
Matthew 1:18
Encyclopedia

Matthew 1
Matthew 1 is the first chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. It contains two distinct sections. The first lists the genealogy of Jesus's legal father Joseph from Abraham...
of the Gospel of Matthew
Gospel of Matthew
The Gospel According to Matthew is one of the four canonical gospels, one of the three synoptic gospels, and the first book of the New Testament. It tells of the life, ministry, death, and resurrection of Jesus of Nazareth...
in the New Testament
New Testament
The New Testament is the second major division of the Christian biblical canon, the first such division being the much longer Old Testament....
. This verse opens the description of the events surrounding the birth of Jesus.
Text
The original Koine GreekKoine Greek
Koine Greek is the universal dialect of the Greek language spoken throughout post-Classical antiquity , developing from the Attic dialect, with admixture of elements especially from Ionic....
, according to Westcott and Hort
The New Testament in the Original Greek
The New Testament in the Original Greek is the name of a Greek language version of the New Testament published in 1881. It is also known as the Westcott and Hort text, after its editors Brooke Foss Westcott and Fenton John Anthony Hort...
, reads:
- του δε [ιησου] χριστου η γενεσις ουτως
- ην μνηστευθεισης της μητρος αυτου μαριας
- τω ιωσηφ πριν η συνελθειν αυτους ευρεθη
- εν γαστρι εχουσα εκ πνευματος αγιου
In the King James Version of the Bible
Bible
The Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
the text reads:
- Now the birth of JesusJesusJesus of Nazareth , commonly referred to as Jesus Christ or simply as Jesus or Christ, is the central figure of Christianity...
ChristChristChrist is the English term for the Greek meaning "the anointed one". It is a translation of the Hebrew , usually transliterated into English as Messiah or Mashiach...
was - on this wise: When as his mother
- Mary was espoused to JosephSaint JosephSaint Joseph is a figure in the Gospels, the husband of the Virgin Mary and the earthly father of Jesus Christ ....
, before - they came together, she was found
- with child of the Holy Ghost.
The World English Bible
World English Bible
The World English Bible is a public domain translation of the Bible that is currently in draft form. Work on the World English Bible began in 1997 and was known as the American Standard Version 1997...
translates the passage as:
- Now the birth of Jesus Christ was
- like this; for after his mother,
- Mary, was engaged to Joseph,
- before they came together, she was
- found pregnant by the Holy Spirit.
For a collection of other versions see BibRef Matthew 1:18
Analysis
As the previous verses contained nothing but a summary of Jesus' genealogy, this verse is the beginning of the narrative of Matthew, and has often been considered the true opening verse of the gospel. Boring notes that this verse is not part of the narrative to come, but is an initial introduction bringing the reader up to date on where things stand at the beginning of Matthew's story.The word translated as birth, geneseos, is the same term that is used in Matthew 1:1
Matthew 1:1
Matthew 1:1 is the opening verse of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. Since Matthew is traditionally placed as the first of the four Gospels, this verse commonly serves as the opening to the entire New Testament....
. English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
editions invariably give different translations for the two, but the author of Matthew may have been trying to link the two verses with the second geneseos symbolically beginning the second section of the chapter.
The word translated as espoused, engaged, or most often betrothed refers to a specific institution of the period very different from the modern idea of an engagement
Engagement
An engagement or betrothal is a promise to marry, and also the period of time between proposal and marriage which may be lengthy or trivial. During this period, a couple is said to be betrothed, affianced, engaged to be married, or simply engaged...
. This period occurred after the main marriage ceremony had taken place and the marriage contracts had been signed. Dissolution thus required a formal divorce or the death of one partner. In general the betrothal ceremony took place when the woman was still very young, generally around age twelve or thirteen. After the ceremony she would remain in their father's house for around a year, and this period is what is referred to in this verse.
The second stage of the marriage was for the husband to take his bride into his own home. Most scholars believe this is what the phrase "coming together" means in this verse. It is not thought to be a euphemism
Euphemism
A euphemism is the substitution of a mild, inoffensive, relatively uncontroversial phrase for another more frank expression that might offend or otherwise suggest something unpleasant to the audience...
for sexual relations, even though it could be interpreted in this way. Only after the bride moved into her husband's house would the marriage be consummated. In Judea
Judea
Judea or Judæa was the name of the mountainous southern part of the historic Land of Israel from the 8th century BCE to the 2nd century CE, when Roman Judea was renamed Syria Palaestina following the Jewish Bar Kokhba revolt.-Etymology:The...
sexual relations during the betrothal were not unheard of. In Galilee
Galilee
Galilee , is a large region in northern Israel which overlaps with much of the administrative North District of the country. Traditionally divided into Upper Galilee , Lower Galilee , and Western Galilee , extending from Dan to the north, at the base of Mount Hermon, along Mount Lebanon to the...
, however, much stricter conventions prevailed. Any infidelity with an outside partner during the betrothal period was considered adultery
Adultery
Adultery is sexual infidelity to one's spouse, and is a form of extramarital sex. It originally referred only to sex between a woman who was married and a person other than her spouse. Even in cases of separation from one's spouse, an extramarital affair is still considered adultery.Adultery is...
, and punished as such under Mosaic Law. Thus when Mary became pregnant she was at a point prior to which she would have had relations with her husband but also a time in which infidelity would be harshly punished, potentially by death.
Matthew does not relate the events surrounding the conception of Jesus, rather he takes the event as having already happened. To Schweizer this signals that Matthew was writing for an audience that was already well aware of story of the Virgin Birth
Virgin Birth
The virgin birth of Jesus is a tenet of Christianity and Islam which holds that Mary miraculously conceived Jesus while remaining a virgin. The term "virgin birth" is commonly used, rather than "virgin conception", due to the tradition that Joseph "knew her not till she brought forth her firstborn...
. Schweizer also observers that the author of Matthew seems rather nonplussed by the Virgin Birth. While today modern scientifically oriented Christians find the Virgin Birth one of the more implausible parts of the Gospel, Schweizer believes that attitudes would have been very different at the time Matthew was writing. There were several Virgin Birth stories in the Jewish tradition
Tradition
A tradition is a ritual, belief or object passed down within a society, still maintained in the present, with origins in the past. Common examples include holidays or impractical but socially meaningful clothes , but the idea has also been applied to social norms such as greetings...
and the idea of virgin births was generally accepted by the population.
Matthew mentions the paternity of the Holy Ghost very quickly, even before any of the characters in his narrative are aware of this fact. Brown argues that this is because Matthew does not want the reader to consider alternate scenarios as to how Mary could have become pregnant. Jane Schaberg
Jane Schaberg
Jane D. Schaberg is a Professor of Religious Studies and Women's Studies at the University of Detroit Mercy. Schaberg earned a BA in Philosophy from Manhattanville College, an MA in Systematic theology from Columbia University and a Ph.D. in Biblical Studies from the Union Theological Seminary. She...
sees this as an apologetic addition, to counter claims of Jesus' illegitimacy that were current among anti-Christian writings of the time, such as the Toledot Yeshu
Toledot Yeshu
Sefer Toledot Yeshu is a medieval version of the story of Jesus from a Jewish perspective. The book concerns Yeshu, son of Joseph and Mary, born in Bethlehem, but also makes this Yeshu a contemporary of Queen Salome Alexandra...
. She links this to Matthew 28
Matthew 28
Matthew 28 is the twenty-eighth and final chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. This chapter covers the events around the resurrection of Jesus.-Content:...
, where the author of Matthew tries to rebut the theory that Jesus' body was stolen.
Despite the capital letters most editions give the phrase, Matthew does not mean the Holy Ghost as understood in modern theology. The modern notion of the Trinity
Trinity
The Christian doctrine of the Trinity defines God as three divine persons : the Father, the Son , and the Holy Spirit. The three persons are distinct yet coexist in unity, and are co-equal, co-eternal and consubstantial . Put another way, the three persons of the Trinity are of one being...
developed over time. The phrase can be read as either "the holy spirit" or "a holy spirit." In Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
the term Holy Ghost is gender neutral and in Semitic languages it is female. This reduces the idea of actual copulation, as was traditional between pagan
Paganism
Paganism is a blanket term, typically used to refer to non-Abrahamic, indigenous polytheistic religious traditions....
gods and mortal women. Feminist scholar Levine sees much importance in Jesus being the child of a woman and feminine spirit. She sees this as a rejection of the traditional patriarchal model for the family. Wainwright
Elaine Wainwright
Elaine Mary Wainwright, BA MTheol PhD, is Richard Maclaurin Goodfellow Professor in Theology at the University of Auckland.She is known for her feminist scholarship in Matthew's gospel, and work on gender and healing within the Graeco-Roman world...
also sees the act of creating a child without the need for a mortal man as a challenge to the androcentric social order. Schaberg disagrees with this approach, writing that Mary is represented in these verses as nothing more than a vehicle reproduction, a very traditional societal role.
Chi Rho monogram
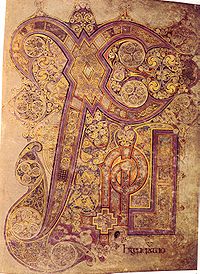
Gospel Book
The Gospel Book, Evangelion, or Book of the Gospels is a codex or bound volume containing one or more of the four Gospels of the Christian New Testament...
s (that is those books produced in monasteries Ireland, England and Scotland or on the continent in monasteries founded by Irish missionaries) this verse has an importance not seen in other medieval Gospel Books. In the Vulgate
Vulgate
The Vulgate is a late 4th-century Latin translation of the Bible. It was largely the work of St. Jerome, who was commissioned by Pope Damasus I in 382 to make a revision of the old Latin translations...
(which was used in these books), the verse reads:
- Christi autem generatio sic erat cum esset desponsata mater eius Maria Ioseph antequam convenirent inventa est in utero habens de Spiritu Sancto
In medieval writing the word Christ was often abbreviated using the Greek
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
letters Chi
Chi (letter)
Chi is the 22nd letter of the Greek alphabet, pronounced as in English.-Greek:-Ancient Greek:Its value in Ancient Greek was an aspirated velar stop .-Koine Greek:...
(X) and Rho
Rho (letter)
Rho is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 100. It is derived from Semitic resh "head"...
(P). The word Christi (of Christ) was then written XPi. The verses Matthew 1:1
Matthew 1:1
Matthew 1:1 is the opening verse of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. Since Matthew is traditionally placed as the first of the four Gospels, this verse commonly serves as the opening to the entire New Testament....
through Matthew 1:17
Matthew 1:17
Matthew 1:17 is the seventeenth verse of the first chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. The verse is the conclusion to the section where the genealogy of Joseph, the father of Jesus, is listed.-Text:...
give the genealogy of Christ, with the actual narrative of Christ's birth starting at Matthew 1:18. Insular scribes treated Matthew 1:1-17 as an almost separate work from the rest of Matthew. Insular scribes also started a tradition of giving the opening few words of each of the Gospels an elaborate decorative treatment (see this example from the Lindisfarne Gospels
Lindisfarne Gospels
The Lindisfarne Gospels is an illuminated Latin manuscript of the gospels of Matthew, Mark, Luke and John in the British Library...
). Accordingly, the Insular scribes gave the opening Chi Rho monogram an increasingly elaborate decoration. This trend culminated in the Book of Kells
Book of Kells
The Book of Kells is an illuminated manuscript Gospel book in Latin, containing the four Gospels of the New Testament together with various prefatory texts and tables. It was created by Celtic monks ca. 800 or slightly earlier...
(see above), where the monogram has taken over the entire page. Although later scribes (such as those of the Carolingian Renaissance
Carolingian Renaissance
In the history of ideas the Carolingian Renaissance stands out as a period of intellectual and cultural revival in Europe occurring from the late eighth century, in the generation of Alcuin, to the 9th century, and the generation of Heiric of Auxerre, with the peak of the activities coordinated...
) followed the Insular tradition of giving elaborate decorative treatments to the opening words of texts, including the Gospels, they did not follow the tradition of decoration this verse. The presence of a decorated Chi Rho monogram within a manuscript can then be seen as indicative of Insular influence.

