
Light scattering by particles
Encyclopedia
Light scattering by particles is the process by which small particles such as ice crystals, dust, planetary dust, and blood cells cause observable phenomena such as rainbows, the color of the sky, and halos.
Maxwell's equations
are the basis of theoretical and computational methods describing light scattering but since exact solutions to Maxwell's equations are only known for selected geometries (such as spherica particle) light scattering by particles is a branch of computational electromagnetics
dealing with electromagnetic radiation scattering and absorption by particles.
In case of geometries
for which analytical solutions are known (such as sphere
s, cluster of spheres, infinite cylinders
), the solutions are typically calculated in terms of infinite series. In case of more complex geometries and for inhomogeneous particles the original Maxwell's equations are discretized
and solved. Multiple-scattering effects of light scattering by particles are treated by radiative transfer techniques (see, e.g. atmospheric radiative transfer codes
).
Relative size of a scattering particle is defined by size parameter which is the ratio of its characteristic dimension and wavelength
. Mie theory, also called Lorenz-Mie theory or Lorenz-Mie-Debye theory, is a complete analytical solution of Maxwell's equations for the scattering of electromagnetic radiation by spherical particles (Bohren and Huffman, 1998).
For more complex shapes such as coated spheres, multispheres, spheroid
s, and infinite cylinders there are extensions which express the solution in terms of infinite series.
is an approximation of the continuum target by a finite array of polarizable points. The points acquire dipole moments in response to the local electric field. The dipoles of these points interact with one another via their electric fields.
regime is the scattering of light, or other electromagnetic radiation, by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the light. Rayleigh scattering can be defined as scattering in small size parameter regime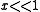 .
.
Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations are a set of partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electrodynamics, classical optics, and electric circuits. These fields in turn underlie modern electrical and communications technologies.Maxwell's equations...
are the basis of theoretical and computational methods describing light scattering but since exact solutions to Maxwell's equations are only known for selected geometries (such as spherica particle) light scattering by particles is a branch of computational electromagnetics
Computational electromagnetics
Computational electromagnetics, computational electrodynamics or electromagnetic modeling is the process of modeling the interaction of electromagnetic fields with physical objects and the environment....
dealing with electromagnetic radiation scattering and absorption by particles.
In case of geometries
Shape
The shape of an object located in some space is a geometrical description of the part of that space occupied by the object, as determined by its external boundary – abstracting from location and orientation in space, size, and other properties such as colour, content, and material...
for which analytical solutions are known (such as sphere
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
s, cluster of spheres, infinite cylinders
Cylinder (geometry)
A cylinder is one of the most basic curvilinear geometric shapes, the surface formed by the points at a fixed distance from a given line segment, the axis of the cylinder. The solid enclosed by this surface and by two planes perpendicular to the axis is also called a cylinder...
), the solutions are typically calculated in terms of infinite series. In case of more complex geometries and for inhomogeneous particles the original Maxwell's equations are discretized
Discretization
In mathematics, discretization concerns the process of transferring continuous models and equations into discrete counterparts. This process is usually carried out as a first step toward making them suitable for numerical evaluation and implementation on digital computers...
and solved. Multiple-scattering effects of light scattering by particles are treated by radiative transfer techniques (see, e.g. atmospheric radiative transfer codes
Atmospheric radiative transfer codes
An Atmospheric radiative transfer model, code or simulator calculates radiative transfer of electromagnetic radiation through a planetary atmosphere, such as the Earth's.- Methods :...
).
Relative size of a scattering particle is defined by size parameter which is the ratio of its characteristic dimension and wavelength

Mie approximation
Scattering from any spherical particles with arbitrary size parameter is explained by the Mie theoryMie theory
The Mie solution to Maxwell's equations describes the scattering of electromagnetic radiation by a sphere...
. Mie theory, also called Lorenz-Mie theory or Lorenz-Mie-Debye theory, is a complete analytical solution of Maxwell's equations for the scattering of electromagnetic radiation by spherical particles (Bohren and Huffman, 1998).
For more complex shapes such as coated spheres, multispheres, spheroid
Spheroid
A spheroid, or ellipsoid of revolution is a quadric surface obtained by rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellipsoid with two equal semi-diameters....
s, and infinite cylinders there are extensions which express the solution in terms of infinite series.
Discrete dipole approximation
There are several techniques for computing scattering of radiation by particles of arbitrary shape. The discrete dipole approximationDiscrete dipole approximation
The discrete dipole approximation is a method for computing scattering of radiation by particles of arbitrary shape and by periodic structures. Given a target of arbitrary geometry, one seeks to calculate its scattering and absorption properties...
is an approximation of the continuum target by a finite array of polarizable points. The points acquire dipole moments in response to the local electric field. The dipoles of these points interact with one another via their electric fields.
T-matrix
The technique is also known as null field method and extended boundary technique method (EBCM). Matrix elements are obtained by matching boundary conditions for solutions of Maxwell equations. The incident, transmitted, and scattered field are expanded into spherical vector wave functions.Finite-difference time-domain method
The FDTD method belongs in the general class of grid-based differential time-domain numerical modeling methods. The time-dependent Maxwell's equations (in partial differential form) are discretized using central-difference approximations to the space and time partial derivatives. The resulting finite-difference equations are solved in either software or hardware in a leapfrog manner: the electric field vector components in a volume of space are solved at a given instant in time; then the magnetic field vector components in the same spatial volume are solved at the next instant in time; and the process is repeated over and over again until the desired transient or steady-state electromagnetic field behavior is fully evolved.Approximate methods
| Approximation | Refractive index Refractive index In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium.... |
Size parameter | Phase shift |
| Rayleigh scattering Rayleigh scattering Rayleigh scattering, named after the British physicist Lord Rayleigh, is the elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the light. The particles may be individual atoms or molecules. It can occur when light travels through... |
abs(mx) very small | very small | |
| Geometric optics | very large | very large | |
| Anomalous Diffraction Theory Anomalous Diffraction Theory Anomalous Diffraction Theory - approximation developed by van de Hulst describing light scattering for optically soft spheres.... |
abs(m-1) very small | x large | |
| Complex Angular Momentum | moderate m | large x | |
Rayleigh scattering
Rayleigh scatteringRayleigh scattering
Rayleigh scattering, named after the British physicist Lord Rayleigh, is the elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the light. The particles may be individual atoms or molecules. It can occur when light travels through...
regime is the scattering of light, or other electromagnetic radiation, by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the light. Rayleigh scattering can be defined as scattering in small size parameter regime
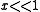 .
.See also
- Codes for electromagnetic scattering by spheresCodes for electromagnetic scattering by spheresCodes for electromagnetic scattering by spheres - this article list codes for electromagnetic scattering by a homogeneous sphere, layered sphere, and cluster of spheres...
- Codes for electromagnetic scattering by cylindersCodes for electromagnetic scattering by cylindersCodes for electromagnetic scattering by cylinders - this article list codes for electromagnetic scattering by a cylinder. Some of the source codes may be available on ....
- Discrete dipole approximation codesDiscrete dipole approximation codesThis article contains list of discrete dipole approximation codes and their applications.The discrete dipole approximation is a flexible technique for computing scattering and absorption by targets of arbitrary geometry. Given a target of arbitrary geometry, one seeks to calculate its scattering...
- Finite-difference time-domain methodFinite-difference time-domain methodFinite-difference time-domain is one of the primary available computational electrodynamics modeling techniques. Since it is a time-domain method, FDTD solutions can cover a wide frequency range with a single simulation run, and treat nonlinear material properties in a natural way.The FDTD method...
- ScatteringScatteringScattering is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of...

