American physicist. A physics professor at Harvard University since 1947, Ramsey also held several posts with such government and international agencies as NATO and the United States Atomic Energy Commission...
in 1951 (and published in 1957) obtaining a limit of . Beams of neutrons were used until 1977 for nEDM experiments. At this point, systematic effects related to the high velocities of the neutrons in the beam became insurmountable. The final limit obtained with a neutron beam amounts to .
After that, experiments with ultracold neutrons
Ultracold neutrons
Ultracold neutrons are free neutrons which can be stored in traps made from certain materials. The storage is based on the reflection of UCN by such materials under any angle of incidence.- Properties :...
took over. It started in 1980 with an experiment at the Leningrad Nuclear Physics Institute obtaining a limit of . This experiment and especially the experiment starting in 1984 at the Institut Laue-Langevin
Institut Laue-Langevin
The Institut Laue–Langevin, or ILL, is an internationally-financed scientific facility, situated in Grenoble, France. It is one of the world centres for research using neutrons...
pushed the limit down by another two orders of magnitude
Order of magnitude
An order of magnitude is the class of scale or magnitude of any amount, where each class contains values of a fixed ratio to the class preceding it. In its most common usage, the amount being scaled is 10 and the scale is the exponent being applied to this amount...
yielding the above quoted best upper limit in 2006.
During these 50 years of experiments, six orders of magnitude
Order of magnitude
An order of magnitude is the class of scale or magnitude of any amount, where each class contains values of a fixed ratio to the class preceding it. In its most common usage, the amount being scaled is 10 and the scale is the exponent being applied to this amount...
have been covered thereby putting stringent constraints on more theoretical models than probably any other experimental value.
Current experiments
Currently, there are at least four experiments aiming at improving the current limit (or measuring for the first time) on the neutron EDM with a sensitivity down to over the next 10 years, thereby covering the range of prediction coming from SupersymmetricSupersymmetry
In particle physics, supersymmetry is a symmetry that relates elementary particles of one spin to other particles that differ by half a unit of spin and are known as superpartners...
extensions to the Standard Model.
- Cryogenic neutron EDM experiment being set up at the Institut Laue-LangevinInstitut Laue-LangevinThe Institut Laue–Langevin, or ILL, is an internationally-financed scientific facility, situated in Grenoble, France. It is one of the world centres for research using neutrons...
- nEDM experiment under construction at the new UCN source at the Paul Scherrer InstitutePaul Scherrer InstituteThe Paul Scherrer Institute is a multi-disciplinary research institute which belongs to the Swiss ETH-Komplex covering also the ETH Zurich and EPFL...
- nEDM experiment being envisaged at the Spallation Neutron SourceSpallation Neutron SourceThe Spallation Neutron Source is an accelerator-based neutron source facility that provides the most intense pulsed neutron beams in the world for scientific research and industrial development...
- nEDM experiment being built at the Institut Laue-LangevinInstitut Laue-LangevinThe Institut Laue–Langevin, or ILL, is an internationally-financed scientific facility, situated in Grenoble, France. It is one of the world centres for research using neutrons...

