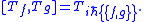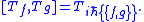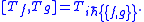Moyal bracket
Encyclopedia
In physics
, the Moyal bracket is the suitably normalized antisymmetrization of the phase-space star product
.
The Moyal Bracket was developed in about 1940 by José Enrique Moyal
, but Moyal only succeeded in publishing his work in 1949 after a lengthy dispute with Dirac . In the meantime this idea was independently introduced in 1946 by Hip Groenewold
.
The Moyal bracket is a way of describing the commutator
of observables in quantum mechanics
when these observables are described as functions on phase space
. It relies on schemes for identifying functions on phase space with quantum observables, the most famous of these schemes being Weyl quantization
. It underlies Moyal’s dynamical equation, an equivalent formulation of Heisenberg’s quantum equation of motion, thereby providing the quantum generalization of Hamilton’s equations
.
Mathematically, it is a deformation
of the phase-space Poisson bracket
, the deformation parameter being the reduced Planck constant
ħ.
Up to formal equivalence, the Moyal Bracket is the unique one-parameter Lie-algebraic deformation of the Poisson bracket. Its algebraic isomorphism to the algebra of commutators bypasses the negative result of the Groenewold–van Hove theorem, which precludes such an isomorphism for the Poisson bracket, a question implicitly raised by Paul Dirac
in
his 1926 doctoral thesis: the "method of classical analogy" for quantization.
For instance, in a two-dimensional flat phase space
, and for the Weyl-map correspondence (cf. Weyl quantization
), the Moyal bracket reads,
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, the Moyal bracket is the suitably normalized antisymmetrization of the phase-space star product
Moyal product
In mathematics, the Moyal product, named after José Enrique Moyal, is perhaps the best-known example of a phase-space star product: an associative, non-commutative product, ∗, on the functions on ℝ2n, equipped with its Poisson bracket .This particular star product is also sometimes called...
.
The Moyal Bracket was developed in about 1940 by José Enrique Moyal
José Enrique Moyal
José Enrique Moyal was a mathematical physicist who contributed to aeronautical engineering, electrical engineering and statistics, among other fields...
, but Moyal only succeeded in publishing his work in 1949 after a lengthy dispute with Dirac . In the meantime this idea was independently introduced in 1946 by Hip Groenewold
Hilbrand J. Groenewold
Hilbrand Johannes Groenewold was a Dutch theoretical physicist who pioneered the largely operator-free formulation of quantum mechanics in phase space known as phase-space quantization....
.
The Moyal bracket is a way of describing the commutator
Commutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.-Group theory:...
of observables in quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
when these observables are described as functions on phase space
Phase space
In mathematics and physics, a phase space, introduced by Willard Gibbs in 1901, is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state of the system corresponding to one unique point in the phase space...
. It relies on schemes for identifying functions on phase space with quantum observables, the most famous of these schemes being Weyl quantization
Weyl quantization
In mathematics and physics, in the area of quantum mechanics, Weyl quantization is a method for systematically associating a "quantum mechanical" Hermitian operator with a "classical" kernel function in phase space invertibly...
. It underlies Moyal’s dynamical equation, an equivalent formulation of Heisenberg’s quantum equation of motion, thereby providing the quantum generalization of Hamilton’s equations
Hamiltonian mechanics
Hamiltonian mechanics is a reformulation of classical mechanics that was introduced in 1833 by Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton.It arose from Lagrangian mechanics, a previous reformulation of classical mechanics introduced by Joseph Louis Lagrange in 1788, but can be formulated without...
.
Mathematically, it is a deformation
Deformation theory
In mathematics, deformation theory is the study of infinitesimal conditions associated with varying a solution P of a problem to slightly different solutions Pε, where ε is a small number, or vector of small quantities. The infinitesimal conditions are therefore the result of applying the approach...
of the phase-space Poisson bracket
Poisson bracket
In mathematics and classical mechanics, the Poisson bracket is an important binary operation in Hamiltonian mechanics, playing a central role in Hamilton's equations of motion, which govern the time-evolution of a Hamiltonian dynamical system...
, the deformation parameter being the reduced Planck constant
Planck constant
The Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
ħ.
Up to formal equivalence, the Moyal Bracket is the unique one-parameter Lie-algebraic deformation of the Poisson bracket. Its algebraic isomorphism to the algebra of commutators bypasses the negative result of the Groenewold–van Hove theorem, which precludes such an isomorphism for the Poisson bracket, a question implicitly raised by Paul Dirac
Paul Dirac
Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac, OM, FRS was an English theoretical physicist who made fundamental contributions to the early development of both quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics...
in
his 1926 doctoral thesis: the "method of classical analogy" for quantization.
For instance, in a two-dimensional flat phase space
Phase space
In mathematics and physics, a phase space, introduced by Willard Gibbs in 1901, is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state of the system corresponding to one unique point in the phase space...
, and for the Weyl-map correspondence (cf. Weyl quantization
Weyl quantization
In mathematics and physics, in the area of quantum mechanics, Weyl quantization is a method for systematically associating a "quantum mechanical" Hermitian operator with a "classical" kernel function in phase space invertibly...
), the Moyal bracket reads,
-
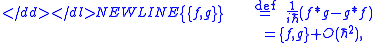
where ∗ is the star-product operator in phase space (cf. Moyal productMoyal productIn mathematics, the Moyal product, named after José Enrique Moyal, is perhaps the best-known example of a phase-space star product: an associative, non-commutative product, ∗, on the functions on ℝ2n, equipped with its Poisson bracket .This particular star product is also sometimes called...
), while f and g are differentiable phase-space functions, and {f,g} is their Poisson bracket.
More specifically, this equals
-
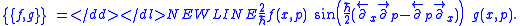
Sometimes the Moyal bracket is referred to as the Sine bracket. E.g., a popular (Fourier) integral representation for it, introduced by George Baker is
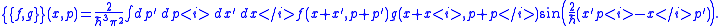
Each correspondence map from phase space to Hilbert space induces a characteristic "Moyal" bracket (such as the one illustrated here for the Weyl map). All such Moyal brackets are formally equivalent among themselves, in accordance with a systematic theory.
The Moyal bracket specifies the eponymous infinite-dimensional
Lie algebraLie algebraIn mathematics, a Lie algebra is an algebraic structure whose main use is in studying geometric objects such as Lie groups and differentiable manifolds. Lie algebras were introduced to study the concept of infinitesimal transformations. The term "Lie algebra" was introduced by Hermann Weyl in the...
—it is antisymmetric in its arguments f and g, and satisfies the Jacobi identityJacobi identityIn mathematics the Jacobi identity is a property that a binary operation can satisfy which determines how the order of evaluation behaves for the given operation. Unlike for associative operations, order of evaluation is significant for operations satisfying Jacobi identity...
.
The corresponding abstract Lie algebra is realized by Tf ≡ f ∗ , so that
On a 2-torus phase space, T2, with periodic
coordinates x and p, each in [0,2π], and integer mode indices mi , for basis functions exp(i (m1x+m2p)), this Lie algebra reads,
In physicsPhysicsPhysics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, the Moyal bracket is the suitably normalized antisymmetrization of the phase-space star productMoyal productIn mathematics, the Moyal product, named after José Enrique Moyal, is perhaps the best-known example of a phase-space star product: an associative, non-commutative product, ∗, on the functions on ℝ2n, equipped with its Poisson bracket .This particular star product is also sometimes called...
.
The Moyal Bracket was developed in about 1940 by José Enrique MoyalJosé Enrique MoyalJosé Enrique Moyal was a mathematical physicist who contributed to aeronautical engineering, electrical engineering and statistics, among other fields...
, but Moyal only succeeded in publishing his work in 1949 after a lengthy dispute with Dirac J.E. MoyalJosé Enrique MoyalJosé Enrique Moyal was a mathematical physicist who contributed to aeronautical engineering, electrical engineering and statistics, among other fields...
, “Quantum mechanics as a statistical theory,” Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 45 (1949) pp. 99–124. doi:10.1017/S0305004100000487
. In the meantime this idea was independently introduced in 1946 by Hip GroenewoldHilbrand J. GroenewoldHilbrand Johannes Groenewold was a Dutch theoretical physicist who pioneered the largely operator-free formulation of quantum mechanics in phase space known as phase-space quantization....
H.J. GroenewoldHilbrand J. GroenewoldHilbrand Johannes Groenewold was a Dutch theoretical physicist who pioneered the largely operator-free formulation of quantum mechanics in phase space known as phase-space quantization....
, “On the Principles of elementary quantum mechanics,” Physica,12 (1946) pp. 405–460. doi:10.1016/S0031-8914(46)80059-4.
The Moyal bracket is a way of describing the commutatorCommutatorIn mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.-Group theory:...
of observables in quantum mechanicsQuantum mechanicsQuantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
when these observables are described as functions on phase spacePhase spaceIn mathematics and physics, a phase space, introduced by Willard Gibbs in 1901, is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state of the system corresponding to one unique point in the phase space...
. It relies on schemes for identifying functions on phase space with quantum observables, the most famous of these schemes being Weyl quantizationWeyl quantizationIn mathematics and physics, in the area of quantum mechanics, Weyl quantization is a method for systematically associating a "quantum mechanical" Hermitian operator with a "classical" kernel function in phase space invertibly...
. It underlies Moyal’s dynamical equation, an equivalent formulation of Heisenberg’s quantum equation of motion, thereby providing the quantum generalization of Hamilton’s equationsHamiltonian mechanicsHamiltonian mechanics is a reformulation of classical mechanics that was introduced in 1833 by Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton.It arose from Lagrangian mechanics, a previous reformulation of classical mechanics introduced by Joseph Louis Lagrange in 1788, but can be formulated without...
.
Mathematically, it is a deformationDeformation theoryIn mathematics, deformation theory is the study of infinitesimal conditions associated with varying a solution P of a problem to slightly different solutions Pε, where ε is a small number, or vector of small quantities. The infinitesimal conditions are therefore the result of applying the approach...
of the phase-space Poisson bracketPoisson bracketIn mathematics and classical mechanics, the Poisson bracket is an important binary operation in Hamiltonian mechanics, playing a central role in Hamilton's equations of motion, which govern the time-evolution of a Hamiltonian dynamical system...
, the deformation parameter being the reduced Planck constantPlanck constantThe Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
ħ.
Up to formal equivalence, the Moyal Bracket is the unique one-parameter Lie-algebraic deformation of the Poisson bracket. Its algebraic isomorphism to the algebra of commutators bypasses the negative result of the Groenewold–van Hove theorem, which precludes such an isomorphism for the Poisson bracket, a question implicitly raised by Paul DiracPaul DiracPaul Adrien Maurice Dirac, OM, FRS was an English theoretical physicist who made fundamental contributions to the early development of both quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics...
in
his 1926 doctoral thesis: the "method of classical analogy" for quantization.P.A.M. Dirac, "The Principles of Quantum Mechanics" (Clarendon Press Oxford, 1958) ISBN 9780198520115
For instance, in a two-dimensional flat phase spacePhase spaceIn mathematics and physics, a phase space, introduced by Willard Gibbs in 1901, is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state of the system corresponding to one unique point in the phase space...
, and for the Weyl-map correspondence (cf. Weyl quantizationWeyl quantizationIn mathematics and physics, in the area of quantum mechanics, Weyl quantization is a method for systematically associating a "quantum mechanical" Hermitian operator with a "classical" kernel function in phase space invertibly...
), the Moyal bracket reads,
-
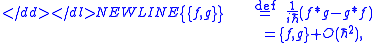
where ∗ is the star-product operator in phase space (cf. Moyal productMoyal productIn mathematics, the Moyal product, named after José Enrique Moyal, is perhaps the best-known example of a phase-space star product: an associative, non-commutative product, ∗, on the functions on ℝ2n, equipped with its Poisson bracket .This particular star product is also sometimes called...
), while f and g are differentiable phase-space functions, and {f,g} is their Poisson bracket.
More specifically, this equals
-
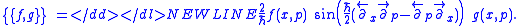
Sometimes the Moyal bracket is referred to as the Sine bracket. E.g., a popular (Fourier) integral representation for it, introduced by George BakerG. Baker, “Formulation of Quantum Mechanics Based on the Quasi-probability Distribution Induced on Phase Space,” Physical Review, 109 (1958) pp.2198–2206. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.109.2198 is
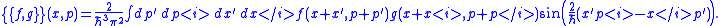
Each correspondence map from phase space to Hilbert space induces a characteristic "Moyal" bracket (such as the one illustrated here for the Weyl map). All such Moyal brackets are formally equivalent among themselves, in accordance with a systematic theory.C.ZachosCosmas ZachosCosmas K. Zachos is a theoretical physicist. He was educated in physics at Princeton University, and did graduate work in theoretical physics at the California Institute of Technology under the supervision of John Henry Schwarz.Zachos is a staff member in the theory group of the High Energy...
, D. Fairlie, and T. CurtrightThomas CurtrightThomas L. Curtright is a theoretical physicist at the University of Miami. He did undergraduate work in physics at theUniversity of Missouri—Columbia , and graduate work at Caltech...
, “Quantum Mechanics in Phase Space” (World Scientific, Singapore, 2005) ISBN 978-981-238-384-6 .
The Moyal bracket specifies the eponymous infinite-dimensional
Lie algebraLie algebraIn mathematics, a Lie algebra is an algebraic structure whose main use is in studying geometric objects such as Lie groups and differentiable manifolds. Lie algebras were introduced to study the concept of infinitesimal transformations. The term "Lie algebra" was introduced by Hermann Weyl in the...
—it is antisymmetric in its arguments f and g, and satisfies the Jacobi identityJacobi identityIn mathematics the Jacobi identity is a property that a binary operation can satisfy which determines how the order of evaluation behaves for the given operation. Unlike for associative operations, order of evaluation is significant for operations satisfying Jacobi identity...
.
The corresponding abstract Lie algebra is realized by Tf ≡ f ∗ , so that
On a 2-torus phase space, T2, with periodic
coordinates x and p, each in [0,2π], and integer mode indices mi , for basis functions exp(i (m1x+m2p)), this Lie algebra reads,
In physicsPhysicsPhysics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, the Moyal bracket is the suitably normalized antisymmetrization of the phase-space star productMoyal productIn mathematics, the Moyal product, named after José Enrique Moyal, is perhaps the best-known example of a phase-space star product: an associative, non-commutative product, ∗, on the functions on ℝ2n, equipped with its Poisson bracket .This particular star product is also sometimes called...
.
The Moyal Bracket was developed in about 1940 by José Enrique MoyalJosé Enrique MoyalJosé Enrique Moyal was a mathematical physicist who contributed to aeronautical engineering, electrical engineering and statistics, among other fields...
, but Moyal only succeeded in publishing his work in 1949 after a lengthy dispute with Dirac J.E. MoyalJosé Enrique MoyalJosé Enrique Moyal was a mathematical physicist who contributed to aeronautical engineering, electrical engineering and statistics, among other fields...
, “Quantum mechanics as a statistical theory,” Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 45 (1949) pp. 99–124. doi:10.1017/S0305004100000487
. In the meantime this idea was independently introduced in 1946 by Hip GroenewoldHilbrand J. GroenewoldHilbrand Johannes Groenewold was a Dutch theoretical physicist who pioneered the largely operator-free formulation of quantum mechanics in phase space known as phase-space quantization....
H.J. GroenewoldHilbrand J. GroenewoldHilbrand Johannes Groenewold was a Dutch theoretical physicist who pioneered the largely operator-free formulation of quantum mechanics in phase space known as phase-space quantization....
, “On the Principles of elementary quantum mechanics,” Physica,12 (1946) pp. 405–460. doi:10.1016/S0031-8914(46)80059-4.
The Moyal bracket is a way of describing the commutatorCommutatorIn mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.-Group theory:...
of observables in quantum mechanicsQuantum mechanicsQuantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
when these observables are described as functions on phase spacePhase spaceIn mathematics and physics, a phase space, introduced by Willard Gibbs in 1901, is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state of the system corresponding to one unique point in the phase space...
. It relies on schemes for identifying functions on phase space with quantum observables, the most famous of these schemes being Weyl quantizationWeyl quantizationIn mathematics and physics, in the area of quantum mechanics, Weyl quantization is a method for systematically associating a "quantum mechanical" Hermitian operator with a "classical" kernel function in phase space invertibly...
. It underlies Moyal’s dynamical equation, an equivalent formulation of Heisenberg’s quantum equation of motion, thereby providing the quantum generalization of Hamilton’s equationsHamiltonian mechanicsHamiltonian mechanics is a reformulation of classical mechanics that was introduced in 1833 by Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton.It arose from Lagrangian mechanics, a previous reformulation of classical mechanics introduced by Joseph Louis Lagrange in 1788, but can be formulated without...
.
Mathematically, it is a deformationDeformation theoryIn mathematics, deformation theory is the study of infinitesimal conditions associated with varying a solution P of a problem to slightly different solutions Pε, where ε is a small number, or vector of small quantities. The infinitesimal conditions are therefore the result of applying the approach...
of the phase-space Poisson bracketPoisson bracketIn mathematics and classical mechanics, the Poisson bracket is an important binary operation in Hamiltonian mechanics, playing a central role in Hamilton's equations of motion, which govern the time-evolution of a Hamiltonian dynamical system...
, the deformation parameter being the reduced Planck constantPlanck constantThe Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
ħ.
Up to formal equivalence, the Moyal Bracket is the unique one-parameter Lie-algebraic deformation of the Poisson bracket. Its algebraic isomorphism to the algebra of commutators bypasses the negative result of the Groenewold–van Hove theorem, which precludes such an isomorphism for the Poisson bracket, a question implicitly raised by Paul DiracPaul DiracPaul Adrien Maurice Dirac, OM, FRS was an English theoretical physicist who made fundamental contributions to the early development of both quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics...
in
his 1926 doctoral thesis: the "method of classical analogy" for quantization.P.A.M. Dirac, "The Principles of Quantum Mechanics" (Clarendon Press Oxford, 1958) ISBN 9780198520115
For instance, in a two-dimensional flat phase spacePhase spaceIn mathematics and physics, a phase space, introduced by Willard Gibbs in 1901, is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state of the system corresponding to one unique point in the phase space...
, and for the Weyl-map correspondence (cf. Weyl quantizationWeyl quantizationIn mathematics and physics, in the area of quantum mechanics, Weyl quantization is a method for systematically associating a "quantum mechanical" Hermitian operator with a "classical" kernel function in phase space invertibly...
), the Moyal bracket reads,
-
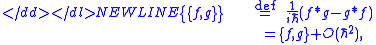
where ∗ is the star-product operator in phase space (cf. Moyal productMoyal productIn mathematics, the Moyal product, named after José Enrique Moyal, is perhaps the best-known example of a phase-space star product: an associative, non-commutative product, ∗, on the functions on ℝ2n, equipped with its Poisson bracket .This particular star product is also sometimes called...
), while f and g are differentiable phase-space functions, and {f,g} is their Poisson bracket.
More specifically, this equals
-
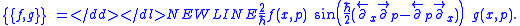
Sometimes the Moyal bracket is referred to as the Sine bracket. E.g., a popular (Fourier) integral representation for it, introduced by George BakerG. Baker, “Formulation of Quantum Mechanics Based on the Quasi-probability Distribution Induced on Phase Space,” Physical Review, 109 (1958) pp.2198–2206. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.109.2198 is
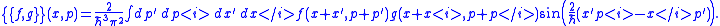
Each correspondence map from phase space to Hilbert space induces a characteristic "Moyal" bracket (such as the one illustrated here for the Weyl map). All such Moyal brackets are formally equivalent among themselves, in accordance with a systematic theory.C.ZachosCosmas ZachosCosmas K. Zachos is a theoretical physicist. He was educated in physics at Princeton University, and did graduate work in theoretical physics at the California Institute of Technology under the supervision of John Henry Schwarz.Zachos is a staff member in the theory group of the High Energy...
, D. Fairlie, and T. CurtrightThomas CurtrightThomas L. Curtright is a theoretical physicist at the University of Miami. He did undergraduate work in physics at theUniversity of Missouri—Columbia , and graduate work at Caltech...
, “Quantum Mechanics in Phase Space” (World Scientific, Singapore, 2005) ISBN 978-981-238-384-6 .
The Moyal bracket specifies the eponymous infinite-dimensional
Lie algebraLie algebraIn mathematics, a Lie algebra is an algebraic structure whose main use is in studying geometric objects such as Lie groups and differentiable manifolds. Lie algebras were introduced to study the concept of infinitesimal transformations. The term "Lie algebra" was introduced by Hermann Weyl in the...
—it is antisymmetric in its arguments f and g, and satisfies the Jacobi identityJacobi identityIn mathematics the Jacobi identity is a property that a binary operation can satisfy which determines how the order of evaluation behaves for the given operation. Unlike for associative operations, order of evaluation is significant for operations satisfying Jacobi identity...
.
The corresponding abstract Lie algebra is realized by Tf ≡ f ∗ , so that
On a 2-torus phase space, T2, with periodic
coordinates x and p, each in [0,2π], and integer mode indices mi , for basis functions exp(i (m1x+m2p)), this Lie algebra reads,D. Fairlie and C. Zachos, "Infinite-Dimensional Algebras, Sine Brackets and SU(∞)," Physics Letters, B224 (1989) pp. 101–107 -
-
-
-
-
-