
National Commission on Terrorism
Encyclopedia
The U.S. Commission on National Security/21st Century (USCNS/21), also known as the Hart-Rudman Commission or Hart-Rudman Task Force on Homeland Security, was chartered by Secretary of Defense William Cohen
in 1998 to provide a comprehensive review of US national security requirements in the 21st century. USCNS/21 was tasked "to analyze the emerging international security environment; to develop a US national security strategy
appropriate to that environment; and to assess the various security institutions for their current relevance to the effective and efficient implementation of that strategy, and to recommend adjustments as necessary".
Released on 31 January 2001, USCNS/21 is the most exhaustive review of US national security strategy since the National Security Act of 1947
. USCNS/21 was released in three distinct phases. The first phase, New World Coming: American Security in the 21st Century (see further below), anticipates the emerging international security environment within the first quarter of the 21st century and examines how the US fits into that environment. The second phase, Seeking a National Strategy: A Concert for Preserving Security and Promoting Freedom (see further below), proposes a new US national security strategy based on the anticipated threats and conditions outlined in the first phase report. The third phase, Roadmap for National Security: Imperative for Change (see further below), recommends changes to the US government's
structure, legislation, and policy to reflect a new national security strategy based on the anticipated 21st century international security environment.


amidst social and political fragmentation.The report provides twelve basic assumptions of that environment and fourteen conclusions based on those assumptions.
based on the anticipated 21st century international security environment. The new strategy must consider how to minimize the potential destabilizing effects of the contradictory trends of globalization
and political fragmentation while promoting US interests and values worldwide.
. They also include preserving America’s founding principles as outlined in the US Constitution. Critical interests are defined as, “causally one step removed from survival interests”. These interests lie in the continuation of key global systems, such as global energy, economic, communications, transportation, and health infrastructures. Other critical interests include the security of US allies and preventing potentially hostile alliances from being formed to threaten US national security. Significant interests, “importantly affect the global environment in which the US must act”. These interests include spreading democracy
abroad and ensuring basic human rights
for all the world's citizens.
:
will result in increased vulnerability to the US homeland. "A direct attack against American citizens on American soil is likely over the next quarter century".
In order protect the homeland against this threat, the Commission suggests:
has failed to restructure itself to the post–Cold War world. It recommends significant restructuring to re-align government offices, branches, and procedures with the global realities of the 21st century as well as ensure that,"strategy once again drives the design and implementation of US national security policies". The Commission urges Congress to expand its understanding of national security matters, and streamline the appropriations and authorizations committees to make intelligence and security related legislation more efficient and effective. The Commission also recommends:
William Cohen
William Sebastian Cohen is an author and American politician from the U.S. state of Maine. A Republican, Cohen served as Secretary of Defense under Democratic President Bill Clinton.-Early life and education:...
in 1998 to provide a comprehensive review of US national security requirements in the 21st century. USCNS/21 was tasked "to analyze the emerging international security environment; to develop a US national security strategy
National Security Strategy of the United States
The National Security Strategy is a document prepared periodically by the executive branch of the government of the United States for Congress which outlines the major national security concerns of the United States and how the administration plans to deal with them. The legal foundation for the...
appropriate to that environment; and to assess the various security institutions for their current relevance to the effective and efficient implementation of that strategy, and to recommend adjustments as necessary".
Released on 31 January 2001, USCNS/21 is the most exhaustive review of US national security strategy since the National Security Act of 1947
National Security Act of 1947
The National Security Act of 1947 was signed by United States President Harry S. Truman on July 26, 1947, and realigned and reorganized the U.S. Armed Forces, foreign policy, and Intelligence Community apparatus in the aftermath of World War II...
. USCNS/21 was released in three distinct phases. The first phase, New World Coming: American Security in the 21st Century (see further below), anticipates the emerging international security environment within the first quarter of the 21st century and examines how the US fits into that environment. The second phase, Seeking a National Strategy: A Concert for Preserving Security and Promoting Freedom (see further below), proposes a new US national security strategy based on the anticipated threats and conditions outlined in the first phase report. The third phase, Roadmap for National Security: Imperative for Change (see further below), recommends changes to the US government's
Federal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States is the national government of the constitutional republic of fifty states that is the United States of America. The federal government comprises three distinct branches of government: a legislative, an executive and a judiciary. These branches and...
structure, legislation, and policy to reflect a new national security strategy based on the anticipated 21st century international security environment.
Charter
According to the US Commission on National Security/21st Century Charter:
The Department of DefenseUnited States Department of DefenseThe United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
recognizes that America should advance its position as a strong, secure, and persuasive force for freedom and progress in the world. Consequently, there is a requirement to:
- conduct a comprehensive review of the early 21st century global security environment, including likely trends and potential 'wild cards
Wild card (Foresight research)In futurology, "wild cards" refer to low-probability, high-impact events. This concept may be introduced into anticipatory decision-making activity in order to increase the ability of organisations adapt to surprises arising in turbulent business environments. Such sudden and unique incidents might...
';- develop a comprehensive overview of American strategic interests and objectives for the security environment we will likely encounter in the 21st century;
- delineate a national security strategy appropriate to that environment and the nation's character;
- identify a range of alternatives to implement the national security strategy, by defining the security goals for American society, and by describing the internal and external policy instruments required to apply American resources in the 21st century; and
- develop a detailed plan to implement the range of alternatives by describing the sequence of measures necessary to attain the national security strategy, to include recommending concomitant changes to the national security apparatus as necessary.
A Commission, the U.S. Commission on National Security/21st Century (USCNS/21), will be established to fulfill this requirement, supported by a Study Group. Two individuals who have national recognition and significant depth of experience and public service will oversee the efforts of this Commission and serve as its Co-chairpersons. The study effort shall be conducted by a Study Group, composed of individuals who will be appointed as Department of Defense personnel. Based on the results of this study and the Commission's consideration thereof, the USCNS/21 will advance practical recommendations that the President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
, with the support of the CongressUnited States CongressThe United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
, could begin to implement in the Fiscal Year 2002 budget, if desired.
Co-Chairs

- Gary HartGary HartGary Hart is an American politician, lawyer, author, professor and commentator. He served as a Democratic Senator representing Colorado , and ran in the U.S...

- Warren Bruce Rudman
Commissioners
- Anne ArmstrongAnne ArmstrongAnne Legendre Armstrong was a United States diplomat and politician, and the first female Counselor to the President; she served in that capacity under both the Ford and Nixon administrations. She was also the recipient of the Presidential Medal of Freedom.- Biography :She was born in New Orleans,...
- Norm R. AugustineNorman Ralph AugustineNorman Ralph Augustine is a U.S. aerospace businessman who served as Under Secretary of the Army from 1975-77. Augustine currently serves as chairman of the Review of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee.-Career:...
- John Dancy
- John R. Galvin
- Leslie H. Gelb
- Newt GingrichNewt GingrichNewton Leroy "Newt" Gingrich is a U.S. Republican Party politician who served as the House Minority Whip from 1989 to 1995 and as the 58th Speaker of the U.S. House of Representatives from 1995 to 1999....
- Lee H. HamiltonLee H. HamiltonLee Herbert Hamilton is a former member of the United States House of Representatives and currently a member of the U.S. Homeland Security Advisory Council. A member of the Democratic Party, Hamilton represented the 9th congressional district of Indiana from 1965 to 1999...
- Lionel H. Olmer
- Donald B. Rice
- James R. SchlesingerJames R. SchlesingerDr. James Rodney Schlesinger is an American politician. He is best known for serving as Secretary of Defense from 1973 to 1975 under Presidents Richard Nixon and Gerald Ford...
- Harry D. Train IIHarry D. Train IIHarry Depue Train II is a retired Admiral in the United States Navy and a Senior Fellow at the Joint Advanced Warfighting School at the Joint Forces Staff College in Norfolk, Virginia.-Naval career:...
- Andrew Jackson Young, Jr.
Study Group Members
- Dr. Jeffrey BergnerJeffrey BergnerJeffrey Bergner is President and Managing Financial Partner of Bergner Bockorny, Inc. He is an adjunct professor at the National Security Studies Program at Georgetown University....
- Dr. Coit D. BlackerCoit D. BlackerDr. Coit Dennis Blacker served as Special Assistant to the President of the United States for National Security Affairs and Senior Director for Russian, Ukrainian and Eurasian Affairs at the National Security Council under National Security Advisor Anthony Lake during the Clinton administration...
- Dr. Christopher J. Bowie
- Dr. Ivo H. DaalderIvo H. DaalderIvo H. Daalder, has been the U.S. Permanent Representative on the Council of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization since May 2009. He is a specialist in European security...
- Rhett Dawson
- Amb. Charles W. Freeman, Jr.Charles W. Freeman, Jr.Charles W. Freeman, Jr. is an American diplomat, author, and writer. He has served for the State and Defense Departments in many different capacities in the past thirty years, with the Washington Report on Middle East Affairs calling his career "remarkably varied"...
- Dr. Adam GarfinkleAdam GarfinkleAdam M. Garfinkle is the editor of The American Interest, a bimonthly public policy magazine. He was previously editor of another such publication, The National Interest. He has been a university teacher and a staff member at high levels of the U.S. government. He was a speechwriter to more...
- Richard HaasRichard HaasRichard John Haas is an American muralist who is best known for architectural murals and his use of the Trompe l'oeil style.-Works:...
- Keith Hahn
- Dr. Charles B. JohnsonCharles B. JohnsonCharles Bartlett Johnson is an American businessman. With an estimated net worth of around $4.3 billion, he is ranked by Forbes as the 147th-richest person in the world ....
- Robert KillebrewRobert KillebrewRobert Winston Killebrew is a professional American and Canadian football linebacker free agent. He was signed by the Calgary Stampeders as a street free agent in 2009. He played college football for the Texas Longhorns.-Early years:...
- Dr. Richard H. Kohn
- Dr. William LewisWilliam LewisWilliam Lewis was involved in English Association Football in various capacities in the early 20th century. He was first a referee, then a director and later manager of Brentford between 1900 and 1903. He became the first club secretary of Chelsea Football Club when it was founded in 1905, with his...
- James R. Locher III
- Dr. Charles MoskosCharles MoskosCharles C. Moskos was a sociologist of the United States Military and a professor at Northwestern University...
- Dr. Williamson Murray
- Dr. Barry Ross Posen
- Dr. Barbara Samuels
- Dr. James S. Thomason
- Ruth WedgwoodRuth WedgwoodRuth N. Wedgwood is an American law professor who holds the Edward B. Burling Chair in International Law and Diplomacy at the School of Advanced International Studies, Johns Hopkins University, in Washington, D.C.- Family origins :...
Phase I report - New World Coming: American Security in the 21st Century
New World Coming: American Security in the 21st Century was the first report completed by the Commission. Released on 15 September 1999, it attempts to provide a picture of the international security environment within the first quarter of the 21st century and the anticipated role of the US in that environment. The Commission anticipates an increasingly technologically, economically, and socially integrated world, i.e. increasing globalizationGlobalization
Globalization refers to the increasingly global relationships of culture, people and economic activity. Most often, it refers to economics: the global distribution of the production of goods and services, through reduction of barriers to international trade such as tariffs, export fees, and import...
amidst social and political fragmentation.The report provides twelve basic assumptions of that environment and fourteen conclusions based on those assumptions.
Assumptions
- An economically strong United States is likely to remain a primary political, military, and cultural force through 2025, and will thus have a significant role in shaping the international environment.
- The stability and direction of American society and politics will help shape US foreign policy goals and capacities, and hence the way the US may affect the global future.
- Science and technology will continue to advance and become more widely available and utilized around the world, but their benefits will be less evenly distributed.
- World energy supplies will remain largely based on fossil fuels.
- While much of the world will experience economic growth, disparities in income will increase and widespread poverty will persist.
- The international aspects of business and commerce (trade, transportation, telecommunications, investment and finance, manufacturing, and professional services) will continue to expand.
- Non-governmental organizations (refugee aid organizations, religious and ethnic advocacy groups, environmental and other single-issue lobbies, international professional associations, and others) will continue to grow in importance, numbers, and in their international role.
- Though it will raise important issues of sovereignty, the US will find in its national interest to work with and strengthen a variety of international organizations.
- The US will remain the principal military power in the world.
- Weapons of mass destruction
Weapons of mass destructionA weapon of mass destruction is a weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to a large number of humans and/or cause great damage to man-made structures , natural structures , or the biosphere in general...
(nuclear, chemical, and biological) and weapons of mass disruption (information warfareInformation warfareThe term Information Warfare is primarily an American concept involving the use and management of information technology in pursuit of a competitive advantage over an opponent...
) will continue to proliferate to a wider range of state and non-state actors. Maintenance of a robust nuclear deterrent therefore remains essential as well as investment in new forms of defense against these threats.- We should expect conflicts in which adversaries, because of cultural affinities different from our own, will resort to forms and levels of violence shocking to our sensibilities.
- As the US confronts a variety of complex threats, it will often be dependent on allies; but it will find reliable alliances more difficult to establish and sustain.
Conclusions
- America will become increasingly vulnerable to hostile attack on our homeland, and our military superiority will not help us.
- Rapid advances in information and biotechnologies will create new vulnerabilities for US security.
- New technologies will divide the world as well as draw it together.
- The national security of all advanced states will be increasingly affected by the vulnerabilities of the evolving global economic infrastructure.
- Energy will continue to have major strategic significance.
- All borders will be more porous; some will bend and some will break.
- The sovereignty of states will come under pressure, but will endure.
- Fragmentation or failure of states will occur, with destabilizing effects on neighboring states.
- Foreign crises will be replete with atrocities and the deliberate terrorizing of civilian populations.
- Space will become a critical and competitive military environment.
- The essence of war will not change.
- US intelligence will face more challenging adversaries, and even excellent intelligence will not prevent all surprises.
- The US will be called upon frequently to intervene militarily in a time of uncertain alliances and with the prospect of fewer forward deployed forces.
- The emerging security environment in the next quarter century will require different military and other national capabilities.
Phase II report - Seeking a National Strategy: A Concert for Preserving Security and Promoting Freedom
Released on 15 April 2000, Seeking a National Strategy: A Concert for Preserving Security and Promoting Freedom proposes a new national security strategyNational Security Strategy of the United States
The National Security Strategy is a document prepared periodically by the executive branch of the government of the United States for Congress which outlines the major national security concerns of the United States and how the administration plans to deal with them. The legal foundation for the...
based on the anticipated 21st century international security environment. The new strategy must consider how to minimize the potential destabilizing effects of the contradictory trends of globalization
Globalization
Globalization refers to the increasingly global relationships of culture, people and economic activity. Most often, it refers to economics: the global distribution of the production of goods and services, through reduction of barriers to international trade such as tariffs, export fees, and import...
and political fragmentation while promoting US interests and values worldwide.
Strategic considerations
In developing this new strategy, the Commission suggests a number of strategic considerations:
- Strategy and policy must be grounded in the national interest.
- The maintenance of America’s strength is a long-term commitment and cannot be assured without conscious, dedicated effort.
- The US faces unprecedented opportunities as well as dangers in the new era.
- The US must find new ways to join with other capable and like-minded nations.
- This nation must set priorities and apply them consistently.
- America must never forget that it stands for certain principles, most importantly freedom under the rule of law.
Suggested categorization of US national interests
Building on these considerations, the Commission suggests categorizing US national interests into three categories: survival, critical, and significant. Survival interests are defined as, “without which America would cease to exist as we know it”. These interests encompass safety from direct attacks by hostile states and terrorists through the use of weapons of mass destructionWeapons of mass destruction
A weapon of mass destruction is a weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to a large number of humans and/or cause great damage to man-made structures , natural structures , or the biosphere in general...
. They also include preserving America’s founding principles as outlined in the US Constitution. Critical interests are defined as, “causally one step removed from survival interests”. These interests lie in the continuation of key global systems, such as global energy, economic, communications, transportation, and health infrastructures. Other critical interests include the security of US allies and preventing potentially hostile alliances from being formed to threaten US national security. Significant interests, “importantly affect the global environment in which the US must act”. These interests include spreading democracy
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
abroad and ensuring basic human rights
Human rights
Human rights are "commonly understood as inalienable fundamental rights to which a person is inherently entitled simply because she or he is a human being." Human rights are thus conceived as universal and egalitarian . These rights may exist as natural rights or as legal rights, in both national...
for all the world's citizens.
Priority objectives
Using these strategic considerations as a foundation, the Commission recommends the following as the priority objectives to the new national security strategyNational Security Strategy
National Security Strategy may refer to—* National Security Strategy * National Security Strategy * National Security Strategy...
:
- “Defend the US and ensure that it is safe from the dangers of a new era”. The proliferation of weapons of mass destructionWeapons of mass destructionA weapon of mass destruction is a weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to a large number of humans and/or cause great damage to man-made structures , natural structures , or the biosphere in general...
and terrorismTerrorismTerrorism is the systematic use of terror, especially as a means of coercion. In the international community, however, terrorism has no universally agreed, legally binding, criminal law definition...
will be the gravest threat to US national security in the 21st century. These threats must be taken seriously and the highest priority must be given to prevention and deterrence from such attacks. - “Maintain social cohesion, economic competitiveness, technological ingenuity, and military strength”. The US must re-focus on education, specifically in the sciences, to ensure its technological dominance in the 21st century. Furthermore, the US must reduce its dependence on fossil fuels and investigate other energy alternatives.
- “Assist the integration of key major powers, especially ChinaPeople's Republic of ChinaChina , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
, RussiaRussiaRussia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, and IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, into the mainstream of the emerging international system”. The US must engage emerging, and in Russia’s case re-emerging, world powers and work to foster their integration into the world’s economy. However, the US must not lose sight of its own interests. These relationships are especially important in relation to the US’s effort to limiting nuclear proliferation; cooperation with these powers is absolutely necessary. - “Promote, with others, the dynamism of the new global economy and improve the effectiveness of international institutions and international law”. The US, along with the G7, must successfully manage the effects, both positive and negative, of globalizationGlobalizationGlobalization refers to the increasingly global relationships of culture, people and economic activity. Most often, it refers to economics: the global distribution of the production of goods and services, through reduction of barriers to international trade such as tariffs, export fees, and import...
on the world stage. - “Adapt US alliances and other regional mechanisms to a new era in which America’s partners seek greater autonomy and responsibility”. The US must maintain its current alliances and relationships with other nations as a mechanism to preserve and foster international peace and security.
- “Help the international community tame the disintegrative forces spawned by an era of change”. The US must work with the international community to address and manage the problem of failed states.
Phase III report - Roadmap for National Security: Imperative for Change
Released on 31 January 2001, Roadmap for National Security: Imperative for Change suggests "significant changes must be made in the structures and processes of the US national security apparatus". The Commission believes that without these reforms, "American power and influence cannot be sustained". Five key areas are highlighted for reform, followed by the Commissions specific recommendations for each area.Recommendations
- ensuring the security of the American homeland
- recapitalizing America's strengths in science and education
- redesigning key institutions of the Executive Branch
- overhauling the US government personnel system
- reorganizing Congress's role in national security affairs
Securing the national homeland
The Commission believes that the combination of weapons proliferation and terrorismTerrorism
Terrorism is the systematic use of terror, especially as a means of coercion. In the international community, however, terrorism has no universally agreed, legally binding, criminal law definition...
will result in increased vulnerability to the US homeland. "A direct attack against American citizens on American soil is likely over the next quarter century".
In order protect the homeland against this threat, the Commission suggests:

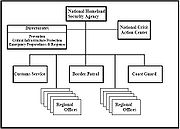
- "the creation of a new independent National Homeland Security Agency (NHSA) with responsibility for planning, coordinating, and integrating various government activities involved in homeland security"
- "that a new office of Assistant Secretary for Homeland Security be created to oversee the various Department of Defense activities and ensure that the necessary resources are made available"
- "that the National Guard be given homeland security as a primary mission, as the US Constitution itself ordains"
- "that CongressUnited States CongressThe United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
reorganize itself to accommodate this Executive Branch realignment, and that it also form a special select committee for homeland security to provide Congressional support and oversight in this critical area"
Recapitalizing America's strengths in science and education
The Commission finds that the scientific and educational systems of the US are in "serious crisis". It notes how the US is in danger of lagging behind other countries in this arena. "In the next quarter century, we will likely see ourselves surpassed, and in relative decline, unless we make a conscious national commitment to maintain our edge". The report further highlights the Commission's belief that this decline in emphasis on science and education is the gravest threat to US national security, even over weapons proliferation and terrorism. The Commission recommends:- "doubling the federal research and development budget by 2010, and instituting a more competitive environment for the allotment of those funds"
- "that the role of the President's Science Advisor be elevated to oversee these and other critical tasks, such as the resuscitation of the national laboratory system and the institution of better inventory stewardship over the nation's science and technology assets"
- "a new National Security Science and Technology Education Act to fund a comprehensive program to produce the needed numbers of science and engineering professionals as well as qualified teachers in science and math"
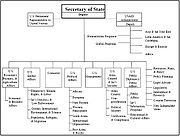
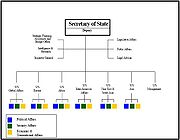
Institutional redesign
The Commission finds that the US governmentFederal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States is the national government of the constitutional republic of fifty states that is the United States of America. The federal government comprises three distinct branches of government: a legislative, an executive and a judiciary. These branches and...
has failed to restructure itself to the post–Cold War world. It recommends significant restructuring to re-align government offices, branches, and procedures with the global realities of the 21st century as well as ensure that,"strategy once again drives the design and implementation of US national security policies". The Commission urges Congress to expand its understanding of national security matters, and streamline the appropriations and authorizations committees to make intelligence and security related legislation more efficient and effective. The Commission also recommends:


- that "the PresidentPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
personally guide a top-down strategic planning process and that process should be linked to the allocation of resources throughout the government" - that "legislative, press communications, and speech-writing functions should reside in the White House staff, not separately in the National Security CouncilUnited States National Security CouncilThe White House National Security Council in the United States is the principal forum used by the President of the United States for considering national security and foreign policy matters with his senior national security advisors and Cabinet officials and is part of the Executive Office of the...
staff as they do today" - "that the Secretary of the Treasury be named a statutory member of the National Security CouncilUnited States National Security CouncilThe White House National Security Council in the United States is the principal forum used by the President of the United States for considering national security and foreign policy matters with his senior national security advisors and Cabinet officials and is part of the Executive Office of the...
" - that "the President should abolish the National Economic Council, distributing its domestic economic policy responsibilities to the Domestic Policy Council"
- "the creation of five Under Secretaries with the responsibility for overseeing the regions of Africa, Asia, Europe, Inter-America, and Near East/South Asia, and a redefinition of the responsibilities of the Under Secretary for Global Affairs"
- "that the activities of the US Agency for International Development be fully integrated into this new State Department organization"
- "that the new Secretary of Defense reduce by ten to fifteen percent the staffs of the Office of the Secretary of DefenseOffice of the Secretary of DefenseThe Office of the Secretary of Defense is a headquarters-level staff of the Department of Defense of the United States of America. It is the principal civilian staff element of the Secretary of Defense, and it assists the Secretary in carrying out authority, direction and control of the Department...
, the Joint Staff, the military services, and the regional commands" - that "the Secretary of Defense should establish a ten-year goal of reducing infrastructure costs by 20-25 percent through steps to consolidate, restructure, outsource, and privatize many Department of DefenseUnited States Department of DefenseThe United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
support agencies and activities as possible" - that "the Secretary of Defense should move the Quadrennial Defense ReviewQuadrennial Defense ReviewThe Quadrennial Defense Review is a study by the United States Department of Defense that analyzes strategic objectives and potential military threats. The Quadrennial Defense Review Report is the main public document describing the United States's military doctrine.As stipulated in the 1997...
to the second year of a Presidential term" - "that the Secretary of Defense introduce a new process that requires the Services and defense agencies to compete for the allocation of some resources within the overall defense budget"
- "establishing and employing a two-track acquisition system, one for major acquisitions and a 'fast track' for a modest number of potential breakthrough systems, especially those in the area of command and control"
- that "the Secretary of Defense should direct the Department of Defense to shift from the threat-based, force sizing process to one which measure requirements against recent operational activity trends, actual intelligence estimates of potential adversaries' capabilities, and national security objectives as defined in the new administration's national security strategy - once formulated"
- "that the Defense Department devote its highest priority to improving and further developing its expeditionary capabilities"
- "the establishment of an Interagency Working Group on Space (IWGS)"
- "that the intelligence communityUnited States Intelligence CommunityThe United States Intelligence Community is a cooperative federation of 16 separate United States government agencies that work separately and together to conduct intelligence activities considered necessary for the conduct of foreign relations and the protection of the national security of the...
should emphasize the recruitment of human intelligenceHUMINTHUMINT, a syllabic abbreviation of the words HUMan INTelligence, refers to intelligence gathering by means of interpersonal contact, as opposed to the more technical intelligence gathering disciplines such as SIGINT, IMINT and MASINT...
sources on terrorism as one of the intelligence community's highest priorities" and "the community should place new emphasis on collection and analysis of economic and science/technology security concerns, and incorporate more open source intelligenceOpen source intelligenceOpen-source intelligence is a form of intelligence collection management that involves finding, selecting, and acquiring information from publicly available sources and analyzing it to produce actionable intelligence...
into its analytical products"
See also
- Federal government of the United StatesFederal government of the United StatesThe federal government of the United States is the national government of the constitutional republic of fifty states that is the United States of America. The federal government comprises three distinct branches of government: a legislative, an executive and a judiciary. These branches and...
- United States Department of Homeland SecurityUnited States Department of Homeland SecurityThe United States Department of Homeland Security is a cabinet department of the United States federal government, created in response to the September 11 attacks, and with the primary responsibilities of protecting the territory of the United States and protectorates from and responding to...
- United States Intelligence CommunityUnited States Intelligence CommunityThe United States Intelligence Community is a cooperative federation of 16 separate United States government agencies that work separately and together to conduct intelligence activities considered necessary for the conduct of foreign relations and the protection of the national security of the...
- National Intelligence Strategy of the United States of AmericaNational Intelligence Strategy of the United States of AmericaThe National Intelligence Strategy of the United States of America is a product of the Office of the Director of National Intelligence . Drafted and implemented in 2005 while John Negroponte served as the DNI, it describes the drastic overhaul the United States intelligence community will carry...
- Intelligence cycle managementIntelligence cycle managementThe intelligence cycle is a investigation process used by end users , which allows that user to gather specific information, understand the possibilities of that information, and the limitations of the intelligence process.Within the context of government, military and business affairs,...
- Homeland SecurityHomeland securityHomeland security is an umbrella term for security efforts to protect states against terrorist activity. Specifically, is a concerted national effort to prevent terrorist attacks within the U.S., reduce America’s vulnerability to terrorism, and minimize the damage and recover from attacks that do...
- USA PATRIOT ActUSA PATRIOT ActThe USA PATRIOT Act is an Act of the U.S. Congress that was signed into law by President George W. Bush on October 26, 2001...
External links
- US Commission on National Security/21st Century
- National Security in the 21st Century: Findings of the Hart-Rudman Commission
- The Hart - Rudman Commission and the Homeland Defense
- National Security Watch - USCNS/21: A Hart-Rudman Commission Primer
- Hart - Rudman Calls For Homeland Defense
- Recommendations of Hart - Rudman National Security Report: Education
- Hart - Rudman Commission Report - A Critique
- Newt Gingrich's Last Boondoggle: The Hart - Rudman National Security Commission shows every sign of being an expensive flop
- A Year After 9/11, America Still Unprepared For A Terrorist Attack, Warns New Hart-Rudman Task Force On Homeland Security
- America - Still Unprepared, Still In Danger
- Revisiting the Hart - Rudman Commission
Further reading
- Intelligence: From Secrets to Policy, by Mark Lowenthal
- Intelligence Analysis: A Target Centric Approach, by Robert M. Clark

