
Mianserin
Encyclopedia
Mianserin is a psychoactive drug
of the tetracyclic antidepressant
(TeCA) chemical class which is classified as a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant
(NaSSA) and has antidepressant
, anxiolytic
, hypnotic
, antiemetic
, orexigenic
, and antihistamine
effects. It was previously available internationally, however in most market
s it has been phased out in favor of its analogue and successor mirtazapine
(Remeron).
An interesting finding is that upon administration, mianserin has been shown to increase the life span
of the nematode
Caenorhabditis elegans
by as much as 30% via dietary restriction
caused by modulation of serotonin receptors in the species
, but if the animals are kept in a high-food environment, mianserin increases obesity and actually decreases the lifespan.
at the H1, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, 5-HT3, 5-HT6, 5-HT7, α1-adrenergic
, and α2-adrenergic receptors
, and also acts as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
(NRI) via blockade of the norepinephrine transporter
(NET). As a high affinity H1 receptor antagonist, mianserin has strong antihistamine
effect
s; however, it has negligible affinity for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
s, and therefore lacks any anticholinergic
properties.
In addition, mianserin also appears to be a potent antagonist of the neuronal octopamine
receptor.
What implications this may have on mood are currently unknown, however octopamine has been implicated in the regulation of sleep, appetite and insulin production and therefore may theoretically contribute to the overall side effect profile of mianserin.
Blockade of the H1 and α1-adrenergic receptors has sedative
and anxiolytic
effects, while antagonism of the 5-HT2A and α1-adrenergic receptors inhibits activation of intracellular
phospholipase C
(PLC), which seems to be common target for several different class
es of antidepressant
s. By antagonizing the somatodendritic and presynaptic α2-adrenergic receptors which function predominantly as inhibitory autoreceptor
s and heteroreceptor
s, mianserin disinhibits the release of norepinephrine
, dopamine
, serotonin
, and acetylcholine
in various areas of the brain
and body
.
s of mianserin may include dizziness
, blurred vision
, sedation
, drowsiness or somnolence
, increased appetite
or hyperphagia and subsequent weight gain
, dry mouth or xerostomia
, and constipation
, among others. Potentially serious adverse reaction
s may include allergic reaction, fainting or syncope
, seizure
s or convulsion
s, and white blood cell
reduction or agranulocytosis
.
of mianserin may provoke a withdrawal
, the effect
s of which may include depression
, anxiety
, panic attack
s, decreased appetite
or anorexia
, insomnia
, diarrhea
, nausea
and vomiting
, and flu-like symptoms, such as allergies or pruritus, among others.
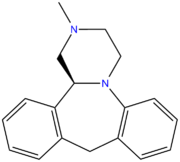 (S)-(+)-Mianserin is approximately 200-300 times more active than its antipode (R)-(–)-mianserin.
(S)-(+)-Mianserin is approximately 200-300 times more active than its antipode (R)-(–)-mianserin.
Psychoactive drug
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, or psychotropic is a chemical substance that crosses the blood–brain barrier and acts primarily upon the central nervous system where it affects brain function, resulting in changes in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, and behavior...
of the tetracyclic antidepressant
Tetracyclic antidepressant
Tetracyclic antidepressants are a class of drugs used primarily as antidepressants that were first introduced in the 1970s. They are named after their chemical structure which contains four rings of atoms and are closely related to the tricyclic antidepressants which contain three rings of...
(TeCA) chemical class which is classified as a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant
Noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant
Noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressants are a class of psychiatric drugs used primarily as antidepressants. They act by antagonizing various adrenergic and serotonin receptors, of which typically consist of α1-adrenergic and α2-adrenergic, and 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, and 5-HT3, respectively...
(NaSSA) and has antidepressant
Antidepressant
An antidepressant is a psychiatric medication used to alleviate mood disorders, such as major depression and dysthymia and anxiety disorders such as social anxiety disorder. According to Gelder, Mayou &*Geddes people with a depressive illness will experience a therapeutic effect to their mood;...
, anxiolytic
Anxiolytic
An anxiolytic is a drug used for the treatment of anxiety, and its related psychological and physical symptoms...
, hypnotic
Hypnotic
Hypnotic drugs are a class of psychoactives whose primary function is to induce sleep and to be used in the treatment of insomnia and in surgical anesthesia...
, antiemetic
Antiemetic
An antiemetic is a drug that is effective against vomiting and nausea. Antiemetics are typically used to treat motion sickness and the side effects of opioid analgesics, general anaesthetics, and chemotherapy directed against cancer....
, orexigenic
Orexigenic
An orexigenic is a drug or hormone that increases appetite. This can be a naturally occurring neuropeptide hormone such as ghrelin, orexin or neuropeptide Y, or a medication which increases hunger and therefore enhances food consumption...
, and antihistamine
Antihistamine
An H1 antagonist is a histamine antagonist of the H1 receptor that serves to reduce or eliminate effects mediated by histamine, an endogenous chemical mediator released during allergic reactions...
effects. It was previously available internationally, however in most market
Market
A market is one of many varieties of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations and infrastructures whereby parties engage in exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services in exchange for money from buyers...
s it has been phased out in favor of its analogue and successor mirtazapine
Mirtazapine
Mirtazapine is a tetracyclic antidepressant used primarily in the treatment of depression. It is also sometimes used as a hypnotic, antiemetic, and appetite stimulant, and for the treatment of anxiety, among other indications...
(Remeron).
An interesting finding is that upon administration, mianserin has been shown to increase the life span
Life expectancy
Life expectancy is the expected number of years of life remaining at a given age. It is denoted by ex, which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged x, according to a particular mortality experience...
of the nematode
Nematode
The nematodes or roundworms are the most diverse phylum of pseudocoelomates, and one of the most diverse of all animals. Nematode species are very difficult to distinguish; over 28,000 have been described, of which over 16,000 are parasitic. It has been estimated that the total number of nematode...
Caenorhabditis elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans is a free-living, transparent nematode , about 1 mm in length, which lives in temperate soil environments. Research into the molecular and developmental biology of C. elegans was begun in 1974 by Sydney Brenner and it has since been used extensively as a model...
by as much as 30% via dietary restriction
Calorie restriction
Caloric restriction , or calorie restriction, is a dietary regimen that restricts calorie intake, where the baseline for the restriction varies, usually being the previous, unrestricted, intake of the subjects...
caused by modulation of serotonin receptors in the species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
, but if the animals are kept in a high-food environment, mianserin increases obesity and actually decreases the lifespan.
Pharmacology
Mianserin is an antagonistReceptor antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that does not provoke a biological response itself upon binding to a receptor, but blocks or dampens agonist-mediated responses...
at the H1, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, 5-HT3, 5-HT6, 5-HT7, α1-adrenergic
Alpha-1 adrenergic receptor
The alpha-1 adrenergic receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor associated with the Gq heterotrimeric G-protein. It consists of three highly homologous subtypes, including α1A-, α1B-, and α1D-adrenergic...
, and α2-adrenergic receptors
Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor
The alpha-2 adrenergic receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor associated with the Gi heterotrimeric G-protein. It consists of three highly homologous subtypes, including α2A-, α2B-, and α2C-adrenergic. Some species other than humans express a fourth α2D-adrenergic receptor as well...
, and also acts as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
A norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor or adrenergic reuptake inhibitor , is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and epinephrine by blocking the action of the norepinephrine transporter...
(NRI) via blockade of the norepinephrine transporter
Norepinephrine transporter
The norepinephrine transporter , also known as solute carrier family 6 member 2 , is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A2 gene....
(NET). As a high affinity H1 receptor antagonist, mianserin has strong antihistamine
Antihistamine
An H1 antagonist is a histamine antagonist of the H1 receptor that serves to reduce or eliminate effects mediated by histamine, an endogenous chemical mediator released during allergic reactions...
effect
Adverse effect
In medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
s; however, it has negligible affinity for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
Muscarinic receptors, or mAChRs, are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled in the plasma membranes of certain neurons and other cells...
s, and therefore lacks any anticholinergic
Anticholinergic
An anticholinergic agent is a substance that blocks the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the central and the peripheral nervous system. An example of an anticholinergic is dicycloverine, and the classic example is atropine....
properties.
In addition, mianserin also appears to be a potent antagonist of the neuronal octopamine
Octopamine
Octopamine is an endogenous biogenic amine that is closely related to norepinephrine, and has effects on the adrenergic and dopaminergic systems. It is also found naturally in numerous plants, including bitter orange. Biosynthesis of the D--enantiomer of octopamine is by β-hydroxylation of...
receptor.
What implications this may have on mood are currently unknown, however octopamine has been implicated in the regulation of sleep, appetite and insulin production and therefore may theoretically contribute to the overall side effect profile of mianserin.
Blockade of the H1 and α1-adrenergic receptors has sedative
Sedative
A sedative or tranquilizer is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement....
and anxiolytic
Anxiolytic
An anxiolytic is a drug used for the treatment of anxiety, and its related psychological and physical symptoms...
effects, while antagonism of the 5-HT2A and α1-adrenergic receptors inhibits activation of intracellular
Intracellular
Not to be confused with intercellular, meaning "between cells".In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word intracellular means "inside the cell".It is used in contrast to extracellular...
phospholipase C
Phospholipase C
Phosphoinositide phospholipase C is a family of eukaryotic intracellular enzymes that play an important role in signal transduction processes. In general, this enzyme is denoted as Phospholipase C, although three other families of phospholipase C enzymes have been identified in bacteria and in...
(PLC), which seems to be common target for several different class
Chemical classification
Chemical classification systems attempt to classify as elements or compounds according to certain chemical functional or structural properties. Whereas the structural properties are largely intrinsic, functional properties and the derived classifications depend to a certain degree on the type of...
es of antidepressant
Antidepressant
An antidepressant is a psychiatric medication used to alleviate mood disorders, such as major depression and dysthymia and anxiety disorders such as social anxiety disorder. According to Gelder, Mayou &*Geddes people with a depressive illness will experience a therapeutic effect to their mood;...
s. By antagonizing the somatodendritic and presynaptic α2-adrenergic receptors which function predominantly as inhibitory autoreceptor
Autoreceptor
An autoreceptor is a receptor located on presynaptic nerve cell membranes and serves as a part of a feedback loop in signal transduction. It is sensitive only to those neurotransmitters or hormones that are released by the neuron in whose membrane the autoreceptor sits.Canonically, a presynaptic...
s and heteroreceptor
Heteroreceptor
A heteroreceptor is a receptor regulating the synthesis and/or the release of mediators other than its own ligand.Heteroreceptors are presynaptic receptors that respond to neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, or neurohormones released from adjacent neurons or cells...
s, mianserin disinhibits the release of norepinephrine
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is the US name for noradrenaline , a catecholamine with multiple roles including as a hormone and a neurotransmitter...
, dopamine
Dopamine
Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter present in a wide variety of animals, including both vertebrates and invertebrates. In the brain, this substituted phenethylamine functions as a neurotransmitter, activating the five known types of dopamine receptors—D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5—and their...
, serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
, and acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
The chemical compound acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter in both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system in many organisms including humans...
in various areas of the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
and body
Body
With regard to living things, a body is the physical body of an individual. "Body" often is used in connection with appearance, health issues and death...
.
Side effects
Common side effectAdverse effect
In medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
s of mianserin may include dizziness
Dizziness
Dizziness refers to an impairment in spatial perception and stability. The term is somewhat imprecise. It can be used to mean vertigo, presyncope, disequilibrium, or a non-specific feeling such as giddiness or foolishness....
, blurred vision
Blurred vision
-Causes:There are many causes of blurred vision:* Use of atropine or other anticholinergics* Presbyopia -- Difficulty focusing on objects that are close. The elderly are common victims....
, sedation
Sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure...
, drowsiness or somnolence
Somnolence
Somnolence is a state of near-sleep, a strong desire for sleep, or sleeping for unusually long periods . It has two distinct meanings, referring both to the usual state preceding falling asleep, and the chronic condition referring to being in that state independent of a circadian rhythm...
, increased appetite
Appetite
The appetite is the desire to eat food, felt as hunger. Appetite exists in all higher life-forms, and serves to regulate adequate energy intake to maintain metabolic needs. It is regulated by a close interplay between the digestive tract, adipose tissue and the brain. Decreased desire to eat is...
or hyperphagia and subsequent weight gain
Weight gain
Weight gain is an increase in body weight. This can be either an increase in muscle mass, fat deposits, or excess fluids such as water.-Description:...
, dry mouth or xerostomia
Xerostomia
Xerostomia is the medical term for the subjective complaint of dry mouth due to a lack of saliva. Xerostomia is sometimes colloquially called pasties, cottonmouth, drooth, or doughmouth. Several diseases, treatments, and medications can cause xerostomia. It can also be exacerbated by smoking or...
, and constipation
Constipation
Constipation refers to bowel movements that are infrequent or hard to pass. Constipation is a common cause of painful defecation...
, among others. Potentially serious adverse reaction
Adverse drug reaction
An adverse drug reaction is an expression that describes harm associated with the use of given medications at a normal dosage. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or result from the combination of two or more drugs...
s may include allergic reaction, fainting or syncope
Syncope (medicine)
Syncope , the medical term for fainting, is precisely defined as a transient loss of consciousness and postural tone characterized by rapid onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery due to global cerebral hypoperfusion that most often results from hypotension.Many forms of syncope are...
, seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s or convulsion
Convulsion
A convulsion is a medical condition where body muscles contract and relax rapidly and repeatedly, resulting in an uncontrolled shaking of the body. Because a convulsion is often a symptom of an epileptic seizure, the term convulsion is sometimes used as a synonym for seizure...
s, and white blood cell
White blood cell
White blood cells, or leukocytes , are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a...
reduction or agranulocytosis
Agranulocytosis
Granulopenia, also known as Agranulosis or Agranulocytosis, is an acute condition involving a severe and dangerous leukopenia , most commonly of neutrophils causing a neutropenia in the circulating blood. It represents a severe lack of one major class of infection-fighting white blood cells...
.
Discontinuation
Abrupt or rapid discontinuationDiscontinuation
Discontinuation is the process of quitting a procedure, such as, the course of treatment with a drug or a consumer product line.*Discontinuation of a treatment is to stop taking a drug...
of mianserin may provoke a withdrawal
Withdrawal
Withdrawal can refer to any sort of separation, but is most commonly used to describe the group of symptoms that occurs upon the abrupt discontinuation/separation or a decrease in dosage of the intake of medications, recreational drugs, and alcohol...
, the effect
Adverse effect
In medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
s of which may include depression
Depression (mood)
Depression is a state of low mood and aversion to activity that can affect a person's thoughts, behaviour, feelings and physical well-being. Depressed people may feel sad, anxious, empty, hopeless, helpless, worthless, guilty, irritable, or restless...
, anxiety
Anxiety
Anxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
, panic attack
Panic attack
Panic attacks are periods of intense fear or apprehension that are of sudden onset and of relatively brief duration. Panic attacks usually begin abruptly, reach a peak within 10 minutes, and subside over the next several hours...
s, decreased appetite
Appetite
The appetite is the desire to eat food, felt as hunger. Appetite exists in all higher life-forms, and serves to regulate adequate energy intake to maintain metabolic needs. It is regulated by a close interplay between the digestive tract, adipose tissue and the brain. Decreased desire to eat is...
or anorexia
Anorexia (symptom)
Anorexia is the decreased sensation of appetite...
, insomnia
Insomnia
Insomnia is most often defined by an individual's report of sleeping difficulties. While the term is sometimes used in sleep literature to describe a disorder demonstrated by polysomnographic evidence of disturbed sleep, insomnia is often defined as a positive response to either of two questions:...
, diarrhea
Diarrhea
Diarrhea , also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having three or more loose or liquid bowel movements per day. It is a common cause of death in developing countries and the second most common cause of infant deaths worldwide. The loss of fluids through diarrhea can cause dehydration and...
, nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
and vomiting
Vomiting
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
, and flu-like symptoms, such as allergies or pruritus, among others.
Enantioselectivity


