
Magnetic bearing
Encyclopedia
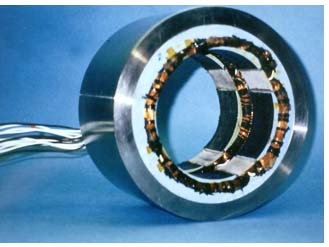
Bearing (mechanical)
A bearing is a device to allow constrained relative motion between two or more parts, typically rotation or linear movement. Bearings may be classified broadly according to the motions they allow and according to their principle of operation as well as by the directions of applied loads they can...
which supports a load using magnetic levitation
Magnetic levitation
Magnetic levitation, maglev, or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is suspended with no support other than magnetic fields...
. Magnetic bearings support moving machinery without physical contact; for example, they can levitate a rotating shaft and permit relative motion with very low friction and no mechanical wear. Magnetic bearings are in service in such industrial applications as electric power generation, petroleum refining, machine tool operation, and natural gas pipelines. They are also used in the Zippe-type centrifuge
Zippe-type centrifuge
The Zippe-type centrifuge is a device designed to collect Uranium-235. It was developed in the Soviet Union by a team of 60 Austrian and German scientists captured after World War II, working in detention...
used for uranium enrichment. Magnetic bearings are used in turbomolecular pump
Turbomolecular pump
A turbomolecular pump is a type of vacuum pump, superficially similar to a turbopump, used to obtain and maintain high vacuum. These pumps work on the principle that gas molecules can be given momentum in a desired direction by repeated collision with a moving solid surface...
s, where oil-lubricated bearings would be a source of contamination. Magnetic bearings support the highest speeds of any kind of bearing; they have no known maximum relative speed.
Description
It is difficult to build a magnetic bearing using permanent magnets due to the limitations described by Earnshaw's theoremEarnshaw's theorem
Earnshaw's theorem states that a collection of point charges cannot be maintained in a stable stationary equilibrium configuration solely by the electrostatic interaction of the charges. This was first proven by British mathematician Samuel Earnshaw in 1842. It is usually referenced to magnetic...
, and techniques using diamagnetic materials are relatively undeveloped. As a result, most magnetic bearings require continuous power input and an active control system to hold the load stable. Many bearings can use permanent magnets to carry the static load, and then only use power when the levitated object deviates from its optimum position. Magnetic bearings also typically require some kind of back-up bearing in case of power or control system failure and during initial start-up conditions.
Two sorts of instabilities are very typically present with magnetic bearings. Firstly, attractive magnets give an unstable static force that decreases with greater distance and increases at close distances. Secondly since magnetism is a conservative force
Conservative force
A conservative force is a force with the property that the work done in moving a particle between two points is independent of the path taken. Equivalently, if a particle travels in a closed loop, the net work done by a conservative force is zero.It is possible to define a numerical value of...
, in and of itself it gives little if any damping, and oscillations may cause loss of successful suspension if any driving forces are present, which they very typically are.
With the use of an induction-based levitation system present in maglev technologies such as the Inductrack
Inductrack
Inductrack is a passive, fail-safe electrodynamic magnetic levitation system, using only unpowered loops of wire in the track and permanent magnets on the vehicle to achieve magnetic levitation. The track can be in one of two configurations, a "ladder track" and a "laminated track"...
system, magnetic bearings could do away with complex control systems by using Halbach Array
Halbach array
A Halbach array is a special arrangement of permanent magnets that augments the magnetic field on one side of the array while cancelling the field to near zero on the other side...
s and simple closed loop coils. These systems gain in simplicity, but are less advantageous when it comes to eddy current
Eddy current
Eddy currents are electric currents induced in conductors when a conductor is exposed to a changing magnetic field; due to relative motion of the field source and conductor or due to variations of the field with time. This can cause a circulating flow of electrons, or current, within the body of...
losses. For rotating systems
Rotordynamics
Rotordynamics is a specialized branch of applied mechanics concerned with the behavior and diagnosis of rotating structures. It is commonly used to analyze the behavior of structures ranging from jet engines and steam turbines to auto engines and computer disk storage...
it is possible to use homopolar magnet designs instead of multipole halbach structures, which reduces losses considerably. An example of this - that has solved the Earnshaws theorem - is the homopolar electrodynamic bearings invented by Dr Torbjörn Lembke.
Active magnetic bearing
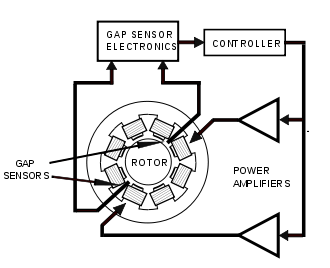
Electromagnetic suspension
Electromagnetic Suspension is the magnetic levitation of an object achieved by constantly altering the strength of a magnetic field produced by electromagnets using a feedback loop...
and consists of an electromagnet
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by the flow of electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off...
assembly, a set of power amplifiers which supply current to the electromagnets, a controller
Controller (control theory)
In control theory, a controller is a device which monitors and affects the operational conditions of a given dynamical system. The operational conditions are typically referred to as output variables of the system which can be affected by adjusting certain input variables...
, and gap sensors with associated electronics to provide the feedback required to control the position of the rotor within the gap. These elements are shown in the diagram. The power amplifiers supply equal bias current to two pairs of electromagnets on opposite sides of a rotor. This constant tug-of-war is mediated by the controller which offsets the bias current by equal but opposite perturbations of current as the rotor deviates by a small amount from its center position.
The gap sensors are usually inductive in nature and sense in a differential mode.
The power amplifiers in a modern commercial application are solid state devices which operate in a pulse width modulation (PWM) configuration. The controller is usually a microprocessor
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
or DSP
Digital signal processor
A digital signal processor is a specialized microprocessor with an architecture optimized for the fast operational needs of digital signal processing.-Typical characteristics:...
.
Active bearings have several advantages, they do not suffer from wear, they have low friction, and they can often accommodate irregularities in the mass distribution automatically, allowing it to spin around its centre of mass with very low vibration.
History
The evolution of active magnetic bearings may be traced through the patents issued in this field. The table below lists several early patents for active magnetic bearings. Earlier patents for magnetic suspensions can be found but are excluded here because they consist of assemblies of permanent magnets of problematic stability per Earnshaw's TheoremEarnshaw's theorem
Earnshaw's theorem states that a collection of point charges cannot be maintained in a stable stationary equilibrium configuration solely by the electrostatic interaction of the charges. This was first proven by British mathematician Samuel Earnshaw in 1842. It is usually referenced to magnetic...
.
Early active magnetic bearing patents were assigned to Jesse Beams
Jesse Beams
Jesse Wakefield Beams was an American physicist at the University of Virginia.Beams completed his undergraduate B.A. in physics at Fairmount College in 1921 and his master's degree the next year at the University of Wisconsin–Madison...
at the University of Virginia
University of Virginia
The University of Virginia is a public research university located in Charlottesville, Virginia, United States, founded by Thomas Jefferson...
during World War II and are concerned with ultracentrifuges for purification of the isotopes of various elements for the manufacture of the first nuclear bombs, but the technology did not mature until the advances of solid-state electronics and modern computer-based control technology with the work of Habermann and Schweitzer. Extensive modern work in magnetic bearings has continued at the University of Virginia in the Rotating Machinery and Controls Industrial Research Program. The first international symposium for active magnetic bearing technology was held in 1988 with the founding of the International Society of Magnetic Bearings by Prof. Schweitzer (ETHZ), Prof. Allaire (University of Virginia), and Prof. Okada (Ibaraki University).
In 1987 further improved AMB designs were created in Australia by E.Croot (see reference below as well) but these designs were not manufactured due to expensive costs of production. However, some of those designs have since been used by Japanese electronics companies, they remain a specialty item: where extremely high RPM is required.
Since then there have been nine succeeding symposia. Kasarda reviews the history of AMB in depth. She notes that the first commercial application of AMB’s was with turbomachinery. The AMB allowed the elimination of oil reservoirs on compressors for the NOVA Gas Transmission Ltd. (NGTL) gas pipelines in Alberta, Canada. This reduced the fire hazard allowing a substantial reduction in insurance costs. The success of these magnetic bearing installations led NGTL to pioneer the research and development of a digital magnetic bearing control system as a replacement for the analog control systems supplied by the American company Magnetic Bearings Inc. (MBI). In 1992, NGTL's magnetic bearing research group formed the company Revolve Technologies Inc http://www.skfmagneticbearings.com. to commercialize the digital magnetic bearing technology. This firm was later purchased by SKF
SKF
SKF, Svenska Kullagerfabriken AB , later AB SKF, is a Swedish bearing company founded in 1907, supplying bearings, seals, lubrication and lubrication systems, maintenance products, mechatronics products, power transmission products and related services globally.-History:The company was founded on...
of Sweden. The French company S2M
S2M
"S2M" is a common text messaging shortcut which means "smiling to myself." The primary motivation and genesis of this meme came from overuse of the text messaging shortcut "LOL", which is often misused and certainly overused...
, founded in 1976, was the first to commercially market AMB’s. Extensive research on magnetic bearings continues at the University of Virginia in the Rotating Machinery and Controls Industrial Research Program http://www.virginia.edu/romac/.
Starting from 1996 the Dutch oil and gas company NAM installed over a period of 10 years 20 large E-motor driven (with variable speed drive) gas compressors of 23 MW fully equipped with AMB's on both the E-motor and the compressor. These compressors are used in the Groningen gas field to deplete the remaining gas from this large gas field and to increase the field capacity. The motor - compressor design is done by Siemens and the AMB are delivered by Waukesha (owned by Dover). (Originally these bearings were designed by Glacier, this company is later on taken over by Federal Mogul and now part of Waukesha) By using AMB's and a direct drive between motor and compressor (so no the gearbox in between) and applying dry gas seals a full so called dry-dry system (=fully oil free) has been installed. A few of the main advantages by applying AMB's in the driver as well as in the compressor (compared to the traditional configuration with a gearbox, plain bearings and a gasturbine-driver) is a relative simple system with a very wide operating envelope, high efficiencies (particularly at partial load) and also, as done in the Groningen field, to install the full installation outdoors (no large compressor building needed).
| Inventor(s) | Year | Patent No. | Invention Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beams, Holmes | 1941 | 2,256,937 | Suspension of Rotatable Bodies |
| Beams | 1954 | 2,691,306 | Magnetically Supported Rotating Bodies |
| Beams | 1962 | 3,041,482 | Apparatus for Rotating Freely Suspended Bodies |
| Beams | 1965 | 3,196,694 | Magnetic Suspension System |
| Wolf | 1967 | 3,316,032 | Poly-Phase Magnetic Suspension Transformer |
| Lyman | 1971 | 3,565,495 | Magnetic Suspension Apparatus |
| Habermann | 1973 | 3,731,984 | Magnetic Bearing Block Device for Supporting a Vertical Shaft Adapted for Rotating at High Speed |
| Habermann, Loyen, Joli, Aubert | 1974 | 3,787,100 | Devices Including Rotating Members Supported by Magnetic Bearings |
| Habermann, Brunet | 1977 | 4,012,083 | Magnetic Bearings |
| Habermann, Brunet, LeClére | 1978 | 4,114,960 | Radial Displacement Detector Device for a Magnetic Bearings |
Electrodynamic bearing
Electrodynamic bearings (EDB) are a novel type of bearing that is a passive magnetic technology. EDBs do not require any control electronics to operate. They work by the electrical currents generated by motion causing a restoring force.Applications
Magnetic bearing advantages include very low and predictable friction, ability to run without lubrication and in a vacuum. Magnetic bearings are increasingly used in industrial machines such as compressors, turbines, pumps, motors and generators.Magnetic bearings are commonly used in watt-hour meters by electric utilities to measure home power consumption. Magnetic bearings are also used in high-precision instruments and to support equipment in a vacuum, for example in flywheel energy storage
Flywheel energy storage
Flywheel energy storage works by accelerating a rotor to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy...
systems. A flywheel in a vacuum has very low windage losses, but conventional bearings usually fail quickly in a vacuum due to poor lubrication. Magnetic bearings are also used to support maglev train
Maglev train
Maglev , is a system of transportation that uses magnetic levitation to suspend, guide and propel vehicles from magnets rather than using mechanical methods, such as friction-reliant wheels, axles and bearings...
s in order to get low noise and smooth ride by eliminating physical contact surfaces. Disadvantages include high cost, and relatively large size.
A new application of magnetic bearings is their use in artificial hearts. The use of magnetic suspension in ventricular assist devices was pioneered by Prof. Paul Allaire and Prof. Houston Wood at the University of Virginia culminating in the first magnetically suspended ventricular assist centrifugal pump (VAD
Ventricular assist device
A Ventricular assist device, or VAD, is a mechanical circulatory device that is used to partially or completely replace the function of a failing heart...
) in 1999.
External links
- Kinematic Models for Design Digital Library (KMODDL) - Movies and photos of hundreds of working mechanical-systems models at Cornell University. Also includes an e-book library of classic texts on mechanical design and engineering.
- MADYN2000, Rotordynamics Software supports computer-aided design of Magnetic Bearing controllers and provides multiple analytic reports of design quality.

