
Mie theory
Encyclopedia
Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations are a set of partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electrodynamics, classical optics, and electric circuits. These fields in turn underlie modern electrical and communications technologies.Maxwell's equations...
(also known as the Lorenz–Mie solution, the Lorenz–Mie–Debye solution or Mie scattering) describes the scattering
Scattering
Scattering is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of...
of electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
by a sphere
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
. The solution takes the form of an analytical infinite series.
The term "Mie theory" is used on occasion but it is misleading, since it does not refer to an independent physical theory or law. The phrase "the Mie solution (to Maxwell's equations)" is therefore preferable. Currently, the term "Mie solution" is also used in broader contexts, for example when discussing solutions of Maxwell's equations for scattering by stratified spheres or by infinite cylinders, or generally when dealing with scattering problems solved using the exact Maxwell equations in cases where one can write separate equations
Separation of variables
In mathematics, separation of variables is any of several methods for solving ordinary and partial differential equations, in which algebra allows one to rewrite an equation so that each of two variables occurs on a different side of the equation....
for the radial and angular dependence of solutions.
Introduction
A modern formulation of the Mie solution to the scattering problem on a sphere can be found in many books, e.g., in J. A. StrattonJulius Adams Stratton
Julius Adams Stratton was a U.S. electrical engineer and university administrator. He attended the University of Washington for one year, where he was admitted to the Zeta Psi fraternity, then transferred to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology , from which he graduated with a bachelor's...
's Electromagnetic Theory. In this formulation, the incident plane wave as well as the scattering field is expanded into radiating spherical vector wave functions. The internal field is expanded into regular spherical vector wave functions. By enforcing the boundary condition on the spherical surface, the expansion coefficients of the scattered field can be computed.
For particles much larger or much smaller than the wavelength of the scattered light there are simple and excellent approximations that suffice to describe the behaviour of the system. But for objects whose size is similar to the wavelength (e.g., water droplets in the atmosphere, latex particles in paint, droplets in emulsions including milk, and biological cells and cellular components) this more exact approach is necessary.
The Mie solution is named after its developer, German physicist Gustav Mie
Gustav Mie
Gustav Adolf Feodor Wilhelm Ludwig Mie was a German physicist.-Biography:Mie was born in Rostock. From 1886 he studied mathematics and physics at the University of Rostock. In addition to his major subjects, he also attended lectures in chemistry, zoology, geology, mineralogy, astronomy as well as...
. Danish physicist Ludvig Lorenz and others independently developed the theory of electromagnetic plane wave scattering by a dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
sphere.
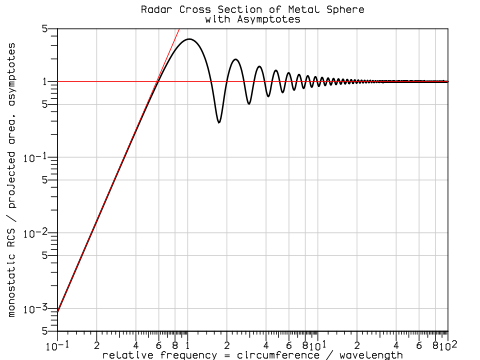
The formalism allows the calculation of the electric and magnetic fields inside and outside a spherical object and is generally used to calculate either how much light is scattered, the total optical cross section, or where it goes, the form factor. The notable features of these results are the Mie resonances, sizes that scatter particularly strongly or weakly. This is in contrast to Rayleigh scattering
Rayleigh scattering
Rayleigh scattering, named after the British physicist Lord Rayleigh, is the elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the light. The particles may be individual atoms or molecules. It can occur when light travels through...
for small particles and Rayleigh–Gans–Debye scattering (after Lord Rayleigh, R. Gans and Peter Debye
Peter Debye
Peter Joseph William Debye FRS was a Dutch physicist and physical chemist, and Nobel laureate in Chemistry.-Early life:...
) for large particles. The existence of resonances and other features of Mie scattering, make it a particularly useful formalism when using scattered light to measure particle size.
Mie scattering codes
Mie solutions are implemented in a number of codes written in different computer languages such as FortranFortran
Fortran is a general-purpose, procedural, imperative programming language that is especially suited to numeric computation and scientific computing...
, Matlab
MATLAB
MATLAB is a numerical computing environment and fourth-generation programming language. Developed by MathWorks, MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages,...
, Mathematica
Mathematica
Mathematica is a computational software program used in scientific, engineering, and mathematical fields and other areas of technical computing...
. These solutions are in terms of infinite series and include calculation of scattering phase function, extinction, scattering, and absorption efficiencies, and other parameters such as asymmetry of parameter or radiation torque. Current usage of "Mie solution" indicate series approximation to solution of Maxwell's equations. There are several known objects which allow such a solution: spheres, concentric spheres, infinite cylinders, cluster of spheres and cluster of cylinders, there are also known series solutions for scattering on ellipsoidal particles. For list of these specialized codes examine these articles
- Codes for electromagnetic scattering by spheresCodes for electromagnetic scattering by spheresCodes for electromagnetic scattering by spheres - this article list codes for electromagnetic scattering by a homogeneous sphere, layered sphere, and cluster of spheres...
- solutions for single sphere, coated spheres, multilayer sphere, cluster of spheres - Codes for electromagnetic scattering by cylindersCodes for electromagnetic scattering by cylindersCodes for electromagnetic scattering by cylinders - this article list codes for electromagnetic scattering by a cylinder. Some of the source codes may be available on ....
- solutions for single cylinder, multilayer cylinders, cluster of cylinders.
Rayleigh approximation (scattering)

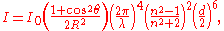
where R is the distance between the particle and the observer, θ is the scattering angle, n is the refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
of the particle, and d is the diameter of the particle.
It can be seen from the above equation that Rayleigh scattering is strongly dependent upon the size of the particle and the wavelengths. The intensity of the Rayleigh scattered radiation increases rapidly as the ratio of particle size to wavelength increases. Furthermore, the intensity of Rayleigh scattered radiation is identical in the forward and reverse directions.
The Rayleigh scattering model breaks down when the particle size becomes larger than around 10% of the wavelength of the incident radiation. In the case of particles with dimensions greater than this, Mie's scattering model can be used to find the intensity of the scattered radiation. The intensity of Mie scattered radiation is given by the summation of an infinite series of terms rather than by a simple mathematical expression. It can be shown, however, that Mie scattering differs from Rayleigh scattering in several respects; it is roughly independent of wavelength and it is larger in the forward direction than in the reverse direction. The greater the particle size, the more of the light is scattered in the forward direction.
The blue colour of the sky results from Rayleigh scattering, as the size of the gas particles in the atmosphere is much smaller than the wavelength of visible light. Rayleigh scattering is much greater for blue light than for other colours due to its shorter wavelength. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, its blue component is Rayleigh scattered strongly by atmospheric gases but the longer wavelength (e.g. red/yellow) components are not. The sunlight arriving directly from the sun therefore appears to be slightly yellow while the light scattered through rest of the sky appears blue. During sunrises and sunsets, the Rayleigh scattering effect is much more noticeable due to the larger volume of air through which sunlight passes.
In contrast, the water droplets which make up clouds are of a comparable size to the wavelengths in visible light, and the scattering is described by Mie's model rather than that of Rayleigh. Here, all wavelengths of visible light are scattered approximately identically and the clouds therefore appear to be white or grey.
Rayleigh Gans Approximation
The Rayleigh Gans Approximation is an approximate solution to light scattering when the relative refractive index of the particle is close to unity, and its size is much smaller in comparison to the wavelength of light divided by |m − 1|, where m is the refractive indexRefractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
.
Anomalous diffraction approximation of van de Hulst
Anomalous diffraction approximation is valid for large and optically soft spheres. Extinction efficiency in this approximation is given by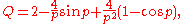
where Q is the efficiency factor of scattering, which is defined as the ratio of the scattering cross section and geometrical cross section πa2;
p = 4πa(n – 1)/λ has a physical meaning of the phase delay of the wave passed through the centre of the sphere;
a is the sphere radius, n is the ratio of refractive indices inside and outside of the sphere, and λ the wavelength of the light.
This set of equations, first described by van de Hulst (1957).
Applications
Mie theory is very important in meteorologicalMeteorology
Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries...
optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, where diameter-to-wavelength ratios of the order of unity and larger are characteristic of many problems regarding haze and cloud
Cloud
A cloud is a visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals made of water and/or various chemicals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of a planetary body. They are also known as aerosols. Clouds in Earth's atmosphere are studied in the cloud physics branch of meteorology...
scattering. A further application is in the characterization of particles
Aerosol science
Aerosol science is the rapidly expanding field of science which investigates the physical, chemical, and biological properties of aerosolized materials , which behave in ways that make them unique from even other forms of similar materials...
via optical scattering measurements. The Mie solution is also important for understanding the appearance of common materials like milk
Milk
Milk is a white liquid produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals before they are able to digest other types of food. Early-lactation milk contains colostrum, which carries the mother's antibodies to the baby and can reduce the risk of many...
, biological tissue
Biological tissue
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
and latex
Latex
Latex is the stable dispersion of polymer microparticles in an aqueous medium. Latexes may be natural or synthetic.Latex as found in nature is a milky fluid found in 10% of all flowering plants . It is a complex emulsion consisting of proteins, alkaloids, starches, sugars, oils, tannins, resins,...
paint.
Atmospheric science
Mie scattering occurs when the particles in the atmosphere are the same size as the wavelengths being scattered. Dust, pollen, smoke and water vapour are common causes of Mie scattering which tends to affect longer wavelengths. Mie scattering occurs mostly in the lower portions of the atmosphere where larger particles are more abundant, and dominates when cloud conditions are overcast.Cancer detection and screening
Mie theory has been used to determine if scattered light from tissue corresponds to healthy or cancerous cell nuclei using angle-resolved low-coherence interferometryAngle-resolved low-coherence interferometry
For the electrical device, see ALCIAngle-resolved low-coherence interferometry is an emerging biomedical imaging technology which uses the properties of scattered light to measure the average size of cell structures, including cell nuclei...
.
Particle sizing
Mie theory has been used in the detection of oil concentration in polluted water.Parasitology
It has also been used to study the structure of Plasmodium falciparumPlasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium falciparum is a protozoan parasite, one of the species of Plasmodium that cause malaria in humans. It is transmitted by the female Anopheles mosquito. Malaria caused by this species is the most dangerous form of malaria, with the highest rates of complications and mortality...
, the most important cause of malaria
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by eukaryotic protists of the genus Plasmodium. The disease results from the multiplication of Plasmodium parasites within red blood cells, causing symptoms that typically include fever and headache, in severe cases...
.
See Also
- Computational electromagneticsComputational electromagneticsComputational electromagnetics, computational electrodynamics or electromagnetic modeling is the process of modeling the interaction of electromagnetic fields with physical objects and the environment....
- Light scattering by particlesLight scattering by particlesLight scattering by particles is the process by which small particles such as ice crystals, dust, planetary dust, and blood cells cause observable phenomena such as rainbows, the color of the sky, and halos....
- List of atmospheric radiative transfer codes
- Optical properties of water and iceOptical properties of water and iceThe refractive index of water at 20°C is 1.332986. The refractive index of normal ice is 1.31. In general, an index of refraction is a complex number with both a real and imaginary part, where the latter indicates the strength of absorption loss at a particular wavelength...
External links
- JMIE (2D C++C++C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
code to calculate the analytical fields around an infinite cylinder, developed by Jeffrey M. McMahon) - Collection of light scattering codes
- www.T-Matrix.de. Implementations of Mie solutions in FORTRANFortranFortran is a general-purpose, procedural, imperative programming language that is especially suited to numeric computation and scientific computing...
, C++C++C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
, IDL, PascalPascal (programming language)Pascal is an influential imperative and procedural programming language, designed in 1968/9 and published in 1970 by Niklaus Wirth as a small and efficient language intended to encourage good programming practices using structured programming and data structuring.A derivative known as Object Pascal...
, MathematicaMathematicaMathematica is a computational software program used in scientific, engineering, and mathematical fields and other areas of technical computing...
and MathcadMathCadMathcad is computer software primarily intended for the verification, validation, documentation and re-use of engineering calculations. First introduced in 1986 on DOS, it was the first to introduce live editing of typeset mathematical notation, combined with its automatic computations... - ScatLab. Mie scattering software for Windows.
- Online Mie solution calculator is available, with documentation in German and English.
- Online Mie scattering calculator produces beautiful graphs over a range of parameters.
- phpMie Online Mie scattering calculator written on PHPPHPPHP is a general-purpose server-side scripting language originally designed for web development to produce dynamic web pages. For this purpose, PHP code is embedded into the HTML source document and interpreted by a web server with a PHP processor module, which generates the web page document...
. - Mie resonance mediated light diffusion and random lasing.

