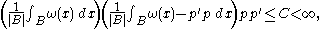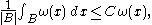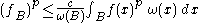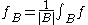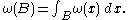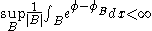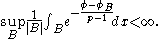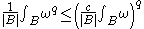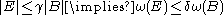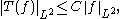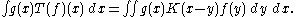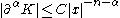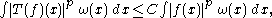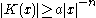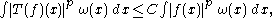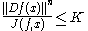Muckenhoupt weights
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, the class of Muckenhoupt weights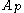 consists of those weights
consists of those weights 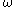 for which the Hardy–Littlewood maximal operator is bounded on
for which the Hardy–Littlewood maximal operator is bounded on 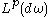 . Specifically, we consider functions
. Specifically, we consider functions 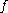 on
on 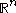 and their associated maximal function
and their associated maximal function
s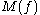 defined as
defined as
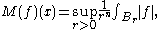
where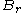 is a ball in
is a ball in 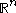 with radius
with radius  and centre
and centre  . We wish to characterise the functions
. We wish to characterise the functions 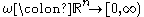 for which we have a bound
for which we have a bound
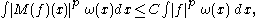
where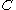 depends only on
depends only on 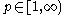 and
and 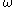 . This was first done by Benjamin Muckenhoupt.
. This was first done by Benjamin Muckenhoupt.
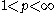 , we say that a weight
, we say that a weight 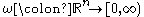 belongs to
belongs to 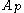 if
if 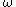 is locally integrable and there is a constant
is locally integrable and there is a constant 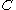 such that, for all balls
such that, for all balls 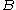 in
in 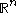 , we have
, we have
where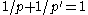 and
and 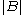 is the Lebesgue measure
is the Lebesgue measure
of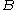 . We say
. We say 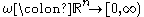 belongs to
belongs to 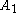 if there exists some
if there exists some 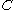 such that
such that
for all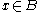 and all balls
and all balls 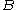 .
.
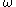 is in
is in 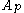 if and only if any one of the following hold.
if and only if any one of the following hold.
(a) The Hardy–Littlewood maximal function is bounded on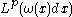 , that is
, that is
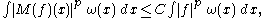
for some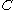 which only depends on
which only depends on 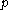 and the constant
and the constant 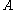 in the above definition.
in the above definition.
(b) There is a constant such that for any locally integrable function
such that for any locally integrable function 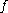 on
on 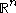
for all balls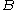 . Here
. Here
is the average of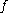 over
over 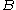 and
and
Equivalently,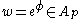 , where
, where 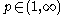 , if and only if
, if and only if
and
This equivalence can be verified by using Jensen's Inequality
.
Reverse Hölder inequalities and
The main tool in the proof of the above equivalence is the following result. The following statements are equivalent
(a)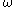 belongs to
belongs to 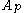 for some
for some 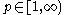
(b) There exists an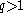 and a
and a  (both depending on
(both depending on 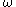 such that
such that
for all balls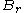
(c) There exists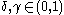 so that for all balls
so that for all balls 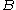 and subsets
and subsets 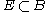
We call the inequality in (b) a reverse Hölder inequality as the reverse inequality follows for any non-negative function directly from Hölder's inequality
. If any of the three equivalent conditions above hold we say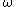 belongs to
belongs to 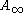 .
.
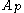 weight and the reverse Hölder inequality indicate that such a weight cannot degenerate or grow too quickly. This property can be phrased equivalently in terms of how much the logarithm of the weight oscillates:
weight and the reverse Hölder inequality indicate that such a weight cannot degenerate or grow too quickly. This property can be phrased equivalently in terms of how much the logarithm of the weight oscillates:
(a) If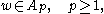 , then
, then 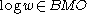 (i.e.
(i.e. 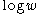 has bounded mean oscillation
has bounded mean oscillation
).
(b) If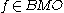 , then for sufficiently small
, then for sufficiently small 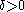 , we have
, we have 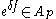 for some
for some 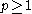 .
.
This equivalence can be established by using the exponential characterization of weights above, Jensen's inequality, and the John–Nirenberg inequality. Note that the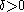 condition in part (b) is necessary for the result to be true, as
condition in part (b) is necessary for the result to be true, as 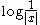 is a BMO function, but
is a BMO function, but 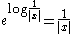 is not in any
is not in any 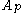 .
.
(i)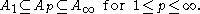
(ii)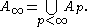
(iii) If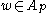 , then
, then 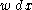 defines a doubling measure: for any ball B, if 2B is the ball of twice the radius, then
defines a doubling measure: for any ball B, if 2B is the ball of twice the radius, then 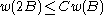 where C > 1 is a constant depending on
where C > 1 is a constant depending on 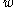 .
.
(iv) If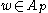 , then there is
, then there is 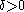 such that
such that 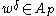 .
.
(v) If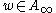 then there is
then there is 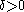 and weights
and weights 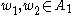 such that
such that 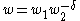 .
.
 spaces. In fact, any Calderón-Zygmund singular integral operator is also bounded on these spaces. Let us describe a simpler version of this here. Suppose we have an operator
spaces. In fact, any Calderón-Zygmund singular integral operator is also bounded on these spaces. Let us describe a simpler version of this here. Suppose we have an operator 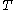 which is bounded on
which is bounded on 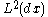 , so we have
, so we have
for all smooth and compactly supported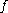 . Suppose also that we can realise
. Suppose also that we can realise 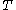 as convolution against a kernel
as convolution against a kernel 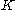 in the sense that, whenever
in the sense that, whenever 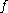 and
and 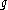 are smooth and have disjoint support
are smooth and have disjoint support
Finally we assume a size and smoothness condition on the kernel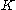 :
:
for all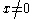 and multi-indices
and multi-indices 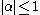 . Then, for each
. Then, for each 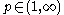 and
and 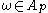 , we have that
, we have that 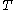 is a bounded operator on
is a bounded operator on 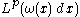 . That is, we have the estimate
. That is, we have the estimate
for all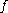 for which the right-hand side is finite.
for which the right-hand side is finite.
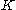 : For a fixed unit vector
: For a fixed unit vector 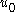
whenever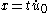 with
with 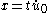 , then we have a converse. If we know
, then we have a converse. If we know
for some fixed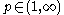 and some
and some 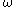 , then
, then 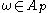 .
.
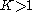 , a K-quasiconformal mapping
, a K-quasiconformal mapping
is a homeomorphism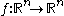 with
with 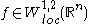 and
and
where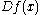 is the derivative
is the derivative
of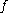 at
at  and
and 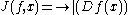 is the Jacobian
is the Jacobian
.
A theorem of Gehring states that for all K-quasiconformal functions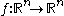 , we have
, we have 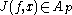 where
where 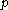 depends on
depends on 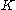 .
.
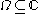 , we say its boundary curve
, we say its boundary curve 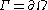 is K-chord-arc if for any two points
is K-chord-arc if for any two points 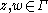 there is a curve
there is a curve 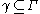 connecting
connecting  and
and 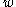 whose length is no more than
whose length is no more than 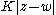 . For a domain with such a boundary and for any
. For a domain with such a boundary and for any 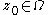 , the harmonic measure
, the harmonic measure
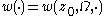 is absolutely continuous with respect to one-dimensional Hausdorff measure
is absolutely continuous with respect to one-dimensional Hausdorff measure
and its Radon–Nikodym derivative is in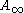 . (Note that in this case, one needs to adapt the definition of weights to the case where the underlying measure is one-dimensional Hausdorff measure).
. (Note that in this case, one needs to adapt the definition of weights to the case where the underlying measure is one-dimensional Hausdorff measure).
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, the class of Muckenhoupt weights
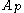 consists of those weights
consists of those weights 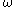 for which the Hardy–Littlewood maximal operator is bounded on
for which the Hardy–Littlewood maximal operator is bounded on 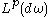 . Specifically, we consider functions
. Specifically, we consider functions 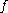 on
on 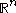 and their associated maximal function
and their associated maximal functionMaximal function
Maximal functions appear in many forms in harmonic analysis . One of the most important of these is the Hardy–Littlewood maximal function. They play an important role in understanding, for example, the differentiability properties of functions, singular integrals and partial differential equations...
s
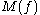 defined as
defined as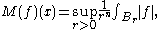
where
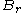 is a ball in
is a ball in 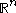 with radius
with radius  and centre
and centre  . We wish to characterise the functions
. We wish to characterise the functions 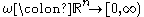 for which we have a bound
for which we have a bound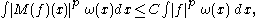
where
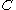 depends only on
depends only on 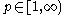 and
and 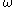 . This was first done by Benjamin Muckenhoupt.
. This was first done by Benjamin Muckenhoupt.Definition
For a fixed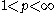 , we say that a weight
, we say that a weight 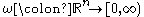 belongs to
belongs to 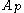 if
if 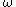 is locally integrable and there is a constant
is locally integrable and there is a constant 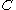 such that, for all balls
such that, for all balls 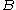 in
in 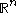 , we have
, we havewhere
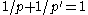 and
and 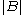 is the Lebesgue measure
is the Lebesgue measureLebesgue measure
In measure theory, the Lebesgue measure, named after French mathematician Henri Lebesgue, is the standard way of assigning a measure to subsets of n-dimensional Euclidean space. For n = 1, 2, or 3, it coincides with the standard measure of length, area, or volume. In general, it is also called...
of
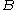 . We say
. We say 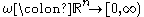 belongs to
belongs to 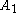 if there exists some
if there exists some 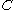 such that
such thatfor all
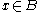 and all balls
and all balls 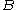 .
.Equivalent characterizations
This following result is a fundamental result in the study of Muckenhoupt weights. A weight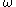 is in
is in 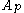 if and only if any one of the following hold.
if and only if any one of the following hold.(a) The Hardy–Littlewood maximal function is bounded on
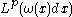 , that is
, that is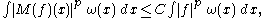
for some
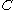 which only depends on
which only depends on 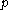 and the constant
and the constant 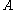 in the above definition.
in the above definition.(b) There is a constant
 such that for any locally integrable function
such that for any locally integrable function 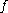 on
on 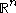
for all balls
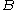 . Here
. Hereis the average of
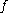 over
over 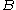 and
andEquivalently,
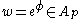 , where
, where 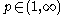 , if and only if
, if and only if
and
This equivalence can be verified by using Jensen's Inequality
Jensen's inequality
In mathematics, Jensen's inequality, named after the Danish mathematician Johan Jensen, relates the value of a convex function of an integral to the integral of the convex function. It was proved by Jensen in 1906. Given its generality, the inequality appears in many forms depending on the context,...
.
Reverse Hölder inequalities and 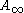
The main tool in the proof of the above equivalence is the following result. The following statements are equivalent(a)
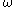 belongs to
belongs to 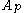 for some
for some 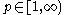
(b) There exists an
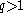 and a
and a  (both depending on
(both depending on 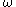 such that
such thatfor all balls
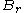
(c) There exists
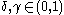 so that for all balls
so that for all balls 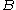 and subsets
and subsets 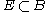
We call the inequality in (b) a reverse Hölder inequality as the reverse inequality follows for any non-negative function directly from Hölder's inequality
Hölder's inequality
In mathematical analysis Hölder's inequality, named after Otto Hölder, is a fundamental inequality between integrals and an indispensable tool for the study of Lp spaces....
. If any of the three equivalent conditions above hold we say
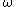 belongs to
belongs to 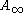 .
.Weights and BMO
The definition of an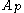 weight and the reverse Hölder inequality indicate that such a weight cannot degenerate or grow too quickly. This property can be phrased equivalently in terms of how much the logarithm of the weight oscillates:
weight and the reverse Hölder inequality indicate that such a weight cannot degenerate or grow too quickly. This property can be phrased equivalently in terms of how much the logarithm of the weight oscillates:(a) If
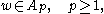 , then
, then 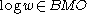 (i.e.
(i.e. 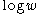 has bounded mean oscillation
has bounded mean oscillationBounded mean oscillation
In harmonic analysis, a function of bounded mean oscillation, also known as a BMO function, is a real-valued function whose mean oscillation is bounded...
).
(b) If
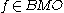 , then for sufficiently small
, then for sufficiently small 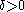 , we have
, we have 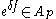 for some
for some 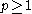 .
.This equivalence can be established by using the exponential characterization of weights above, Jensen's inequality, and the John–Nirenberg inequality. Note that the
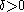 condition in part (b) is necessary for the result to be true, as
condition in part (b) is necessary for the result to be true, as 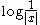 is a BMO function, but
is a BMO function, but 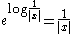 is not in any
is not in any 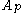 .
.Further properties
Here we list a few miscellaneous properties about weights, some of which can be verified from using the definitions, others are nontrivial results:(i)
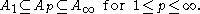
(ii)
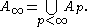
(iii) If
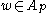 , then
, then 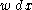 defines a doubling measure: for any ball B, if 2B is the ball of twice the radius, then
defines a doubling measure: for any ball B, if 2B is the ball of twice the radius, then 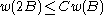 where C > 1 is a constant depending on
where C > 1 is a constant depending on 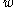 .
.(iv) If
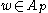 , then there is
, then there is 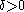 such that
such that 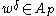 .
.(v) If
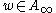 then there is
then there is 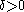 and weights
and weights 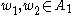 such that
such that 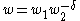 .
.Boundedness of singular integrals
It is not only the Hardy–Littlewood maximal operator that is bounded on these weighted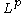 spaces. In fact, any Calderón-Zygmund singular integral operator is also bounded on these spaces. Let us describe a simpler version of this here. Suppose we have an operator
spaces. In fact, any Calderón-Zygmund singular integral operator is also bounded on these spaces. Let us describe a simpler version of this here. Suppose we have an operator 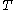 which is bounded on
which is bounded on 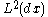 , so we have
, so we havefor all smooth and compactly supported
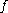 . Suppose also that we can realise
. Suppose also that we can realise 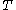 as convolution against a kernel
as convolution against a kernel 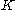 in the sense that, whenever
in the sense that, whenever 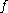 and
and 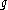 are smooth and have disjoint support
are smooth and have disjoint supportFinally we assume a size and smoothness condition on the kernel
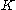 :
:for all
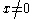 and multi-indices
and multi-indices 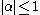 . Then, for each
. Then, for each 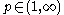 and
and 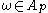 , we have that
, we have that 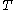 is a bounded operator on
is a bounded operator on 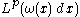 . That is, we have the estimate
. That is, we have the estimatefor all
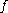 for which the right-hand side is finite.
for which the right-hand side is finite.A converse result
If, in addition to the three conditions above, we assume the non-degeneracy condition on the kernel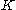 : For a fixed unit vector
: For a fixed unit vector 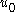
whenever
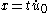 with
with 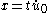 , then we have a converse. If we know
, then we have a converse. If we knowfor some fixed
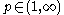 and some
and some 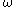 , then
, then 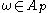 .
.Weights and quasiconformal mappings
For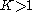 , a K-quasiconformal mapping
, a K-quasiconformal mappingQuasiconformal mapping
In mathematical complex analysis, a quasiconformal mapping, introduced by and named by , is a homeomorphism between plane domains which to first order takes small circles to small ellipses of bounded eccentricity....
is a homeomorphism
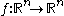 with
with 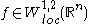 and
andwhere
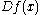 is the derivative
is the derivativeDerivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
of
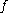 at
at  and
and 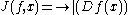 is the Jacobian
is the JacobianJacobian
In vector calculus, the Jacobian matrix is the matrix of all first-order partial derivatives of a vector- or scalar-valued function with respect to another vector. Suppose F : Rn → Rm is a function from Euclidean n-space to Euclidean m-space...
.
A theorem of Gehring states that for all K-quasiconformal functions
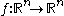 , we have
, we have 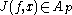 where
where 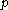 depends on
depends on 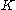 .
.Harmonic measure
If you have a simply connected domain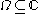 , we say its boundary curve
, we say its boundary curve 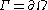 is K-chord-arc if for any two points
is K-chord-arc if for any two points 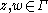 there is a curve
there is a curve 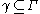 connecting
connecting  and
and 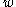 whose length is no more than
whose length is no more than 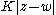 . For a domain with such a boundary and for any
. For a domain with such a boundary and for any 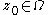 , the harmonic measure
, the harmonic measureHarmonic measure
In mathematics, especially potential theory, harmonic measure is a concept related to the theory of harmonic functions that arises from the solution of the classical Dirichlet problem. In probability theory, harmonic measure of a bounded domain in Euclidean space R^n, n\geq 2 is the probability...
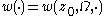 is absolutely continuous with respect to one-dimensional Hausdorff measure
is absolutely continuous with respect to one-dimensional Hausdorff measureHausdorff measure
In mathematics a Hausdorff measure is a type of outer measure, named for Felix Hausdorff, that assigns a number in [0,∞] to each set in Rn or, more generally, in any metric space. The zero dimensional Hausdorff measure is the number of points in the set or ∞ if the set is infinite...
and its Radon–Nikodym derivative is in
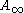 . (Note that in this case, one needs to adapt the definition of weights to the case where the underlying measure is one-dimensional Hausdorff measure).
. (Note that in this case, one needs to adapt the definition of weights to the case where the underlying measure is one-dimensional Hausdorff measure).