
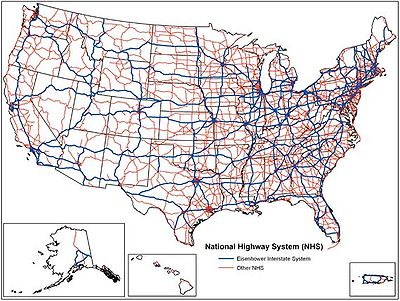
National Highway System (United States)
Encyclopedia
Highway
A highway is any public road. In American English, the term is common and almost always designates major roads. In British English, the term designates any road open to the public. Any interconnected set of highways can be variously referred to as a "highway system", a "highway network", or a...
s within the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, including the Interstate Highway System
Interstate Highway System
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, , is a network of limited-access roads including freeways, highways, and expressways forming part of the National Highway System of the United States of America...
and other roads serving major airports, ports, rail or truck terminals, railway stations, pipeline terminals
Pipeline transport
Pipeline transport is the transportation of goods through a pipe. Most commonly, liquids and gases are sent, but pneumatic tubes that transport solid capsules using compressed air are also used....
and other strategic transport facilities.
Individual states
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
are encouraged to focus federal funds on improving the efficiency and safety of this network which makes up 4% of the nation's roads, but carries 40% of the traffic and 75% of heavy truck traffic. About 90% of America's population lives within 5 miles (8 km) of an NHS road. The roads within the system were identified by the United States Department of Transportation
United States Department of Transportation
The United States Department of Transportation is a federal Cabinet department of the United States government concerned with transportation. It was established by an act of Congress on October 15, 1966, and began operation on April 1, 1967...
in cooperation with the states, local officials, and metropolitan planning organization
Metropolitan planning organization
A metropolitan planning organization is a federally-mandated and federally-funded transportation policy-making organization in the United States that is made up of representatives from local government and governmental transportation authorities...
s and approved by the United States Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
in 1995.
Legislation
The Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991 provided that certain key routes such as the Interstate Highway System, be included.The National Highway System Designation Act of 1995 is a United States Act of Congress
Act of Congress
An Act of Congress is a statute enacted by government with a legislature named "Congress," such as the United States Congress or the Congress of the Philippines....
that was signed into law by President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation...
on November 28, 1995 The legislation
Legislation
Legislation is law which has been promulgated by a legislature or other governing body, or the process of making it...
designated about 160955 miles (259,031.3 km) of roads, including the Interstate Highway System, as the NHS.
Aside from designating the system, the act served several other purposes, including restoring $5.4 billion in funding to state highway departments, giving Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
the power to prioritize highway system projects, repealing all federal speed limit
National Maximum Speed Law
The National Maximum Speed Law in the United States was a provision of the 1974 Emergency Highway Energy Conservation Act that prohibited speed limits higher than . It was drafted in response to oil price spikes and supply disruptions during the 1973 oil crisis...
controls, and prohibiting the use of federal-aid highway funds to convert existing signs or purchase new signs with metric units.
The act also created a State Infrastructure Bank pilot program. Ten states were chosen in 1996 for this new method of road financing. These banks would lend money like regular banks, with funding coming from the federal government or the private sector
Private sector
In economics, the private sector is that part of the economy, sometimes referred to as the citizen sector, which is run by private individuals or groups, usually as a means of enterprise for profit, and is not controlled by the state...
, and they would be repaid through such means as highway tolls
Toll road
A toll road is a privately or publicly built road for which a driver pays a toll for use. Structures for which tolls are charged include toll bridges and toll tunnels. Non-toll roads are financed using other sources of revenue, most typically fuel tax or general tax funds...
or taxes. In 1997, 28 more states asked to be part of the program. Ohio
Ohio
Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
was the first state to use a state infrastructure bank to start building a road. An advantage to this method was completing projects faster; state laws and the lack of appropriate projects were potential problems.
Overview
- The Interstate Highway SystemInterstate Highway SystemThe Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, , is a network of limited-access roads including freeways, highways, and expressways forming part of the National Highway System of the United States of America...
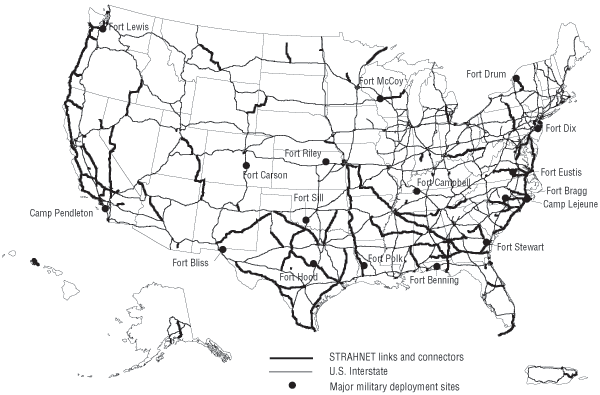
- The Strategic Highway Network (STRAHNET) of importance to the United States' strategic defense policy including links from major military installations and this Strategic Highway Network
- Access to 207 airports, 198 ports, 190 rail or truck terminals, 67 AmtrakAmtrakThe National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak , is a government-owned corporation that was organized on May 1, 1971, to provide intercity passenger train service in the United States. "Amtrak" is a portmanteau of the words "America" and "track". It is headquartered at Union...
railway stations, 58 pipelinePipeline transportPipeline transport is the transportation of goods through a pipe. Most commonly, liquids and gases are sent, but pneumatic tubes that transport solid capsules using compressed air are also used....
terminals as well as 82 intercity busBusA bus is a road vehicle designed to carry passengers. Buses can have a capacity as high as 300 passengers. The most common type of bus is the single-decker bus, with larger loads carried by double-decker buses and articulated buses, and smaller loads carried by midibuses and minibuses; coaches are...
terminals, 307 public transit stations, 37 ferryFerryA ferry is a form of transportation, usually a boat, but sometimes a ship, used to carry primarily passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo as well, across a body of water. Most ferries operate on regular, frequent, return services...
terminals and 20 multi-purpose passenger terminals
The system includes 4% of the nation's roads, but carries more than 40% of all highway traffic, 75% of heavy truck traffic, and 90% of tourist traffic. All urban areas with a population of over 50,000 and about 90% of America's population live within 5 miles (8 km) of the network, which is the longest in the world.
External links
- STRAHNET description at US military's Transportation Engineering Agency's website.
- STRAHNET article at the GlobalSecurity.orgGlobalSecurity.orgGlobalSecurity.org, launched in 2000, is a public policy organization focusing on the fields of defense, space exploration, intelligence, weapons of mass destruction and homeland security...
website. - Weingroff, Richard F. "Backbone: Creation Of The National Highway System"

